Operating Systems Finals
1/667
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
668 Terms
An operating system is responsible for which task?
loading applications into memory
A privileged instruction executed in user mode
changes the mode bit to kernel mode
For time-sharing to work between applications, which technique should be used?
Interrupt
Improving system performance is achievable with which solution?
Additional physical CPUs
Which one is not True?
Time-sharing is possible without interrupts
The concept of unification and simplification by combining simple objects into more complex objects is referred to as
Abstraction
______ determines the cause of the interrupt and invokes the appropriate kernel function to provide the response
Interrupt Handler
Request from an application for an OS service
System Call
Which one is Not True?
A release resource function has been called and the waiting list is empty. As a result, the resource is marked as allocated.
An application process stops executing. Which PCB field maintains hardware registers and flags that will be used when the application process resumes?
CPU_state
What happens first when a process is destroyed?
Child processes are destroyed.
Which is Not True?
A process is in ready state when both CPU and necessary resources are available
Two concurrent applications, a1 and a2, execute the sequences of instructions (j1, j2, j3) and (k1, k2, k3), respectively. Execution switches between the applications whenever a timeout interrupt occurs or when one application terminates. If a1 starts, and interrupts occur after instructions k1 and j1, then what is the order in which the 6 instructions will execute?
j1, k1, j2, j3, k2, k3
This series of process state transitions is valid.
new ➛ ready ➛run ➛ suspended ➛ ready ➛ run➛ terminated
True
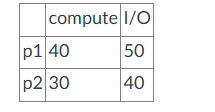
Processes p1 and p2 execute on a system with a single CPU and two identical I/O devices. Each process executes a compute-bound phase followed by an I/O-bound phase. The system uses multiprogramming without time-sharing. The following table shows the lengths of each phase.
p1 starts first at time 0.
Without multiprogramming, the computation terminates at time 160
You add everything straight:
→ 40 (p1 compute) + 50 (p1 I/O) + 30 (p2 compute) + 40 (p2 I/O) = 160
With multiprogramming, the computation terminates at time 110
total time = p1 compute + max(p1 I/O, p2 compute + p2 I/O)
So:
p1 compute = 40
p2 compute + I/O = 30 + 40 = 70
p1 I/O = 50
Now take max of overlapping parts:
→ max(50, 70) = 70
Then:
➡ total time = 40 + 70 = **110**
Which of the following instructions should be non-privileged?
Issue a trap instruction
Which one is NOT contained in process control block (PCB)?
resource status
The linked-list implementation for PCB is more time-efficient than the list-free implementation.
False
Which one is Not True?
Scheduler() call must be made inside of the destroy() function to guarantee that the scheduler executes multiple times.
Which is Not True?
To close files should be the responsibility of the programmer, rather than being performed automatically as part of the destroy function
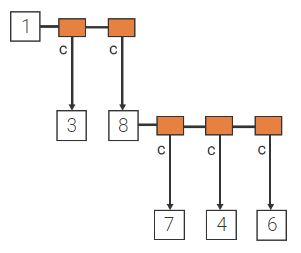
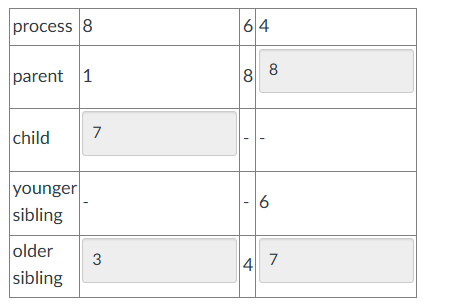
Process 8 creates a child process, process 0. Complete the resulting PCB tables.
3 independent processes are executing on 2 physical CPUs. Decreasing the number of CPUs from 2 to 1 will decrease speed of execution.
True
Which technique improves system resource utilization by holding active programs in memory while the programs wait for I/O completion or for an event to take place?
Multiprogramming
An application process is in a running state. Which PCB field cannot change?
Parent
Transferring control of the CPU from one process to another is _________
context switch
A test-and-set machine instruction has a form of TS(R, x) where R is a register and x is a memory location. What operations are performed with R and x?
Copy x to R, then set x to 0.
Which one is Not True?
In Monitor, a conditional variable can take any integer value
When a process repeatedly executes a loop while waiting for a condition to change, CPU resources are wasted. This behavior is called _____.
busy-waiting
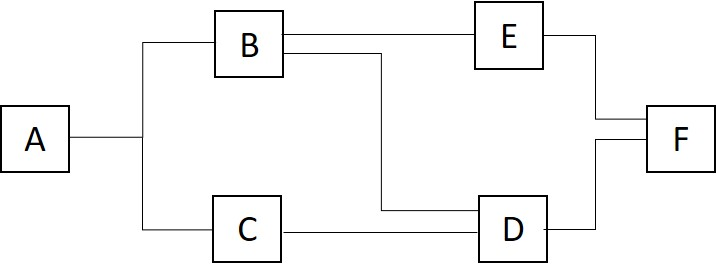
Two processes are executing the computations A through F. Please insert P and V operations into the code to enforce the prescribed order. (Hint: use 3 semaphores)
P1 P2
A C
B D
E F
The computations must be executed in the order given by the following precedence graph. (start A, end F)
A must complete before B and C start
B must complete before E starts
C must complete before D starts
D and E must both complete before F starts
Let’s name three semaphores:
S1: signals completion of A, allowing B and C to proceedS2: signals completion of B and C, allowing E and D to proceedS3: signals completion of D and E, allowing F to proceed
Initialization:
semaphore S1 = 0; // unlocks B and C after A
semaphore S2 = 0; // unlocks D and E after B and C
semaphore S3 = 0; // unlocks F after D and E
Process P1:
A;
V(S1); // signal A is done, B and C can start
P(S1); // wait for A
B;
V(S2); // signal B is done, E can start
P(S2); // wait for D and E to finish
E;
V(S3); // signal E is doneProcess P2:
P(S1); // wait for A
C;
V(S2); // signal C is done, D can start
P(S2); // wait for B and C
D;
V(S3); // signal D is done
P(S3); // wait for D and E
F;
P(x)is the "wait" operation (decrements and waits if 0)V(x)is the "signal" operation (increments, releasing any waiting processes)
The implementation of P(s), where s is a general semaphore, avoids busy-waiting by _____.
blocking the invoking process
When the value of s in a general semaphore implementation is less than 0, s corresponds to the _____.
number of blocked processes
Which one is Not True about Monitor?
The monitor operation c.signal blocks the invoking process
Which one is Not True about monitor implementation of the bounded-buffer problem?
The producer must wait when full_slots = 0
A monitor with priority waits keeps blocked processes sorted _____.
by priority
In the readers-writers problem, _____ enter the critical section concurrently, but only one _____ can enter at a time.
readers, writer
Which one is Not True about dining-philosopher problem (given 5 philosophers) ?
When p[4] is eating then p[0] or p[2] can eat concurrently.
The solution to the dining-philosophers problem where all philosophers pick up the left fork first may lead to _____.
deadlock
A solution to the dining-philosophers problem where both forks must be picked up at the same time in a critical section prevents _____ but may lead to _____.
deadlock, a concurrency violation
In the monitor solution to the dining-philosophers problem, forks are implemented using _____.
state transitions
With readers-writers Monitor, please determine the order in which all requests currently in the system pass through the CS.
w1, (r1, r2, r3, r4), w2
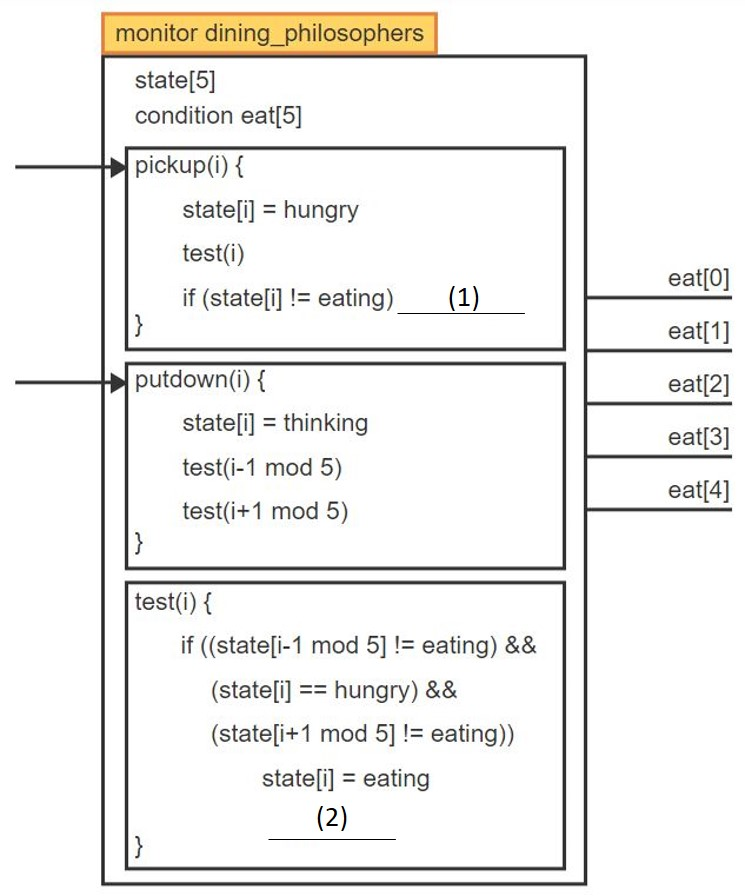
Following figure shows a monitor model for dining philosophers problem. Please find the right code for (1) and (2) respectively.
(1) eat[i].wait (2) eat[i].signal
A situation where multiple processes are blocking each other indefinitely
Deadlock
A situation where a process not attempting to enter a CS prevents other processes from entering the CS
Lockout
A situation where a process can repeatedly enter the CS while other processes are waiting to enter
Starvation
The requirement that only one process may execute in a CS
Mutual Exclusion
Three processes execute the following sequences concurrently:
p1: | p2: | p3: |
If s1 = 1 and s2 = 0, in which order can the statements A, B, and C execute.
C, A, B
is a non-negative integer variable that can be accessed using only two special operations, P and V
Semaphore
is a segment of code that cannot be entered by a process while another process is executing a corresponding segment of the code.
Critical Section
is a named queue on which processes can wait for some condition to become true
Condition Variable

Processes p and q execute the instructions x = x + 1 and x = x + 2, respectively.
Initially x = 0. After execution of the interleaved code, x = _____
1
Which is Not True?
When a process is in the ready state, the CPU attained time is changing.
Two processes, p1 and p2, are executing using RR scheduling. The context switching time is S = 3.
Determine the maximum quantum size Q such that the gap between the end of a process p1's quantum and the start of p1's next quantum does not exceed
M = 28 time units.
What is quantum size? 22
Determine the percentage of CPU time wasted on context switching. 12%
Which is True?
With the rate monotonic algorithm, the shorter period process always has the higher priority.
Using the program shown below, identify the values of pid1 and pid at lines A, B, C, and D. Assume that the actual process id of the parent and child processes are 700 and 701, respectively.
int main() {
pid_t pid, pid1;
pid = fork();
if (pid < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Fork Failed");
return 1;
} else if (pid > 0) {
pid1= getpid();
printf(“pid = %d\n”, pid); /* A */
printf(“pid1= %d\n”, pid1); /* B */
wait (NULL);
return 0;
} else {
pid1= getpid();
printf(“pid = %d\n”, pid); /* C */
printf(“pid1 = %d\n”, pid1); /* D */
}
}
A: 701 B:700 C:0 D:701
Which one is NOT contained in process control block (PCB)?
interrupt service ID
Transferring control of the CPU from one process to another
Context Switch
In Round Robin algorithm, ______ is a small amount of time during which a process is allowed to use the CPU
time quantum
________ perform critical operations that access I/O devices and the CPU's status and control registers
privileged instructions
The sum of the total CPU time and the waiting time is called _____
turnaround time
When CPU utilization is 80%, _____ scheduling is likely to produce a feasible schedule.
only EDF
Please list and briefly explain three Linux/Unix shell commands.
pwd(Print Working Directory)
This command displays the full path of the current directory you are working in. It helps you know your location in the filesystem hierarchy.
➤ Example: Typingpwdmight return/home/student/projects.cd(Change Directory)
Used to navigate between directories. You specify the name or path of the folder you want to enter.
➤ Example:cd Documentsmoves you into the "Documents" folder.nano
A terminal-based text editor used to create or modify text files directly in the command line. It's simple and beginner-friendly.
➤ Example:nano notes.txtopens the filenotes.txtfor editing (or creates it if it doesn’t exist).
For time-sharing to work between applications, which technique should be used?
Interrupt
Which is NOT true?
Process state of PCB field maintains hardware registers and flags
Which one is Not True?
Multiple threads of the same process share CPU registers and stacks for code efficiency
This series of process state transitions is valid.
new -> ready -> run -> ready -> run -> blocked -> run -> terminated
False
In Realtime system, three periodic processes with the following characteristics are to be scheduled.
Process | Period | Total CPU time |
|---|---|---|
p1 | 20 | 5 |
p2 | 100 | 15 |
p3 | 50 | 4 |
How many more processes, each with CPU time = 3 and period = 20, can run concurrently under EDF?
3
The sum of the individual fractions of CPU time used by each process is known as _____
CPU utilization
Multilevel feedback scheduling addresses the problems of starvation and fairness by using which technique?
Changing the priority of every process dynamically and using different time quantum values for priorities
server accepts and processes requests from clients. The server keeps the results of the most recent requests in memory as a cache.
A new request arrives on average every 20 ms.
The processing of each request takes 10 ms.
If the requested result is not in the memory cache, additional 65 ms are needed to access the disk.
On average, 80% of all requests can be serviced without disk access
The creation of a new thread takes 10 ms.
(1) Should the server be implemented as a single-threaded or a multi-threaded process? __Answer 1:__
(2) What percentage of requests would have to be satisfied without disk access for the single-threaded approach to be feasible? Please round to the first decimal point __Answer 2:___
Answer 1:multi-threaded
Answer 2: 84.6
A video streaming application is an example of a periodic process
True
The hardware/user gap is bridged by the OS or by other system software. Which of the following tasks would require OS support?
Input a character from the keyboard.
Definitely
The hardware/user gap is bridged by the OS or by other system software. Which of the following tasks would require OS support?
Invoke a high-level matrix manipulation operation.
Not necessarily
The hardware/user gap is bridged by the OS or by other system software. Which of the following tasks would require OS support?
Allocate n bytes of memory for a new data structure
Most likely
The hardware/user gap is bridged by the OS or by other system software. Which of the following tasks would require OS support?
Load a program into memory.
Definitely
The hardware/user gap is bridged by the OS or by other system software. Which of the following tasks would require OS support?
Change the layout of a document.
not necessarily
The hardware/user gap is bridged by the OS or by other system software. Which of the following tasks would require OS support?
Call a shared library function.
Most likely
The hardware/user gap is bridged by the OS or by other system software. Which of the following tasks would require OS support?
Call a function defined within the current program.
not necessarily
The hardware/user gap is bridged by the OS or by other system software. Which of the following tasks would require OS support?
Exit current program.
Definitely
The hardware/user gap is bridged by the OS or by other system software. Which of the following tasks would require OS support?
Sleep for n seconds.
Definitely
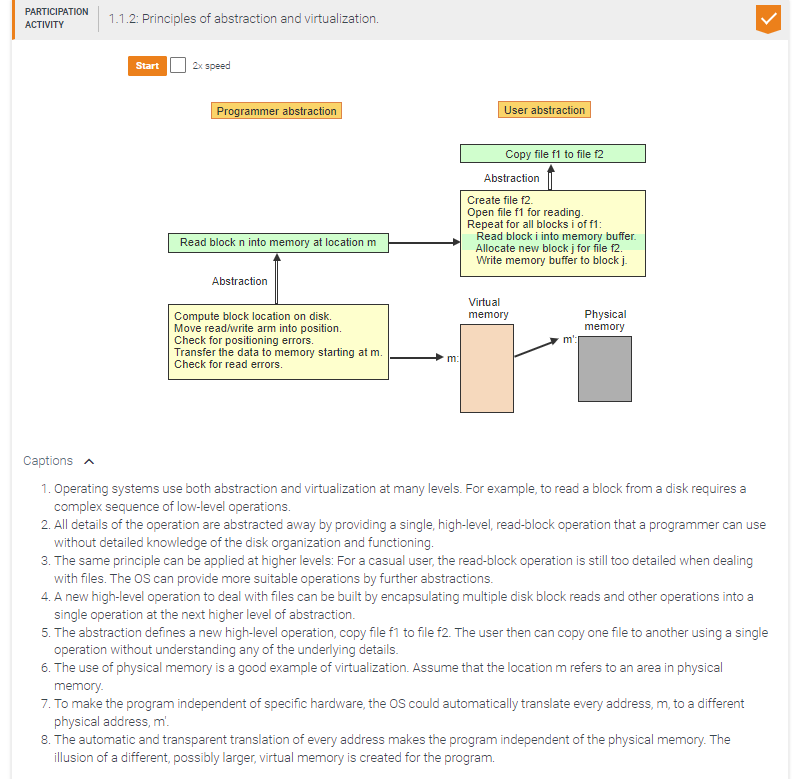
Match the higher-level constructs to the corresponding low-level instruction sequences.
Copy f into a temporary file f'.
Wait until printer P not busy.
Reserve printer P.
Send file f' to printer P.
Release printer P.
Send file to printer p
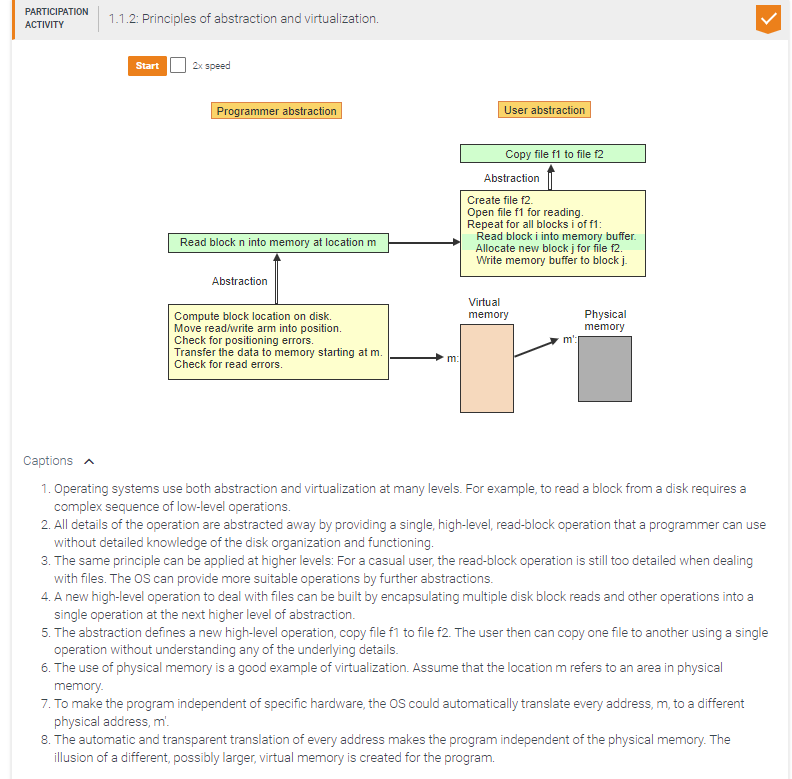
Match the higher-level constructs to the corresponding low-level instruction sequences.
for all i:
for all j:
for all k:
Cij = Cij + Aik × Bkj
C = A x b where
A,B,C are matrices
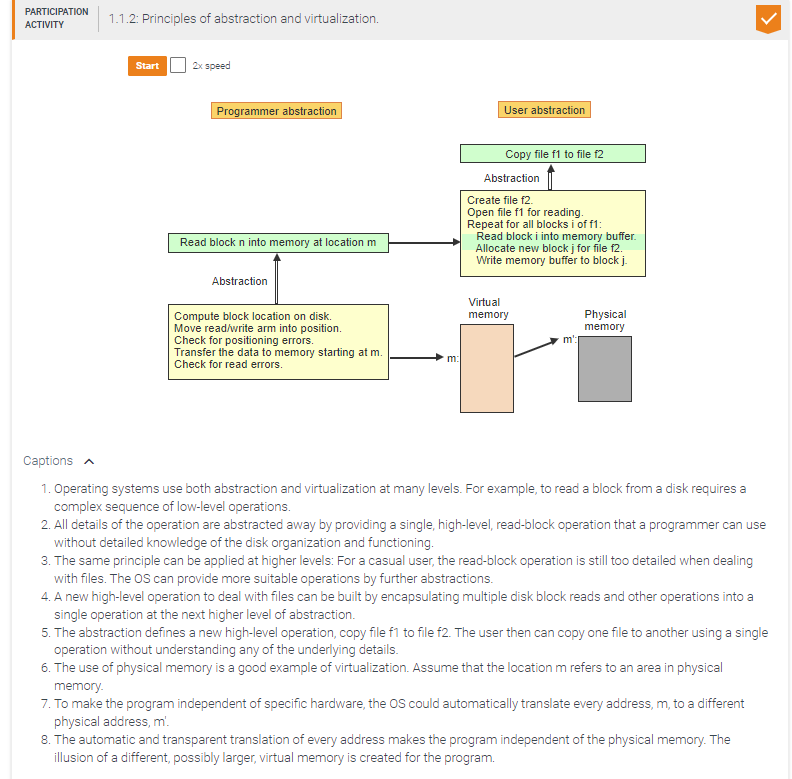
Match the higher-level constructs to the corresponding low-level instruction sequences.
Given a file block i, determine the track number t and the block number j within t that correspond to block i.
Access block j on track t.
Access disk block i
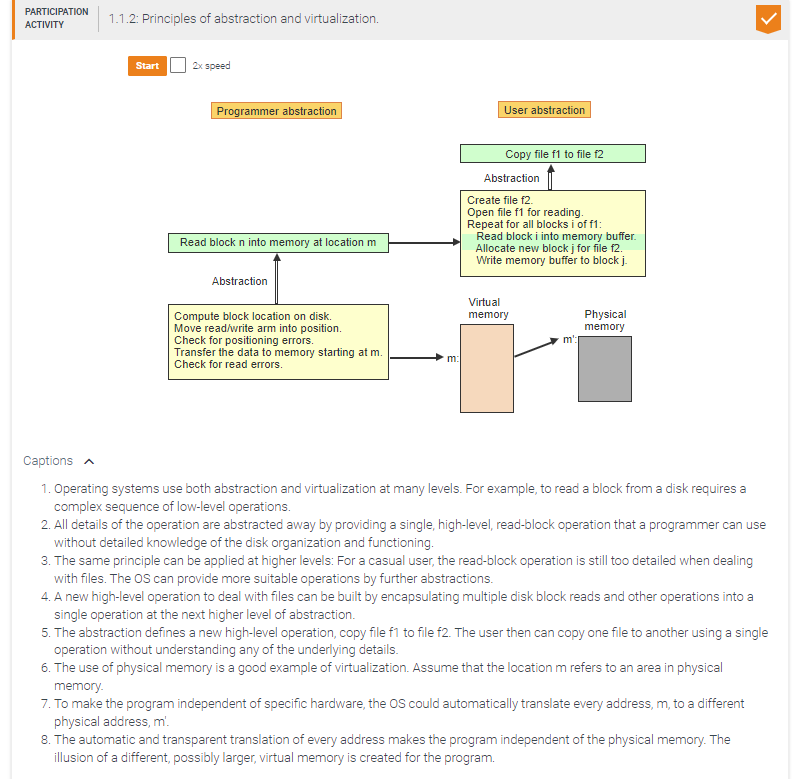
Match the higher-level constructs to the corresponding low-level instruction sequences.
If program p is too large to fit into memory, divide p into smaller partitions p1, p2, ...
Load p1 and start execution.
Whenever a different partition pi is needed, save current partition and load pi.
Resume execution.
Load program p into memory and execute p
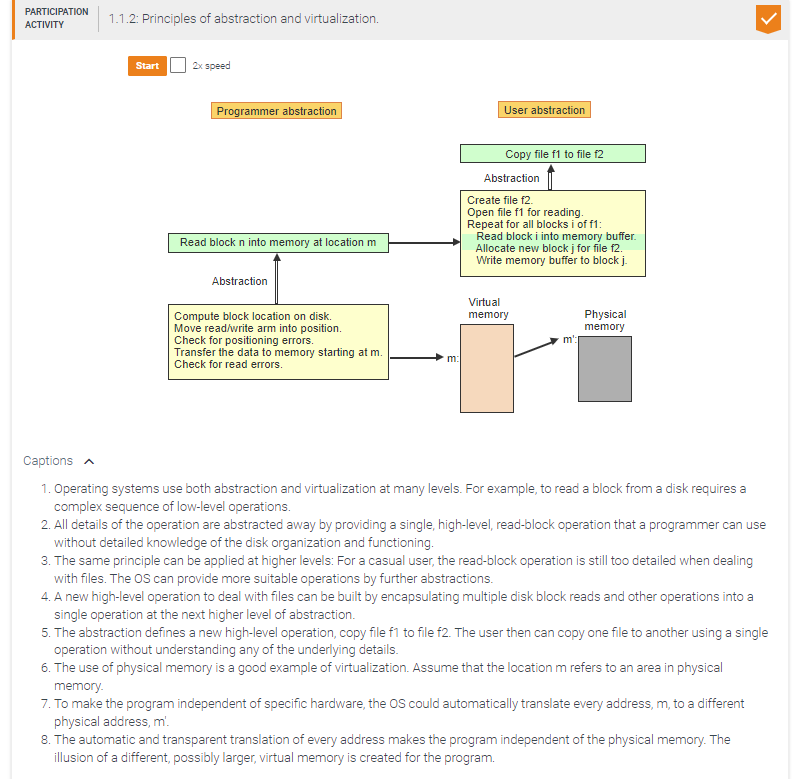
Match the higher-level constructs to the corresponding low-level instruction sequences.
Allocate new queue element e.
Copy x into e.
Insert e at rear of Q.
Enqueue x into Q
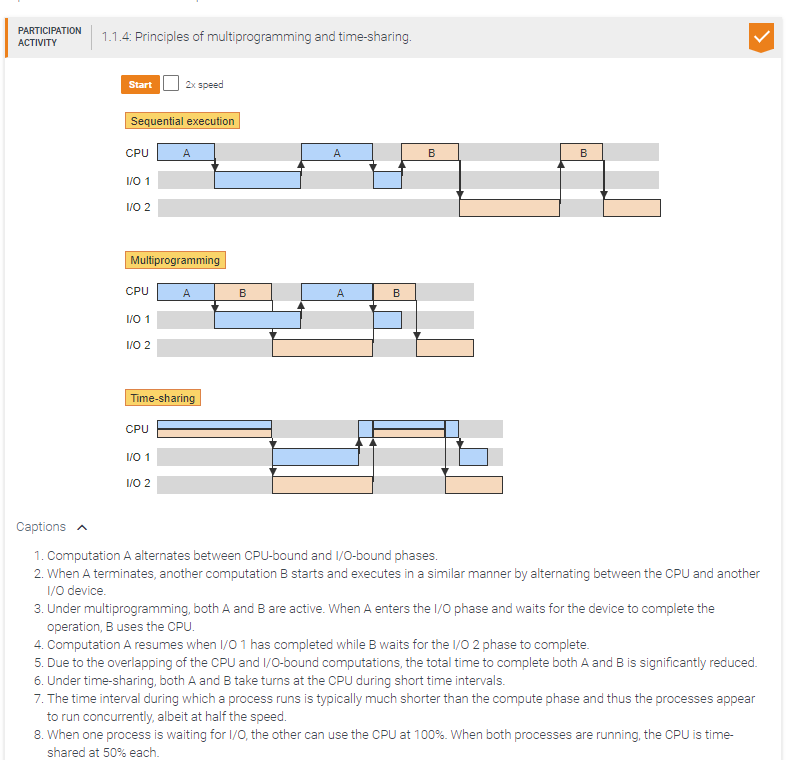
Multiprogramming generally improves CPU utilization and throughput.
True
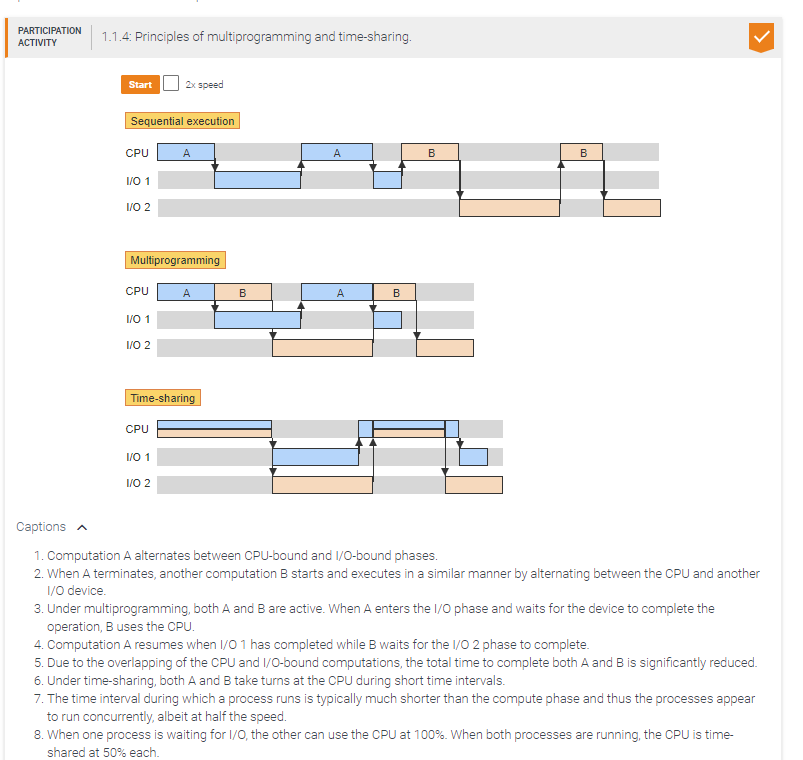
The main objective of time-sharing is to improve resource utilization.
False
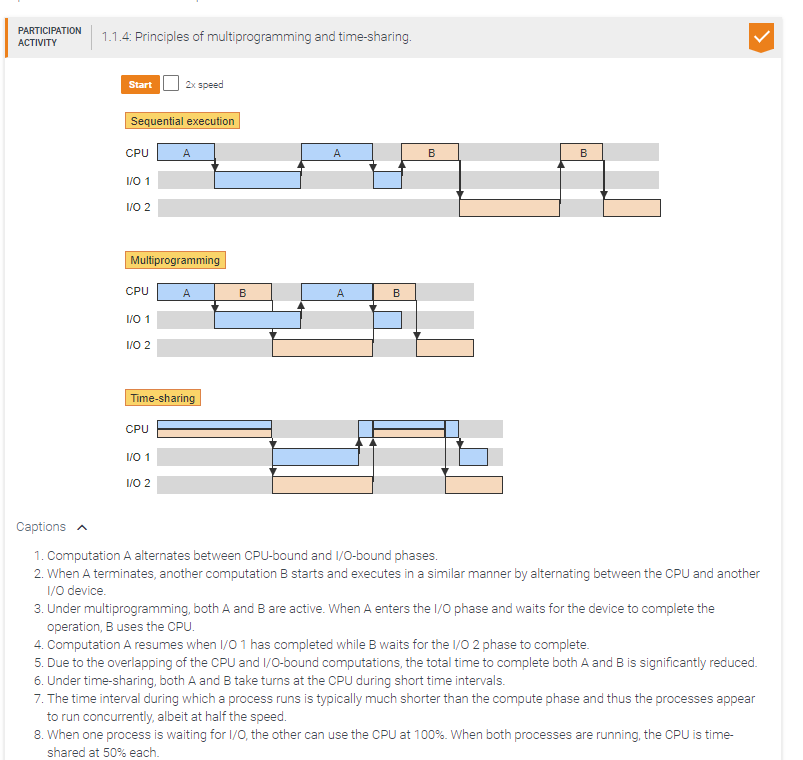
Multiprogramming and time-sharing are not used together.
False
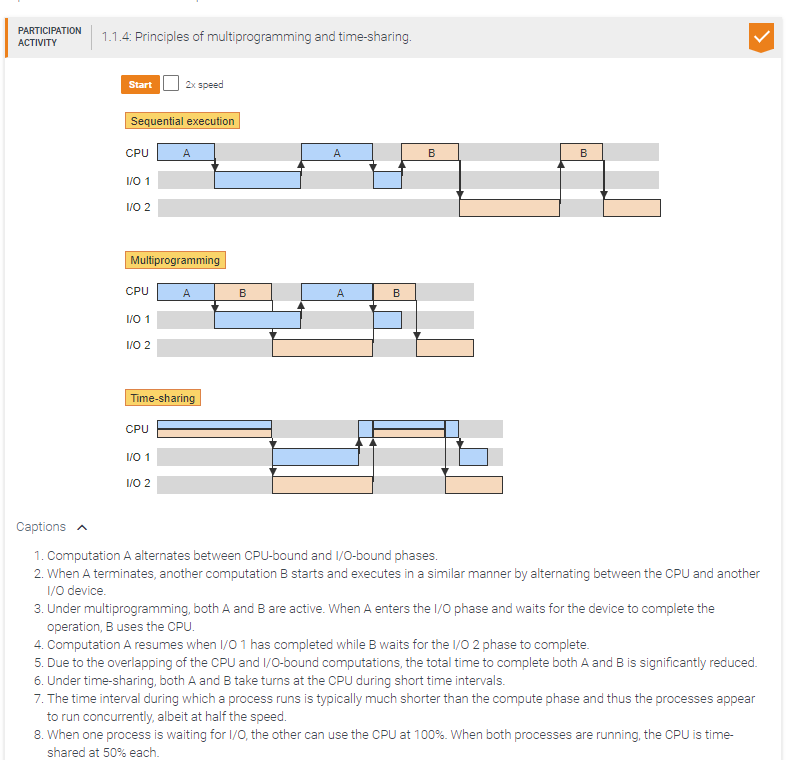
In a hypothetical system, the average computation spends 50% of total time using the CPU and the remaining 50% waiting for I/O.
To achieve best CPU utilization, _____ computations should run simultaneously.
more than 2
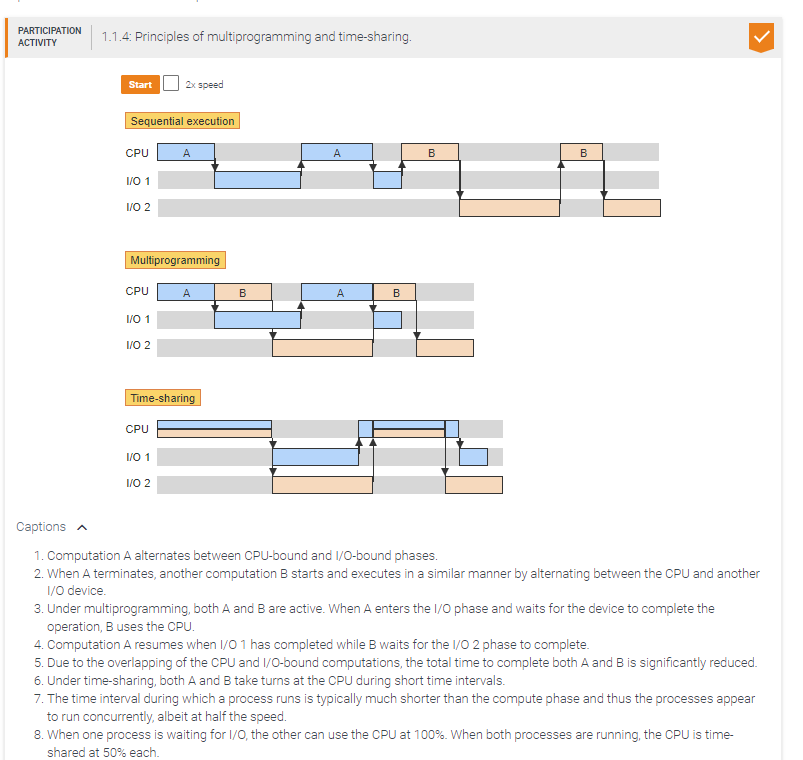
In a hypothetical system, the average computation spends 50% of total time using the CPU and the remaining 50% waiting for I/O.
The use of time-sharing will _____.
guarantee reasonable response to each computation
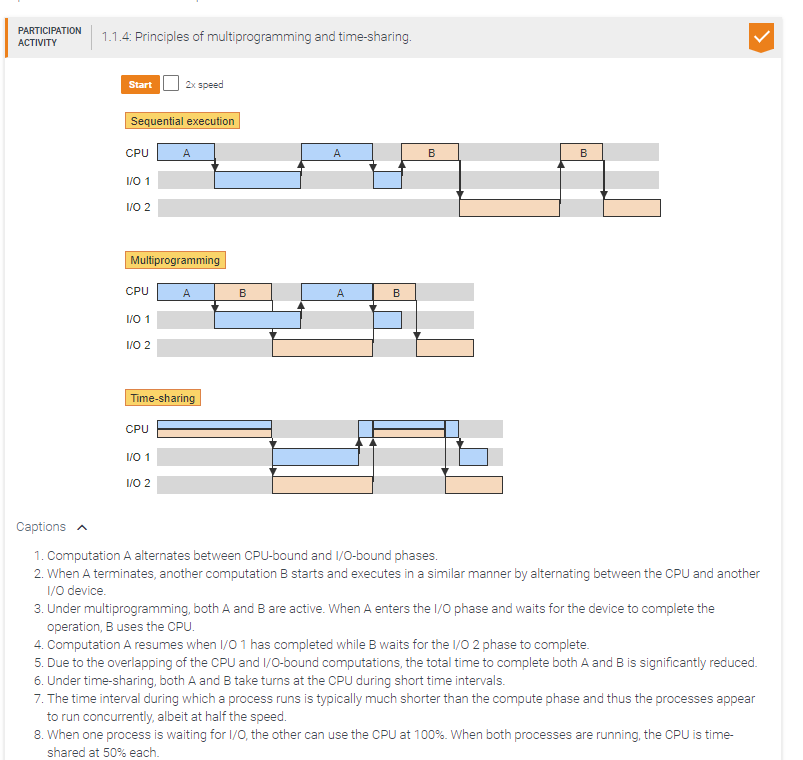
Processes p1 and p2 share a single CPU and 2 independent I/O devices. Each process executes a compute-bound phase of 10 time units followed by an I/O-bound phase of 10 units.
Without multiprogramming, the total execution time of both processes is ____ time units.
40
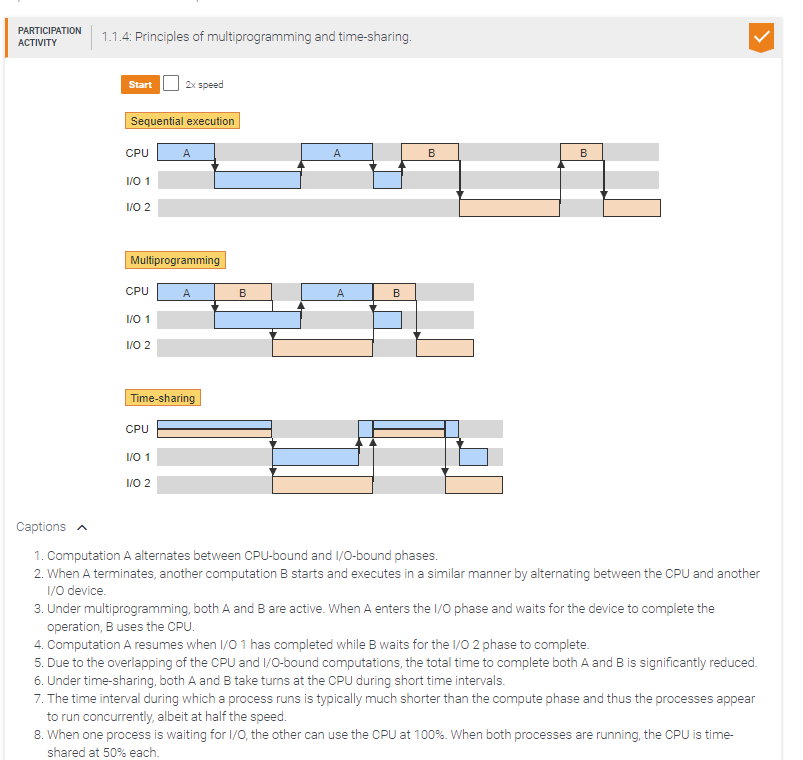
Processes p1 and p2 share a single CPU and 2 independent I/O devices. Each process executes a compute-bound phase of 10 time units followed by an I/O-bound phase of 10 units.
With multiprogramming, the total execution time of both processes is ____ time units.
30
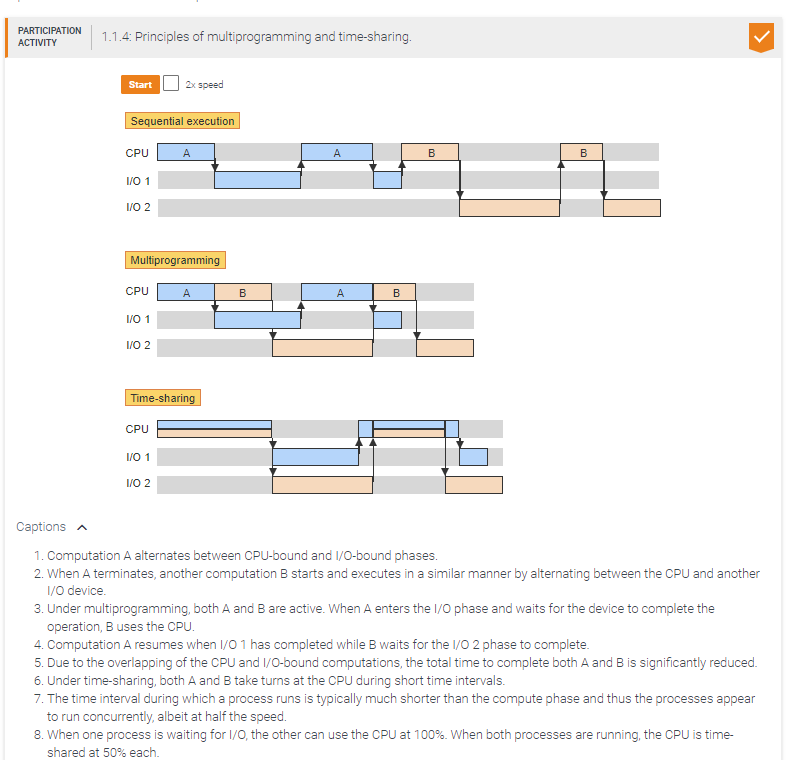
Processes p1 and p2 share a single CPU and 2 independent I/O devices. Each process executes a compute-bound phase of 10 time units followed by an I/O-bound phase of 10 units.
If p1 and p2 use time sharing and the length of the time interval allocated to each process is negligible compared to the 10 time units of execution, then the total execution time of both processes is ____ time units.
30
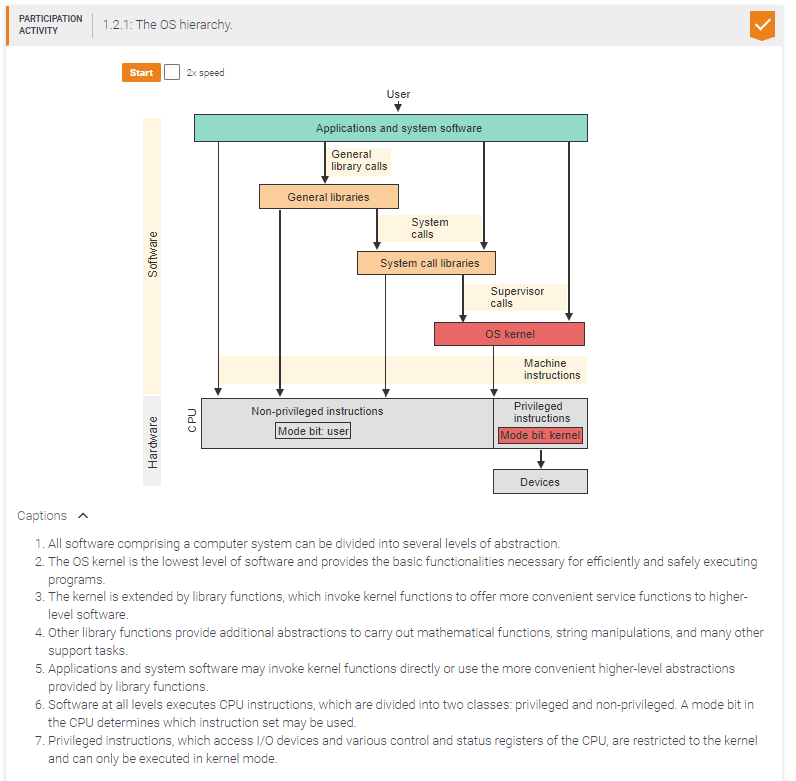
Kernel functions may be invoked by _____.
any program
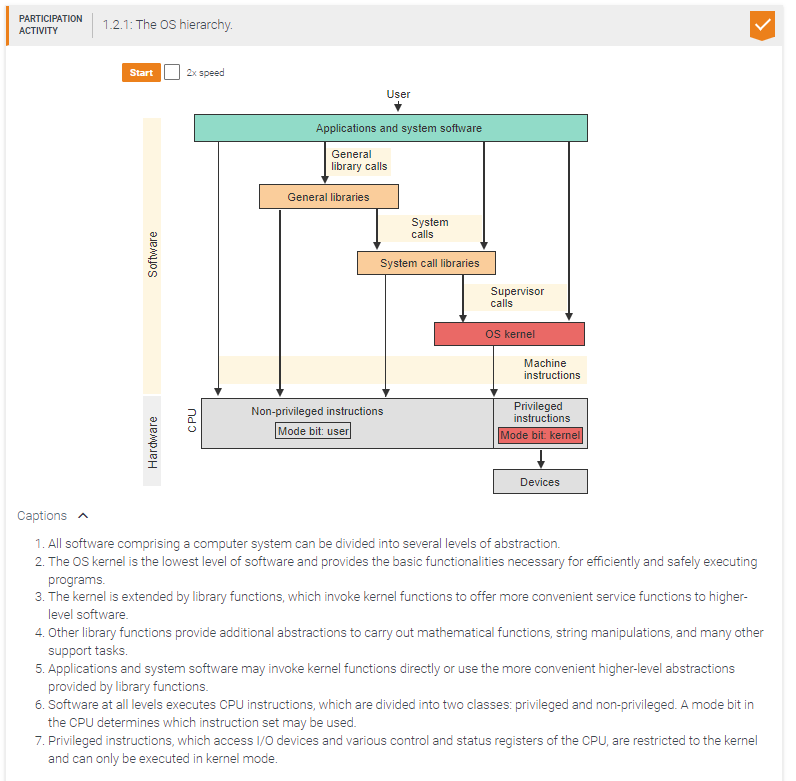
Privileged instructions may be executed by _____.
only the kernel
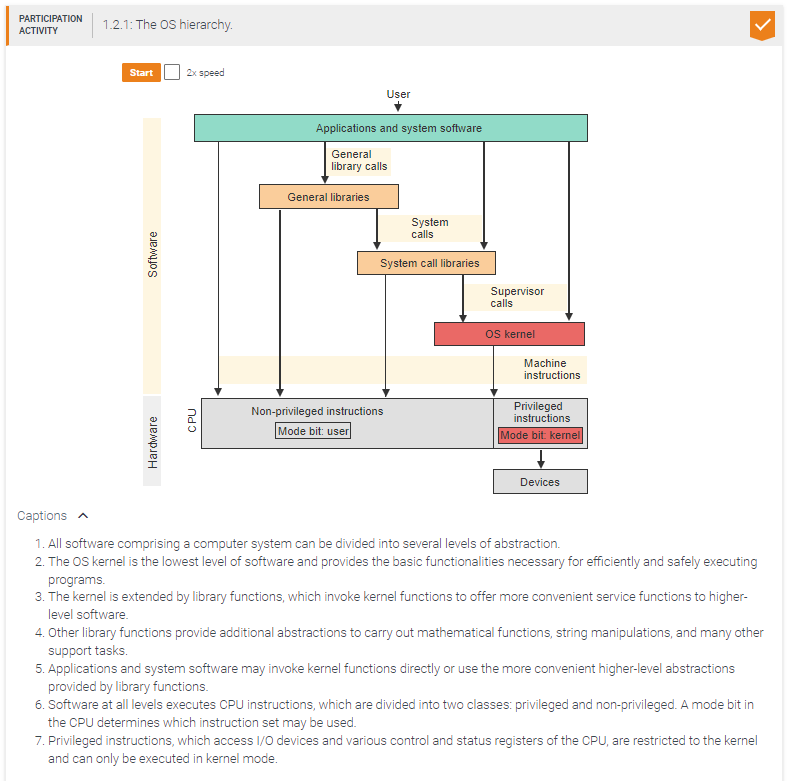
An application that needs to access an I/O device could not be written without _____.
kernel functions
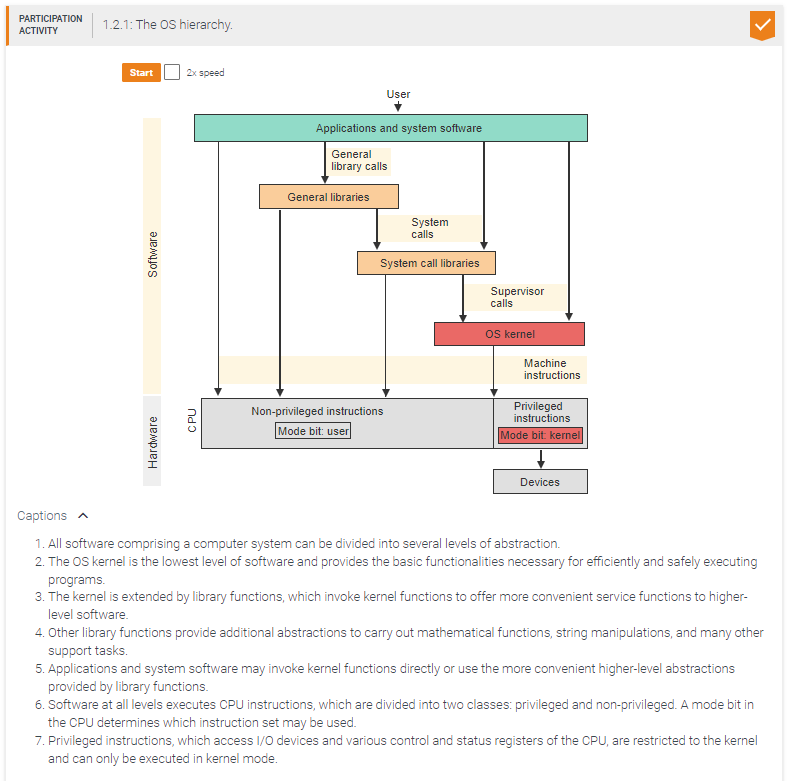
The kernel can execute _____ instructions.
both privileged and non-privileged
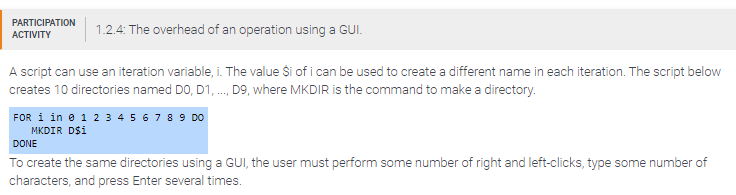
The required number of right-clicks is _____.
10
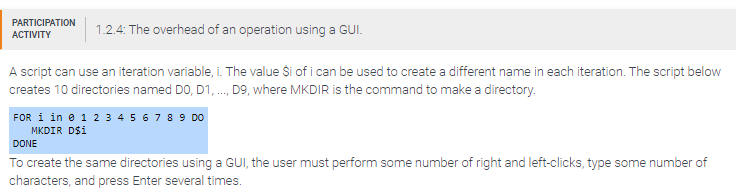
The number of characters typed is _____.
20
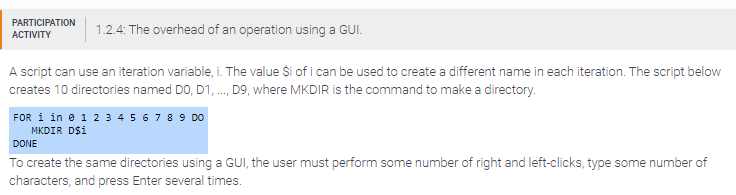
he number of times Enter is pressed is _____.
10
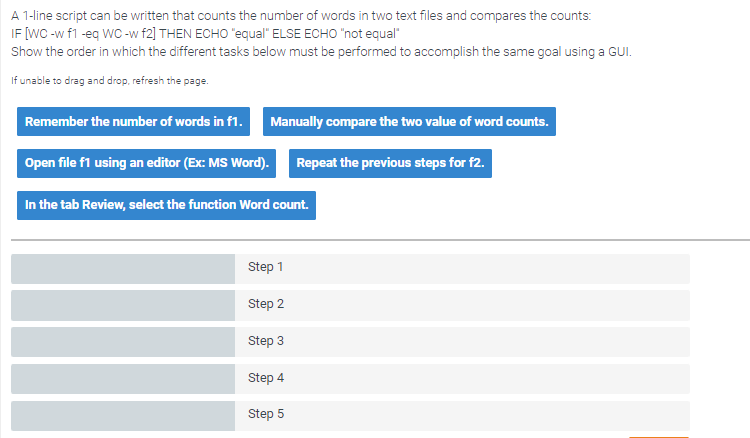
Step 1
Open file f1 using an editor