Key terms for free standing sculpture
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Archaic period
early period of Greek history from 600 to 490/480 BC
a man scraping off oil from his body
Apoxyomenos
Canon
title employed by the sculptor Polykleitos for his treatise (written work) on statue proportions
clothed female figures used to up architecture in place of columns
Caryatid
the curve that an idealized chain or cable forms when hanging freely from two fixed points
used to describe u shaped folds in drapery
Catenary
Chiton
a rectangular piece of linen clothing, worn by both men and women, which is sewn and buttoned along the shoulders to make sleeves
Classical period
middle period of ancient Greek history
early classical = 490 to 450 BC
high classical = 450 to 400 BC
late classical = 400 to 323 BC
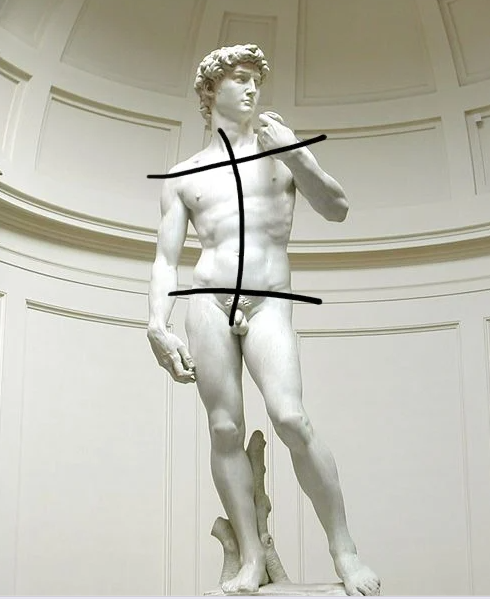
Contrapposto
literally meaning COUNTER POSE in italian
the figures shoulders and hips are angled in different directions because it’s weight is on one foot
Cult statue
a statue that embodied and depicted a specific deity
often situated within the main room of a temple
an athlete throwing a discus
Diskobolos
a spear bearer
Doryphoros
a sculptural technique where a grid was drawn on a stone block to determine the figure’s proportions
adopted by the Greeks in the mid 7th century BC
Egyptian grid block technique
statues carved in the round so detached from any background
free standing
frontal
a sculpture can be described as frontal when it has a definite orientation towards the prospective of the viewer
i.e. the front of the statue is the intended view
geometric style
an influential style from 8th and 7th centuries where geometric motifs were employed in greek art
e.g. on statues we see triangular torsos and ovoid heads
himation
a cloak worn by both men and women consisting of heavy fabric, probably wool
usually worn draped diagonally over one shoulder and wrapped around the body
Iliac crest
the v shaped crest of muscle that seperates the groin from the hips
often exaggerated in greek sculpture
In-the-round
a sculpture meant to be viewed from all sides
3 dimensional with all it’s parts fully rendered
this causes the viewer to work around the figure
Kore
plural = korai
literally meaning a maiden or unmarried girl in greek
a type of draped female sculpture from the archaic period
Kouros
plural = koroi
literally a male youth in greek
a type of male sculpture from the archaic period
Lost wax carving method
a sculptural technique where wax is employed to create a space between inner and outer clay moulds
which allows the casting of large- scale hollow bronze statues
this method was employed from the late archaic period onwards
Modelling lines
sculptural technique, in which ridges of stone in sweeping curves at right angles to a rounded , model the forms
Motion lines
long, double-curving lines in drapery suggestive of movement
Orientalising
a transitional period of c 750 - 650 BC
greek artists were heavily influenced by near eastern art most notably from Egypt, Syria and Phoenicia
human and animal figures become more significant
MOST IMPORTANT the idea of using stone for monumental architecture and sculpture was embraced
Peplos
a rectangular piece of woollen clothing without sleeves worn by women
pinned at the shoulders,
belted at the waist
and worn either alone or over a chiton

plinth
slab like bottom section of a marble statue immediately beneath its feet
planes
flat or rounded
an area of two dimensional surface
e.g. early kouroi display flat planes whilst later ones have more rounded planes
Polychromy
the multicoloured painting of sculptures
marble, limestone, bronze, terracotta or wood
principal colours = blue and red
yellow, green, brown, black and white to a lesser degree
Severe style
the transitionary period between the archaic and classical periods
dating roughly between 490 and 450 BC (sometimes also called the early classical period)
thick eyelids
heavy and simple drapery
increase in characterisation
tensile strength
the resistance of a material to sideways stress and it’s liability to break
e.g. marble has a low tensile strength and bronze has a high tensile strength
torso
the trunk of a human body which remains when the head and limbs are removed
Transparency or the wet drapery technique
sculptural technique which leaves ridges standing up to otherwise nude forms to suggest they are covered by a thin veil of drapery
volute
a spiral, scroll like pattern often seen in the hair of Greek sculptures