Evolution and Biodiversity
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
state the taxonomic classification, in hierarchical order
kingdom
phylum
class
order
family
genus
species
mnemonic to memorize taxonomic order
“keep ponds clean or fish get sick”
outline how we determine the scientific name for species using a bionomial system
genus+species
describe what natural classification is and how scientists use natural classification to classify new species
is how scientists aim to classify species in a way that reflects evolutionary paths
scientists look at a species’ ancestry and compare it to those species who have similar traits
state the three domains of life
bacteria
archaea
eukarya
state the six different phylum of the animal kingdom
porifera
cnidaria
platyhelminthes
annelida
mollusca
arthopoda
state three traits of the porifera
no segmentation
no symmetry
no mouth or anus

state three traits of the cnidaria
no segmentation
radial symmetry
has mouth; no anus

state three traits of the platyhelminthes
no segmentation
bilateral symmetry
has mouth; no anus

state three traits of the annelida
very segmented
bilateral symmetry
mouth & anus

state three traits of the mollusca
not visible (segmented)
bilateral symmetry
mouth & anus
state three traits of the arthropoda
segmented
bilateral symmetry
mouth & anus

state five major vertebrate classes
amphibians
reptiles
birds
mammals
fish
state three traits of amphibians
soft skin permeable to water
lungs with moist skin
pentedactyl limbs
state three traits of reptiles
skin with scales impermeable to water
lungs with extensive folding
pentedactyl limbs
state three traits of birds
skin with feathers
lungs with air sacs
pentedactyl limbs
state three traits of mammals
skin with hair follicles
lungs with alveali
pentedactyl limbs
state three traits of fish
bony scales
breathe via gills
no limbs
state what louis pasteur proved
designed an experiment to show that cells can only arise from pre-existing cells
outline how pasteur set up his experiment
the first swan-necked flask was filled with nutrient broth and boiled
boiling killed any bacteria and the swan neck kept any unwanted organisms from entering
the second flask was also boiled but had a broken neck that allowed free air
outline what the results were from pasteurs experiment
after some time passed, he observed micro-bacterial growth in the flask with the broken neck
the broken neck had allowed micro-organisms to enter freely into the nutrient broth
he was able to deduce that organisms in the atmosphere had colonized the open flask and that growth was not spontaneous as people at the time had believed
state what are 4 complex structures needed to be present for life to form and explain why they’re necessary
carbon compounds (amino acids, fatty acids)
must be produced as they are they are the building blocks in life
carbon compounds must assemble into polymers (polysaccharides, proteins)
without polymers it won’t be possible to build complex molecules such as DNA or proteins to be replicated
membranes must be formed
a phospholipids bilayer must be present for all cells to be formed
without one a cell won’t be able to maintain homeostasis nor be able to shield itself from unwanted materials
as well as let any chemical properties occur.
mechanism of inheritance
RNA is most likely to occur as it can self-replicate and act as a catalyst to speed up the polymerization of proteins
state what the urey-miller experiment observed
their experiment successfully synthesized amino acids from inorganic components
outline how the urey-miller experiment was carried out and outline the results
they built a closed system containing a heated pool of water and a mix of gases. they sent electricity sparks to simulate lightning.
although they were successful in creating monomers (carbohydrates, amino acids) there was no possible way to create large molecules (DNA, proteins)
define endosymbiosis
is described as how the eukaryotic cell arrived via endocytosis
describe how the first eukaryotic cells were developed via endosymbiosis
a large prokaryotic cell engulfed a smaller cell but instead of digesting it, the large cell allowed it to live in symbiosis
the large cell provided protection while the smaller provided energy
state what features of the chloroplast and mitochondria suggest they evolved from prokaryotes
they both have:
double membranes
smaller ribosomes (70S)
circular DNA
replicate via binary fission
define evolution
the gradual change in the heritable characteristics of species over time
define natural selection
how organisms better adapt to their environment tend to survive and produce more offspring
define fossil records
sequence of related species and sequence of changes within the species
it provides evidence for evolution
scientists can determine the age of fossils via fossil record
define selective breeding
deliberate breeding of organisms to obtain or continue a favorable trait done by humans
the practice shows that heritable characteristics in a species can change over time
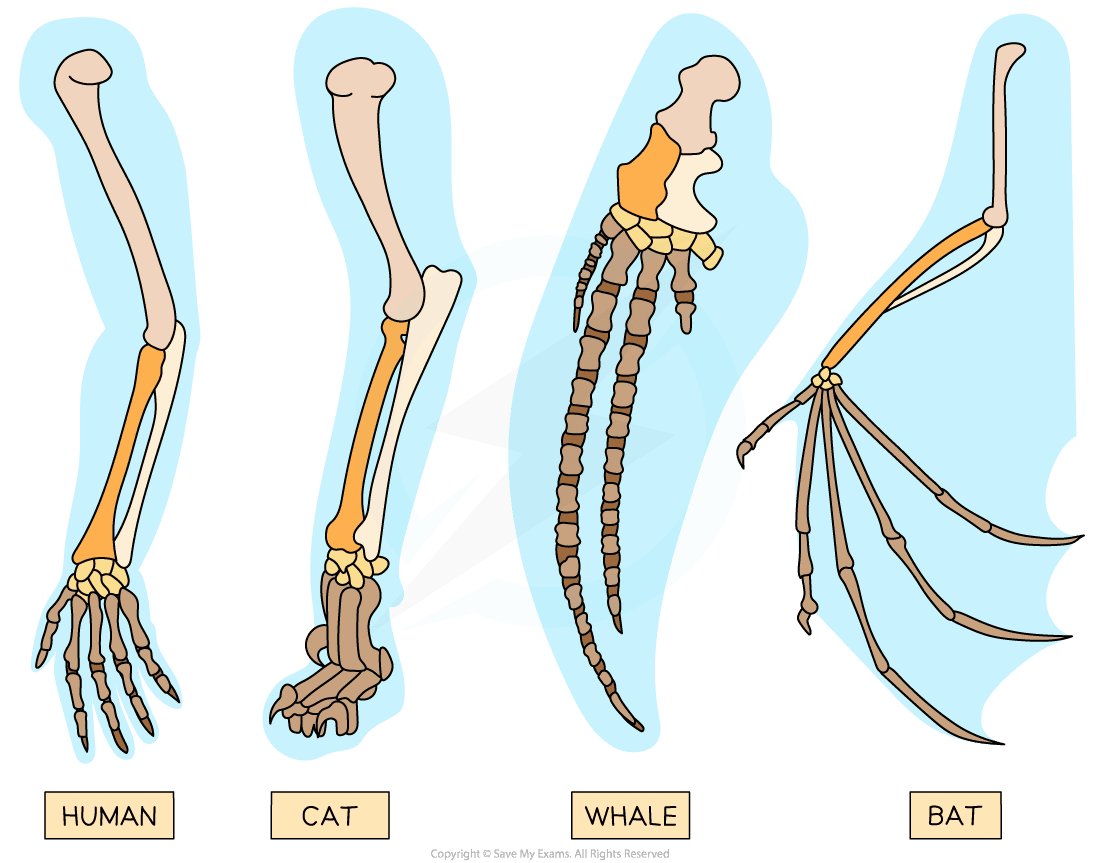
define homologous structures
similar structures in different species that have different functions due to common ancestry
define analogous structures
different structures but similar function due to convergent traits
define adaptive radiation
diversification of species into several related species
homologous structures are the result of adaptive radiation
this typically occurs when the environment changes, creating new needs for organisms to fill
define speciation
occurs when a single species evolves into a separate species
define gradual convergence
change in environment or location that leads to speciation
define industrial melanism and describe the peppered moth
occurs in species in response to increased levels of pollution in the environment
increases in sulfur dioxide and soot changes the surface of trees forcing the peppered moths to adapt and change
explain how genetic variation between individuals of a species can be generated
variation can be shown via meiosis, sexual reproduction, and mutation
meiosis: provides new combinations of alleles, which vary in each off spring
sexual reproduction: allows for new combinations of traits in an organism from the two parents
mutation: are changes in genetic code. a codon can either be switched out or added in.
define adaptions
are traits that make an individual better suited to its environment
explain how natural selection can cause traits such as drought resistance to develop in wild plants
after generations the plant will learn how to better adapt to its environment
this then leads to traits being favorable so a plants offspring can survive for a much longer period
these favorable traits are advantageous because then an organism has a better chance at survival
define antibiotics
chemicals that are used to kill or inhibit the growth of bacteria
they are used to control infection by pathogenic cells
state what antibiotics target
DNA
cell wall
proteins
define antibiotic resistance
when bacteria are able to respond to changes in their environment and are capable of evolving resistance to antibiotics
define overproduction in natural selection
when species tend to produce far more individuals than can survive in maturity
describe natural selection in overproduction of organisms
species tend to compete with each other for survival as well as territory, mating, and food.
those that obtain these tend to survive and produce more offspring
those that are less adapted tend to die off or produce fewer offspring
define cladistics
a system of classifying organisms based on shared characteristics from common ancestry
define clades
a group of organisms that evolved from a common ancestor and are related
define cladogram
tree diagrams that show the most probable sequence of divergence in clades
define “root” in cladograms
the initial ancestor common to all organisms with the cladogram
define “node” in cladograms
a hypothetical ancestor that speciated to give rise to two daughter taxa
state what evidence can be used on caldograms
quantifying different traits between a set of organisms
DNA or amino acid sequence
DNA mutations
DNA can be used as a molecular clock to observe changes in DNA sequences
define reclassification and state the importance of it
it is when scientists regroup species due to an incorrect placement in a cladogram
it can lead to more accurate information/research