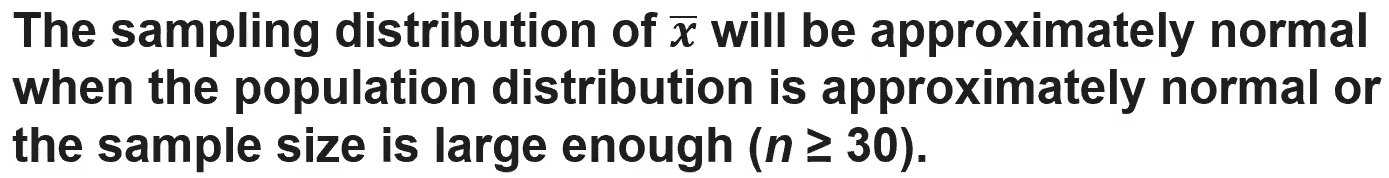AP Statistics Unit 5
1/15
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
(5.1) What is important to include in the solution of a normal distribution?
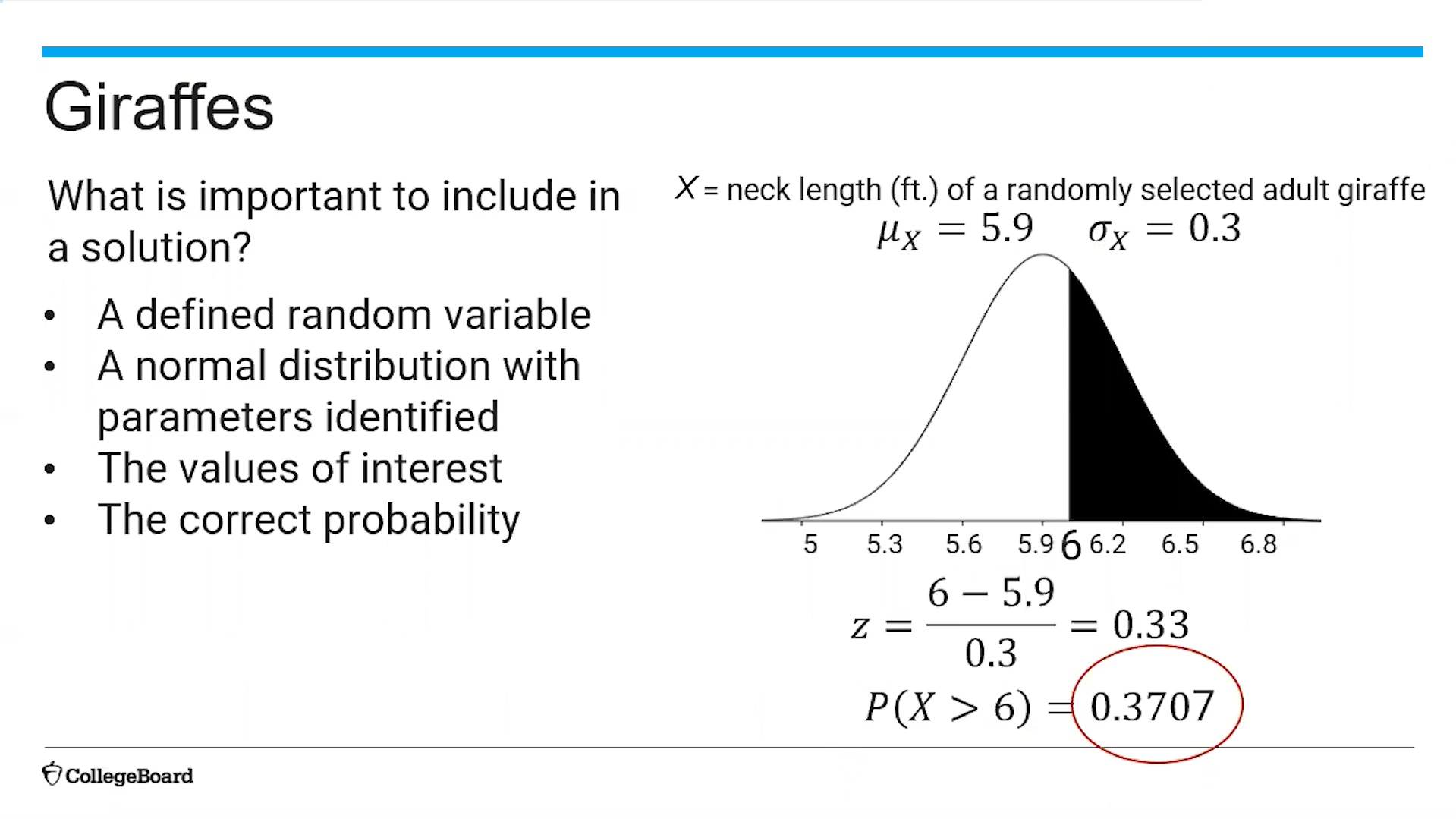
(5.1) Example of an inverse normal distribution?
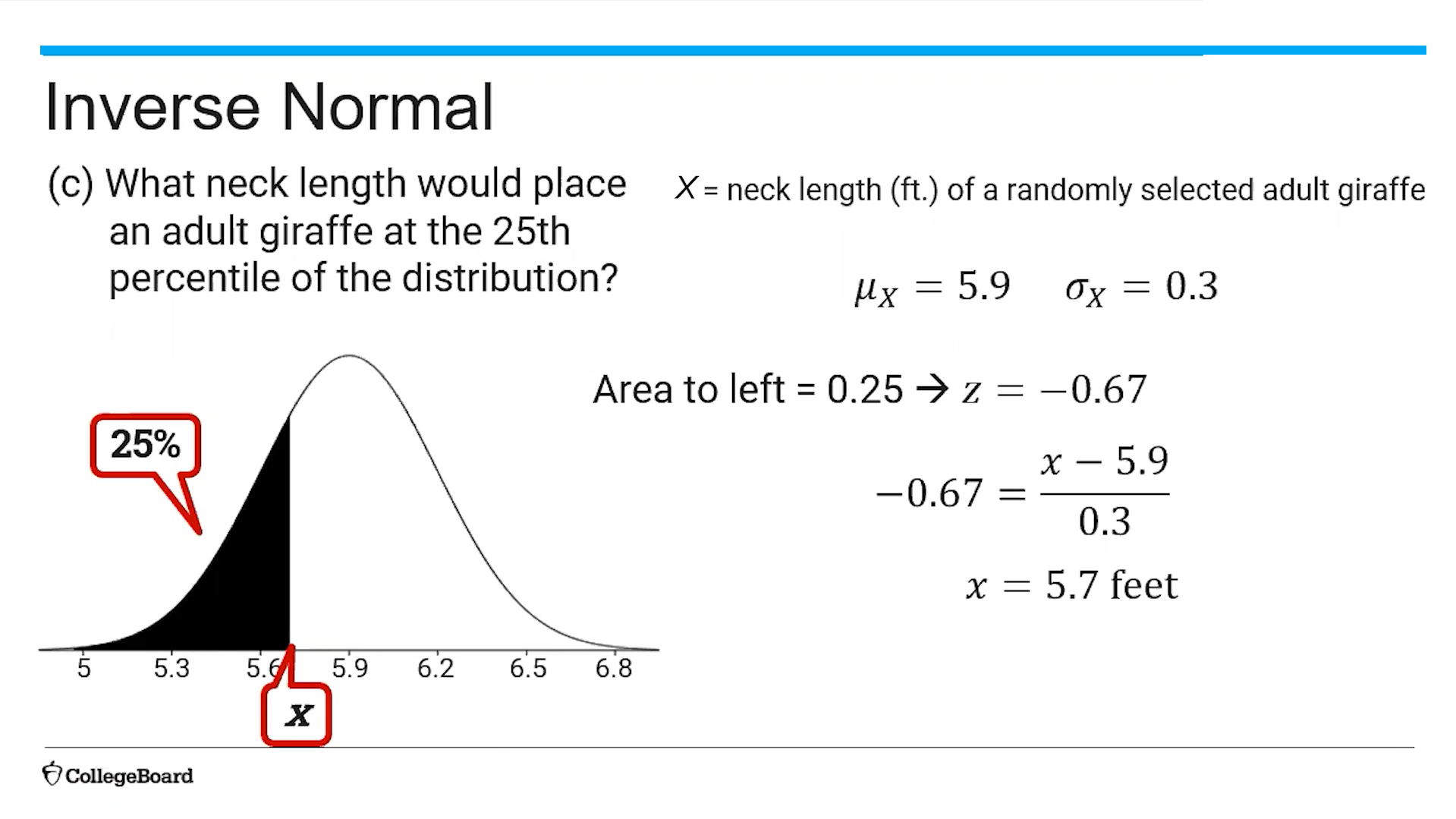
(5.2) How do you find the differences of a mean for a normal distribution?
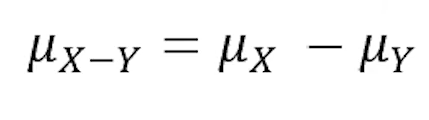
(5.2) How do you find the differences of standard deviation for a normal distribution?
You must first take the variances and then, always add.
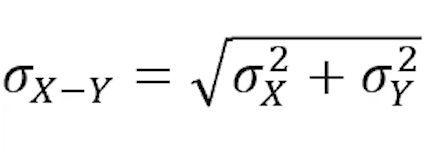
(5.3) What is a sampling distribution?
A sampling distribution of a statistic is the distribution of all values for the statistic for all possible samples of the same size from a given population. It is simulated by generating repeated random samples from a population.
(5.3) What is the Central Limit Theorem (CLT)?
The Central Limit Theorem (CLT) states that when the sample size is sufficiently large, a sampling distribution of the mean of a random variable will be approximately normally distributed.
(5.3) What is randomization distribution?
A randomization distribution for a randomized experiment is a collection of statistics generated by simulation to reallocate response values to treatment groups.
A randomization distribution can be used to assess the likelihood of an observed outcome happening by chance alone.
(5.4) What is a point estimator
A sample statistic is a point estimator of the corresponding population parameter.
(5.4) How do you know if an estimator is unbiased?
An estimator is unbiased if, on average, the value of the estimator is equal to the population parameter.
(5.5) How do we determine the parameters of a sampling distribution of a sampling proportion
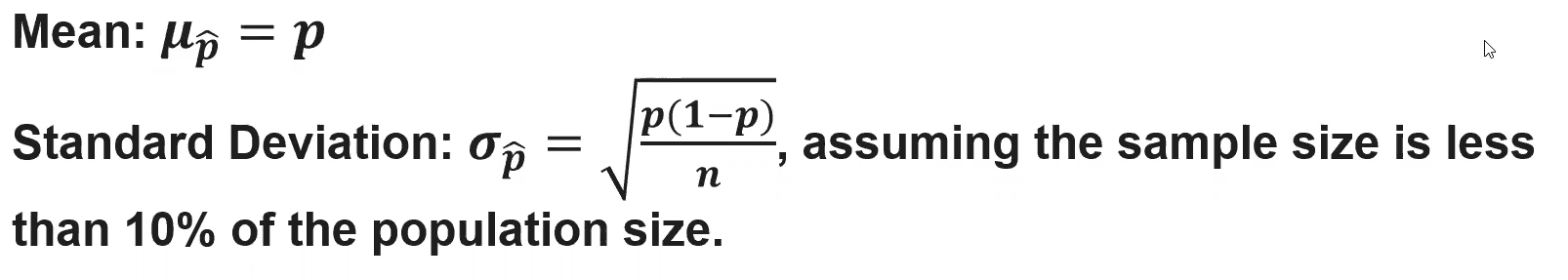
(5.5) How do we determine if a sampling distribution of a sample proportion is approximately normal
The sampling distribution of p̂ will be approximately normal
when np ≥ 10 and n(1 − p) ≥ 10.
(5.5) What words to use when talking about standard deviations.
For standard deviation, include “typically“ or “on average“ when describing how much the values vary from the truth
(5.6) How do we determine the parameters of a distribution of a difference in sample proportions
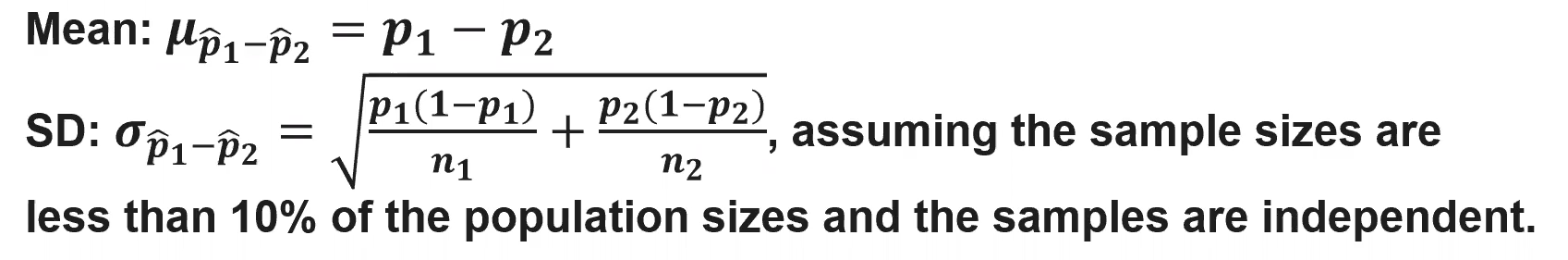
(5.6) How do we determine if the shape of a sampling distribution of a difference in sampling proportions is approximately normal
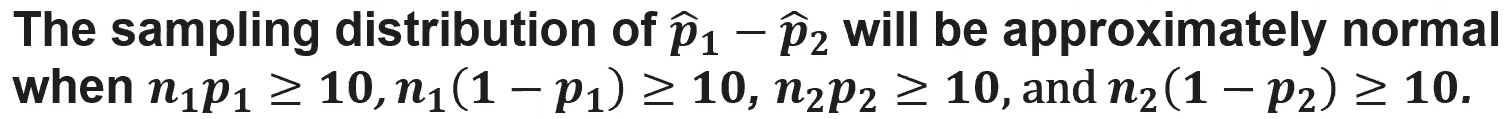
(5.7) How do we determine the parameters of a sampling distribution of a sample mean?

(5.7) How do we determine if the shape of sampling distribution of a sample mean is approximately normal?