Waves
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
What do waves do?
Waves transfer energy and information from one place to another
What is the difference between a mechanical and electromagnetic wave?
Mechanical wave → needs a medium to travel in
Electromagnetic wave → travels through a vacuum
What happpens to the displacement of particles in a transverse wave?
The displacement of the particles are perpendicular to the direction of energy transfer
What happens to the displacement of particles in a longitudinal wave?
The displacement of the particles are parallel to the direction of energy transfer
Give examples of a transverse wave
Electromagnetic waves
Water
Give examples of longitudinal waves
Sound
Ultrasound
Define wavelength
The length of 1 whole wave
Define amplitude
The distance that the particles vibrate from equilibrium
Define frequency
The number of waves pasing a point per second
Define wave speed
The distance travelled by a wave each second
Define time period
The time it takes for 1 wave to pass a certain point
What can happen when a wave meets a different medium?
It can either be :
Absorbed
Transmitted
Reflected
What is the name given for light reflecting off shiny surfaces? What will the image in the mirror be?
Specular reflection
↳ Upright
↳ Virtual
What is the name given for ligh which reflects off rough surfaces?
Diffuse reflection
What speed does light travel?
300,000,000 m/s
What are ultrasound waves?
Waves which are too high of a frequency for humans to hear
How do prenatal ultrasounds work?
Ultrasound from a tranducer travels at different speeds in different tissues
↳ due to differences in density
When the ultrasound waves meet the boundary between different tissue, the waves can be absorbed or passed through
Some however, can be reflected
Reflected waves are picked up by the tranducer
By measuring the time taken for the ultrasound wave to return, an image can be formed
List the layers of the Earth
Crust → 10-100km thick
Mantle → Has properties of a solid but can flow (plasma)
Outer core → >3000-5000C
↳ made of molten iron and nickel at high pressure
Inner core → 5000C
↳ Solid iron and nickel
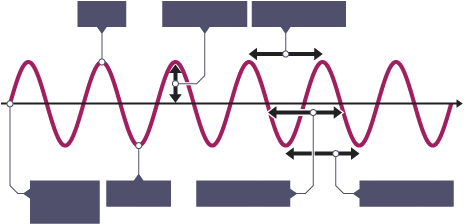
Lable the diagram
Rest position/equilibrium position
Peak
Trough
Amplitude
Wavelength x3
Explain how we hear
Air is made up of many little particles
When sound is created, the air particles vibrate and collide with eachother
↳ This causes vibrations to pass between air particles
The vibrating particles pass the sound through to a person's ear
↳ This vibrates their ear drum at the same frequency as the sound wave
What is the law of reflection?
Angle of incidence = angle of reflection
What is the range of human hearing?
20Hz-20KHz
Why can't humans hear ultrasound and infrasound waves?
The eardrum vibrates best at 20-20,000Hz
↳ Too low → energy transfer is inefficient
↳ Too high → energy loss can prevent effective vibration
How do lenses form images?
By refracting light
Define refraction
The change in direction of a wave at a boundary
↳ i.e between air and glass
Why does refraction happen?
Light travels slower in denser materials
↳ If a light ray meets the boundary at an angle to the normal, it will bend towards the normal
What are the differences between seismic P-waves and seismic S-waves?
P-waves:
Longitudinal
Faster
Can travel through liquids and solids
S-waves:
Transverse
Slower
Only travels through solids
Explain how seismic waves can be used to investigate the Earth's structure
Seismic waves can be discovered all around the world
↳ Paths are curved since the waves refract due to changing densities
S-waves are not detected on the opposite side of the Earth
↳ Mantle is solid but outer core is liquid
P-waves are detected on the other side of the Earth
↳ Refractions between layers cause 2 shadow zones where no P-waves are detected
↳ Size and position of these zones suggests the inner core is solid
What happens when a wave is absorbed by the surface?
The energy of the wave is transferred to the particles in the surface
↳ Increases the internal energy of the particles
How do colour filters work?
When white light (visible light) passes through the colour filter, all the colours are absorbed, except for the colour of the filter (which is transmitted)
Why can objects appear black?
An object can be black if it absorbs all the wavelengths of visible light
What is a perfect black body?
A theoretical object which would :
Absorb all radiation
Not reflect or transmit radiation
Be the best emitter of radiation
What is the link between absorbers and emitters?
A poor absorber = a poor emitter
A good absorber = a good emitter
What kind of surfaces are the worst absorbers and emitters?
White and shiny, silvery surfaces
↳ reflect all visible light wavelengths
When are seismic waves produced?
During earthquakes → measured by seisometers