Lactation
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
List milk composition
normally:
4.5% lactulose
4% fat
3.2% protein
What are some non-nutritional influences on composition and milk yield
Frequency of milking
more milking = longer production therefore increased yield.
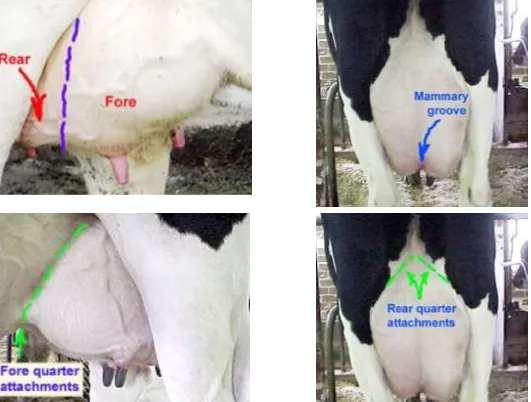
Describe gross udder anatomy
Rear and Fore quarters. Mammary groove down middline.
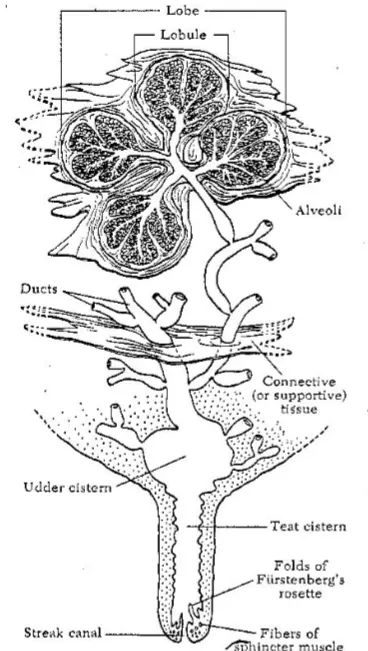
Describe internal udder anatomy
Alveoli lying on basement membrane, surrounded by smooth muscle.
Myoepithelial cells eject milk into ducts
Ducts move milk from alveoli to teats, udder cistern stored milk and opens into teat cistern (sphincter muscle contracts, annular fold separates.
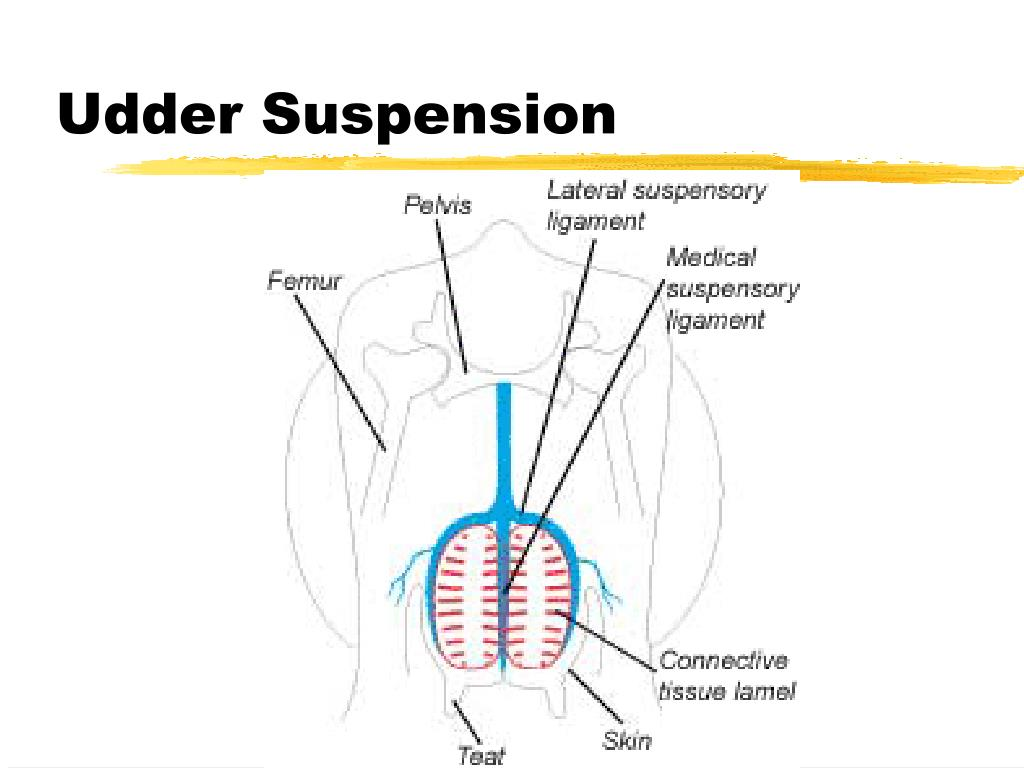
Describe the suspensor system in udders.
Contains the median suspensory ligament, pre-pubic and sub-pubic ligaments
Describe mammogenesis
Isometric growth until puberty.
Puberty
oestrogen, duct branching + widening
progesterone - alveoli formation at terminal portions
prolactin + GH - rapid development of ducts
Gestation needed to complete development.
Explain the physiological control of mammogenesis
During puberty:
oestrogen, duct branching + widening
progesterone - alveoli formation at terminal portions
prolactin + GH - rapid development of ducts
Gestation = completed development
Describe allometric growth + regression during oestrus cycle
initially - extensive duct system lying in fat pad
during gestation - secretory cells proliferate (displace fat)
during lactation - mainly differentiation
drying-off - gradual apoptosis
after drying off - rapid apoptosis
Explain the physiological control of lactogenesis (2 stages)
stage 1 - acquisition of secretory capability pre-partum
stage 2 - onset of secretion at parturition
systemic endocrine control - progesterone withdrawal
local control

Explain the physiological control of galactopoiesis
= maintenance of established lactation
local = IGF-1
systematic = GH and prolactin
prevents milk stasis
Explain the physiological control of apoptosis
after peak lactation
cell no and yield decline together
after cessation of suckling
rapid increase
gland returns to less developed state
controlled by prolactin, GH, IGF-1.
stimulated by weaning, milk stasis, IGFBP5
Describe mechanisms of milk let down
Teat stimulation → neuro-endocrine reflex
positive pressure in udder
bulk of milk obtained
stimulated by machine
How does milk let down influence milking routine
clean - pre-dip
identify animal
foremilk - inspect for clots
leave 30-45 seconds - oxytocin + pre-dip action
wipe off pre-dip
cluster on
milk flow reduced → cluster off
post-milking teat dip
loafing time - teat dip action + teat closure
Name 5 milking systems
Herringbone
50 or 30 degrees through the legs
Tandem
2 rows of 2 cows
Rapid exit
long line, fast release
Rotatory
cows on floating rotating thing, staff standing still
Automated
cows choice?