lec 5/6/7: Coagulation and hemostasis
1/138
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
139 Terms
clot
end product of hemostasis and coagulation, this term is used many ways, can be normal or pathologic
thrombus
a solid mass of blood-borne elements formed within (and attached to) a vessel, synonymous with "blood clot", may be normal or pathologic
white thrombus
clot formed of mostly platelets and fibrin
red thrombus
clot formed with platelets, fibrin, and RBCs
thrombosis
inappropriate activation of hemostasis leading to pathologic thrombus formation. However, it is also used as a normal term when referring to endothelium and its properties of physiologically appropriate clotting
plasma
portion of blood without cellular elements, has clotting factors
serum
blood plasma that does not contain fibrinogen or clotting factors
hemostasis, inflammation, regeneration
what are the three core responses to injury?
platelets/thrombocytes
annucleate cells that function for hemostasis
Bone marrow --> Megakaryocytes ---> Capillaries --> fragmented into platelets
origin of platelets
Thrombopoietin (TPO)
stimulus development of platelets
circulate for 8-12 days then removed from circulation by spleen and tissue macrophages
lifespan of platelets
thrompoietin and IL3
maturation of progenitors to mekakaryocytes is dependent upon
resting vs activated platelet
Resting looks like a circle, activated looks like a splat
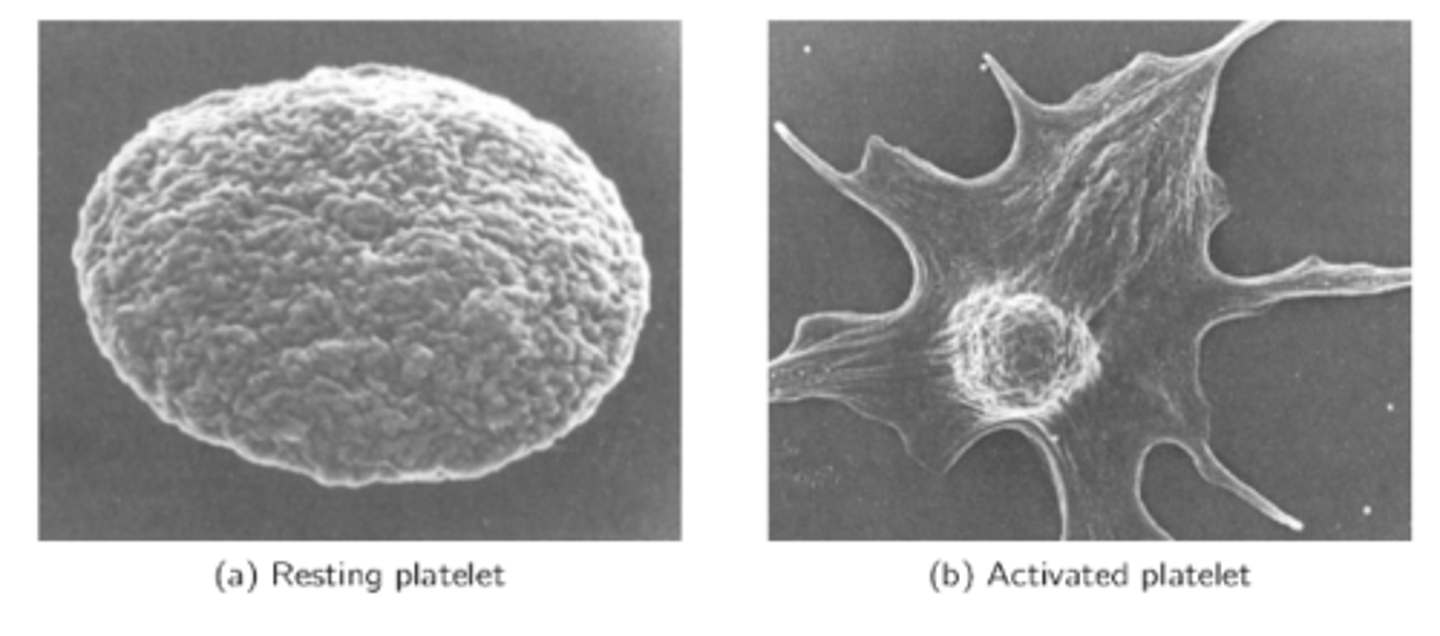
vWF binding to GPIb
-leads to increase in calcium ---> activation of prothrombin to thrombin
the first binding that allows activation of platelet
gray platelet syndrome
pts lack alpha granules in circulating platelets
-pts present with bleeding and marrow fibrosis
1. vasoconstriction at site of injury
2. primary hemostasis: platelet plug
3. secondary hemostasis: coagulation cascade
4. clot retraction: growth of fibrous tissue into the clot to close the breach
5. fibrinolysis
6. healing: cellular proliferation and remodeling
what are the fundamental steps of hemostasis
-endothelin from endothelium
-thromboxane A2 from platelets
-serotonin from platelets
POTENT vasoconstrictors
modulators of vasoconstriction in the first step of hemostasis
Weibel-Palade bodies
in the second step of hemostasis, injury releases these bodies containing vWF and P-selectin
von Willebrand factor
adhesion molecule that allows platelets to attach to exposed to attach to exposed matrix with ligand GpIib
-ADP
-platelet activating factor
-thromboxane 2
once platelet is adhered to GpIb, the platelet releases
platelet actiivating factor
-released by platelet after adhesion to GpIb
-promotes recruitment and aggregation of more platelets
•Increased shearing force on platelet/endothelium
•Vessel injury
•Humoral signals
triggers of platelet plug formation
platelet adhesion, platelet activation, platelet aggregation
what are the 3 steps of platelet plug formation
-AAA
-platelets adhere to exposed subendothelial tissue through key receptors
what is the first step of platelet plug formation
GPIa binds directly to collagen
this binding causes conformational changes in platelet and tis receptors, facilitating vWF-platelet initeraction
strongest adhesion point in the formation of platelet plug
-leads to conformational change that unmasks GIIb-IIIa binding sites
effects of GPIb binding to vWF onn exposed collagen
GPIb and GPIa
conformational changes in ______ during adhesion lead to platelet ACTIVATION
-receptors undergo conformational change involving calcium influx ultimately leading to release of granules by exocytosis
-activated platelets go dramatic shape change mediated by calcium and structural proteins
-activate platelets recruit and activate nearby platelets
mechanism of step 2 of platelet plug formation: activation
-ligands from subendothelial tissue in adhesion
-ADP from platelets: activates nearby platelets, increases TXA2
-thrombin
-serotoinin
key agonists of activation in platelet plug formation
calcium
secretory product of platelet activation that is required for platelet conformation change
Activation step of platelet aggregation exposes and activates platelet receptor GPIIb-IIIa which binds fibrinogen from the blood
-fibrinogen links platelets, creating a plug
mechanism of aggregation step in platelet plug formation
fibrinogen
-linker protein between platelets that creates a plug
-formed ini the liver and is released from platelets
relatively weak (but formed fast)
Minor injuries that occur daily may be healed merely by the platelet plug. In more severe injuries, the platelet plug is strengthened into a secondary hemostatic plug by coagulation.
strength of the platelet plug?
-site specificity!
-near by NORMAL endothelium have glycocalyx (heparin sulfate) to prevent non specific adhesion, vasodilators (PGI2, NO)
what prevents overzealous platelet plug formation?
formation of fibrin which becomes cross-linked and firmly stabilizes the platelet plug in a mesh like web
what is the goal of secondary hemostasis?
calcium and prothrombin activator
what is required to turn prothrombin into thrombin?
thrombin
turns fibrinogen into fibrin
within a few minutes of clot formation and is completed in 20-60 min
when does clot retraction occur?
thrombin!
requires calcium and platelets
clot retractiion is triggered by
actin, myosin, and thrombosthenin
clot retraction occurs due to the interaction between ____, ______, and ________ in the platelets
-expulsion of serum
-approximation of wound edges
results of clot retraction
liver
where is fibrinogen synthesized
-platelet aggregation (binds GPIb-IIIa)
-substrate firbin formation
-binding site for thrombin funciton
function of fibrinogen
fibrin fibers, which result ini soft clot (non-covalent bonds)
fibrin monomers spontaneously polymerize and form
Factor XIIIa
-factor that crosslinks the fibrni fibers and stabilizes the clot (covalent bonds)
source: plasma and platelet secretion
-activated by thrombin
source and activation of factor XIII
normal intact vascular wall is antithrombotic
-negatively charged via heparin sulfate
intirinsic tissue properties inhibiting clot formation
conversion of plasminogen to plasmin
first step of fibrinolysis
plasminogen
plasma protein made in the liver that circulates and gets trapped in the clot with other molecules
plasmin
plasma protein that converts stable fibrin to fibrin degradation products
altepase, reteplase, urokinase
name the t-PA analogs used for acute thrombotic events
D dimer
-measurement of fibrin degradation products
a2-antiplasmin (from liver)
as form of regulation of clot lysis, if plasmin isn't bound to fibrin, it is quickly bound to:
plasminogen activator inhibitors (PAI1 and PAI2)
proteins that inhibit activation of plasmin by inhibiting its activators
-produced by endothelial cells and inhibits tPA
protein C
activated ____________ inhibits plasminogen activator inhibitors, facilitating fibrinolysis
results in reduced a2-antiplasmin, causing excessive plasmin activity---> bleeding problems
how does liver disease effect plasmin activity?
1. vasoconstriction
2. primary hemostasis
3. secondary hemostasis
4. clot retraction
5. fibrinolysis
6. proliferation and remodeling
steps to repair of an injured vessel
thrombin
factor IIa is aka
factor VIII
factor ____ deficiency causes hemophilia A
-signifiacnt cause of inappropriate bleeding
hematoma
spilled blood that leads to swelling
ecchymosis
blood released into tissues without significant swelling
factor Xa
factor required to activate prothrombinase to prothrombin
Factors 2, 7, 9, 10
-protein C and S (anticoagulant factors)
Factors requiring activation by vitamin K
prothrominase
enzyme complex that converts prothrombin (factor II) to thrombin
factor Xa, factor Va, calcium, phospholiipipd
what are the key components of the prothrombinase complex?
factor Va
cofactor that stabiliizes/accelerates thrombin productioin
-component of the prothrombinase compplex
formation of prothrombinase
what is the rate limiting step of the common coagulation cascdee?
proteolyzes fibrinogen to fibrin
primary action of thrombin
factor VIIIA
factor that crosslinks fibrin into mesh of stable fibrin
-clot stabilization
intrinsic pathway
coagulation pathway that takes longer (1-6 min) and is measured by PTT
(you Play Table Tennis Inside)
•Involves Factors XII, XI, IX, VIII also HK and Kallikrien
factors inivolved in the intrinsic pathway
trauma to blood or blood exposure to collagen
what activates the intrinsic pathway?
extrinsic pathway
-coagulation pathway with rapid onset, measured by PT
-Play Tennis Outside
trauma to vessels and tissue--> tissue factor exposed
-inflammation can drive tissue factor expression
-factor XII is activated by negatively charged surface
the extrinsic pathway is activated by
lipoprotein on non-vascular cell membranes or exosomes
where is tissue factor of the extrinsic pathway from?
Factor VII, activating to VIIa
initiating the extrinsic pathway, tissue factor binds
TF-VIIa-Ca2+ complex
complex from the extrinsic pathway that activates factor X
all its factors are from blood
-in extrinsic pathway, tissue factor is NOT from blood
why is it called the intrinsic pathway?
High Molecular Weight Kininogen (HMWK)
co-activates Factor XII as an anchor and is a bradykinin precursor
Kallikrein
HMWK activates _____, which accelerates XIIa formation
HMWK anchored to XIa activates factor IX (christmas factor)
what cofactor activates factor IX?
IXa-VIIIa-Ca2+ (tenase)
intrinsic pathway complex that actiivates factor X
Factor VIIIa
serves as a cofactor to stabilize the initrinsic pathway complex to activate common pathway
thrombin
the major protease of the clotting cascade
-activates fibrinogen
-activates factor XIII
-activates factor Va and VIIIa
-paracrine effects on surrounding endothelial cells (NO, PGI2, tPA)
main functions of thrombin
thrombin (plays a role)
what actiivates factor VIII and V?
TFPI (tissue factor pathway inhibitor)
-anticoagulant factor that blocks formation of the TF-VIIa-Ca2+ pathway
-blocks factor VIII (extrinsic pathway )
antithrombin III
-inhibits factor Xa and thrombin
-complex with heparin sulfate enhances the binding to inhiibit coagulatiion
-SLOWLY neutralizes thrombin without heparin
Va and VIIIa (anticoag)
Protein C and S (bound to phospholipid and calcium) work together to inactivate what cofactors?
thrombomodulin-thrombin complex
what activates protein C?
heparin
catalyst for the binding of antithrombin III to thrombiin
-vitamin K dependent carboxylation reaction required for binding factors to calcium and platelet membranes for activation
what is the importance of vitamin K in activation of some clotting facotrs?
reduced vitamin K (by epoxide reductase in the liver) is active
what form of vitamin is active?
warfarin blocks epoxide reductase, which is necessary to activating vitamin K
how does warfarin work as an anticoagulant drug?
-intrinsic!
-PTT prolonged via interaction with antithrombin III
is heparin's affect on the intrinsic or extrinsic pathway?
extrinsic
-PT is prolonged
is warfarin's affect on the intrinsic or extrinsic pathway?
thrombocytopenia--- indicate splenectomy
thrombocytosis--- indicate splenomegaly
platelet findings associated with spleen pathologies
bleeding time (3mm puncture made with lancets)
-time wound takes to stop bleeding
best measurement of primary hemostasis (soft clot formation)
3-6 minutes
-abnormal is greater than 6 min
what is a normal bleeding time?