Enzymes
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
Define Enzyme
biological catalysts made from proteins or RNA
define catalyst
speeds up a chemical reaction without being used up
catabolic
breaks down a substance
anabolic
builds a substance
Characteristics of enzymes
can be reused
unchanged after a reaction
lowers activation energy
required for all metabolic reactions
only needed in small amounts
substrate specific
saturated by high sub concentration
affected by temp, ph, inhibitors etc.
Exergonic vs Endergonic
(Include in each case whether products or reactions have more energy etc etc)
Exergonic | Endergonic |
means that the reactants have more energy that the products, so they released energy | means that the products have more energy than the reactants so energy is absorbed |
ENERGY RELEASED | ENERGY REQUIRED |
Gibbs Free Energy
delta G
energy available to do work within a cell
DOES NOT CHANGE WITH A CATALYST!!!
Negative Gibbs Free Energy
exergonic (reaction releases energy)
Positive Gibbs Free Energy
endergonic reaction (requires energy)
Activation energy
energy required for chemical reaction to get started
activation and rate of reactions, how do enzymes affect this
High EA means a slow rate of reaction
enzymes lower EA to speed up the rate of reaction
3 main areas where enzymes are found
suspended in solution - glyolysis of respiration
in cell membranes - enzymes used to transport amino acids and sugars
part of an organelle membrane - enzymes found on thylakoid membrane of chloroplasts, or etc of respiration in mitochondria
function of an enzyme is related to
tertiary and quaternary structure
by which bonds does an enzyme-substrate complex form
hydrogen bonds
ionic bonds
hydrophobic/hydrophilic interactions
2 main theoretical models concerning enzyme-substrate complex
Lock and Key Hypothesis
Induced Fit Hypothesis
Lock and Key Hypothesis
enzyme is rigid and specific to enzyme due to shape, size and charge of active site
complementary binding
Induced Fit Hypothesis
enzyme is flexible and can change its conformation to fit around the substrate
increases bond strain and facilitates reaction to take place
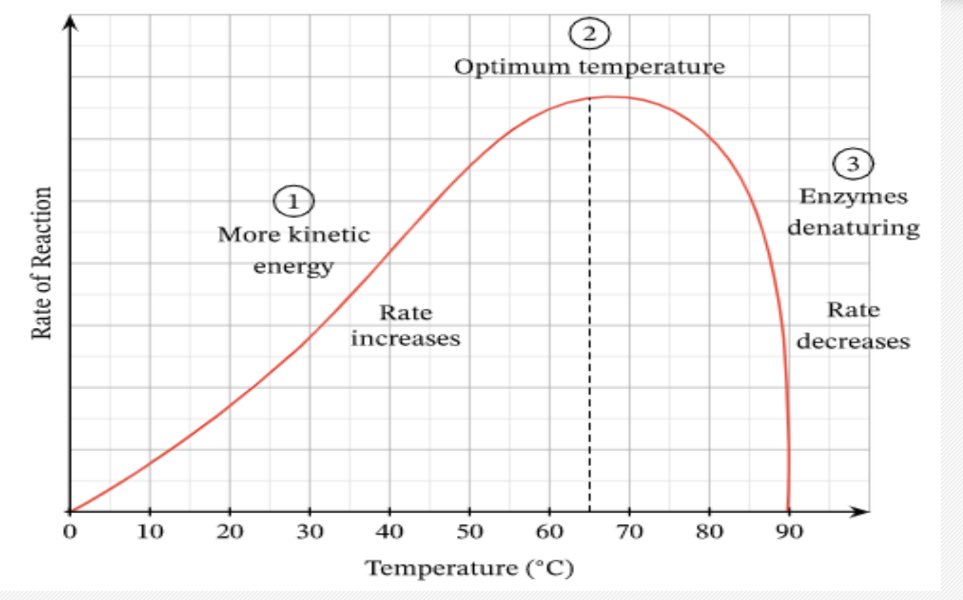
Effect of Temperature on Enzymes
optimum temperature - when an enzyme is functioning most efficiently
low temperatures - enzyme is inactive due to low kinetic energy, decreases chances of enzyme substrate collision happening
high temperatures enzyme is denatured as heat causes molecule to twist so rapidly that hydrogen and ionic bonds break destroying tertiary structure
Q10 - temperature coefficient
Q10
temperature coefficient
effect of temperature on the rate of reaction w
what can be said about the rate of an enzyme controlled reaction with an increase of 10c
with every rise in 10c the rate of reaction double
GRAPH FOR ENZYME CONTROLLED REACTION
Effect of pH on Enzymes
narrow range
low/high pH enzymes become denatured this is because the charges on the -COOH and -NH2 - tertiary structures change
More acidic = more h+ so disruption of ionic bonding
most cases is reversible but some cases it is permanent
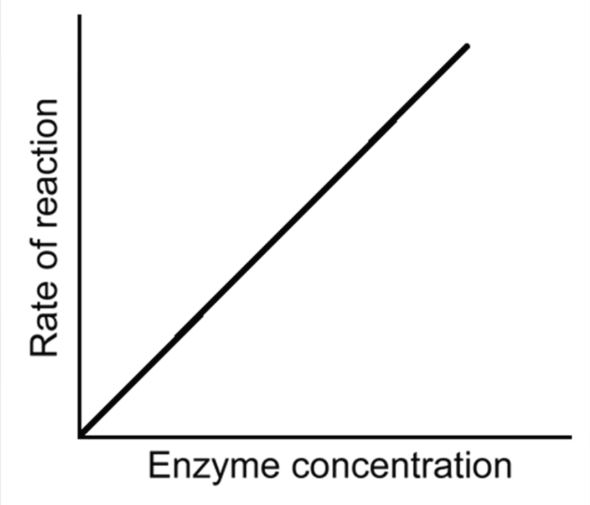
Effect of Enzyme concentration on Enzymes
if substrate conc, ph and temp are kept constant with increasing enzyme conc comes an increase in rate of reaction
more active sites are open
even at low conc - ror is still high as they process and release products quickly
rate at which an enzyme uses a substrate is turnover number
graph for enzyme conc
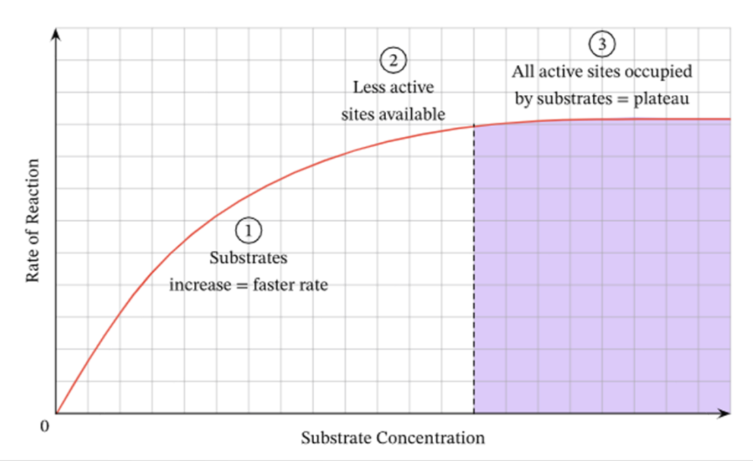
Substrate conc and its effect on enzymes
with increasing substrate concentration comes an increase in ror, then a plateu is reached
this is saturation when all active sites are full
Vmax theoretical value which all enzymes are forming an ES complex is never actually reached
graph for substrate conc
Non - Protein Parts
needed for proper enzyme function
changes to fulfil shape of active site
Inorganic Ions as Cofactors
Prosthetic Groups
Coenzyme
Inorganic Ions as Co-Factors
mould enzyme into a specific shape allowing ES to form
Cl- increases activity of salivary amylase
Prosthetic group
organic compounds bound tightly to enzyme’s active site
carrier of electrons - needed in metabolic pathways
Haem
Coenzyme
organic compounds, loosely associated with an enzyme
derived from vitamins - NAD+ ATP
Inhibitor
small molecules which decrease the rate of reaction of enzymes
found naturally in cells or in drugs or poision
Irreversible inhibitor
permanently binds to side chain of active site
destroys catalytic properties
heavy metals and insecticides
Reversible Inhibitor
temporarily bind to enzyme
resume catalytic properties once removed
Competitive and Non competitive
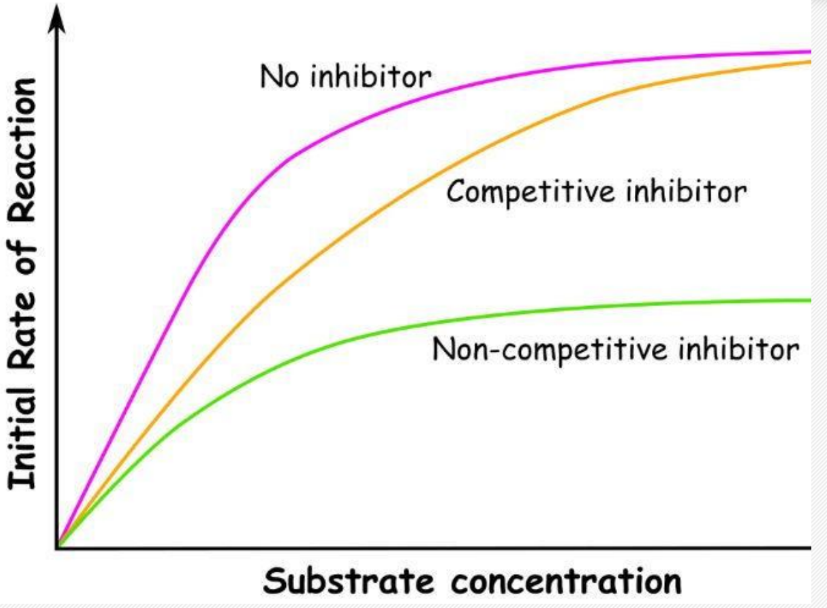
Competitive Inhibitors
structurally similar to substrate and bind to enzyme instead of it
no reaction occurs
removed by increasing substrate concentration as this raises the chances that a collision between substrate
Non Competitive Inhibitors
binds to allosteric site on enzyme
changes the conformation of the enzyme,(triggers certain bonds to break temporarily) substrate can still bind but NO CATALYSIS OCCURS
enzyme inhibitor complex is formed instead
cannot be removed with increasing substrate concentration
graph of inhibitors
what is an allosteric enzyme
large quaternary structures
can be regulated by an effector binding to their allosteric site → undergo a conformational change
two types of effectors
allosteric activators
allosteric inhibitors
allosteric inhibitors
bind to allosteric site
cause a conformational change → change in affinity
decreased ror
Allosteric activators
bind to enzymes allosteric site, allowing for shape to be restored
allow es to form
Increase R.O.R
negative feedback
change in a system triggers a response to counteract that change to maintain a stable environment
negative feedback and allosteric regulation
form of negative feedback
prevents excess product formation as this can reduce catalysis of previous enzymes
allosteric inhibition → end product acts as allosteric inhibitor
prevents build up of product and makes sure reactants are used efficiently
PFK
phosphofructokinase - enzyme in respiration
inhibition of PFK
ATP (end product) inhibits phosphofructokinase
stops conversion between fructose 6 phosphate, to fructose 1-6 biphosphate
ADP and AMP activate it
they activate it as, when atp gets low all youll have is ADP and AMP this will make production of AMP start again
oxidoreductases
remove or add electrons O or H
transferases
transfer chemical groups between molecules
hydrolases
adding water to break chemical bonds
proteases
hydrolysis of proteins
ligases
formation of bonds using ATP