Quiz: Muscle Type & Vocab
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
1
New cards
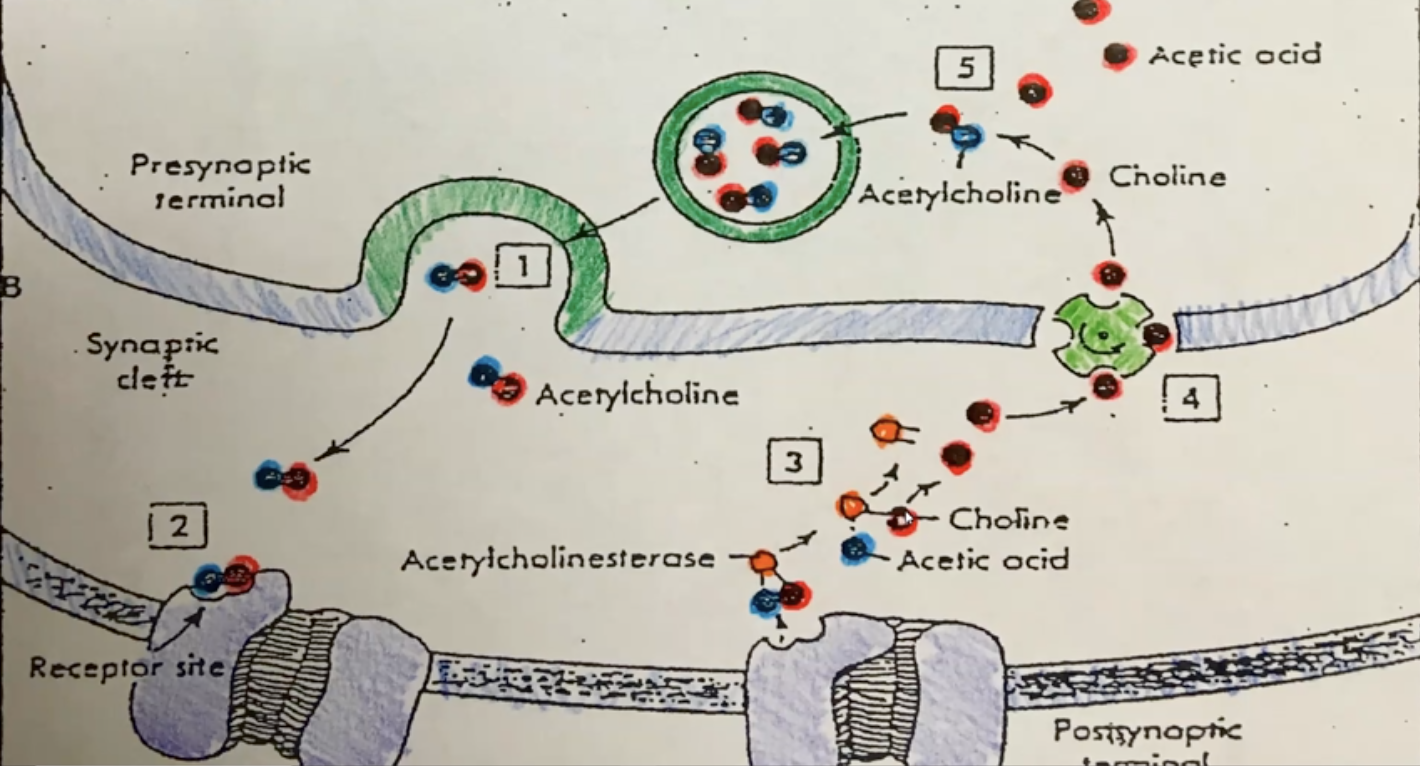
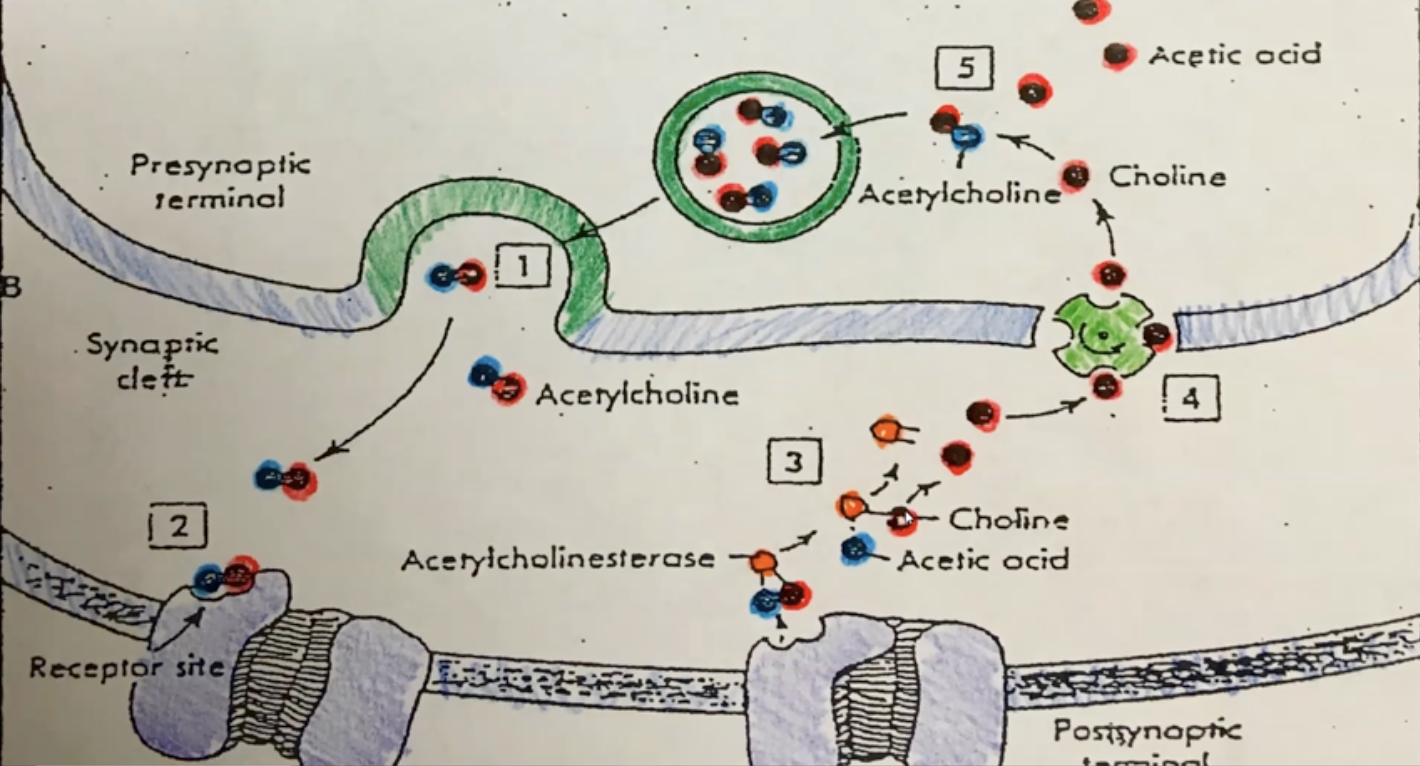
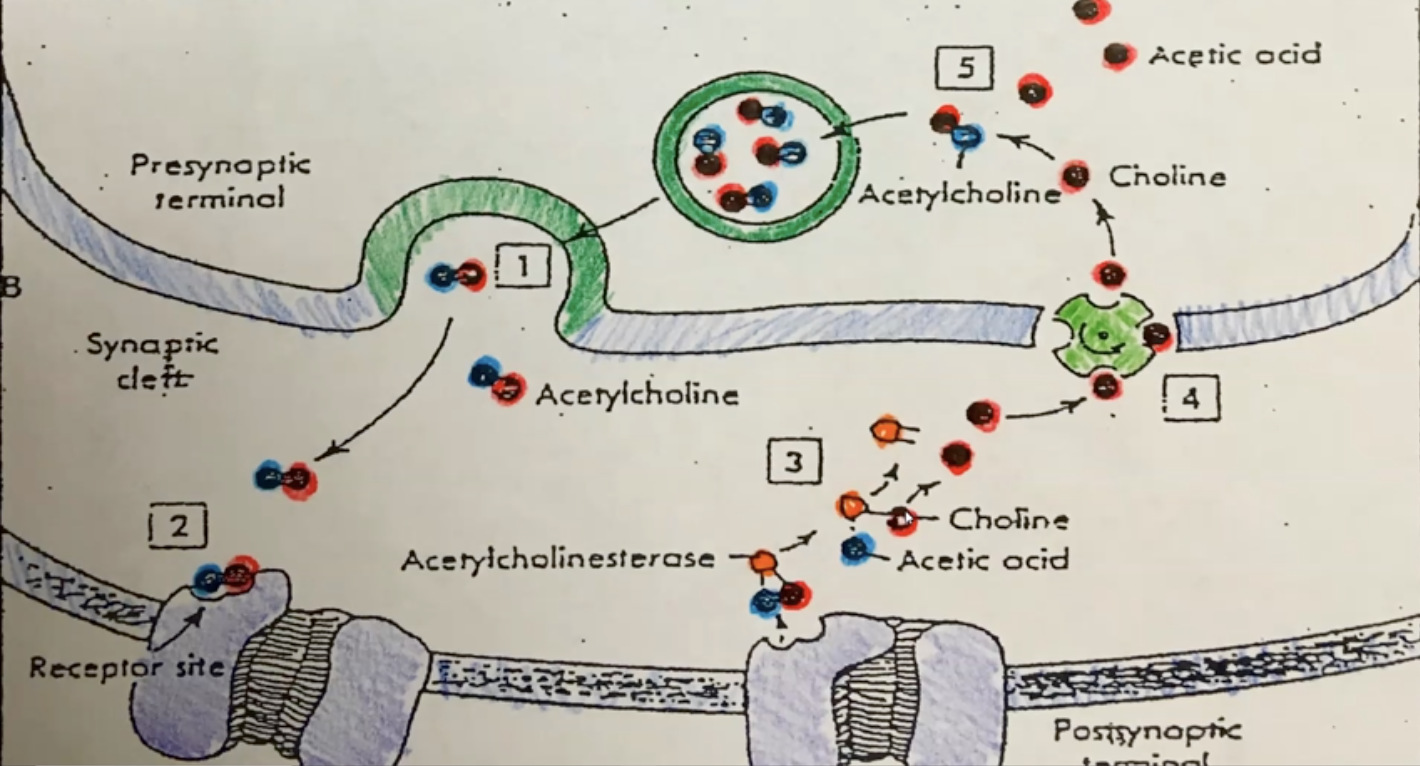
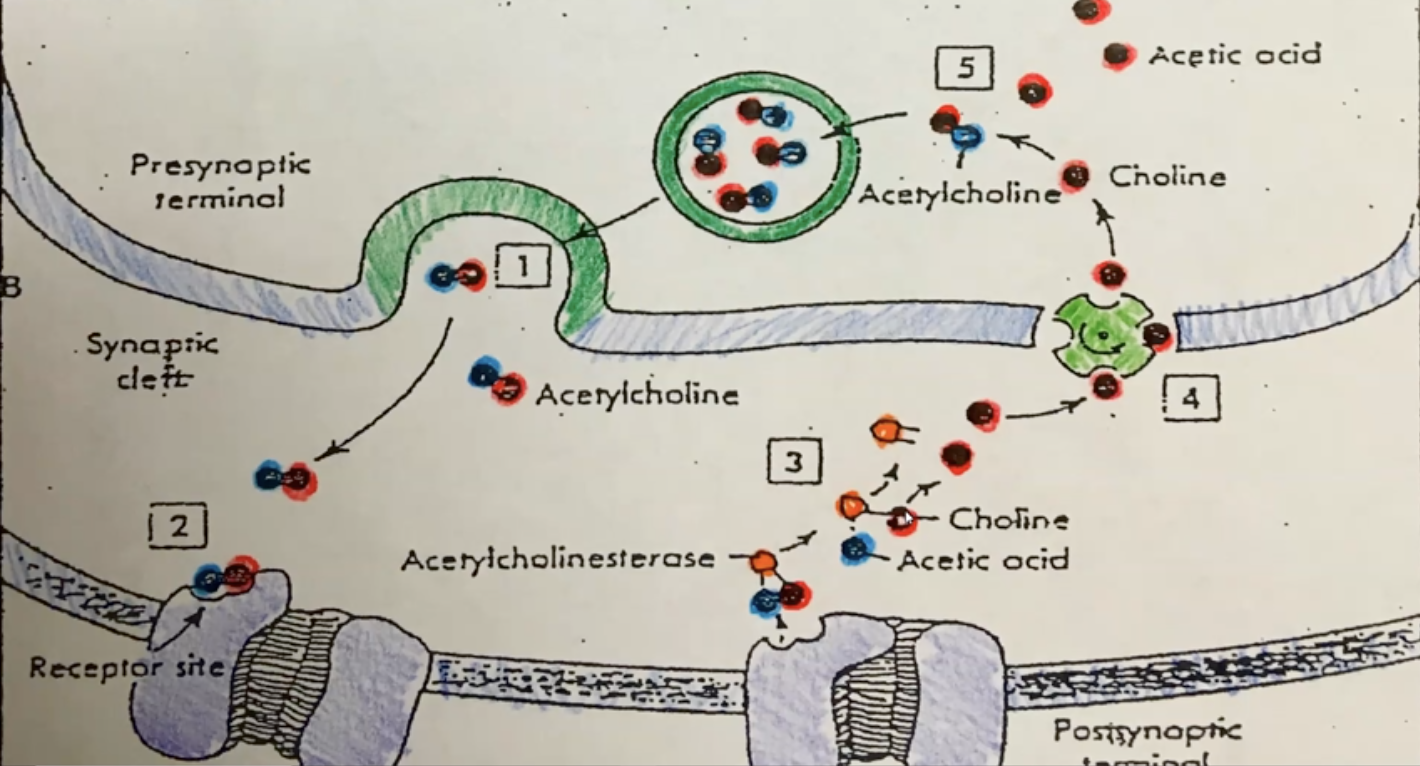
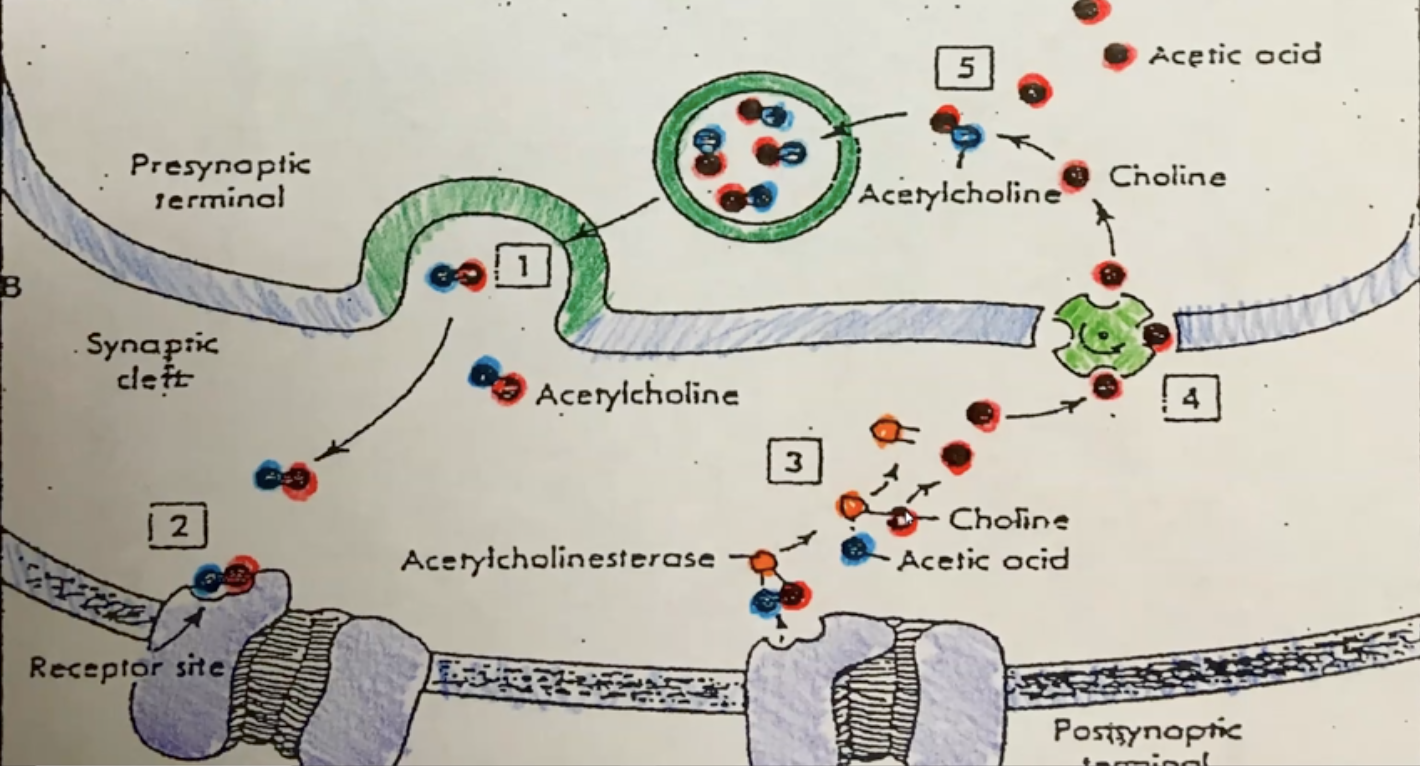
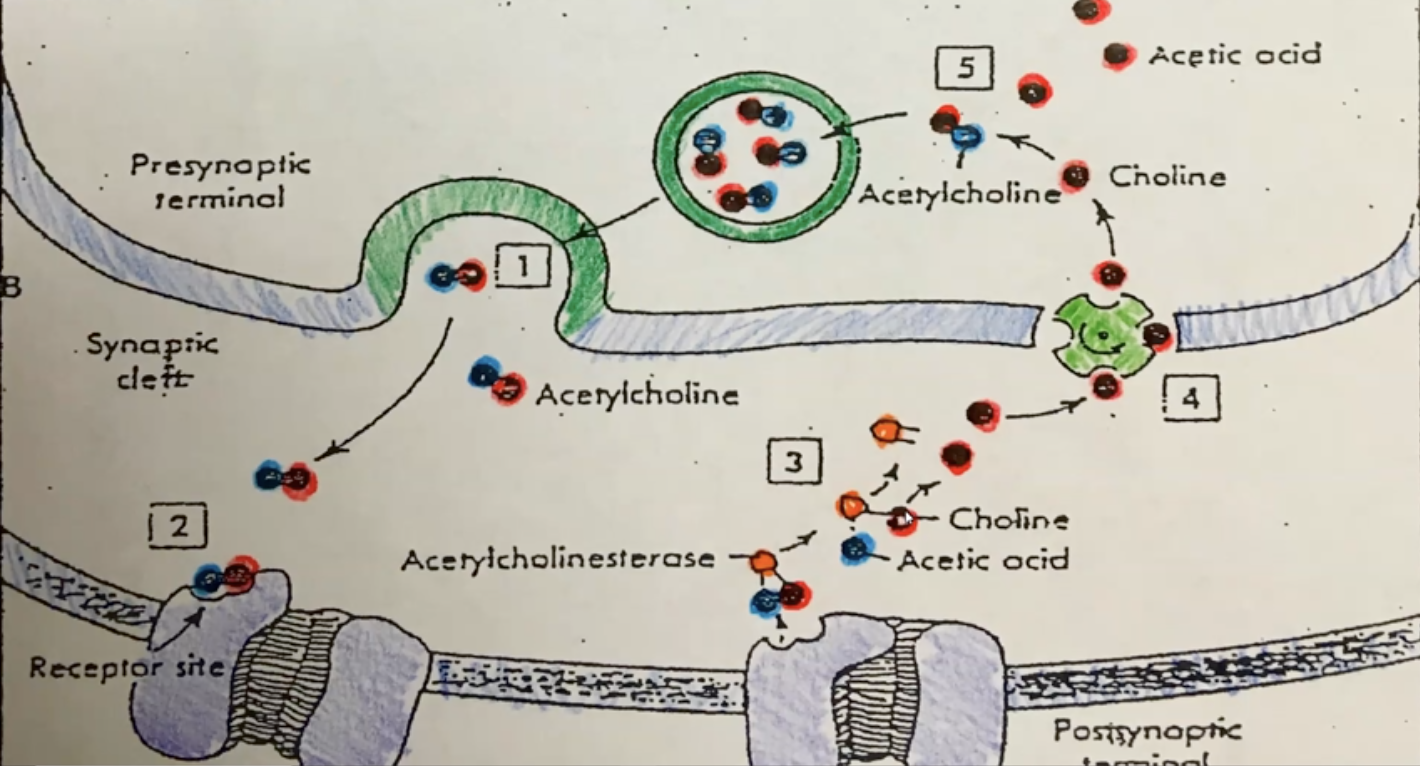
acetylcholinesterase (AChase)
an enzyme used to decompose a neurotransmitter**
2
New cards
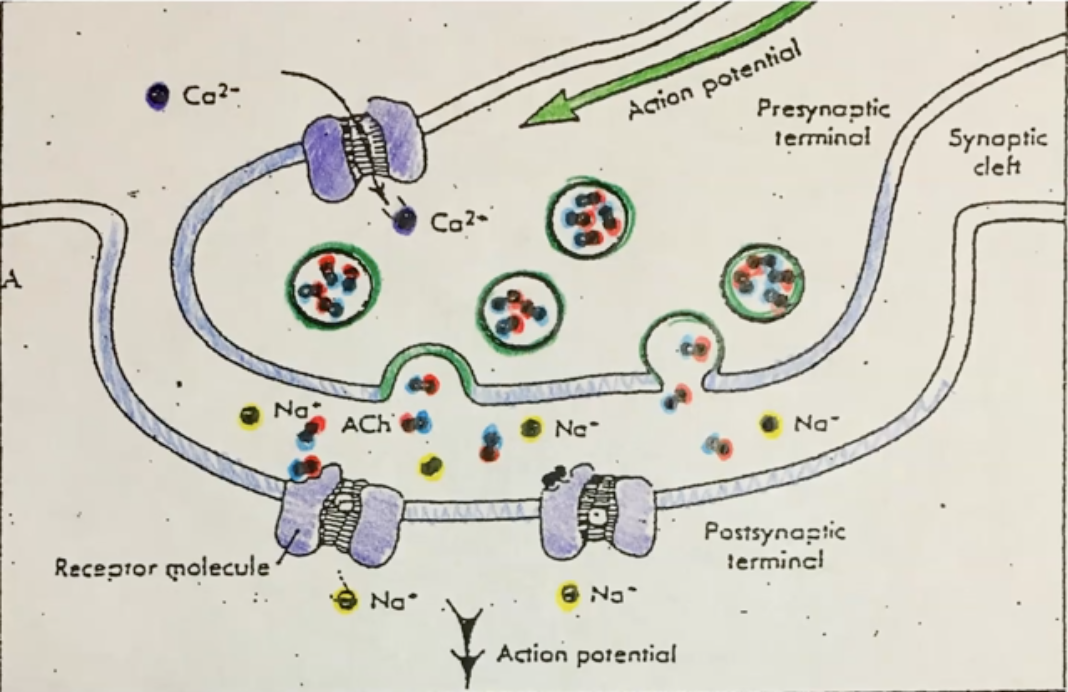
acetylcholine (ACh)
a neurotransmitter substance stored in synaptic vesicles; binds to a specific receptor protein on the sarcolemma; made from acetic acid and choline**
3
New cards
presynaptic terminal
another term for bouton**
4
New cards
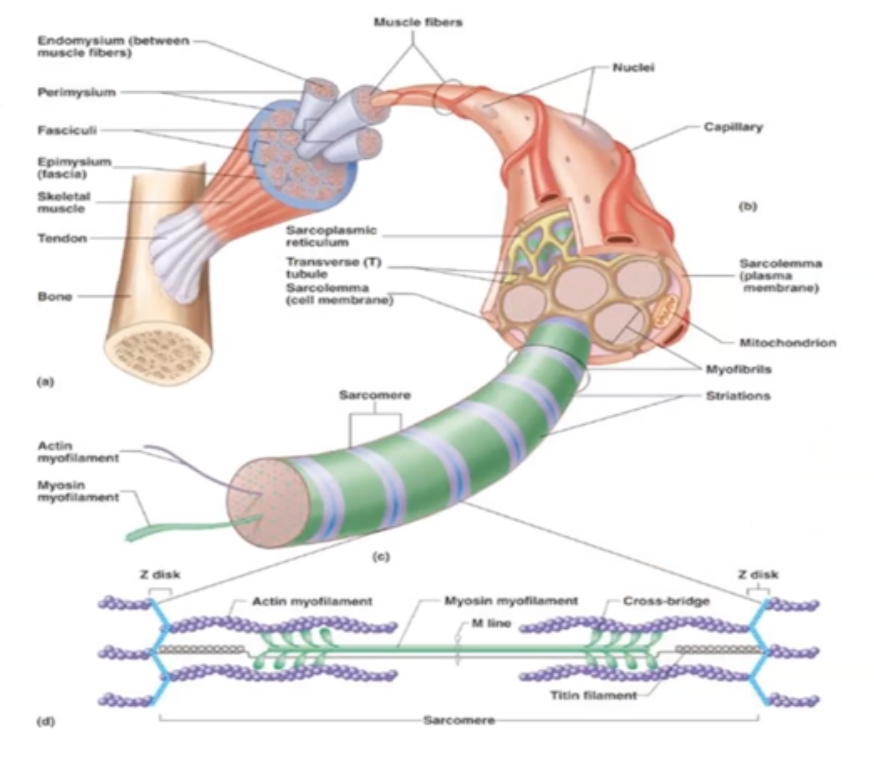
sarcolemma
the technical name for the cell membrane of a muscle cell (fiber)
5
New cards
synaptic cleft
the space found between 2 neurons or a neuron & a muscle fiber
6
New cards
synaptic vesicle
a sac-like organelle that stores neurotransmitter substances like ACh
7
New cards
acetic acid
used to make acetylcholine; is also a waste product & will be removed by the bloodstream; it will enter the liver where it will be molecularly broken down into units which can be excreted by the kidneys
8
New cards
aerobic respiration
cellular respiration that requires oxygen to produce energy
9
New cards
ATP
adenosine triphosphate (adenine, ribose sugar & phosphate groups); contains energy stored in its phosphate bonds
10
New cards
calcium
An important ion in the regulation of nerve impulses; found in high concentration outside the sarcolemma of the cell and low concentration inside the cell
11
New cards
cellular respiration
the process of breaking down glucose and converting it to a source of energy (ATP) that can be used by the cell
12
New cards
choline
used to make acetylcholine; is conserved, recycled and stored in the neuron
13
New cards
creatine phosphate
an organic compound of creatine and phosphoric acid; when broken down, it releases energy for muscle contraction
14
New cards
depolarization
The inside of the cell becomes positively charged for a brief period of time
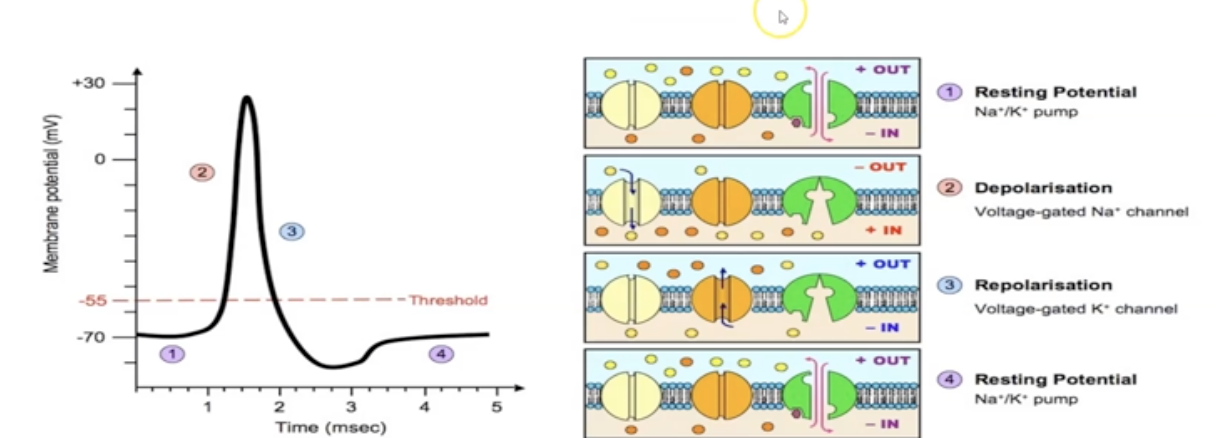
15
New cards
fermentation
the process of breaking down glucose when oxygen is not available to produce energy; produces less ATP than aerobic respiration
16
New cards
glucose
a simple sugar (monosaccharide) that serves as an important intermediate energy source
17
New cards
glycogen
a polysaccharide composed of many glucose molecules; a source of energy stored in the liver and muscles
18
New cards
lactic acid
an organic acid that is a byproduct of anaerobic respiration
19
New cards
(mighty) mitochondria
organelle in the cell where cellular respiration takes place to produce energy for the cell
20
New cards
oxygen debt
the amount of extra oxygen required by muscle tissue during recovery from vigorous exercise (requirement of oxygen beyond the normal resting state
21
New cards
repolarization
The cell's internal environment changes from an overall positive charge to an overall negative charge and therefore returns to its resting state
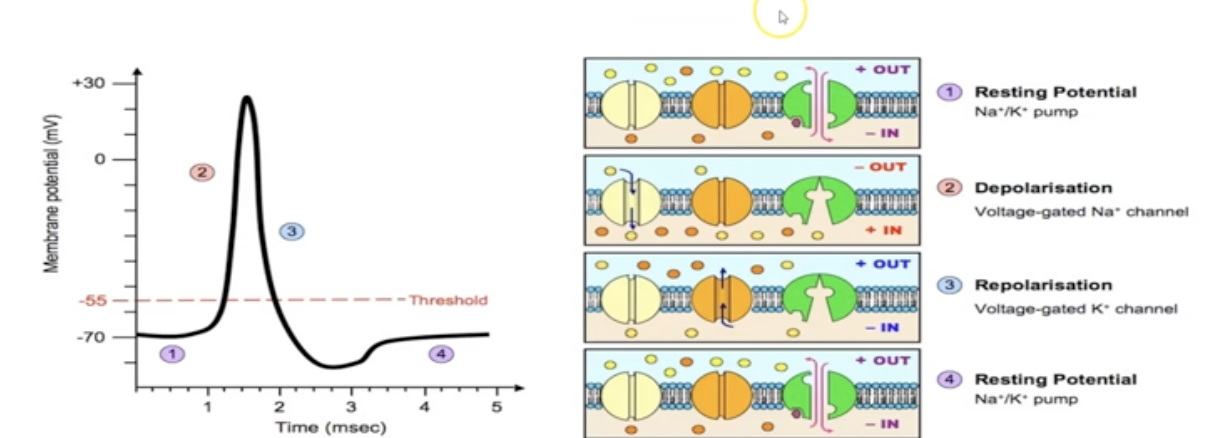
22
New cards
resting state
The cell is negatively charged inside compared to its surrounding environment
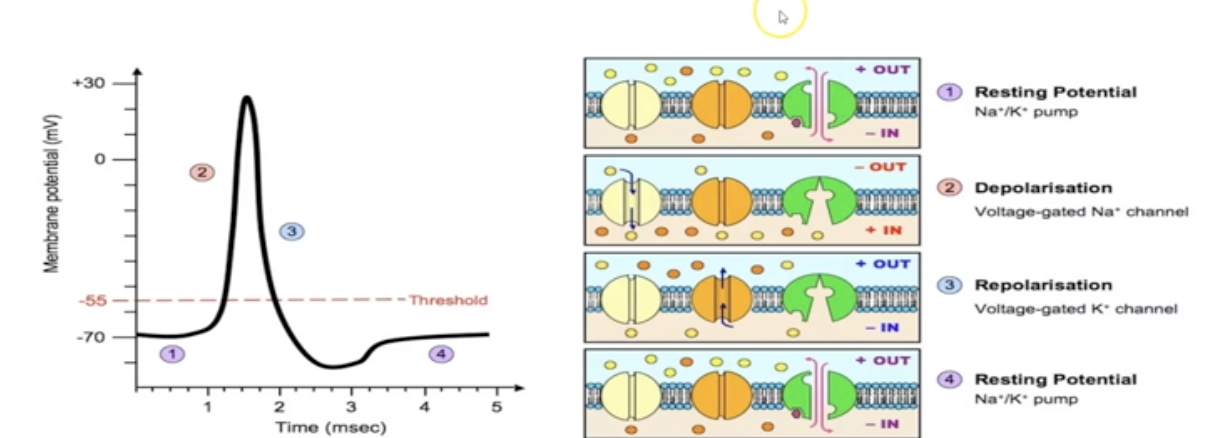
23
New cards
What are the 7 functions of muscle
1. Body Movement
2. Maintain Posture
3. Respiration
4. Produce body heat
5. Communication
6. Construction of organs and vessels
7. Heart Beat
\
==not that important to remember==
24
New cards
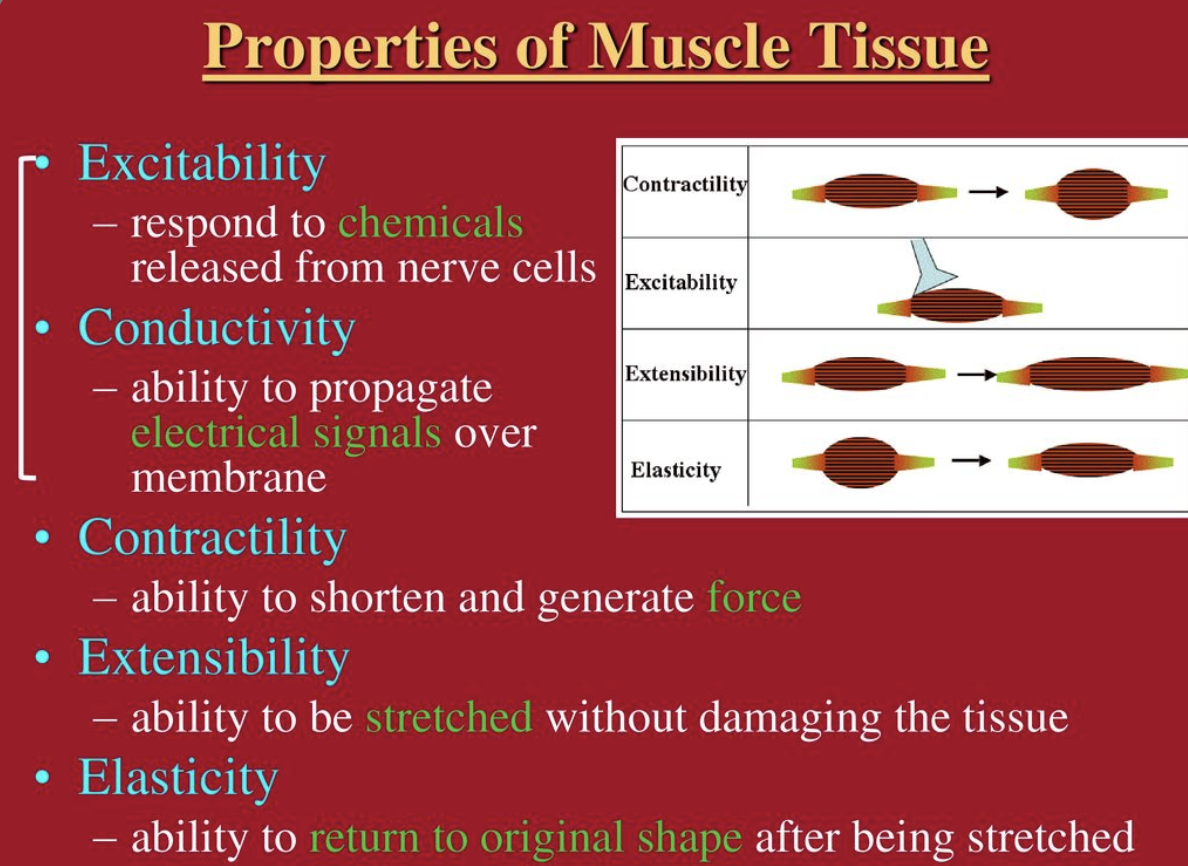
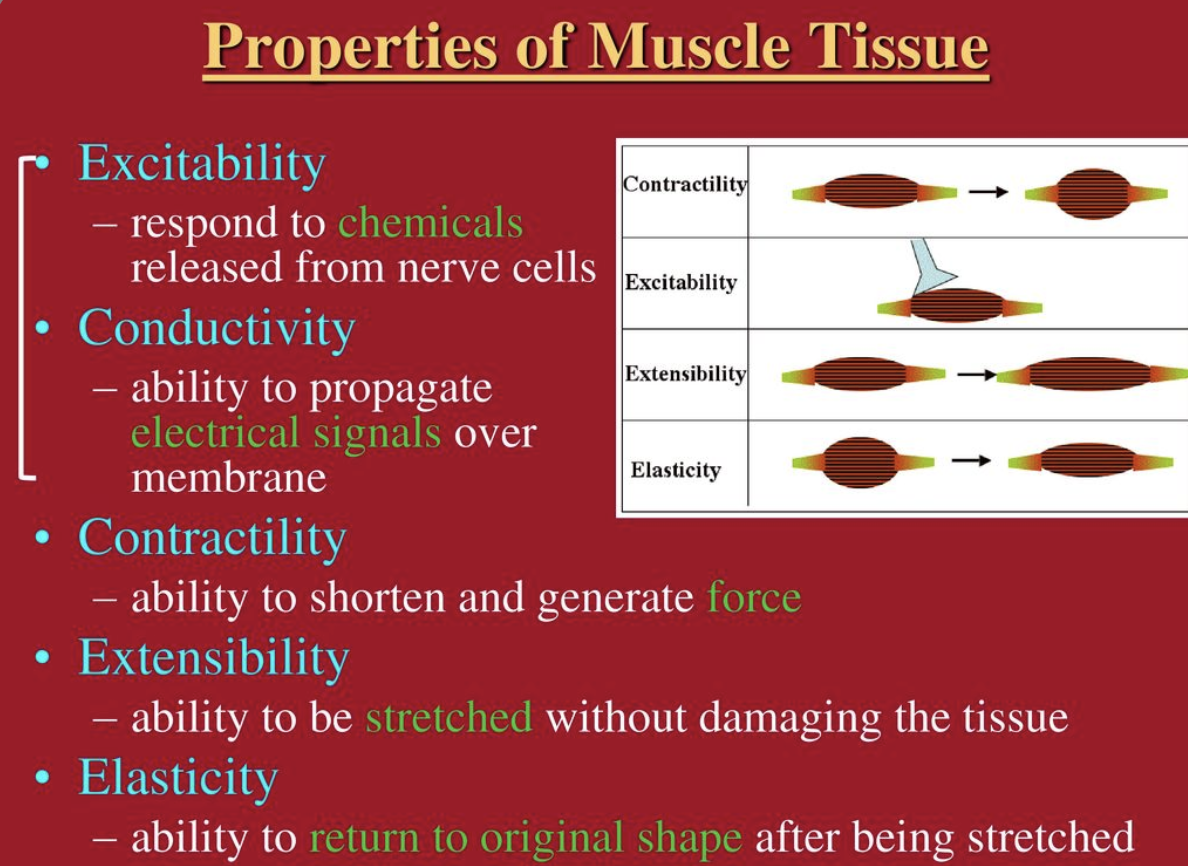
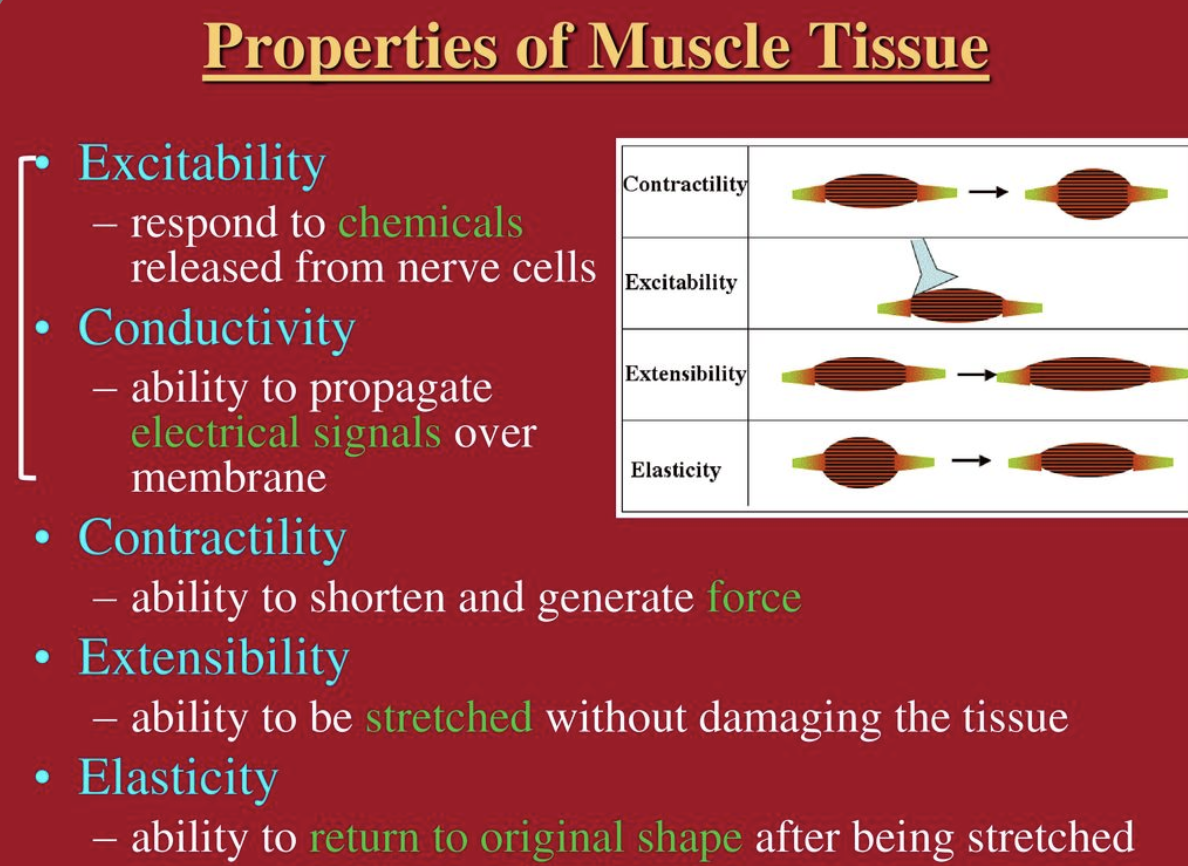
What are the 4 properties of muscles
Contractility, Excitability, Extensibility and Elasticity
\
==Remember using CEEE==
\
==Remember using CEEE==
25
New cards
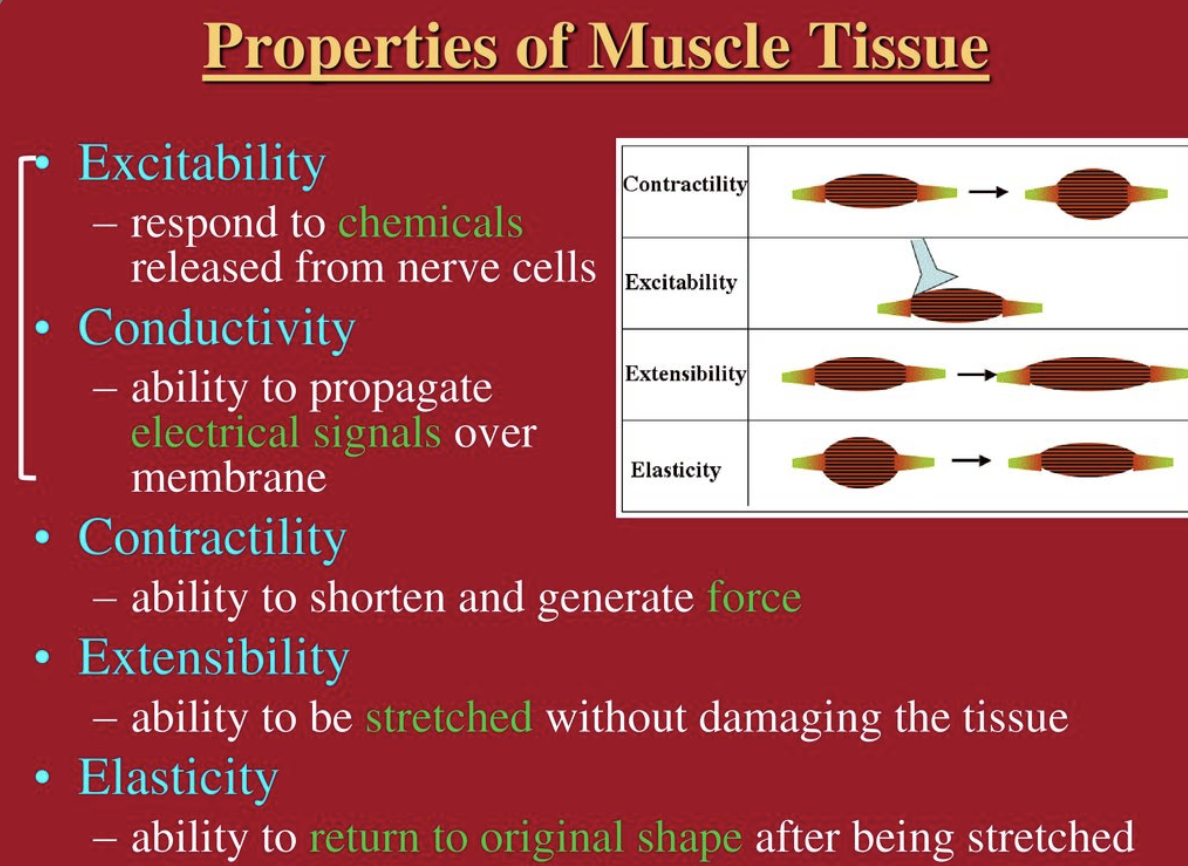
What is ==contractility==?
ability to shorten when an adequate stimulus is received
26
New cards
What is ==excitability==?
ability to receive and respond to a stimulus
27
New cards
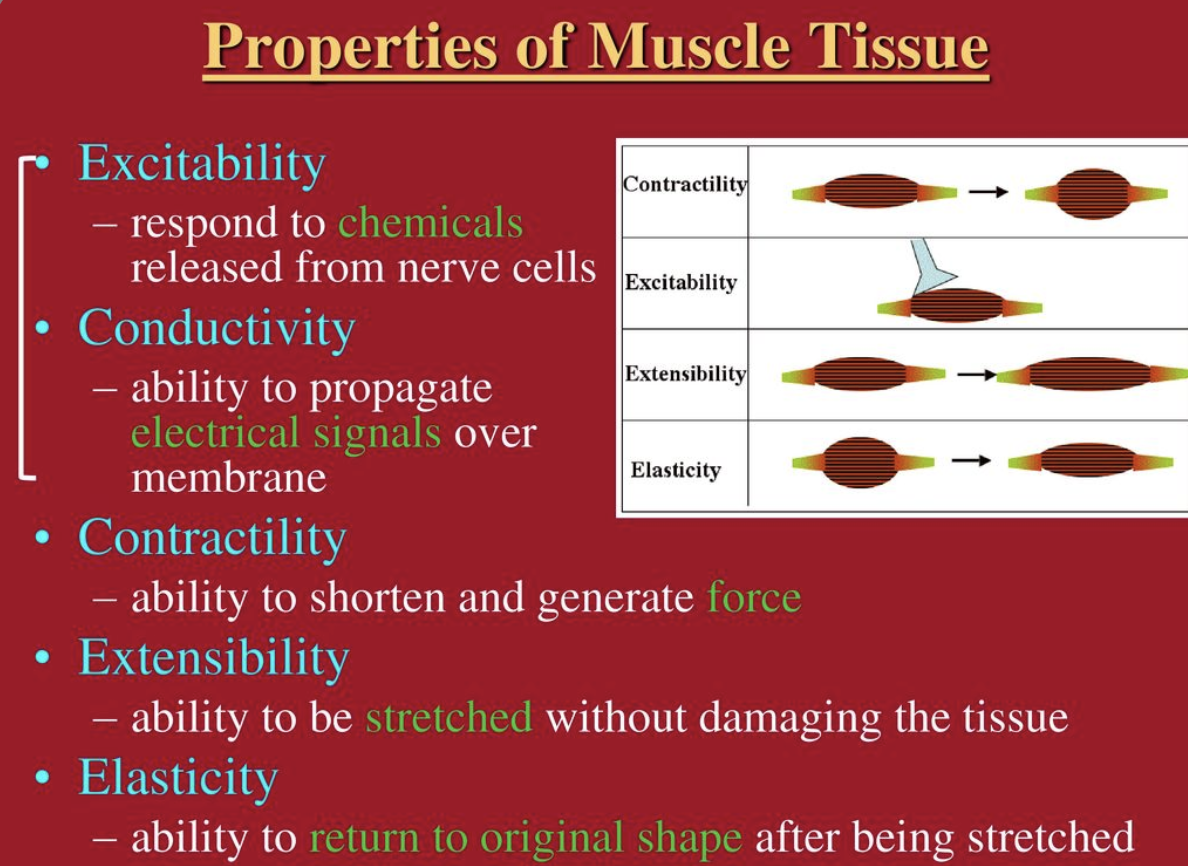
what is ==extensibility==?
ability to lengthen when an adequate stimulus is received
28
New cards
what is ==elasticity==?
ability to return to standard shape
29
New cards
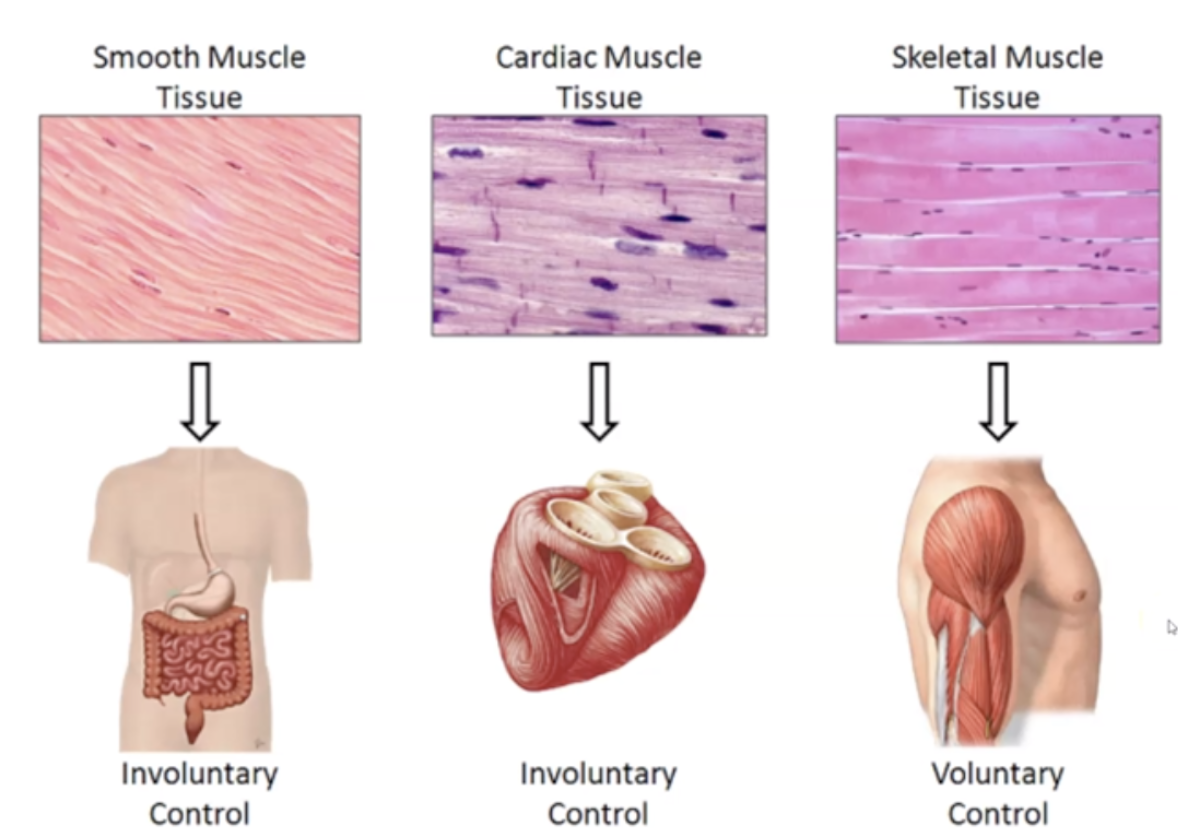
What are the 3 muscle types?
Skeletal Muscles, Cardiac muscles and Smooth muscles
30
New cards
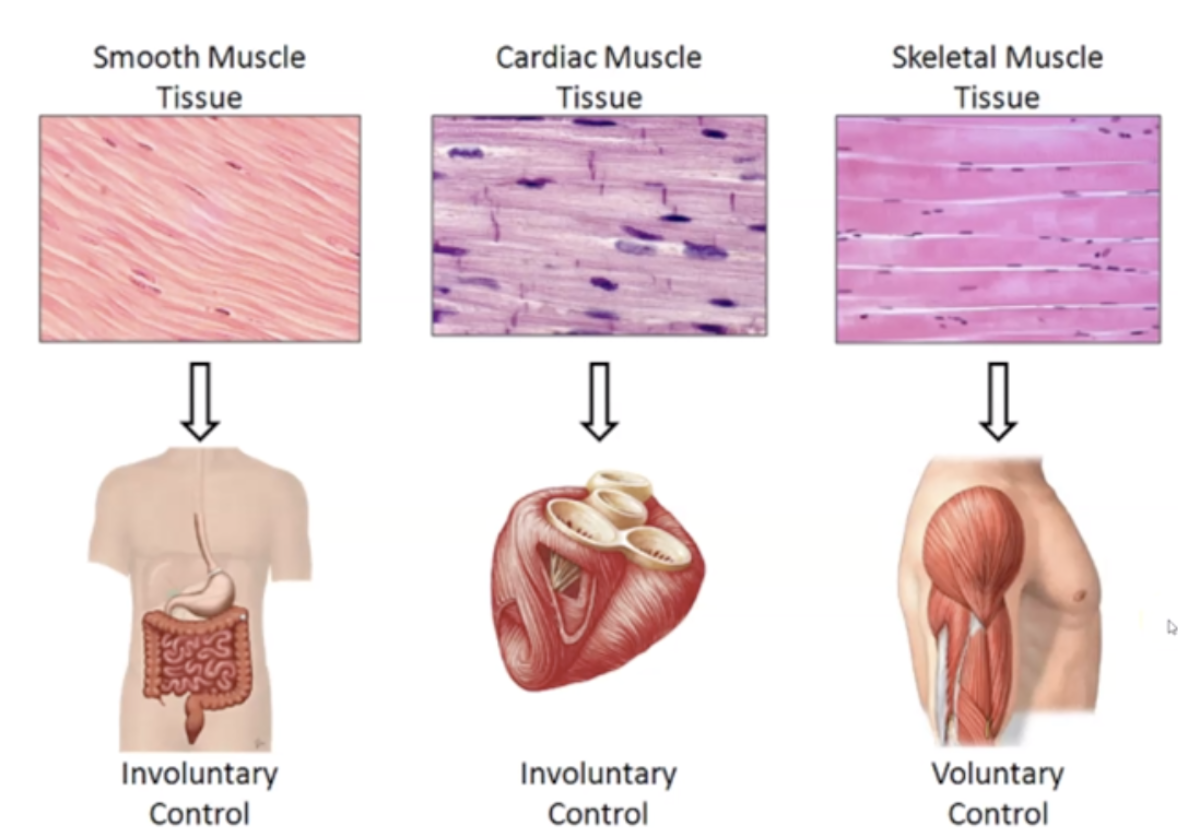
==Skeletal Muscles== location, function, nuclei type and appearance
1. Attached to bone
2. Body movement
3. Voluntary Control
4. Striated
5. Multinucleate
31
New cards
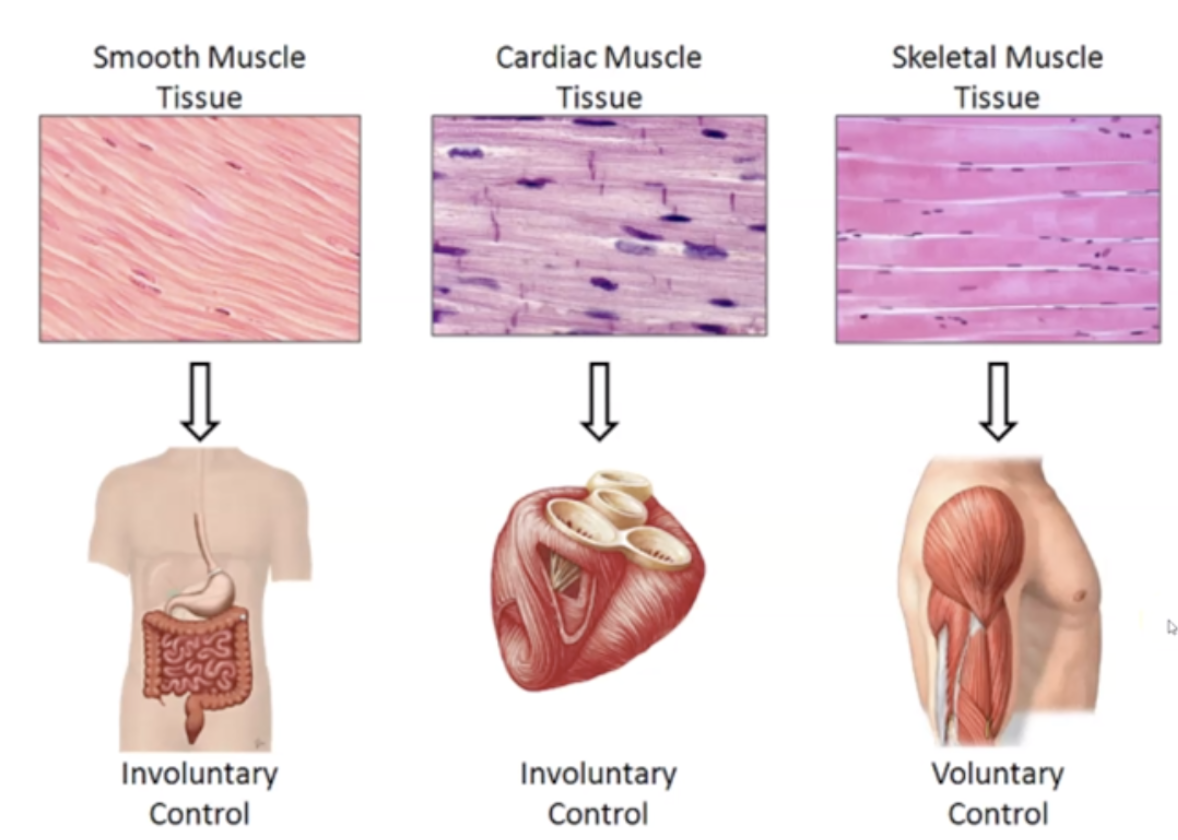
==Cardiac Muscle’s== location, function, nuclei type, and appearance
\
\
1. Found in Heart
2. Involuntary Contraction
3. Single Nuclei
4. Intercalated disks
5. Circulate blood
32
New cards
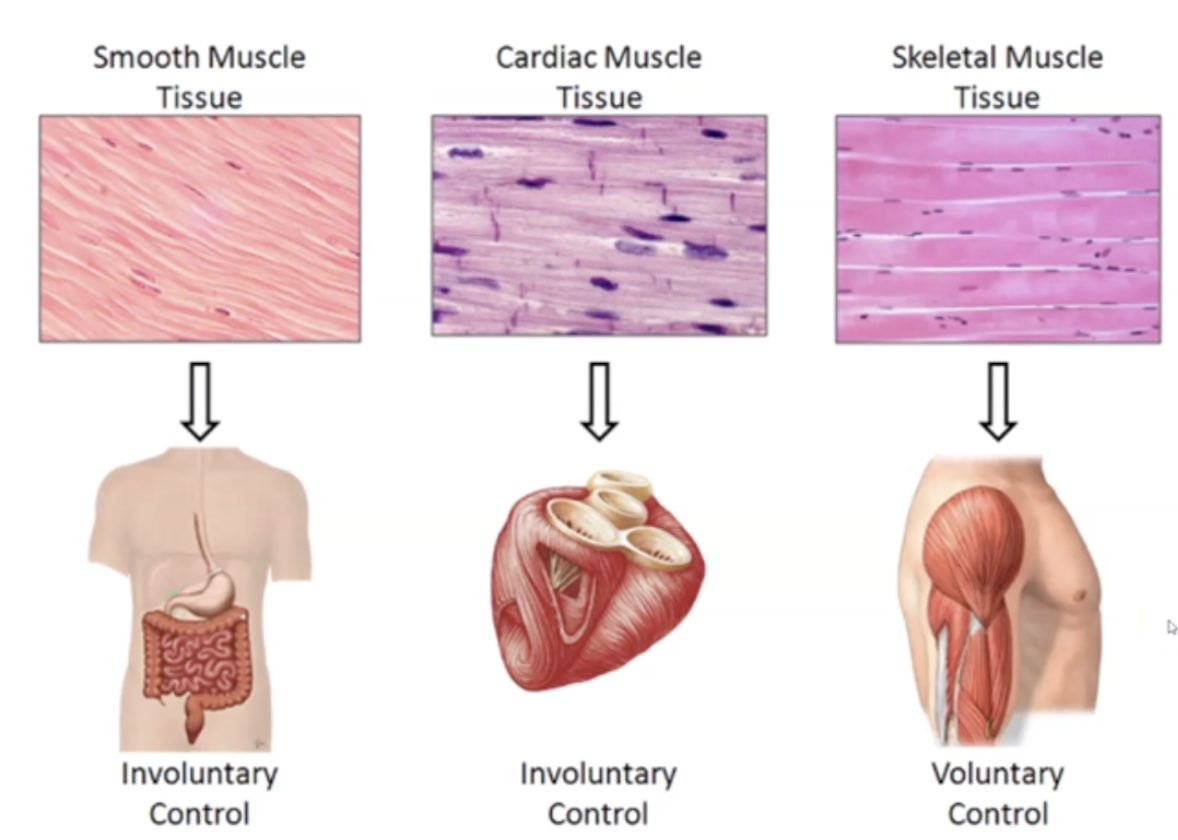
==Smooth Muscle’s== location, function, nuclei type, and appearance
1. Found in blood vessels, glands, etc
2. Spindle Shaped
3. Single Nuclei
4. Involuntary contraction
5. No striations
33
New cards
Muscles can only ___(push/pull) and donot ___(push/pull)
pull; push. Just remember Muscles cannot push thats it
34
New cards
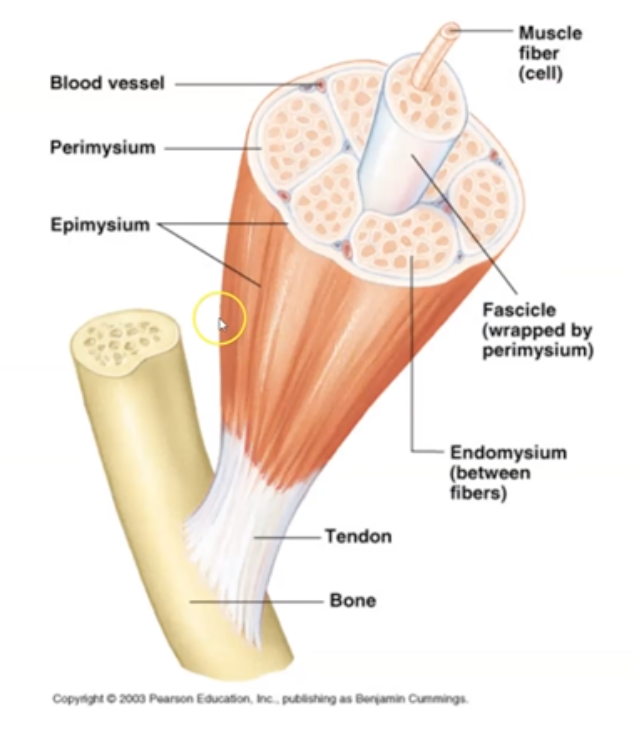
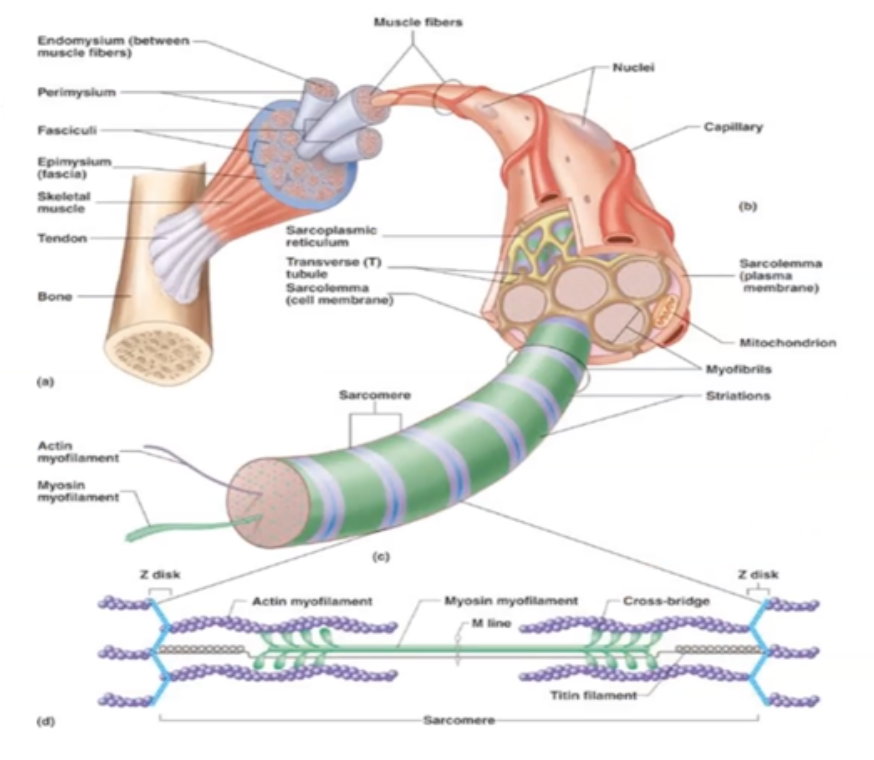
What are the 5 muscle components?
Muscle, Fascicle, Muscle Fiber, Myofibril and Myofilament
==Remember: (m, f, mf, m, mm)==
==Remember: (m, f, mf, m, mm)==
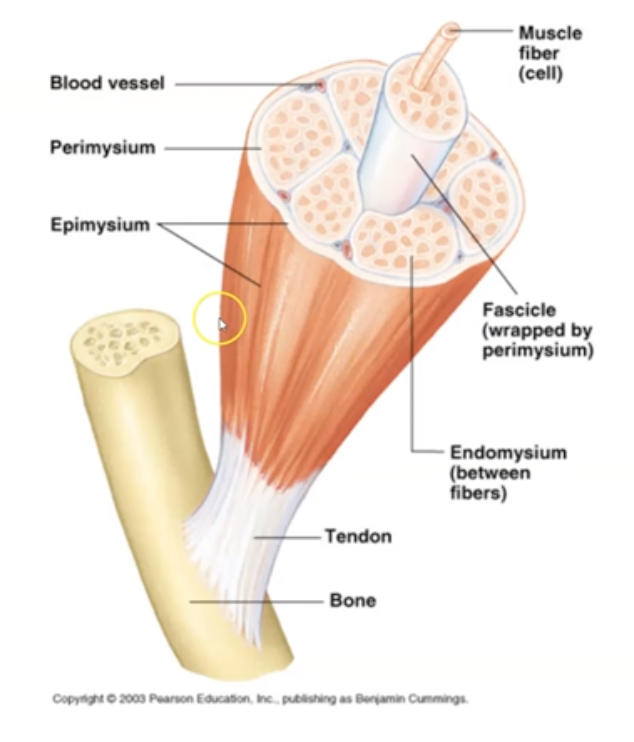
35
New cards
what is a ==Muscle==?
Groups of fascicle bundles
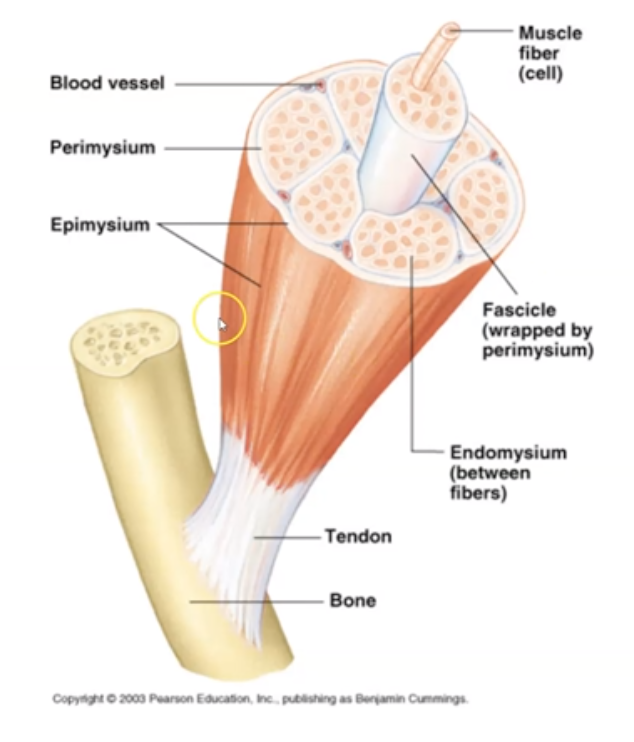
36
New cards
what is a ==Fascicle==?
Groups of muscle fibers surrounded by connective tissue
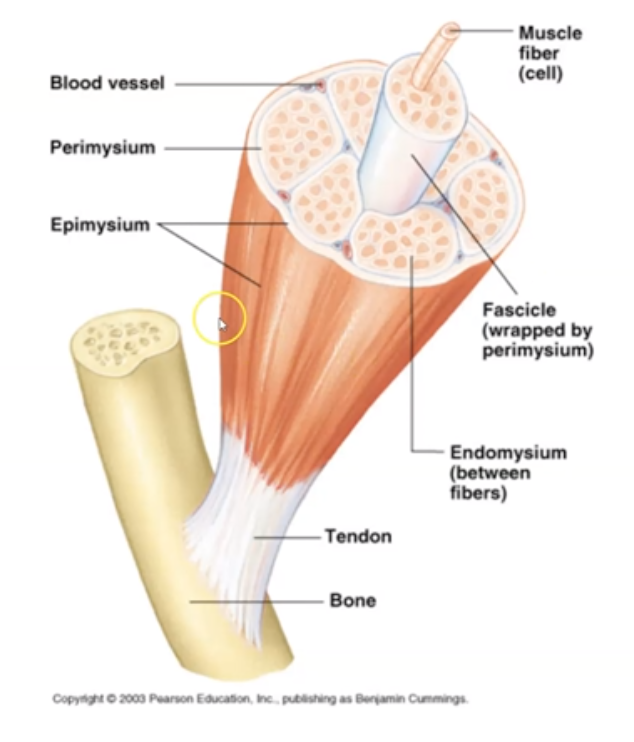
37
New cards
what is a ==Muscle Fiber==?
Single Muscle cell comprised of myofibrils
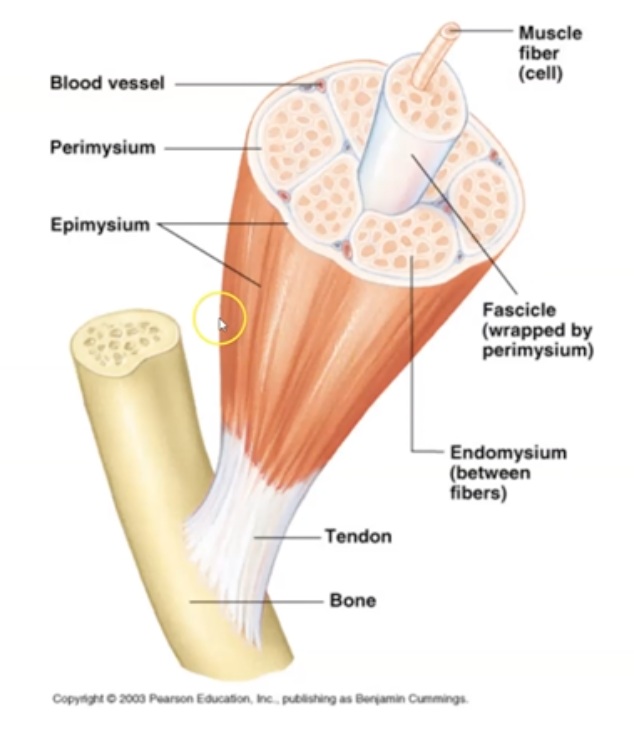
38
New cards
what is a ==Myofibril==?
Contractile unit within muscle cell
39
New cards
what is ==Myofilament?==
Shortest unit of muscle cell containing actin and myosin
40
New cards
____ muscle causes digestion of your food
smooth muscle
41
New cards
___ causes muscles to shorten
contractility
42
New cards
___ feature allows cardiac muscle cells to work in sync with one another
intercalated discs
43
New cards
___ muscle type has the longest cells and many nuclei?
Skeletal muscle
44
New cards
write the correct order from largest to smallest
muscle, fascicle, muscle fiber, myofibril, myofilament
(m, f , mf , m , m)
(m, f , mf , m , m)
45
New cards
___ is another name for single muscle cell
Sacomore