BM topic 4 - key terms and formulae
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Market orientation
An approach to marketing that focuses on meeting the specific demands of customers. Thus, the businesses focus on making products they can sell and that customers would want.
Product orientation
An approach to marketing that focuses on making products a business knows how to make well, prioritizing R&D over market research, rather than concentrating on the needs and desires of potential customers.
Market share
Refers to the sales revenue that an organization accounts for within a given market or industry. It is measured by expressing the firm’s sales revenue as a percentage of the whole industry’s sales revenue: (Firm’s sales / Total sales in the market) x 100
Product
As aspect of the marketing mix, this is a physical good or intangible service provided by a business.
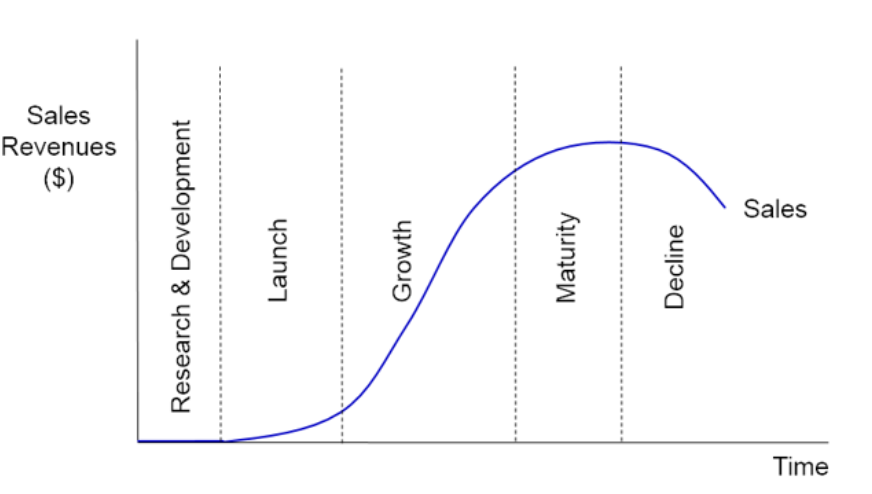
The product life cycle
R&D, launch, growth, maturity, and decline.
Pricing methods
Cost-plus: Adding a profit margin to the cost of production to determine price.
Penetration: Setting a low price in order to enter an industry.
Loss leader: Pricing below cost of production to attract customers who will also purchase products with higher profit margins.
Predatory: Charging a low price, even below cost of production, to damage the sales of rivals. Typically done to prevent new entrants into the industry.
Premium: Consistently charging a high price because of the associated image of the brand with high-quality products.
Above the line promotion
Refers to paid-for marketing communications through the use of independent mass media: television, radio, cinemas, billboards, magazines and national newspapers. Hence, control and responsibility of this promotion is passed to another organization.
The main advantage of using ATL promotion is the potential to reach a very large audience of potential customers.
Below the line promotion
Refers to marketing activities which the organization has direct control over. It is aimed directly at a targeted audience instead of a general audience
Distribution
The process of getting the product to the customer.
Zero-channel distribution network: zero intermediaries
One-channel distribution network involves the use of a single intermediary, such as an agent or retailers.
Two-channel distribution network involves the use of two intermediaries, usually wholesalers and retailers.
Three-channel distribution network uses three intermediaries, often involving an agent who sells the goods to wholesalers on behalf of the producer. In turn, wholesalers sell to retailers.
People
An aspect of the marketing mix, this refers to the importance of employee-customer relations.
Process
An aspect of the marketing mix, the way in which a service is provided or delivered to customers
Physical evidence
An aspect of the marketing mix that refers to the tangible aspects of a service, such as the physical appearance or tangible aspects of a restaurant, coffee shop, retail outlet, school or hotel. Has a direct impact on customers’ perceptions of a business and the quality of the services it provides.