Socio-Cultural Unit Vocab
1/52
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
culture
generally defined as societal rules based on shared values, beliefs, experiences, morals, and ideation that a community of people follows to dictate their behavior
culture is on a continuum
a spectrum to measure cultural dimensions
a concept used to describe food, eating habits, gender roles, rituals, communication patterns, and use of free time
Cultural Dimensions
Individual vs collective
how people define themselves and their relationships with others
Power distance
the extent to which a culture respects authority and status
Masculine vs feminine
how competitive a society is
Uncertainty avoidance
a societies tolerance for ambiguity
Short vs long-term orientation
connections to the past and attitude towards the future
Indulgence vs restraint
a society’s tolerance for relaxation versus strictness
dimensions
how the values of a society affect behavior in a given culture
factor analysis
taking questionnaire data and focusing on the key differences submitted by people of different backgrounds
etic approach
studying culture from outside of the culture rather than observing the culture
taken within cross-cultural psychology where behavior is compared across specific cultures
draws on the notion of universal behaviors
ecological fallacy
when one looks at two different cultures, it should not be assumed that two members from two different cultures must be different from one another or that a single member of a culture will always demonstrate the dimensions which are the norm of that culture
cultural norm
a set of rules based on socially or culturally shared beliefs of how an individual ought to behave to be accepted within that group
used to regulate behavior within a group
surface culture
what is easily seen as different when in contact with another group
deep culture
the beliefs, attitudes, and values of a group
could be a result of cultural factors
ethnocentric
viewing other cultures from the perspective of your culture
universal behaviors
looking for “rules“ of human behavior that could be applied to all cultures globally
emic approach
researchers immerse themselves in the culture they want to study to develop an understanding
research questions are developed through interactions with locals
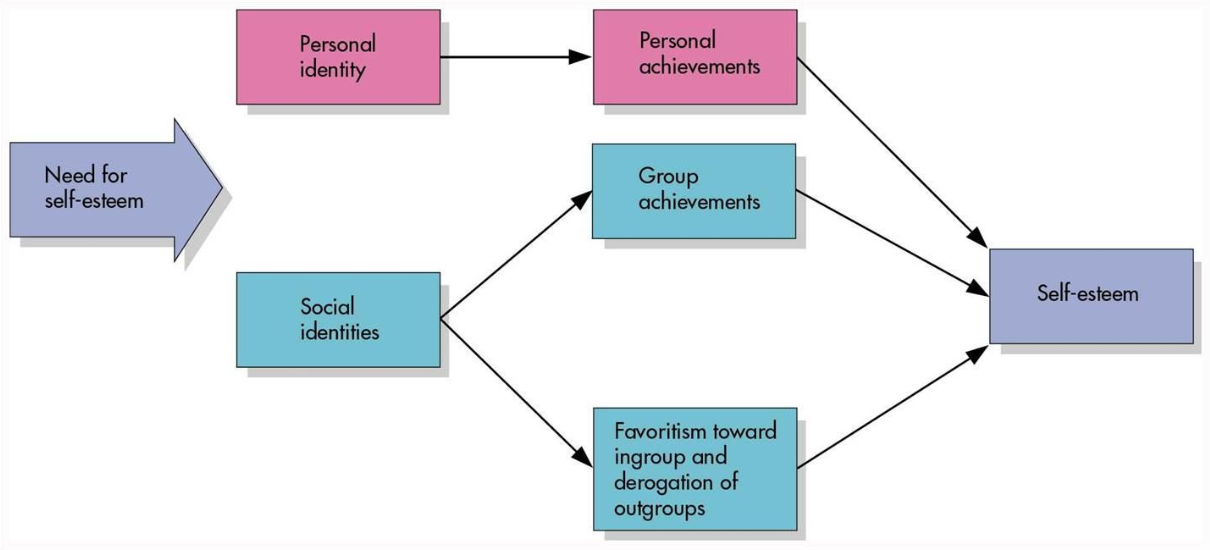
Social Identity Theory
a theory for analyzing intergroup relations
states that the in-group will discriminate against the out-group to enhance their self image
in-group
any group that an individual is apart of
groups may try to maintain positive identity by discriminating against other groups
social identity
ones self-concept based on membership in a social group and the value that is attached to that membership
positive in-group distinctiveness
a good standing within an in-group
principles of identity
categorization
identification
comparison
naturalistic
done in environments in which the behavior is most likely to take place
participant observation
when researchers immerse themselves in a social setting for an extended period of time and observe behavior
overt observation can occur
overt observation
when participants in the group know they are being observed
require researchers to gain the trust of the group that is to be observed and must attempt to experience the world the way the participants experience it
covert observation
sometimes used in groups that would be hostile to an outsider observing their behavior who would not be open or honest
the researcher must gain the trust of the group members, but is done through deceit
data is prone to deception and there are many ethical considerations
interviews cannot be carried out
Social Identity Theory
argues that a person is not just one “personal self“ but rather several social selves that correspond to group membership
salient
we can become more aware of classifying people into groups based on similar characteristics
social categorization
the process of classifying people into groups based on similar characteristics
gives rise to in-groups and out-groups
has a tendency to hold bias towards groups we are apart of, in-group favoritism
social comparison
a way to maintain self-esteem
the benefits of belonging to an in-group versus the out-group
positive distinctiveness
we are more positive toward anything that our own group represents
operant conditioning
learning based on positive or negative reinforcement
classical conditioning
a type of unconscious learning that occurs when a neutral stimulus is paired with a produces a natural response, resulting in the neutral stimulus producing the same response
social cognitive theory
AKA: social cognitive learning theory
suggests that behavior is learned from the environment through the process of modeling and reinforcement
do not need personal experiences to learn
based on the assumption that people learn not only through direct experience, but also by observing others
we learn the consequences by watching what happens to others
modeling
involves learning through the observation of other people which leads to imitation of behavior and then leads to desirable consequences
you will receive vicarious reinforcement
social learning
to social learn the individual must fit this criteria:
attention
becoming aware
retention
remembering what happened
reproduction
developed skills
motivation
reward
stereotype
a mental representation and a form of social categorization made about specific individuals or a group and its members
a social perception of an individual in terms of group membership or physical attributes
a generalization that is made about a group then attributed to group members
a result of schema
a form of categorization that affects the behavior of those who hold the stereotype
once formed, it is difficult to change
provides an easy way to generalize information and acts as a brain shortcut
out-group homogeneity
we see our out-groups as all having similar traits
grain of truth hypothesis
a way stereotypes are developed
argues that an experience with a group will then be generalized to the group
illusory correlation
a cause of stereotyping
where people see a relationship between two variables even when there is none
this includes prejudice against certain groups
an example of cognitive bias
a persons tendency to make errors in judgement based on cognitive factors, including attribution errors
fulfilled by conformation bias where people seek out information to support the relationship
stereotype threat
occurs when one is in a situation where there is a threat of being judged or treated stereotypically or fear of doing something that would confirm the stereotype
spotlight anxiety
can happen due to stereotype threat
causes emotional distress and pressure that may undermine performance
memory distortion
an effect of stereotyping
when things occur that don’t align with our stereotypes, our memories are more prone to distortion
gatekeepers
parents, media, members of our culture, etc.
influence how stereotypes form
Enculturation
the process by which people lean the necessary and appropriate norms of their own culture
an essential requirement for survival
the very first familiarization process to a particular culture
the process is learned through cultural transmission and enculturation
Acculturation
the process of change as a result of contact or interaction between cultures
a process of cultural and psychological change where people move into another culture and they often begin to adopt the norms and behaviors of the majority culture
not an essential requirement to survival
not the first, but second or third familiarization to various cultures
cultural norms
the unique set of attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors specific to a particular culture
cultural transmission
passing cultural norms from one generation to the next
values enculturation
enculturation on cognition is seen through attitudes about social relations, gender roles, time orientation, beliefs on health and illness, and beliefs about morality
direct tuition
when enculturation occurs by your parents telling you what you are supposed to do
participatory learning
when enculturation occurs through learning where children engage in an activity and then transfer the learning to other situations
gender role
a social role encompassing a range of behaviors and attitudes considered acceptable, appropriate, or desirable for people based on their biological or perceived sex
four acculturation strategies
assimilation
when an individual abandons their original culture and adopts the cultural behaviors and values of their new culture
integration
is when there is an interest in adopting the behaviors and values of their new culture
separation
is when migrants maintain their own culture and minimize contact with the new culture
marginalization
results when it isn’t possible to maintain the original culture but due to exclusion or discrimination it is not possible to assimilate into the new culture
acculturative stress
the psychological, somatic, and social difficulties that may accompany acculturation
a reduction in the mental health and well-being of ethnic minorities that occurs during the process of adapting to a new culture
“culture shock“
acculturation gaps
generational differences in acculturation and how this leads to conflict within a family
children develop and acculturate faster than parents due to school which leads to conflict and pressure from two different cultures
reactive identification
when the individual strengths his or her ethnic or racial identity in response to discrimination
a response to high levels of acculturative stress
immigrant paradox
the “greater“ degrees of acculturation were associated with problematic health outcomes
alternation model
people move back and forth between their own culture and the host culture depending on the situation