MicroEconomics Chapter 1
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
The Study of Economics
is the study how people make choices under conditions of scarcity and of the results of those choices in society
Scarcity
The limited nature of society’s resources.
Economics
the study of how society manages scarce resources.
Effeciency
aims at maximizing the size of the “economic pie” / An improvement in efficiency means that the entire “economic pie” has gotten larger.
Equity
aims at equating the size of every individual’s “slice” of the “Economic Pie” / a more equal “cutting” of the pie means an improvement in equity"
Opportunity Cost
The Opportunity cost of any item is whatever must be given up to obtain it
It is the relevant cost for decision making
Rational People
systematically and purposefully do the best they can achieve to their objectives.
Rational People Think at the margin.
Marginal Changes
Incremental adjustments to an existing plan
rational people make decisions by evaluating costs and benefits of marginal changes.
Optimize
Given a choice amongst alternatives, a rational individual will choose the one that is best for him//her/they
Rational People optimize
Incentive
something that induces a person to act, i.e. the prospect of a reward or punishment.
Knowing the incentives people face makes it easier to predict how they will behave
Market
A group of buyers and sellers (need not be in specific location)
Market Economy
Allocates resources through the decentralized decisions of many house holds and firms as they interact in markets.
Market Failure
when the market fails to allocate society’s resources efficiently
Externalities (i.e. pollution)
Market Power ( Monopolies)
Public Goods ( National Defense)
Asymmetric Information ( Insurance Markets)
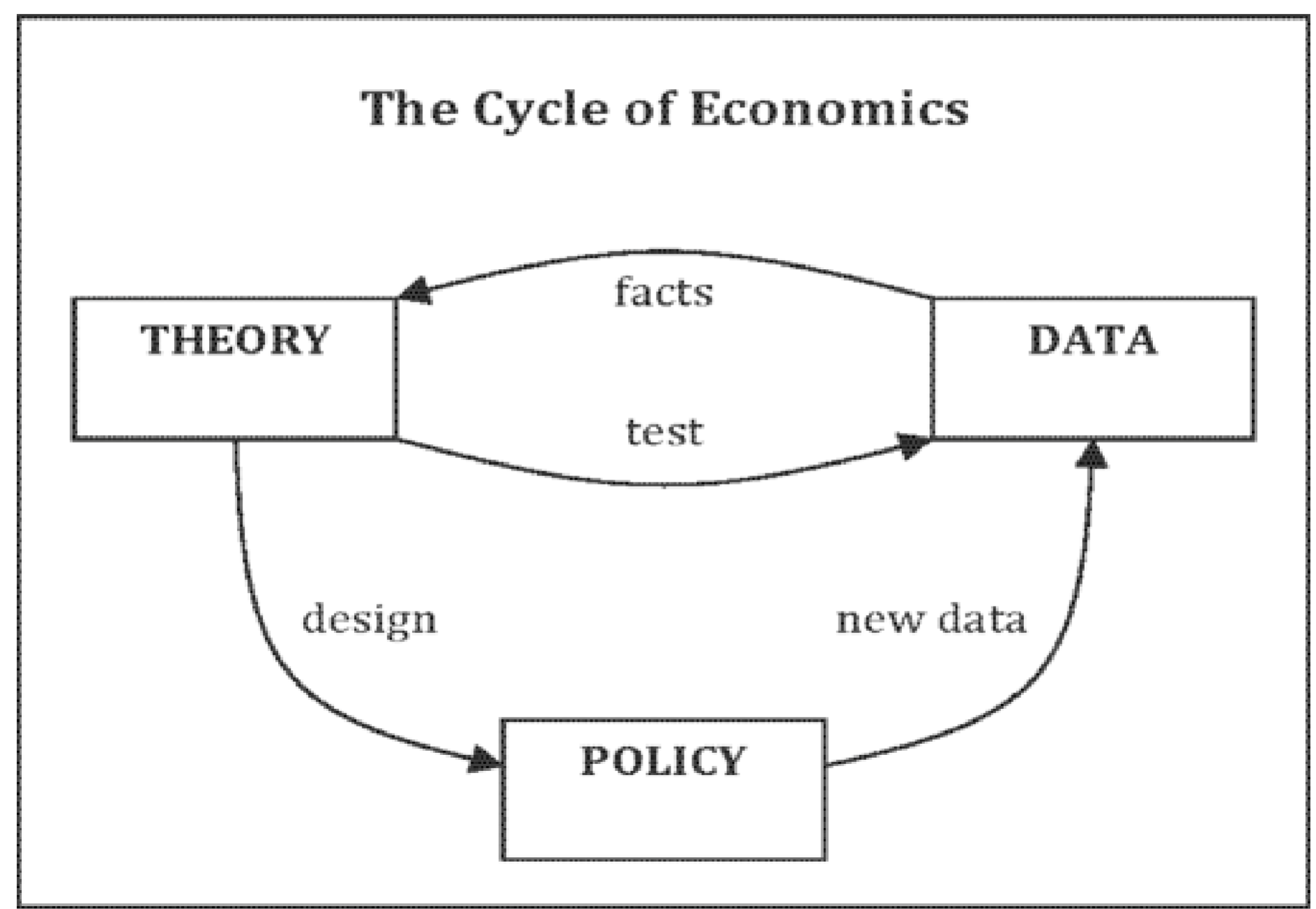
Scientific Method (in economy)
the dispassionate development and testing of theories about how the world works.
Positive Statements
As scientist, economist make positive statements which attempt to describe the world how as it is
Positive statements can be confirmed or refuted, normative statements cannot
Normative Statements
As policy advisors, economists make normative statements which attempt to prescribe how the world should be
Positive statements can be confirmed or refuted, normative statements cannot
A model
Simplified representation of reality (thought experiments) (complexity)
Assumptions
Economists make assumptions in building models to analyze how the world works
Assumptions simplify the complex world to make it easier to understand
Circular Flow Diagram
A visual of the economy, shows how dollar flow through the market among households and firms
Factors of Production
Labor, Land, Capital ( buildings and machines used in production), Entrepreneurial spirit (abstract), Knowledge (abstract)
Households
Own the factors of production, sells/rent them firms for income
Buy and consumes goods & services
Firms
Buy/Hire factors of production, use them to produce goods and services
Sell goods & services
Explicit cost
require a cash outlet (tuitons,books,room board)
Implicit cost
could been working in the job industry, instead of going to college
The Central assumtpion of economics
Rationality
Example of Postitive statement
cutting taxes tend to results in increased economic (output)
The Market for good a Services
Output
The Market for “Factors of Production”
Input