Space, Light, & Seasons Science
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
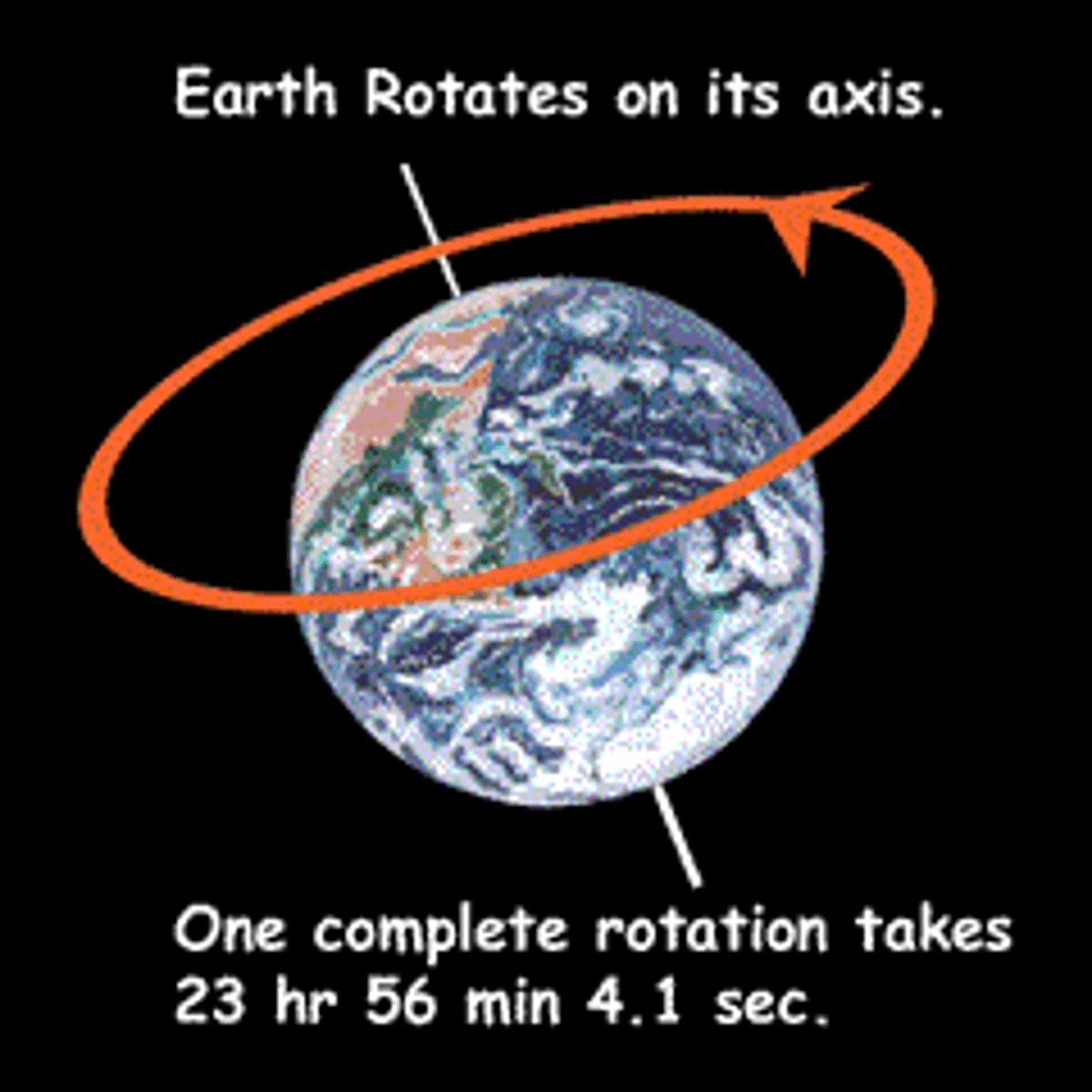
axis
-the imaginary line that passes trhough the Earth's center and the North and South poles
-imaginary line on which the Earth spins
-tilted at 23.5 degrees
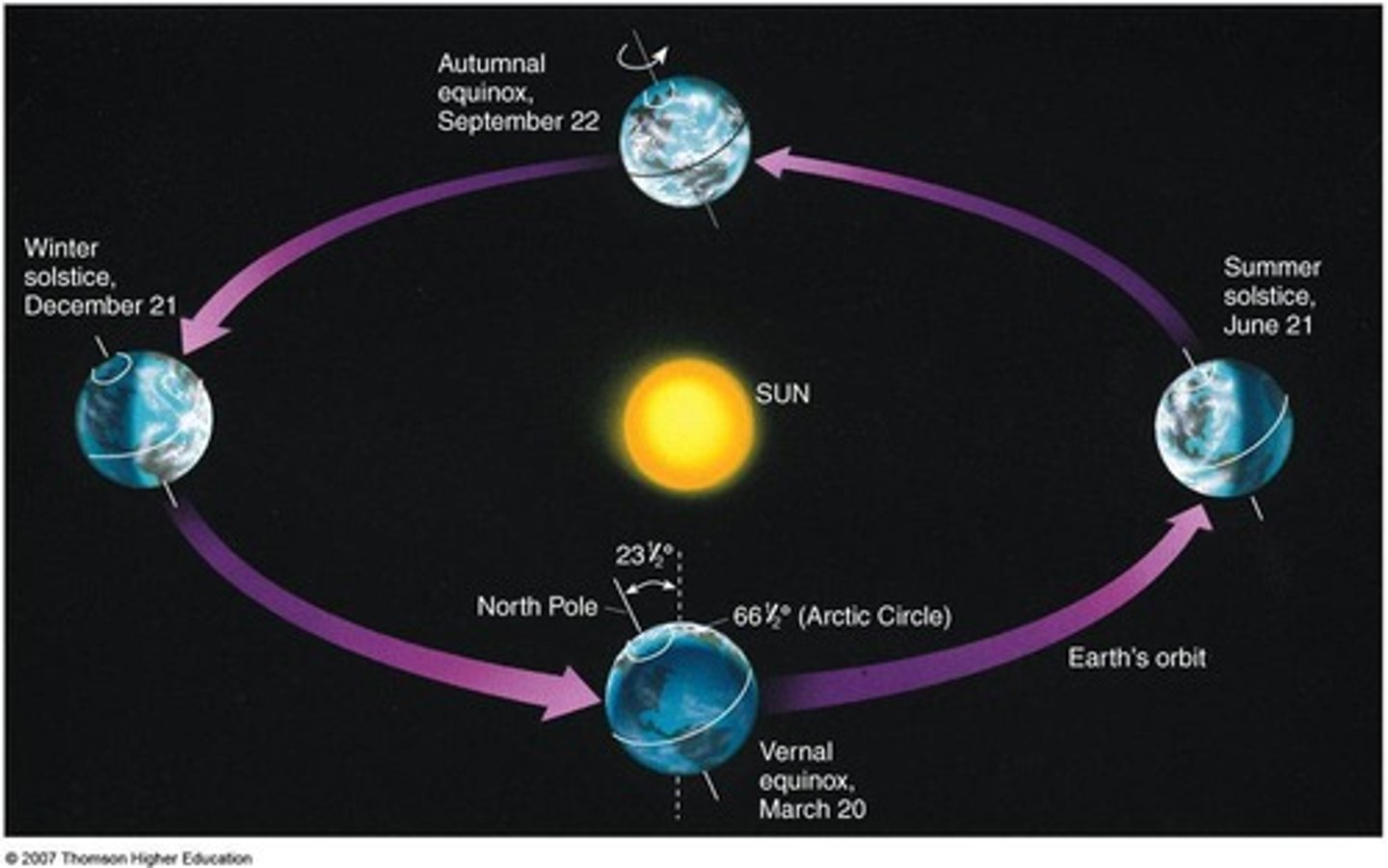
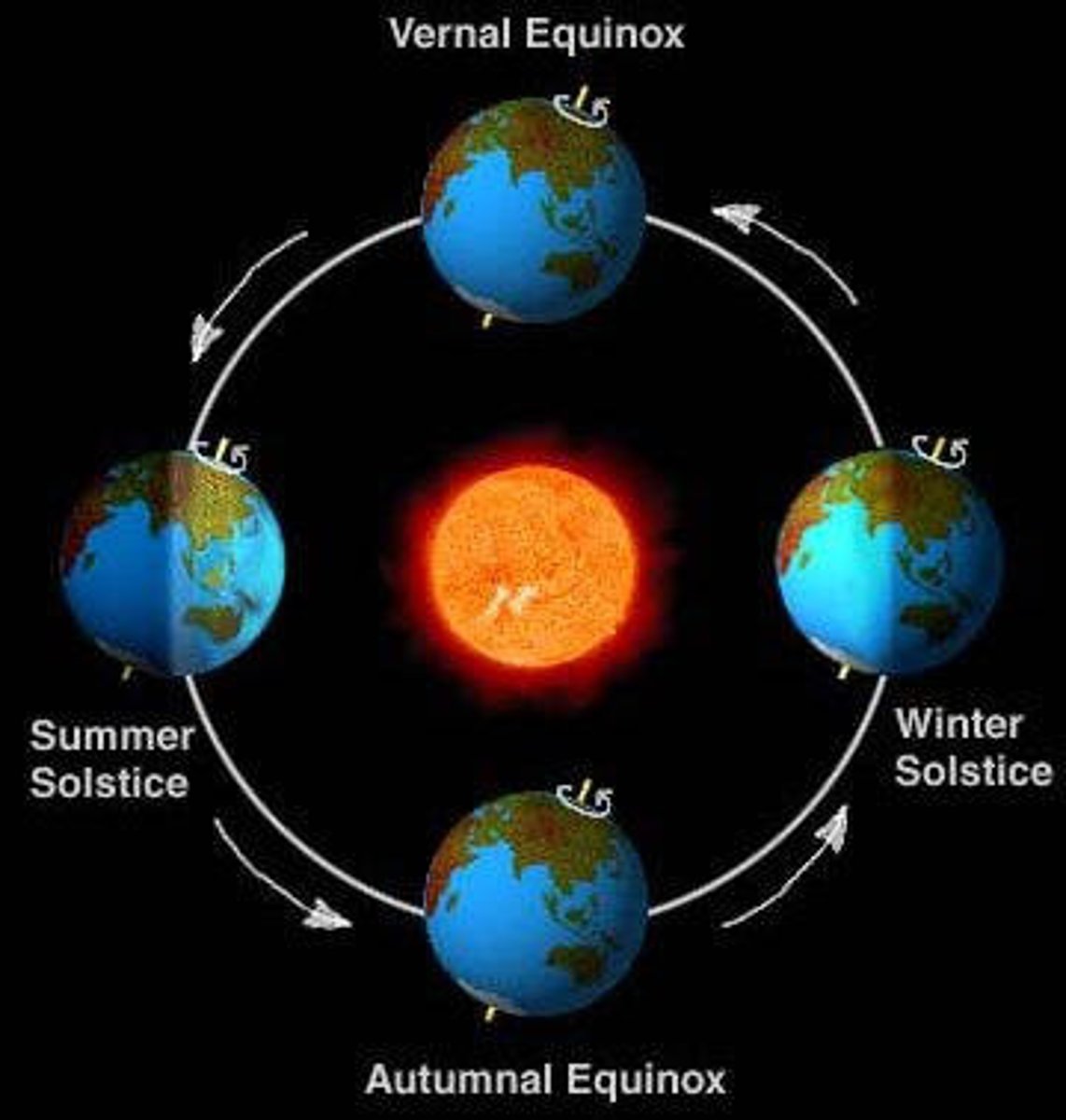
seasons
-caused by the Earth's tilt on its axis as it moves (revolves) around the sun
Poles
-Energy from the sun is spread out over a greater area, causes these areas to have lower temperatures
-Sunlight hits these areas at an angle because the Earth is tilted on its axis
Equator
Sunlight hits this area more directly. This is an imaginary line that goes around the center of the Earth at 0 degrees latitude.
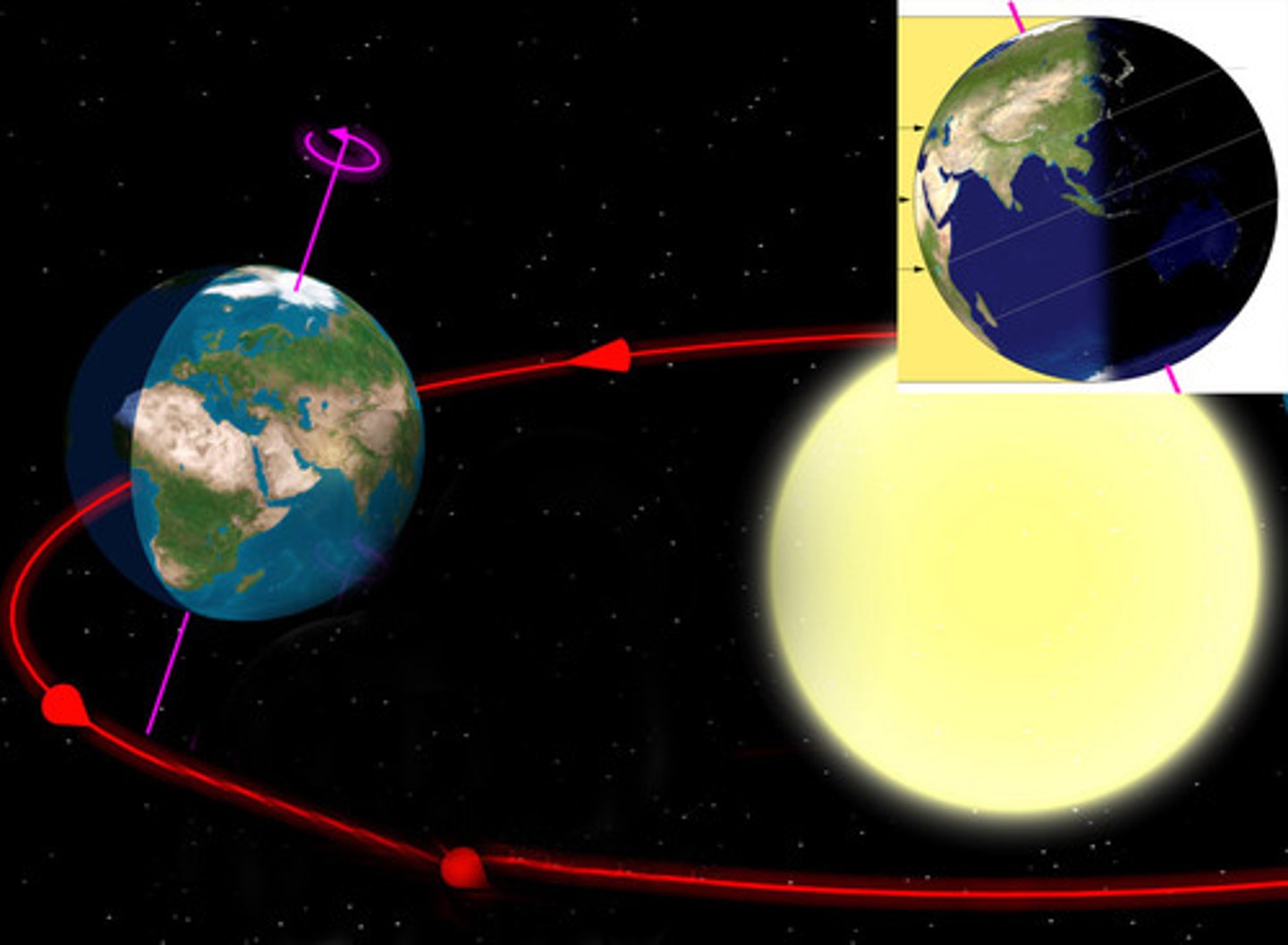
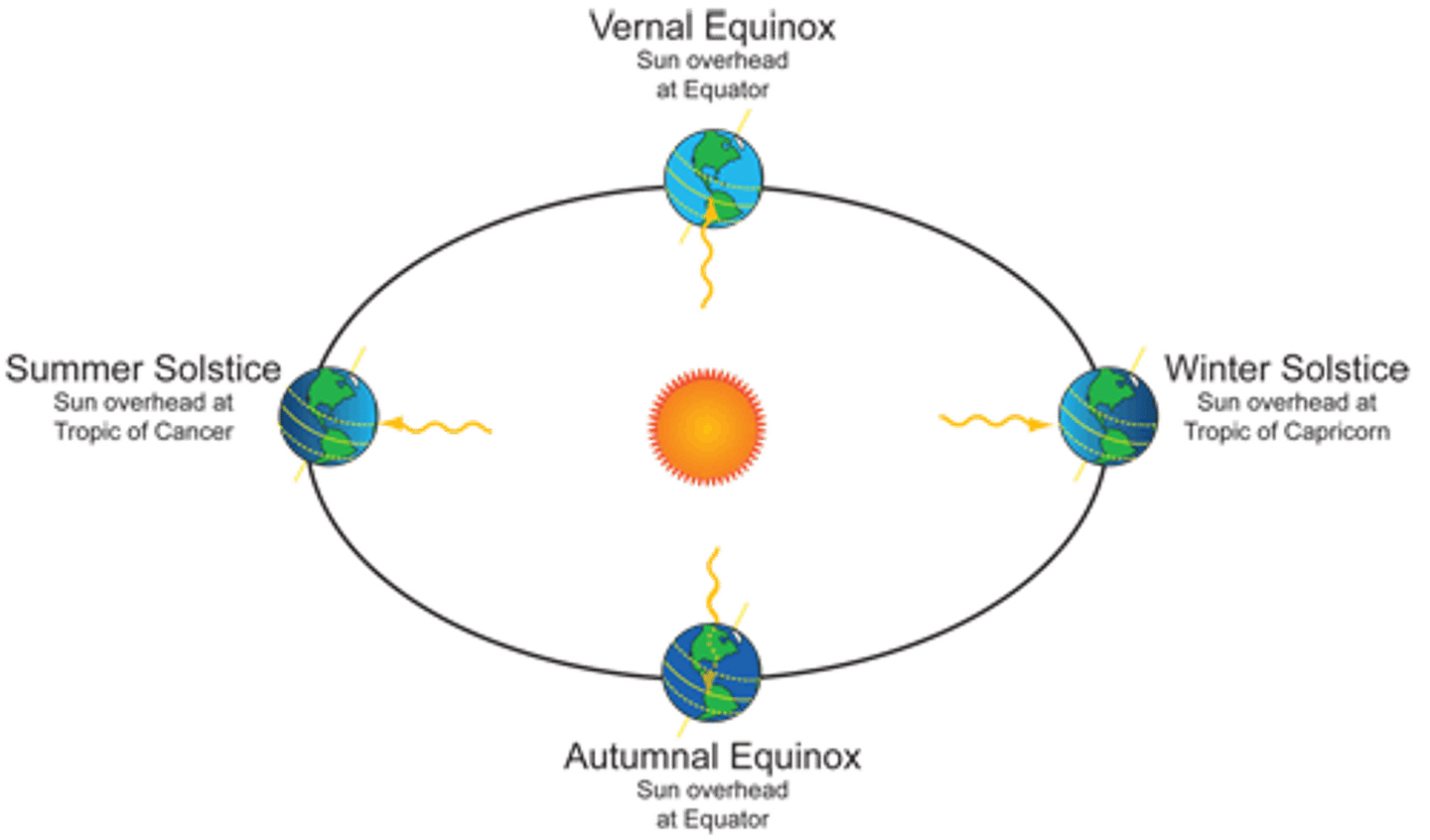
summer
When the north end of Earth's axis is tilted toward the sun, the Northern Hemisphere has ________________.
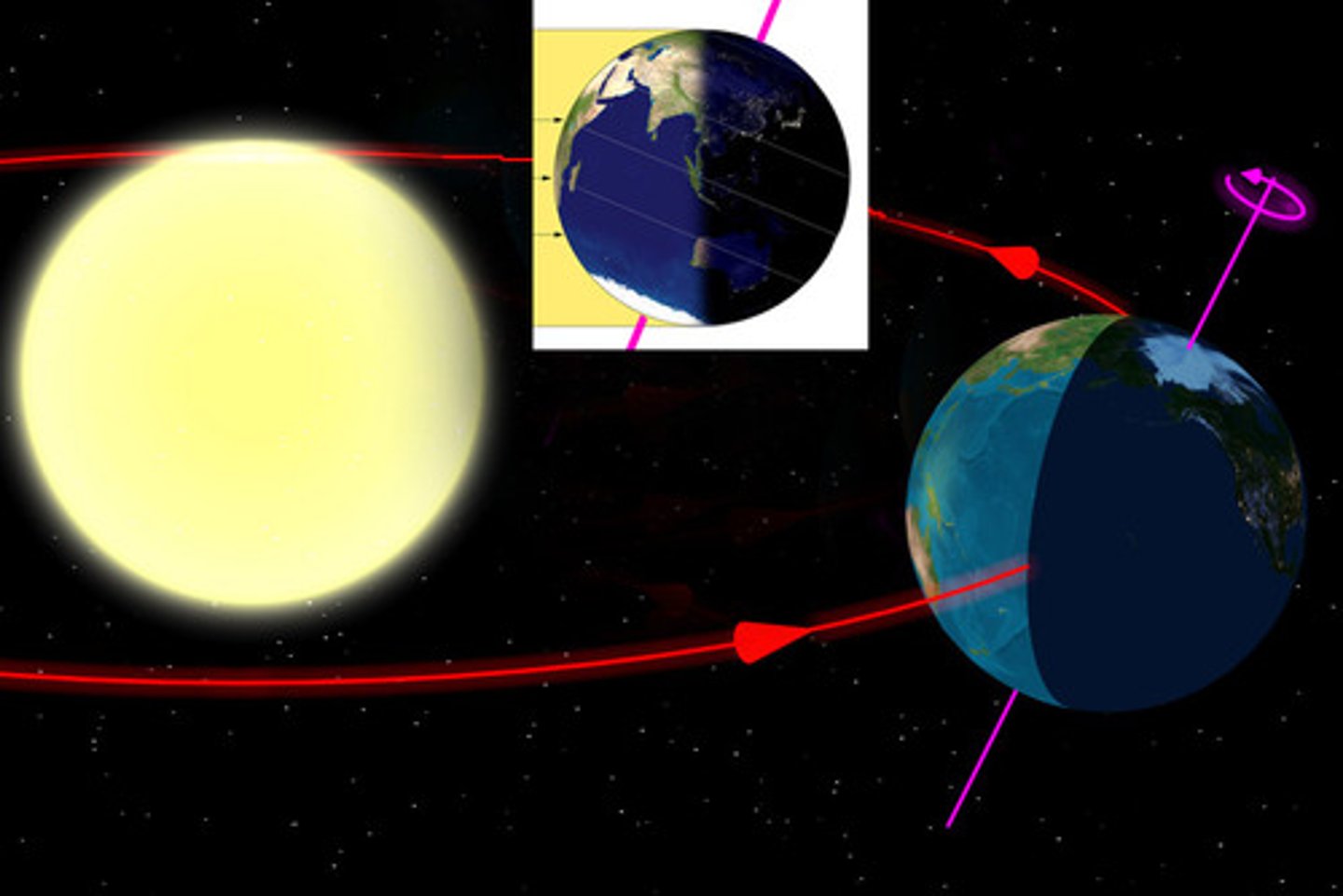
winter
When it is Summer in the Northern Hemisphere it is ___________ in the Southern Hemisphere
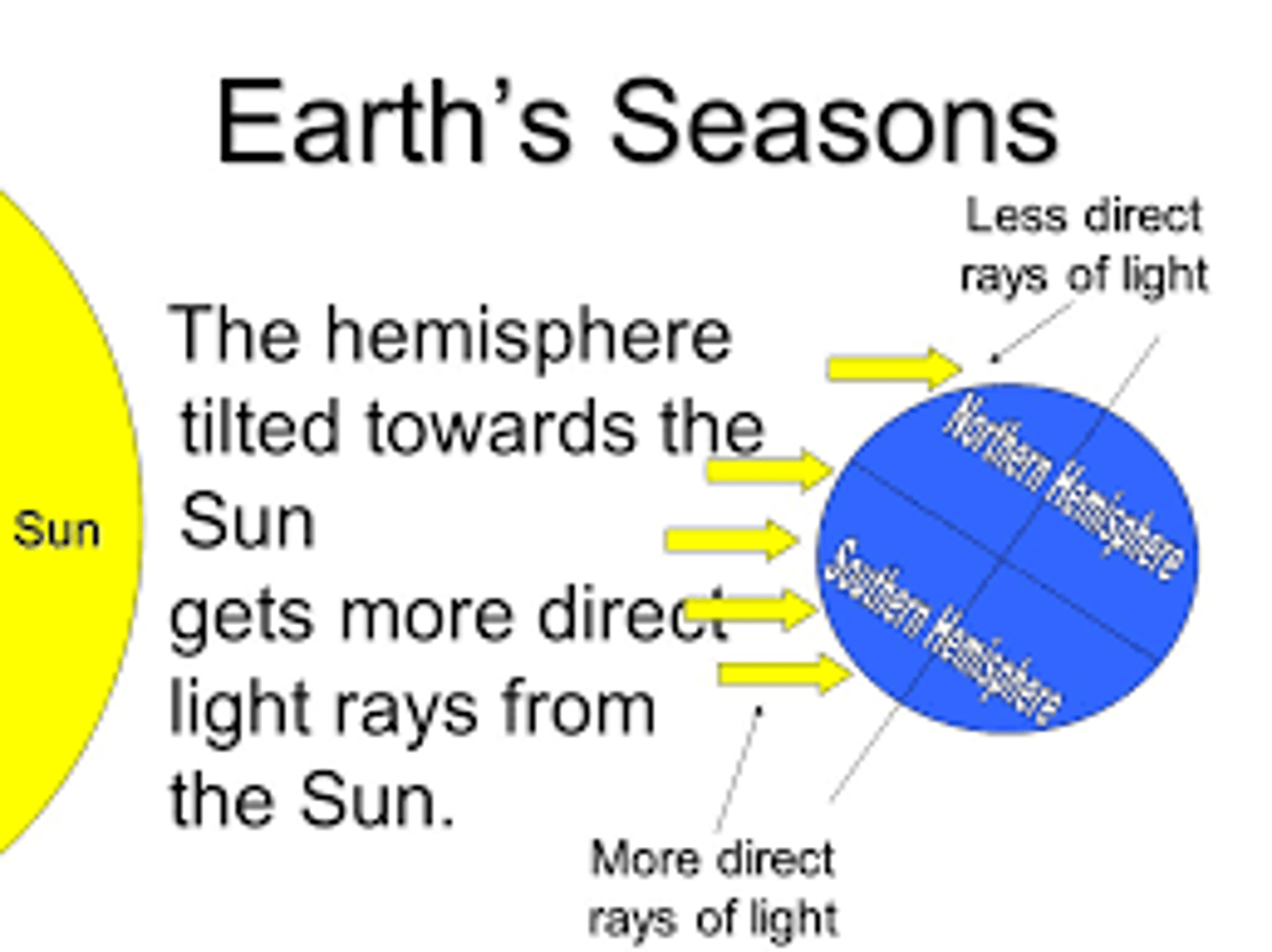
true
Summer and Winter (the seasons) are caused by the tilt of the Earth.
-(true or false)
longer
The hemisphere that is tilted toward the sun will have ____________ days
- (shorter or longer)
direct
The hemisphere that is tilted toward the sun will recieve more ___________ rays from the sun.
- (direct or indirect)
solstice
-two days each year, when the noon sun is overhead at either 23.5 degrees south or 23.5 degrees north (longest and shortest day of the year)
-occurs June 21 in the Northern Hemisphere-longest day of the year, marks the start of Summer
-occurs December 21 in the Northern Hemisphere-shortest day of the year,marks the start of Winter
false
We have summer because the Earth is closer to the Sun during summer.
-(true or false)
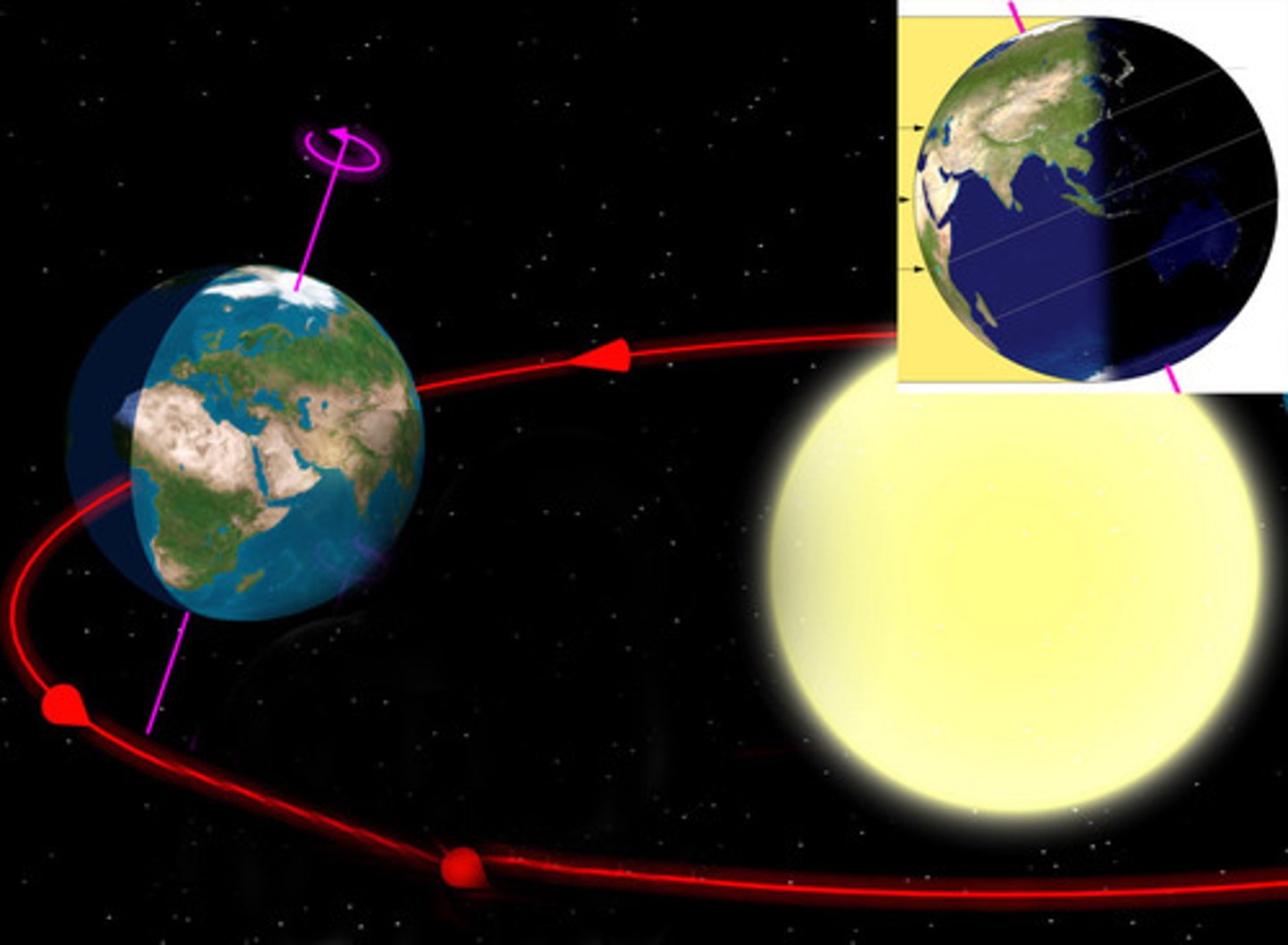
The Sun
By far, the primary source of external energy for the Earth system. Changes in the amount of energy reaching Earth's surface from this source results in seasonal changes and causes weather.

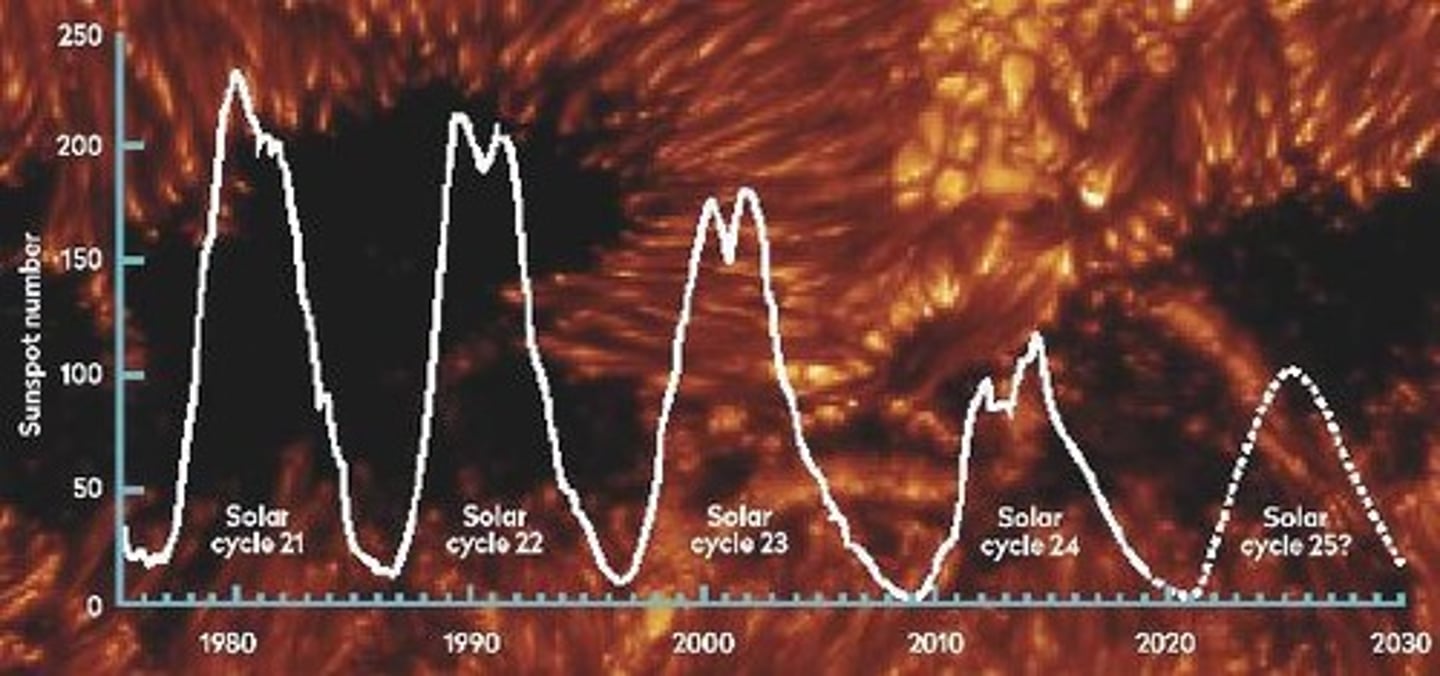
solar cycle
an 11-year cycle in which sunspot activity increases and decreases (as does the risk of solar storms).
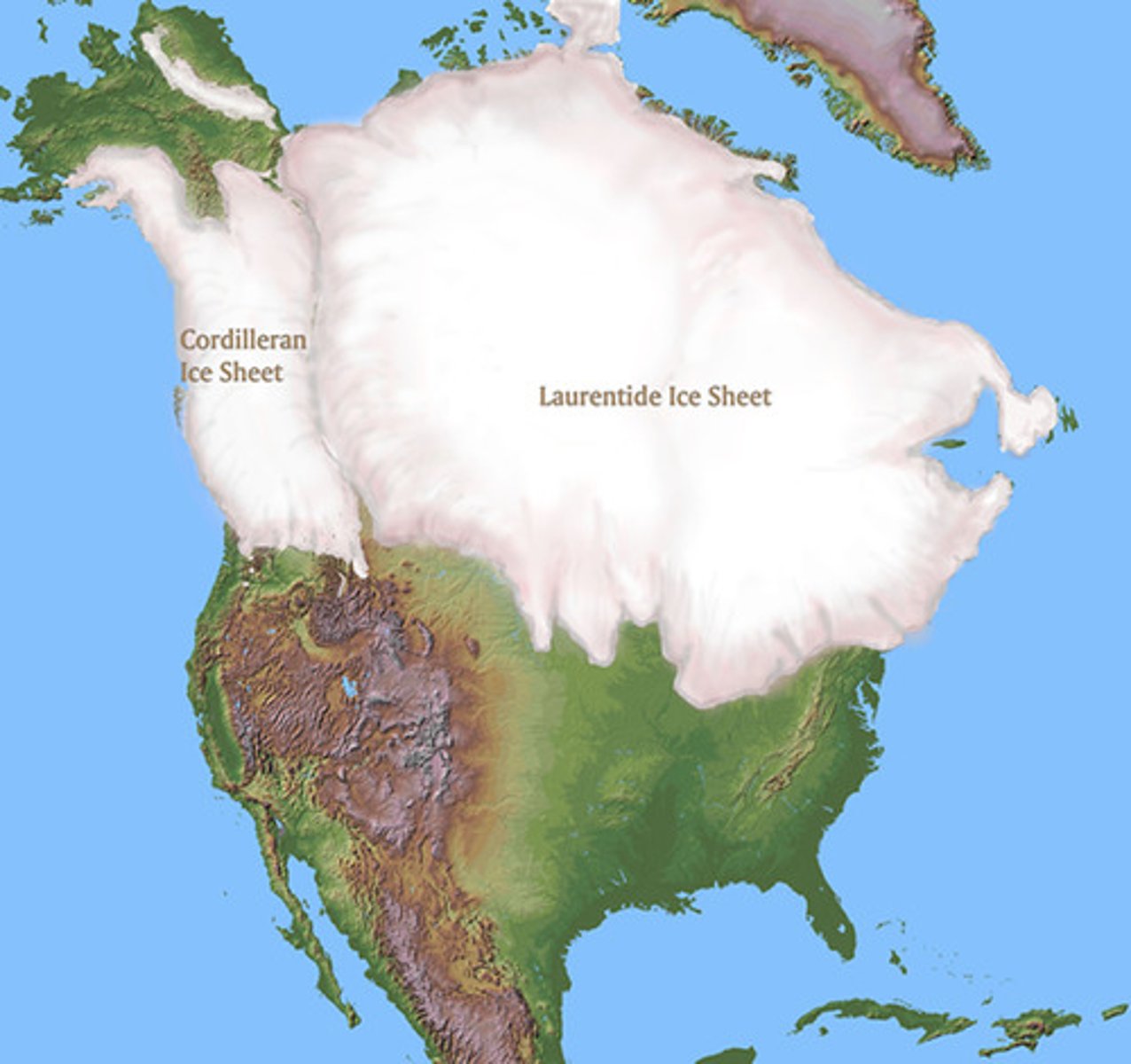
ice ages
Caused by long-term changes in the tilt and wobble of the Earth (10,000-100,000 years), the climate changes from deep cold periods (glacials) to the relatively warmer times (interglacials) such as we live in right now.
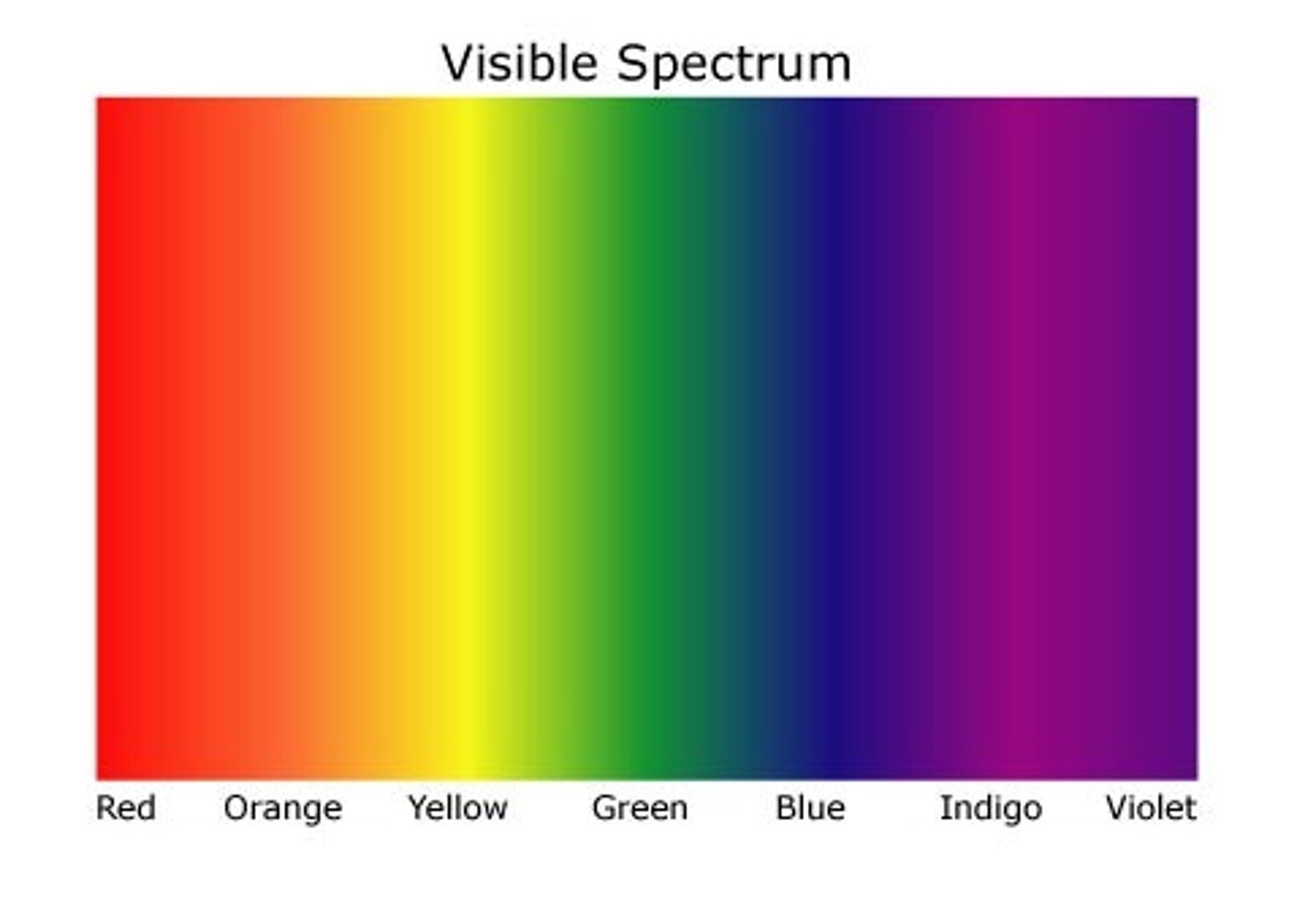
Visible Light
The type of light energy we can see.
Infrared Light
We can't see this type of light, but we can sense it as heat. Studying this energy using telescopes helps us to study the temperature of objects and can help us to "see back in time" (seeing light that has been stretched out by the expanding universe).

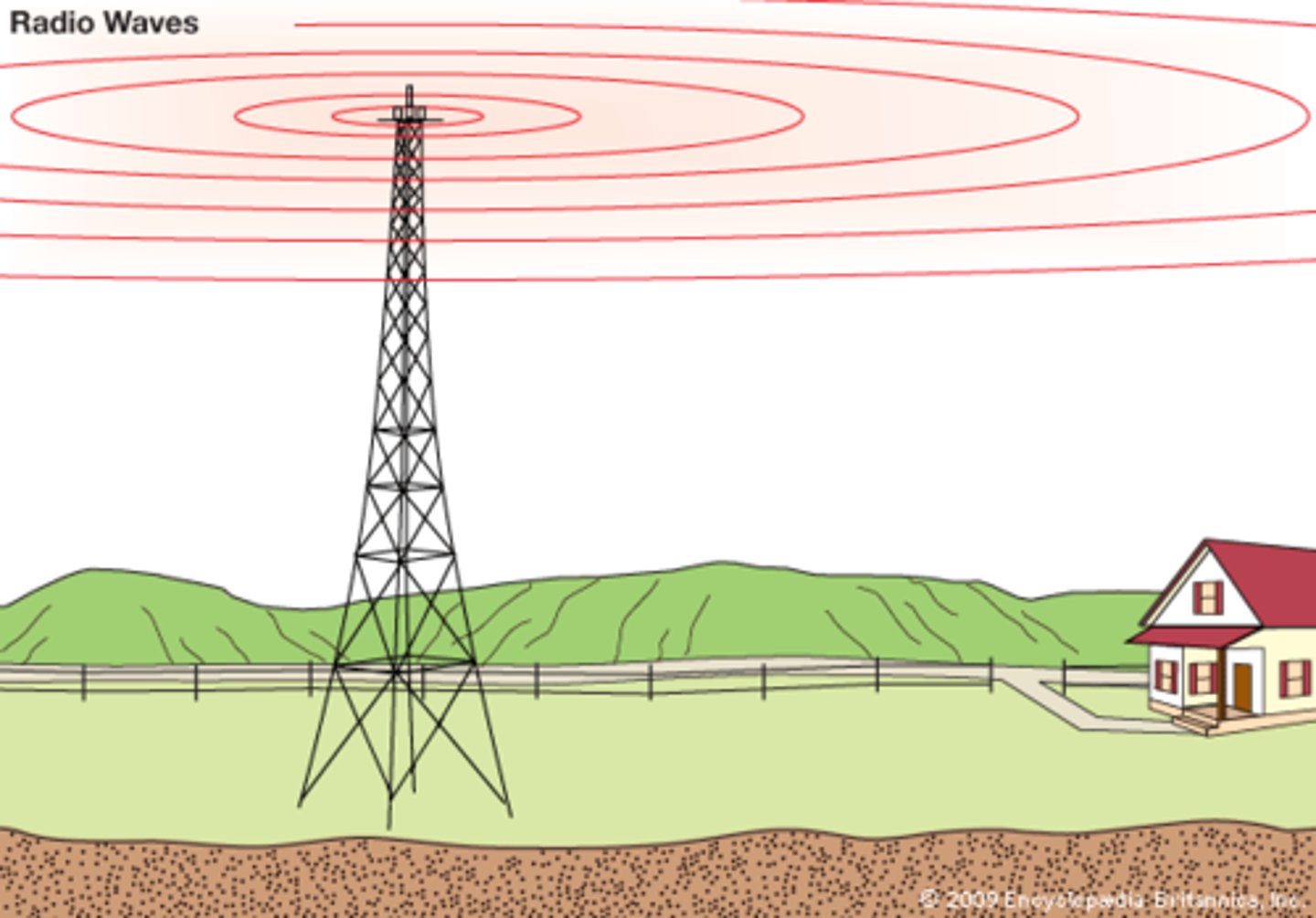
Radio Waves
A type of very long wavelength light that is used for communications.
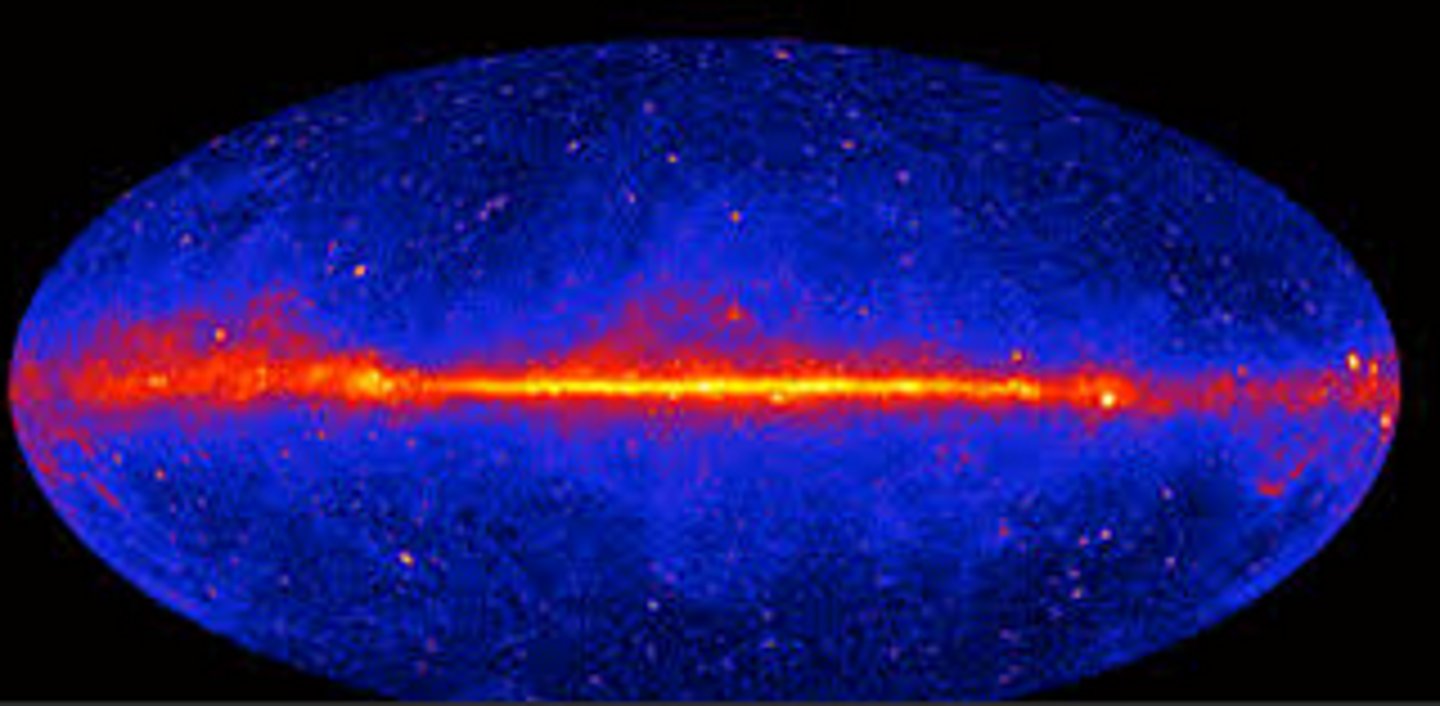
Gamma Rays
The highest energy type of light. Used to study very energetic space objects such as supernova explosions. Damages DNA, causing cancer (unless you are Bruce Banner and get transformed into the Hulk).
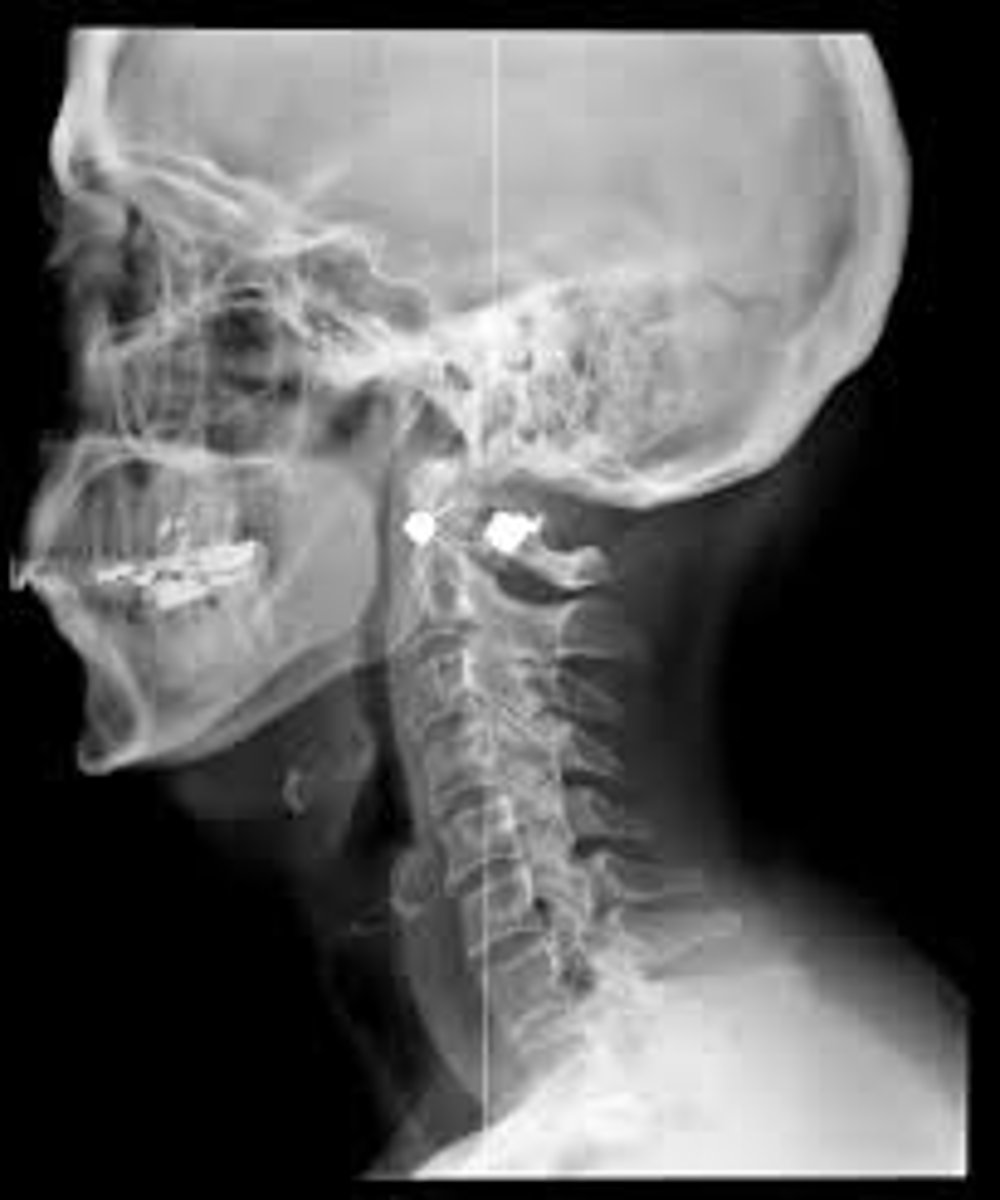
X-Rays
A very energetic form of energy used to "see through" objects in medicine (but it also has other uses).
Microwave Light
EM radiation with a longer frequency than visible light, but a shorter frequency than radio waves. Also used for communication. A narrow part of this energy can be used to cook food.
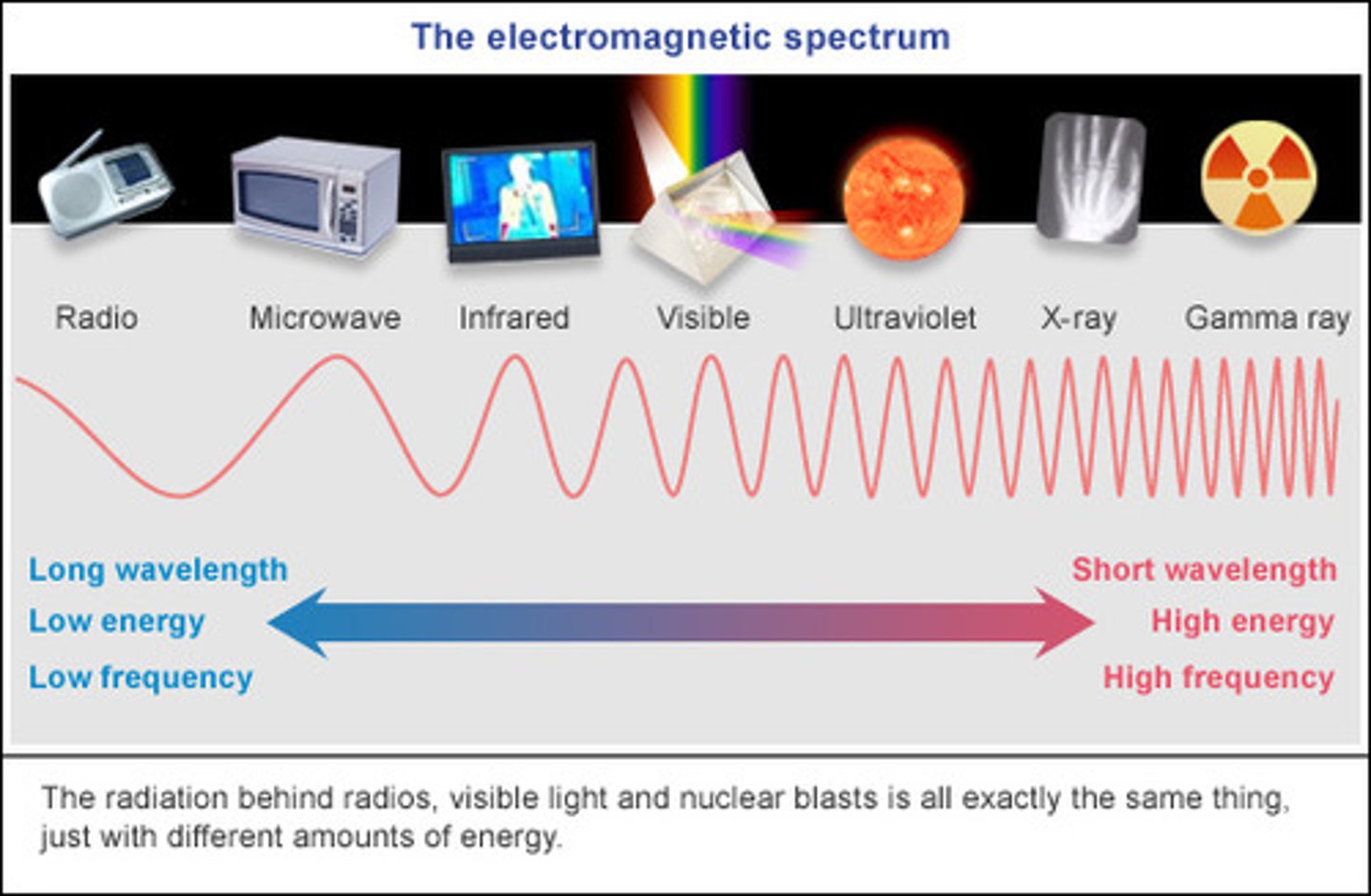
Ultraviolet Light
Invisible light that has more energy than visible light but less energy than x-rays. Exposure to this light can give you sunburns (and increased cancer risk). Abbreviated as "UV."

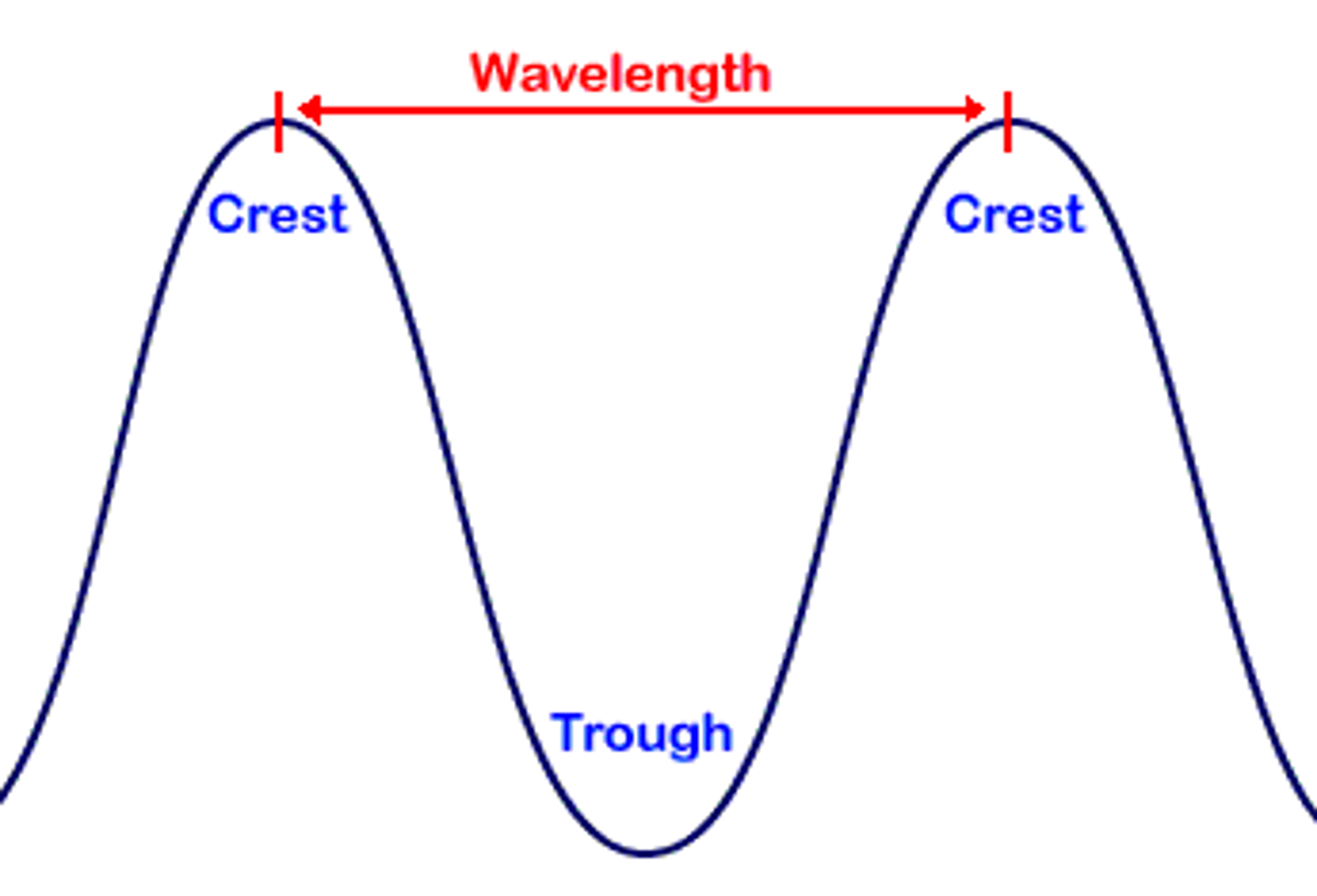
Wavelength
Horizontal distance between the crests or between the troughs of two adjacent waves
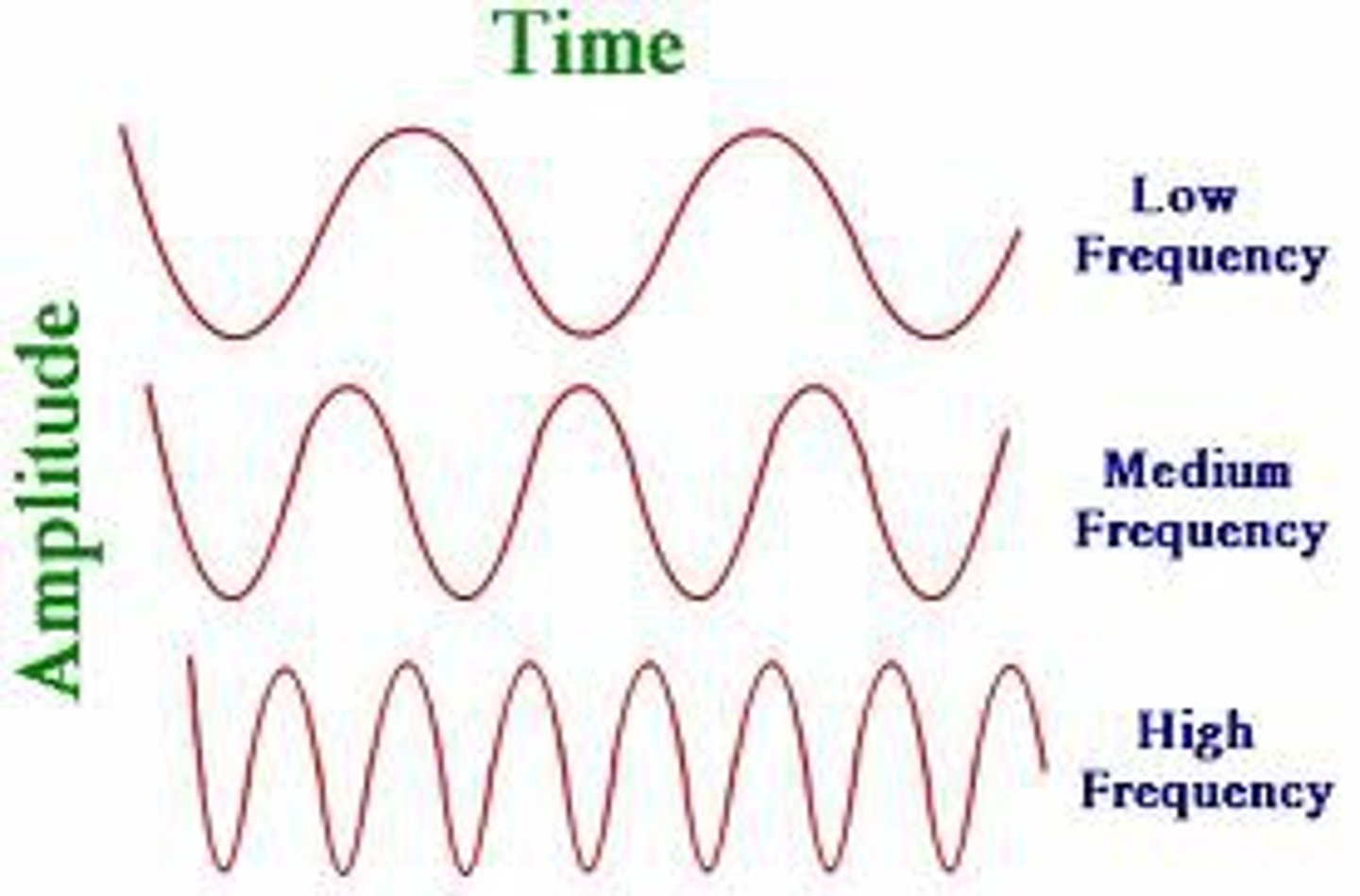
Frequency
How many wave peaks pass a certain point per given time
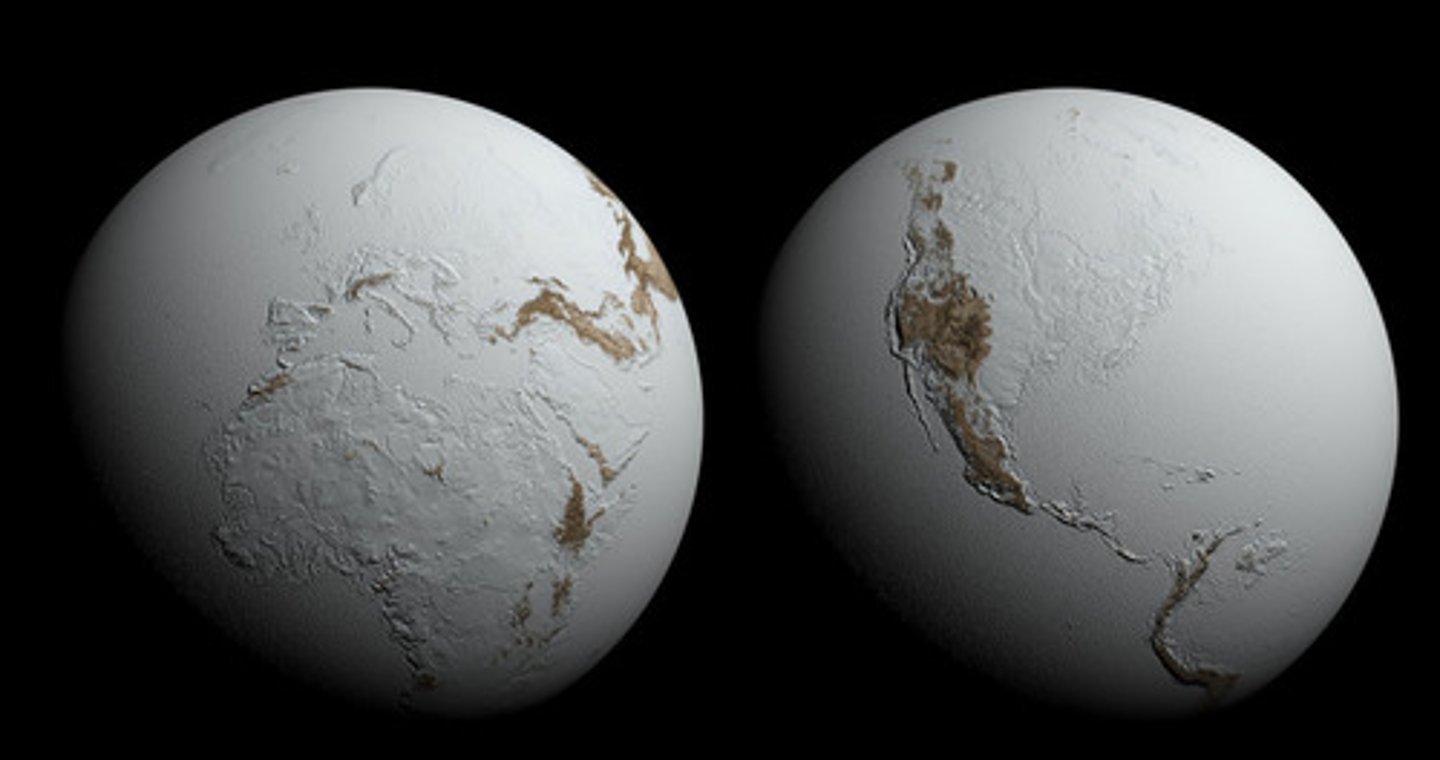
Cooling: Ice Albedo Feedback (Example - Snowball Earth)
A feedback mechanism where the Earth is covered by ice, which reflects light back to space, which causes the Earth to cool further and grow more ice.
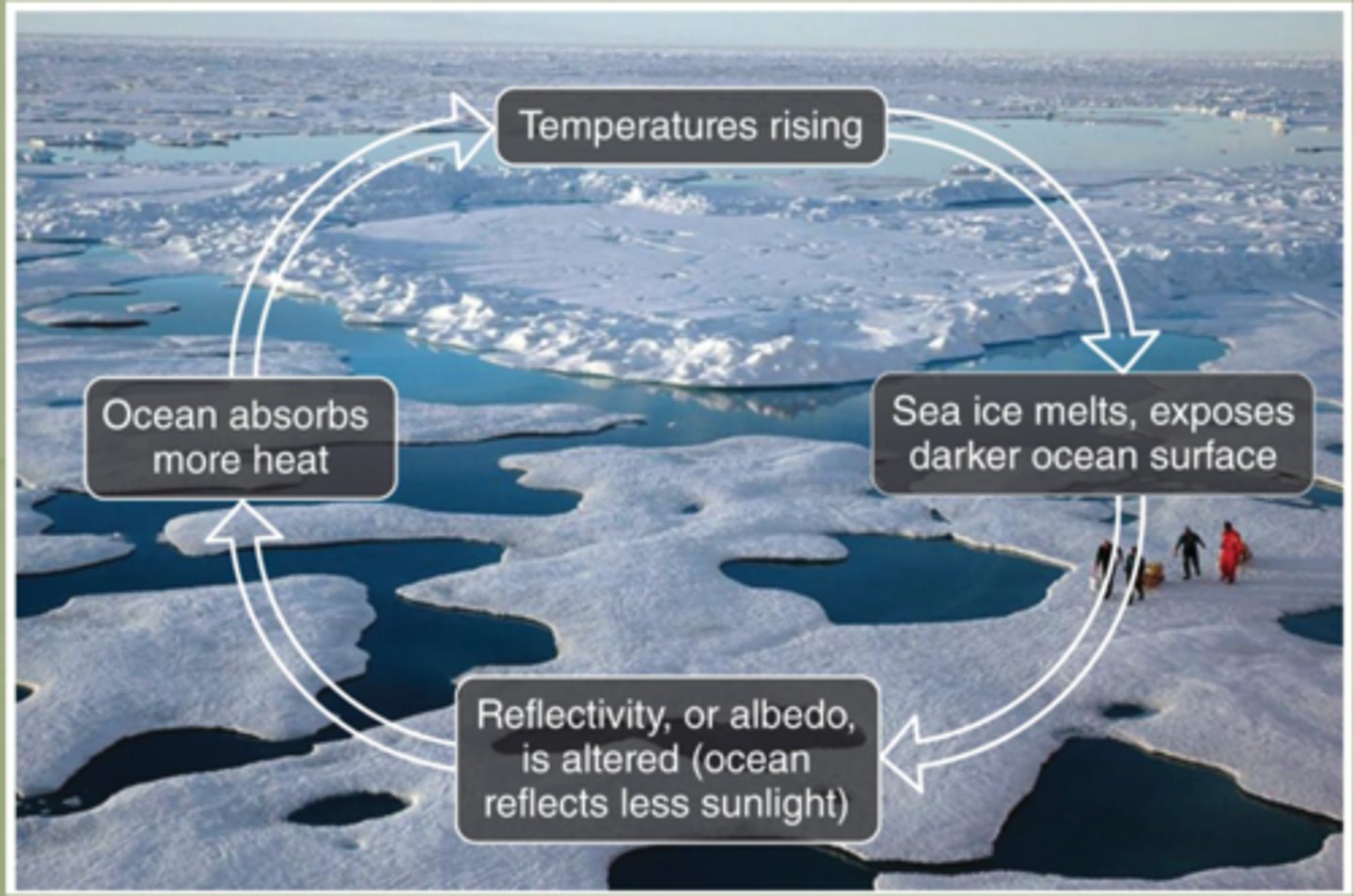
Warming: Ice Albedo Feedback (Example: Current Earth Losing Ice)
A feedback mechanism where the ice sheets begin to melt, leaving behind darker surfaces (such as soil and water) that absorb more light energy and heat up. This melts more ice and causes more warming.
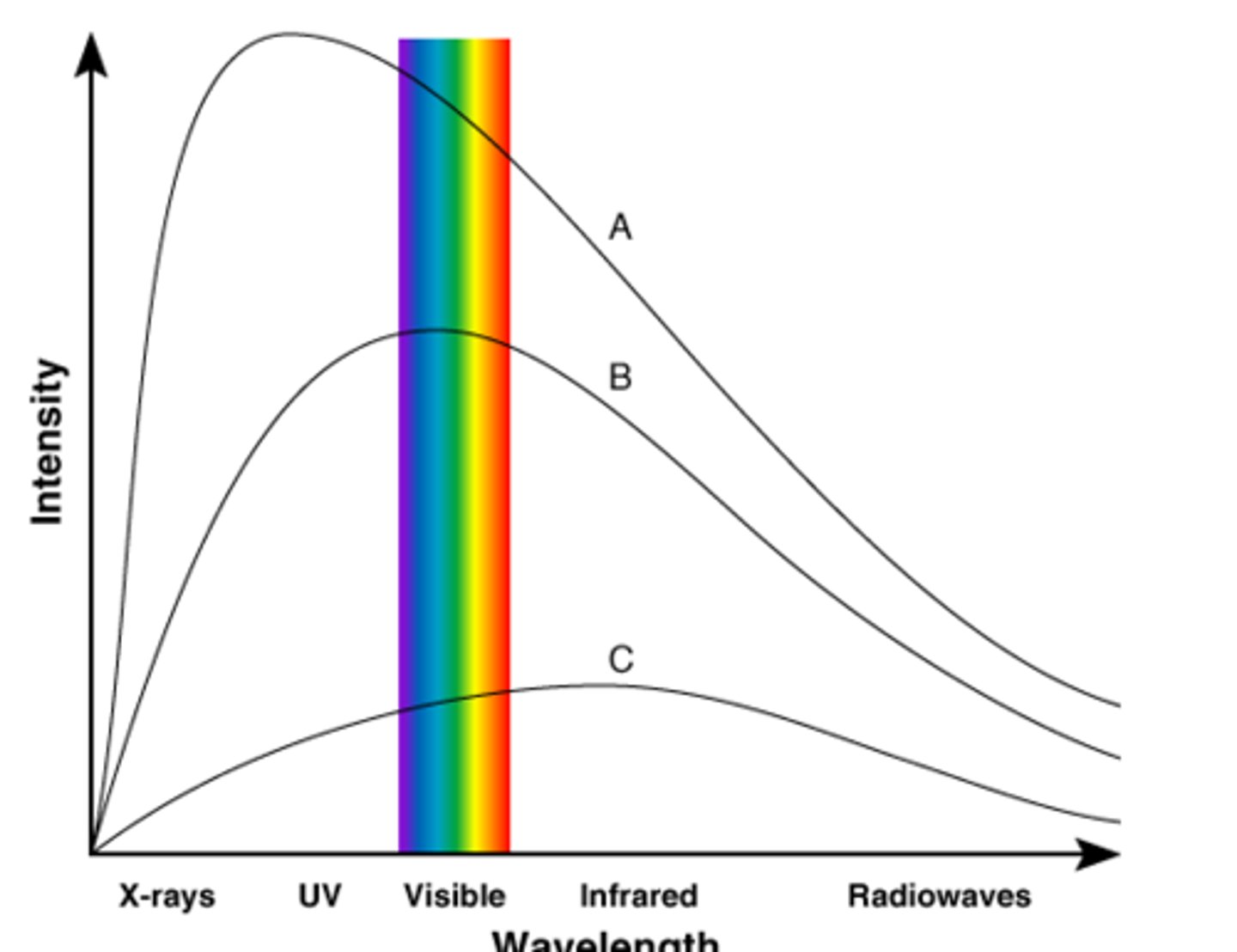
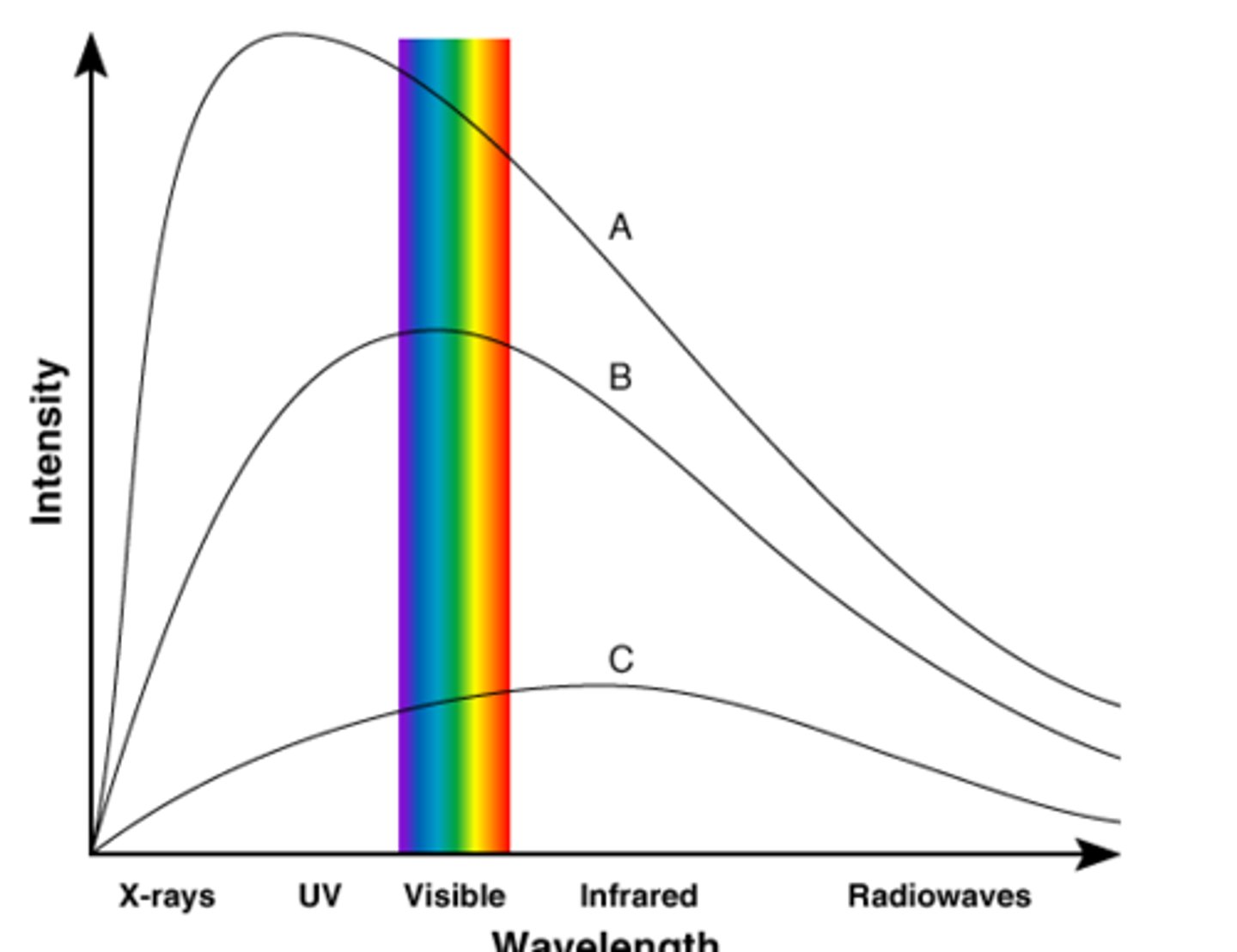
Blue Star (peaks in ultraviolet)
The color of star we see when it is the hottest type of star.
White / Yellow Star (peaks in the visible spectrum)
The color of medium-temperature stars (like our own Sun).
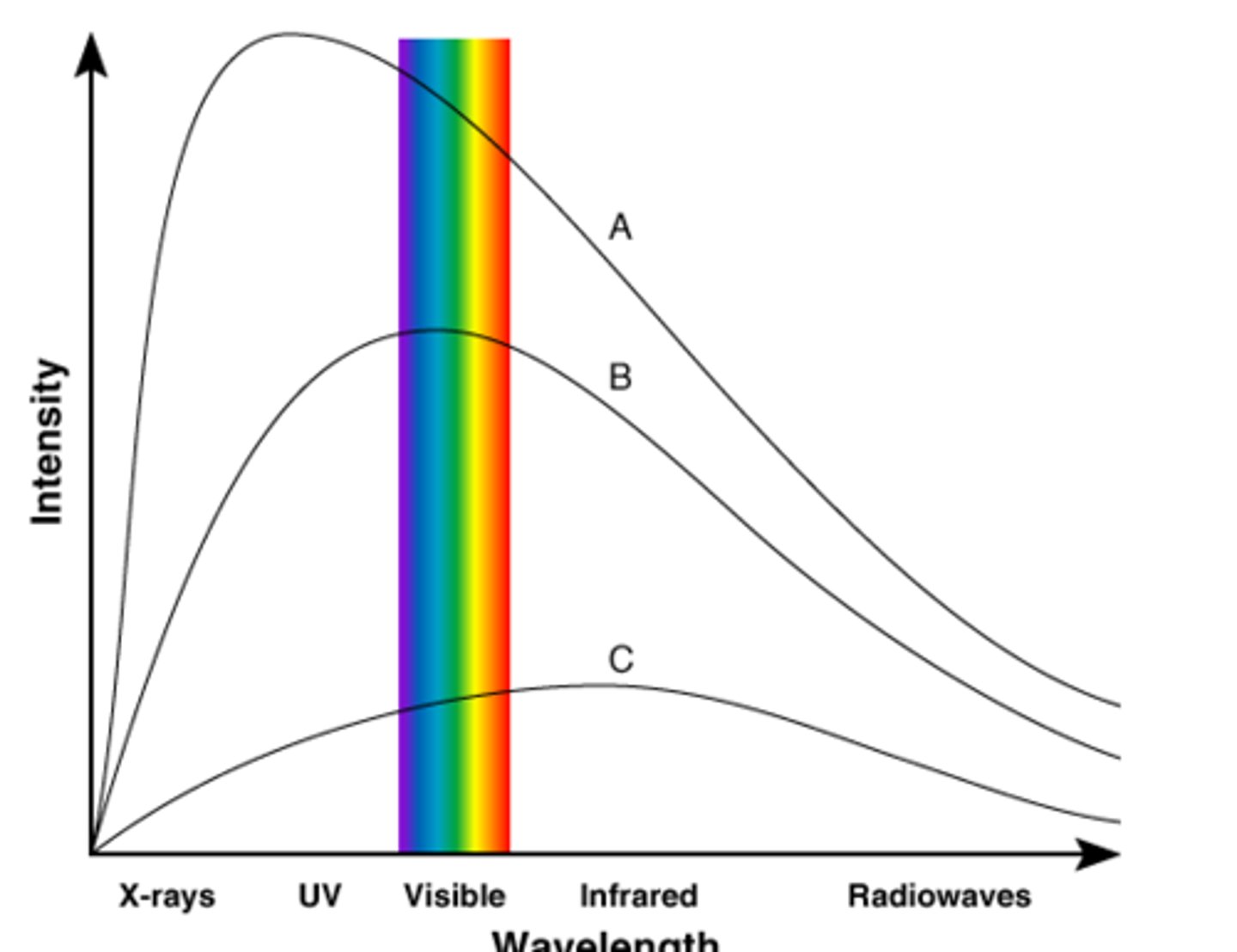
Red Star (peaks in the infrared part of the spectrum)
The color of cooler stars.