Female Reproduction
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Week 15: Tuesday, December 2nd: Reproduction: Males (cont.); Reproduction: Females; Week 15: Thursday, December 4th: Female Reproduction (cont.)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
the hypothalamus releases GnRH, which stimulates the anterior pituitary to release _______ and _______
LH and FSH
LH and FSH stimulate the ovaries to release _______ and _______, which stimulates the hypothalamus to induce _______
estrogen, progesterone, estrus (sexual receptivity)
estrogen and progesterone stimulate _______ and _______, and prepare the uterus for implantation and pregnancy
follicular growth, ovulation
in the ovarian cortex, _______ and _______ cells produce steroid hormones estrogen, progesterone, and androgens
granulosa, theca
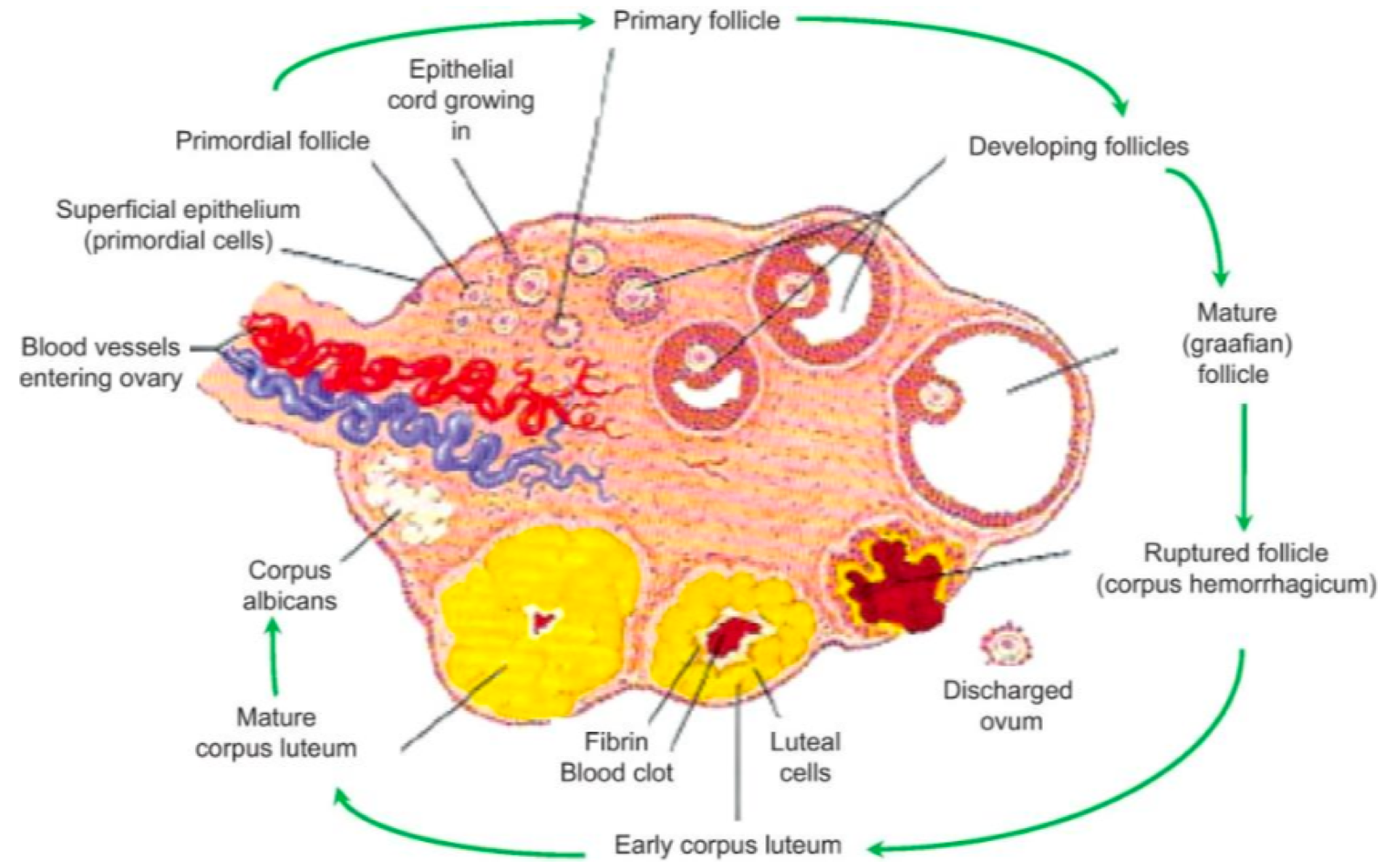
in the ovarian cortex, granulosa and theca cells produce peptide hormones _______, _______, and _______
inhibin, relaxin, paracrine growth factors
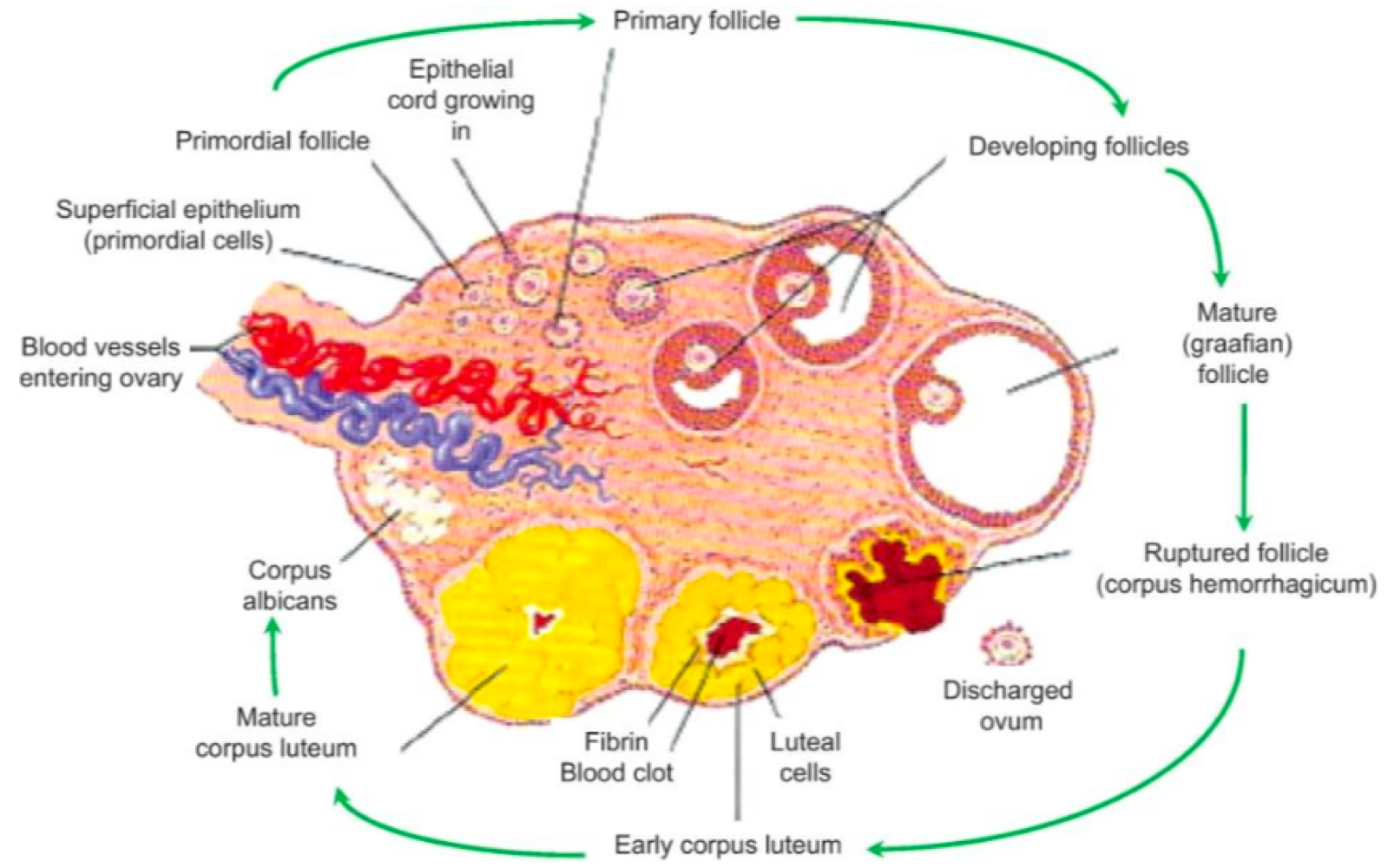
in the ovarian hillum, _______ and _______ enter the ovaries
nerves, blood vessels
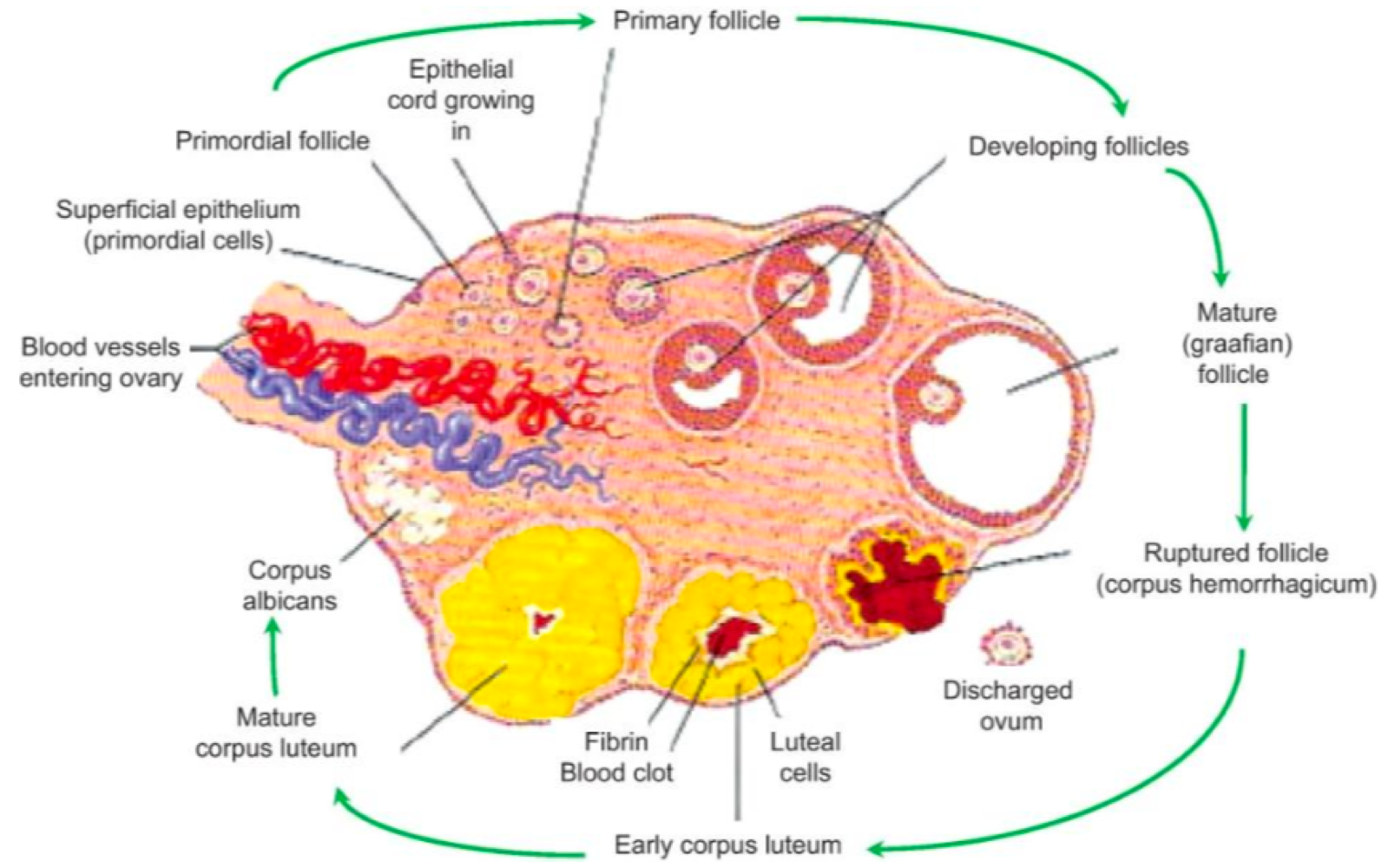
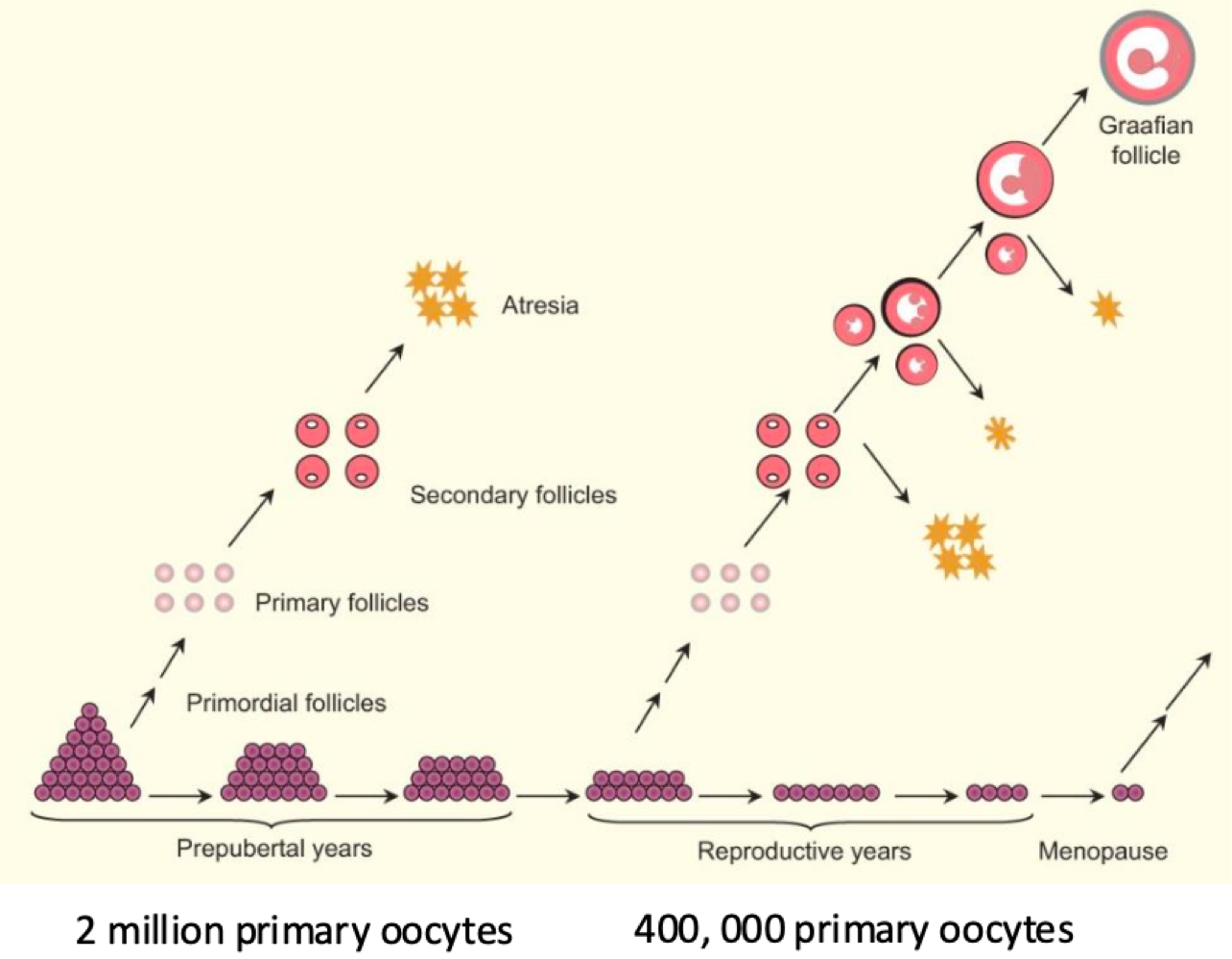
before birth, primoridal germ cells move from the _______ to the _______, then divide into 7 million via _______. only some become _______ via mitosis 1
cortex, ovary, mitosis, primary oocytes
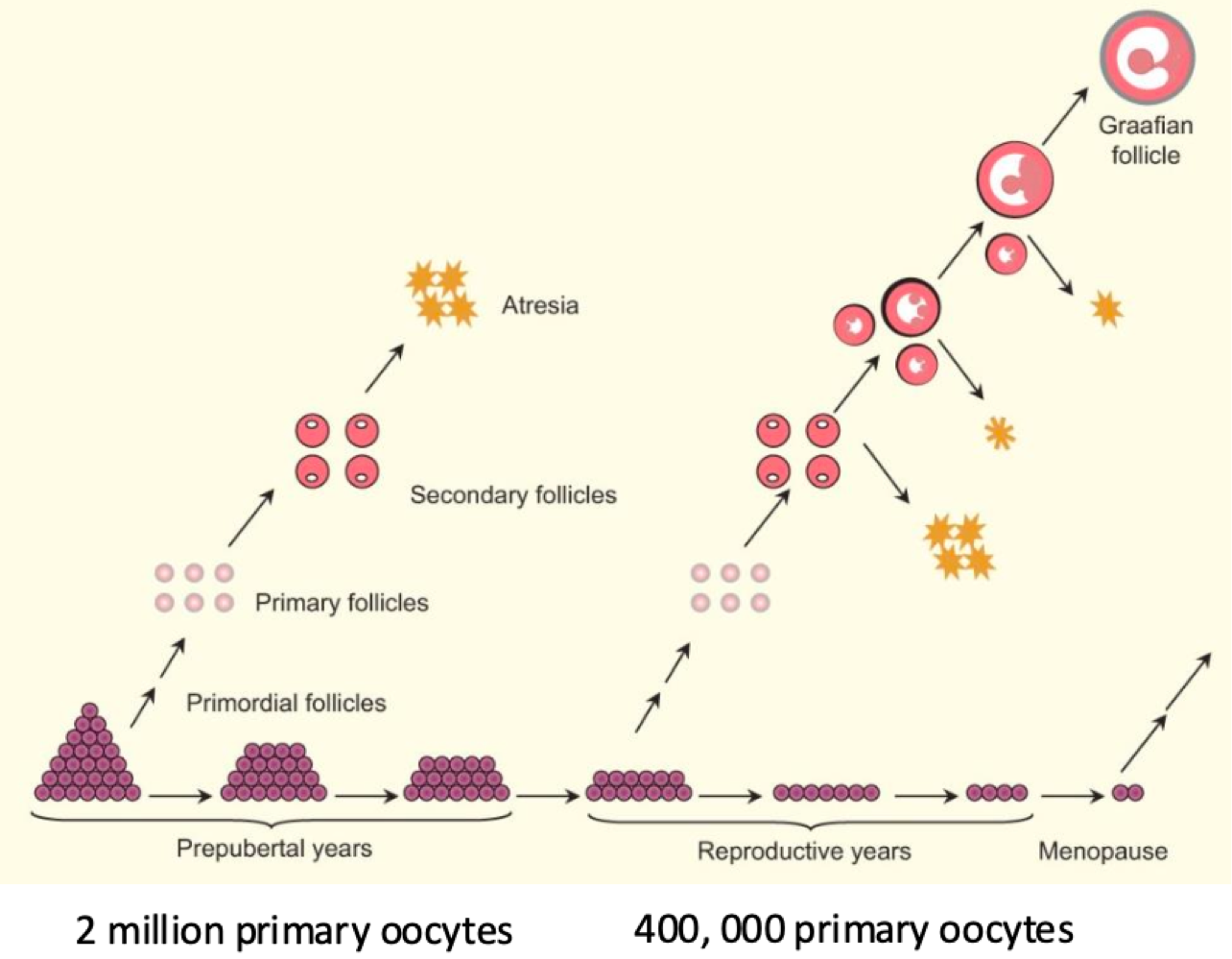
at birth, how many eggs does each ovary have?
2 million
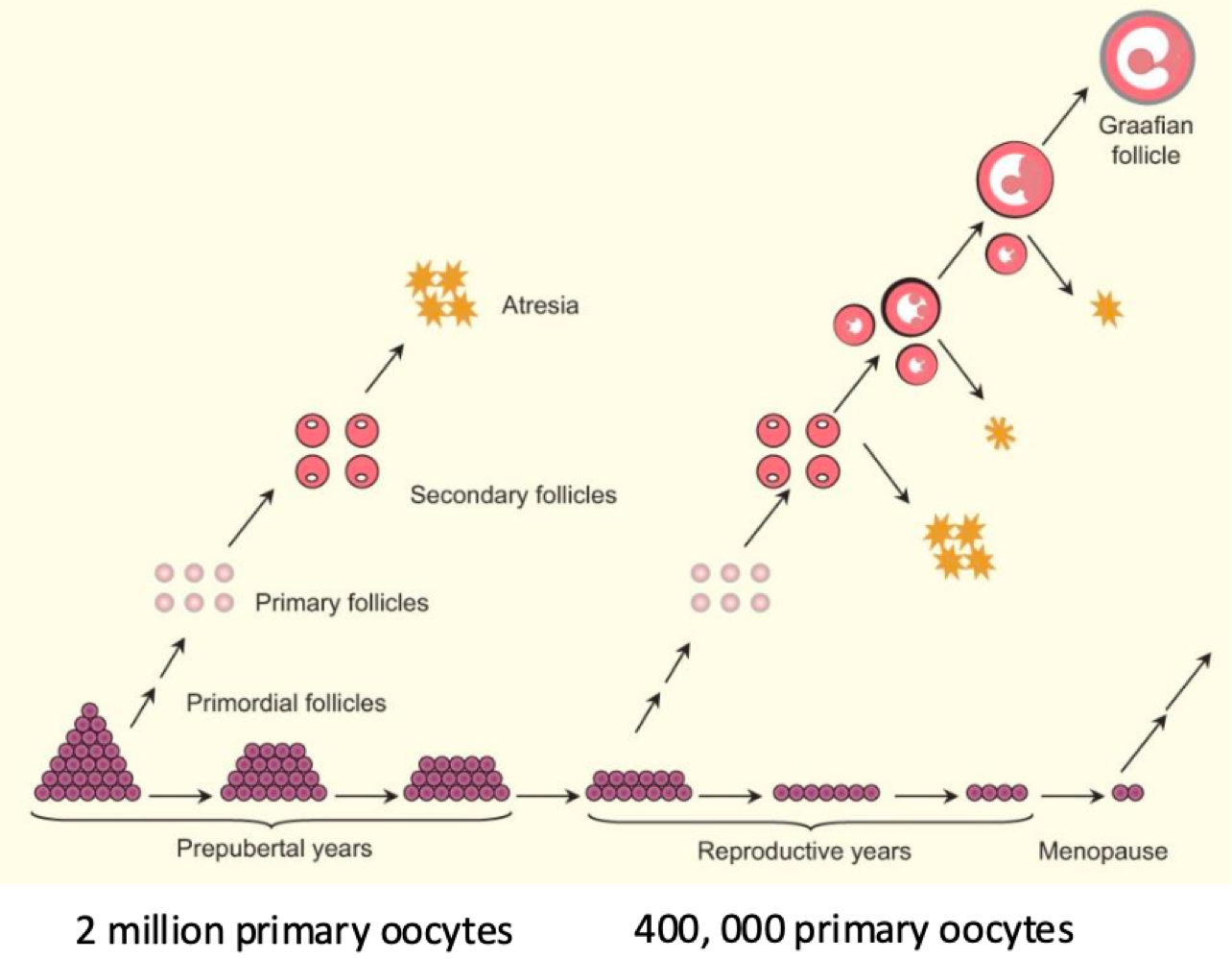
at puberty, how many eggs does each ovary have?
400,000
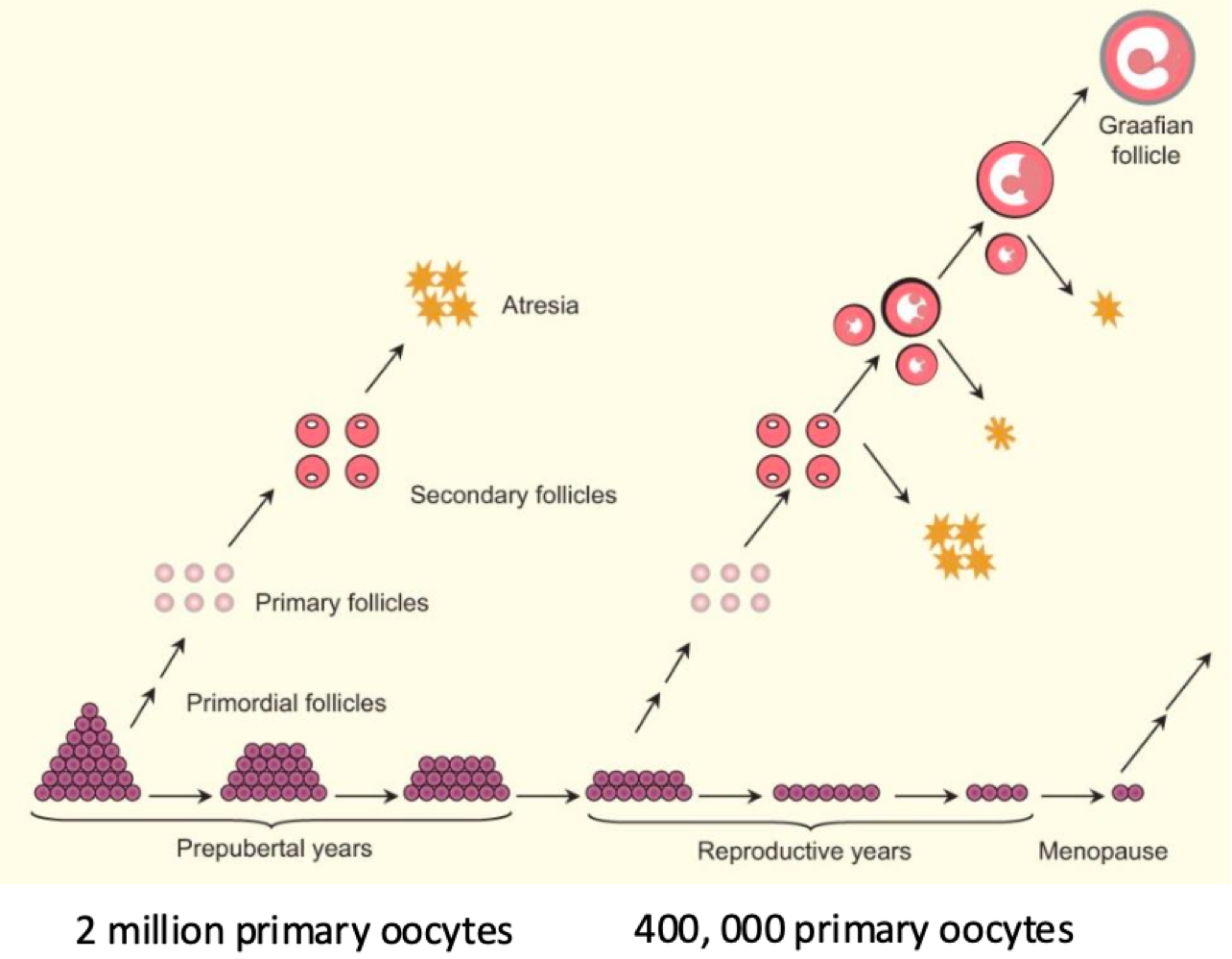
after puberty, one primary oocyte enters _______, and is released into the _______ monthly.
meiosis 2, oviduct
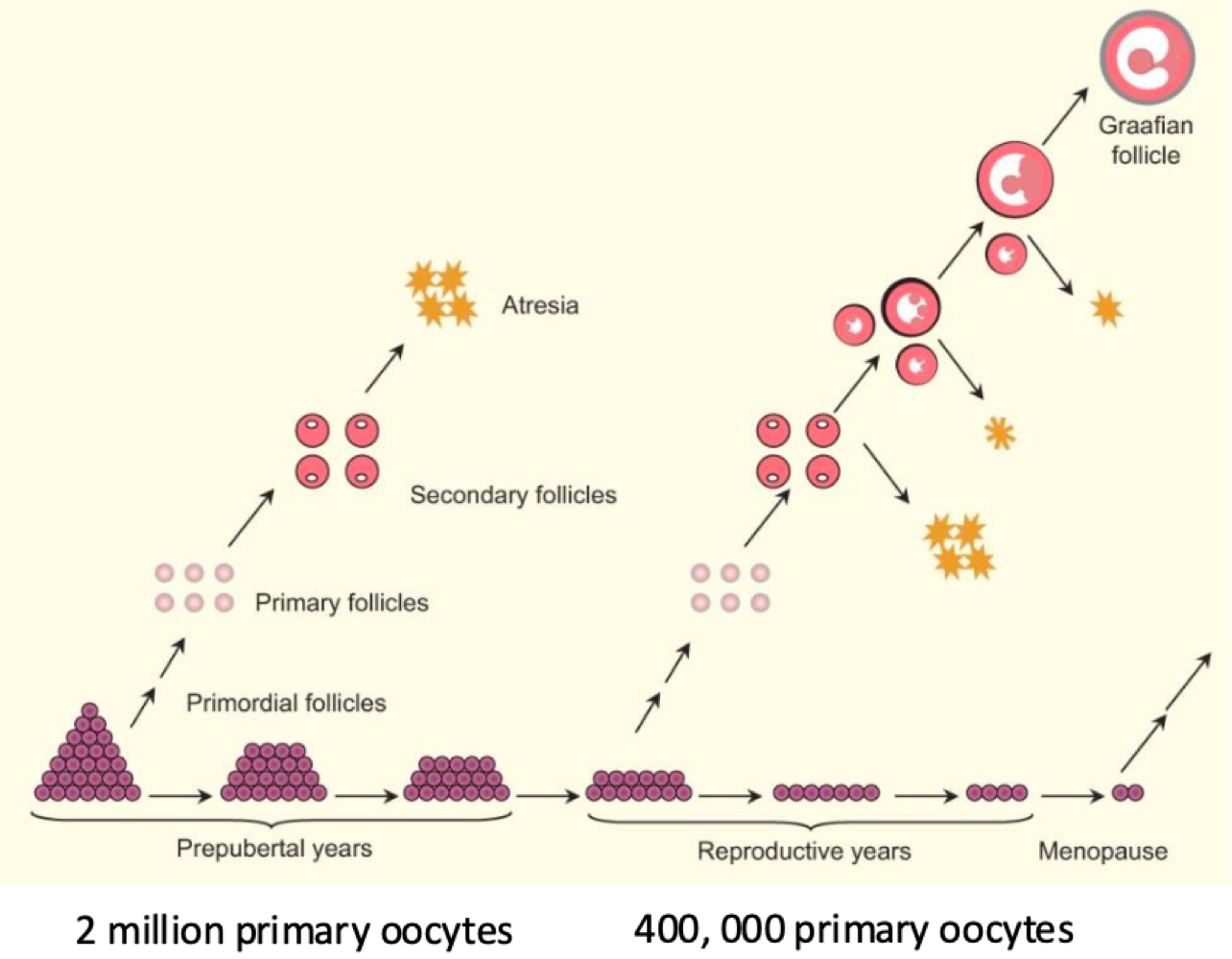
during _______, 300-400 oocytes are released during reproductive years, then the remaining die
menopause
the ovarian cycle conisists of what three phases/events?
follicular phase, ovulation, luteal phase
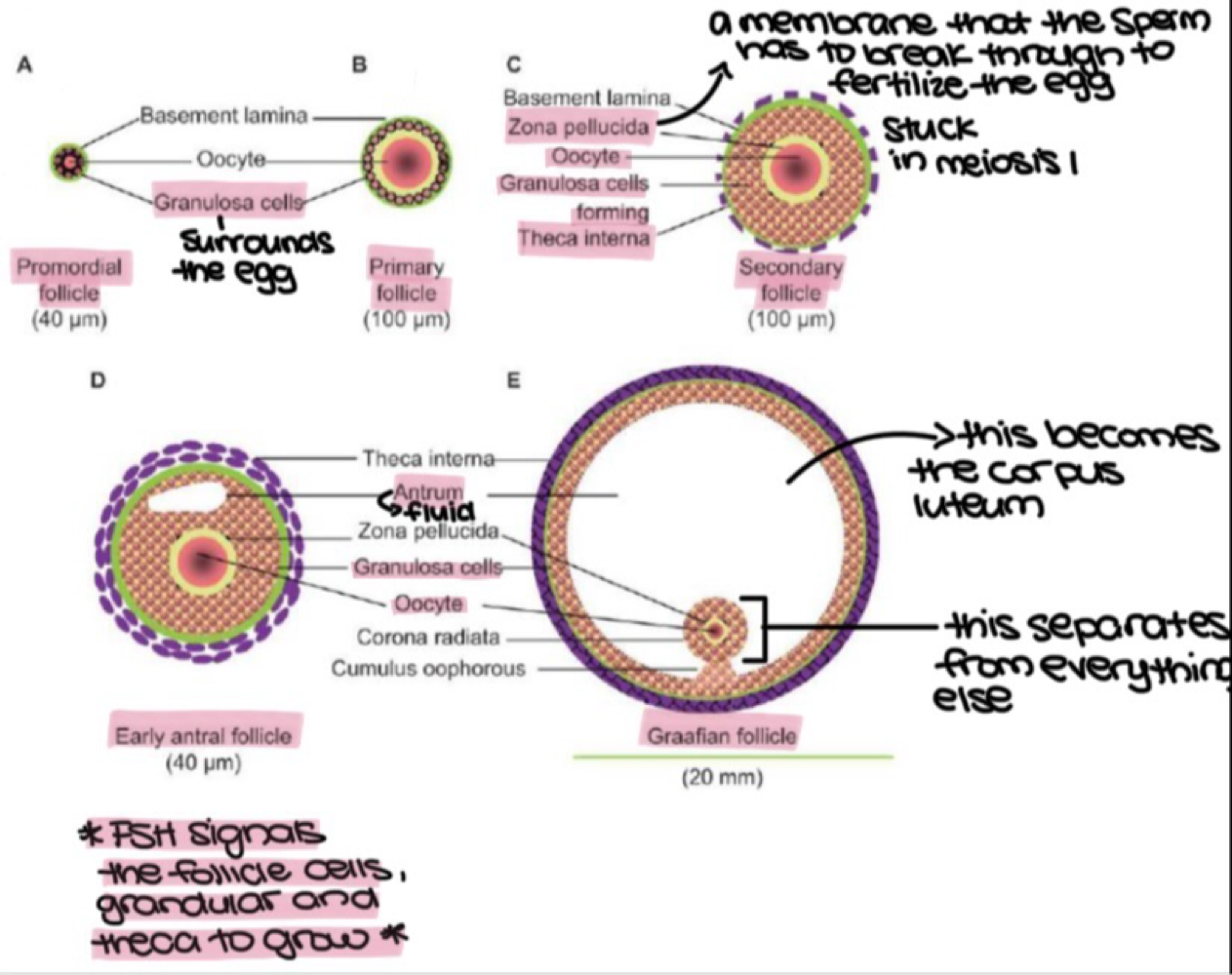
most primary follices are at rest. when a few start to grow:
the _______ forms (membrane surrounding th e oocyte that sperm breaks through for fertilization)
_______ grow and multiply in 120 days (surrounds the oocyte)
internal and external _______ forms
_______ filled with fluid forms
_______ grow in response to FSH, but only one survives to dominate
zona pellucida
granulosa cells
theca folliculi
antrum
antral follicles
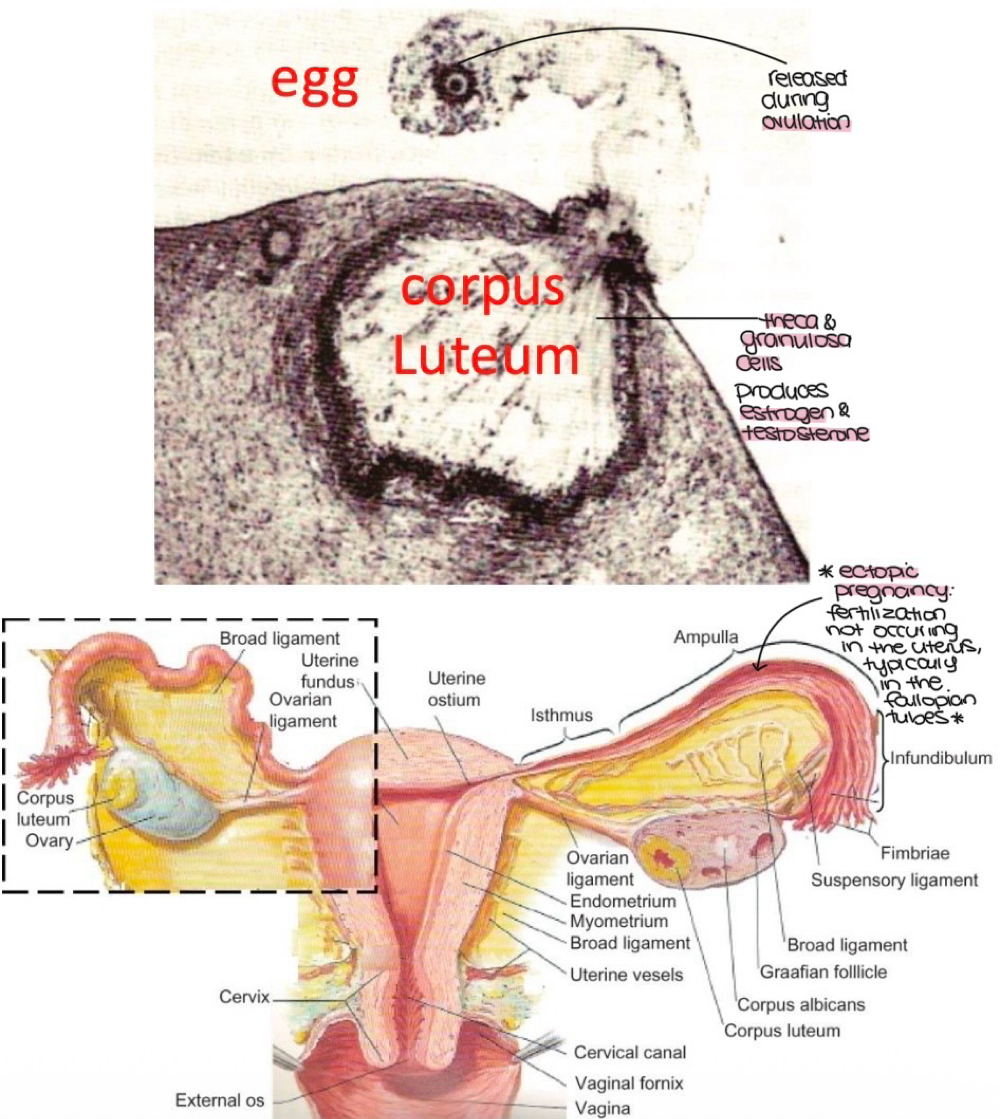
during _______, LH stimulates the release of an oocyte and fluid into the _______, into the oviduct for possible fertilization
ovulation, peritoneal cavity

during ovulation, the remaining Graafian follicle becomes the _______, which becomes the _______ if the oocyte isnt implanted
corpus lutem, corpus albicans
the Graafian follicle, which is dominant, inhibits other follicles via negative feedback during the _______, which prevents other follicles from growing because the developing follicle releases _______ and _______ to inhibit FSH and LH release
follicular phase, estradiol, inhibin B
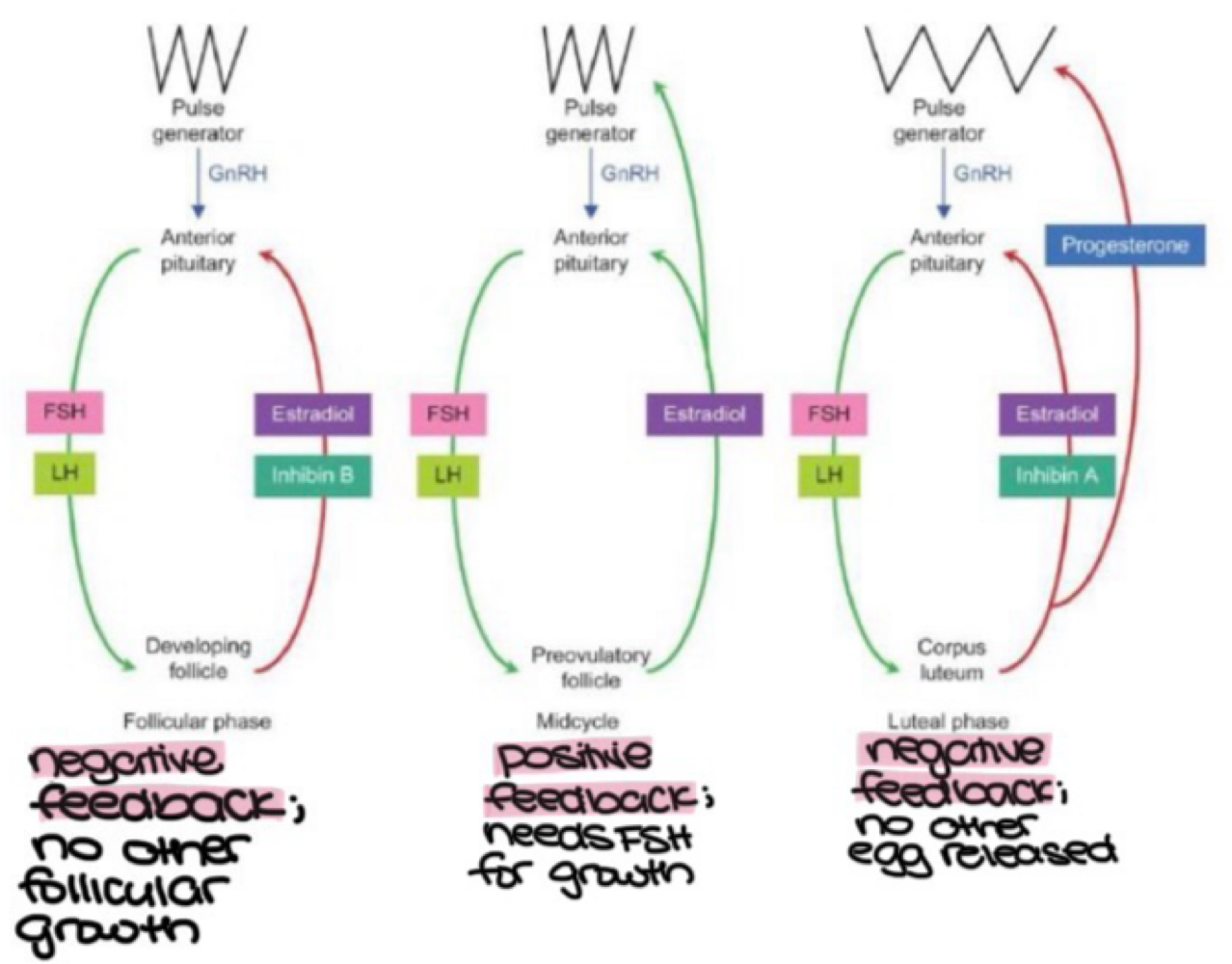
the Graafian follicle, which is dominant, inhibits other follicles via positive feedback during the midcycle, which increases FSH for follicle growth because the _______ releases estradiol to increase GnRH, FSH, and LH
preovulatory follicle
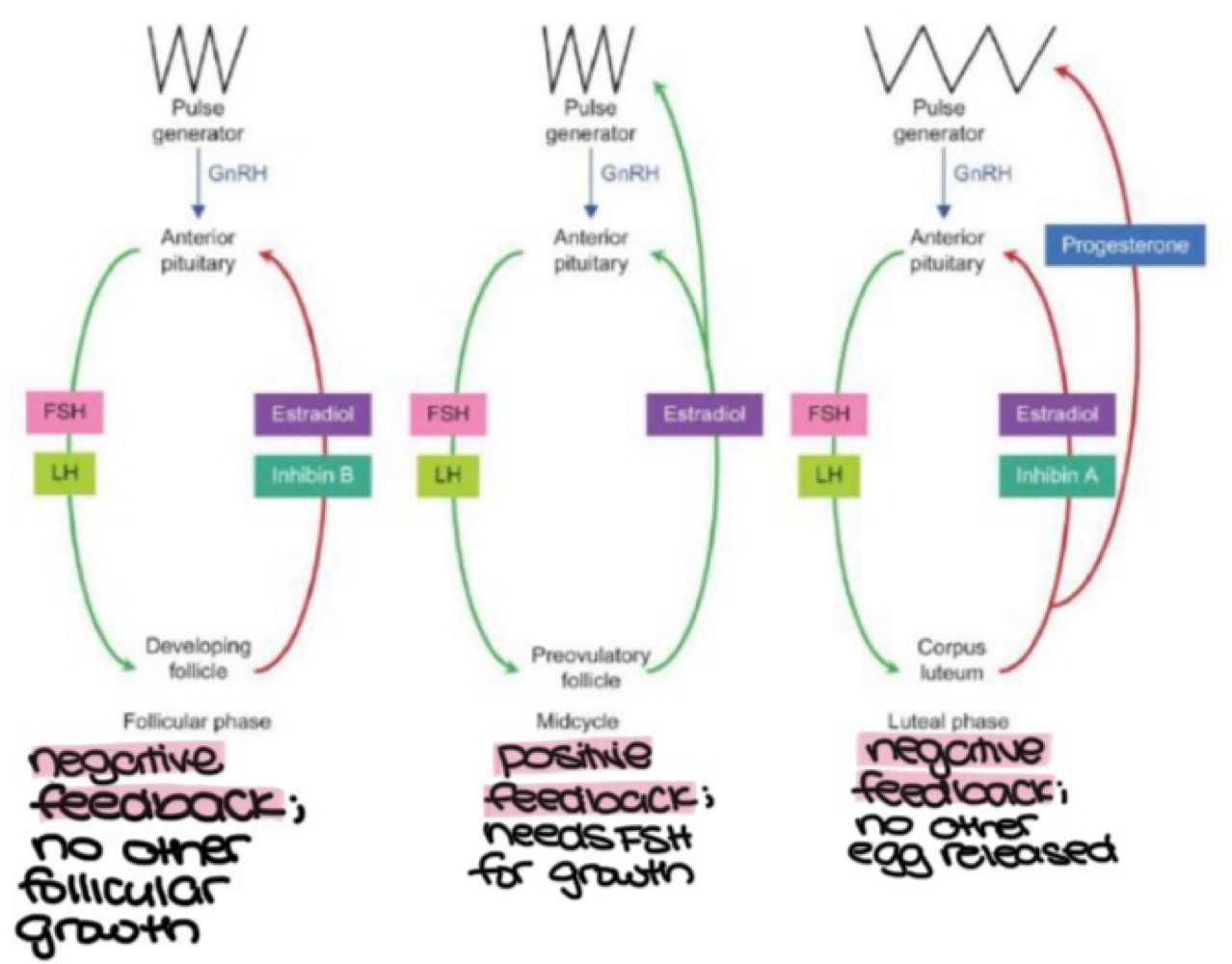
the Graafian follicle, which is dominant, inhibits other follicles via negative feedback during the _______, which prevents other eggs from being released because the corpus luteum releases _______ and _______ to inhibit FSH and LH release, and _______ to inhibit GnRN release
luteal phase, estradiol, inhibin A, progesterone
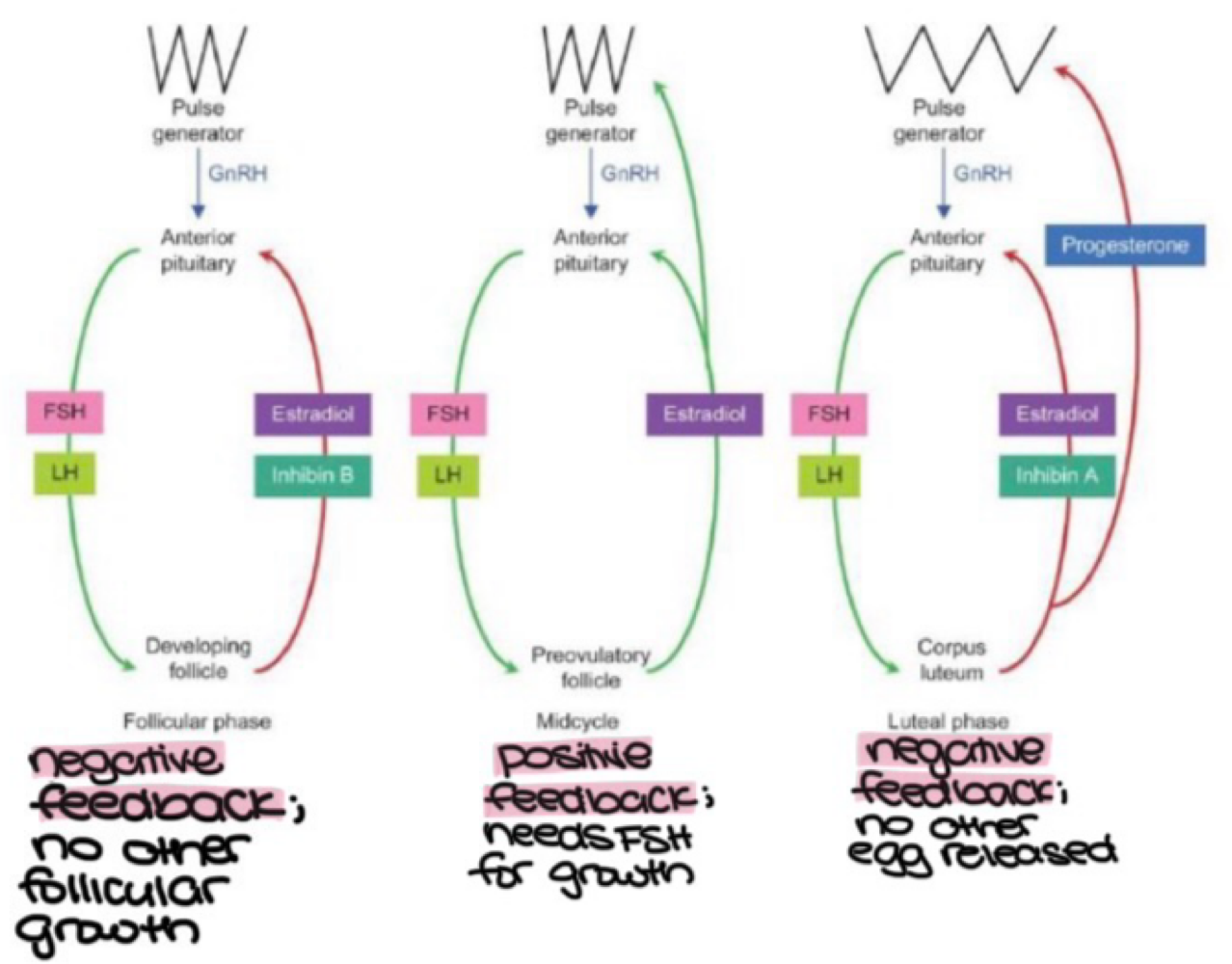
estradiol production involves the following steps:
LH binds to _______ on theca cells, stimulating _______ to activate P450c17
cholesterol enters _______ cells, and is converted into _______ via StAR, which moves into _______ cells, then is converted into _______ via p45017
androstendione moves across the _______, into granulosar cells to be converted into _______ via aromatase
G⍺s, CREB
granulosa, pregnenelone, theca, androstendione
basal lamina, estradiol
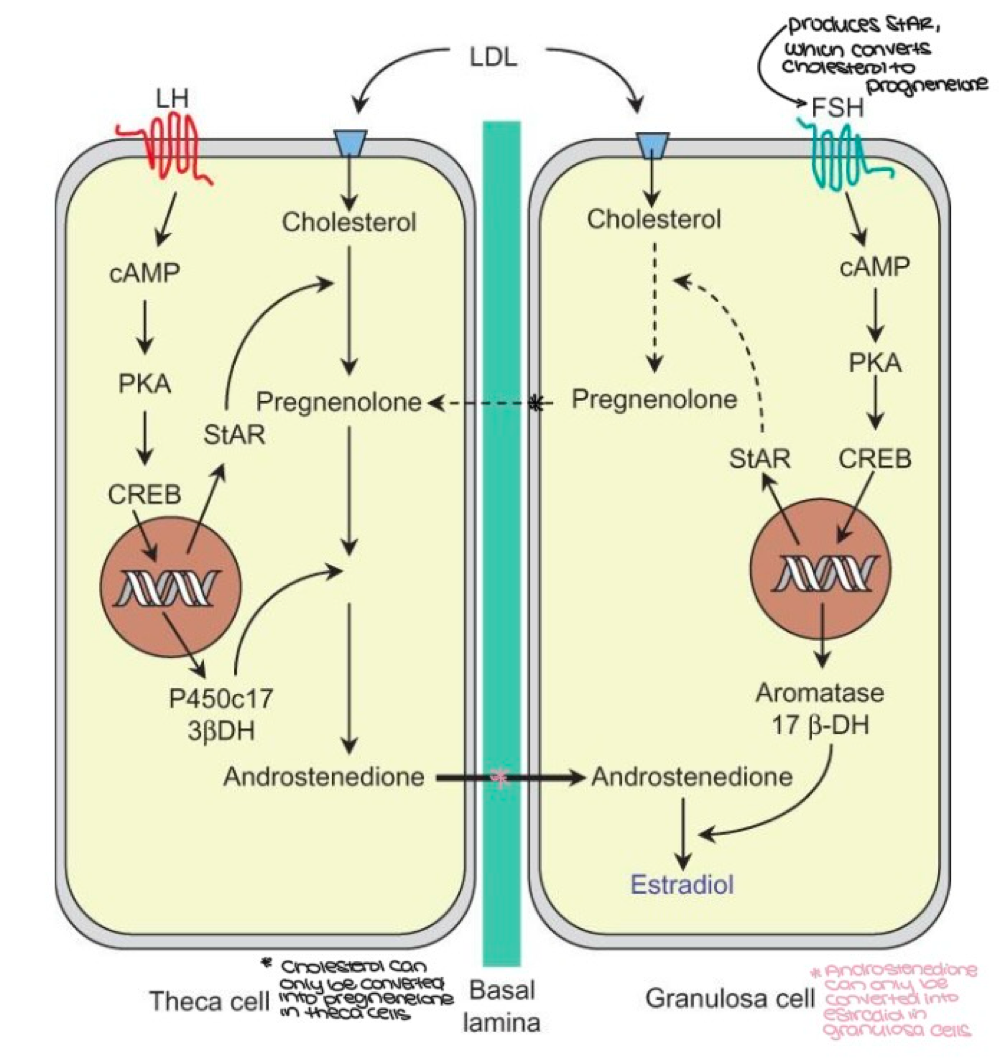
the uterine cycle conisists of what three phases/events?
menstruation, proliferation phase, secretory phase
during which ovarian cycle phase does the following occur? (early follicular, late follicular, ovulation, early luteal or late luteal):
FSH and LH increase
follicles grow from low FHS levels
estrogen is high
progesterone is low
the endometrium of the uterus sheds (menstruation)
early follicular
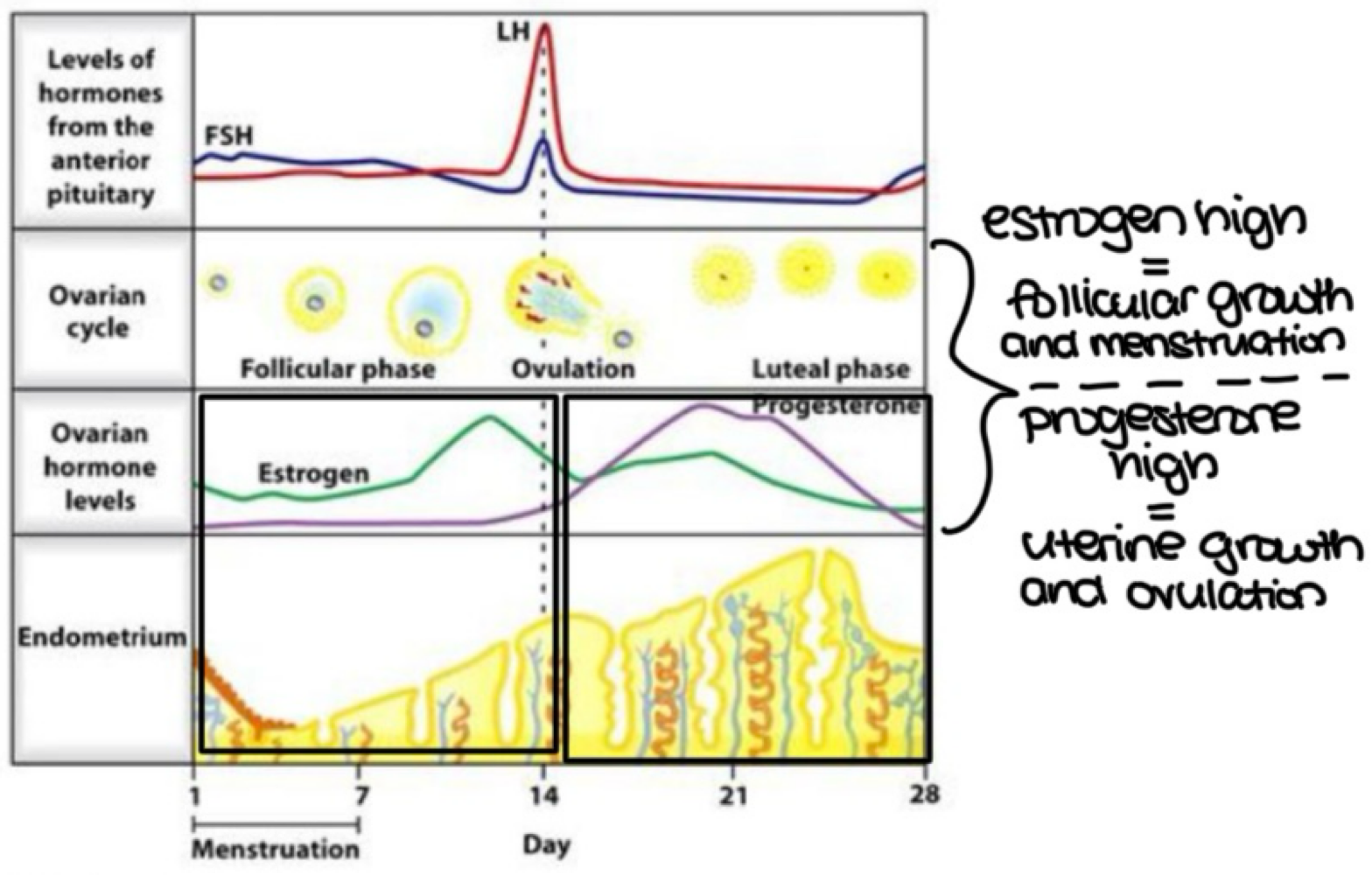
during which ovarian cycle phase does the following occur? (early follicular, late follicular, ovulation, early luteal or late luteal):
follicles grow and increase estrogen
LH and FSH increase
progesterone increases in response to LH
the endometrium layer grows in response to progesterone
late follicular
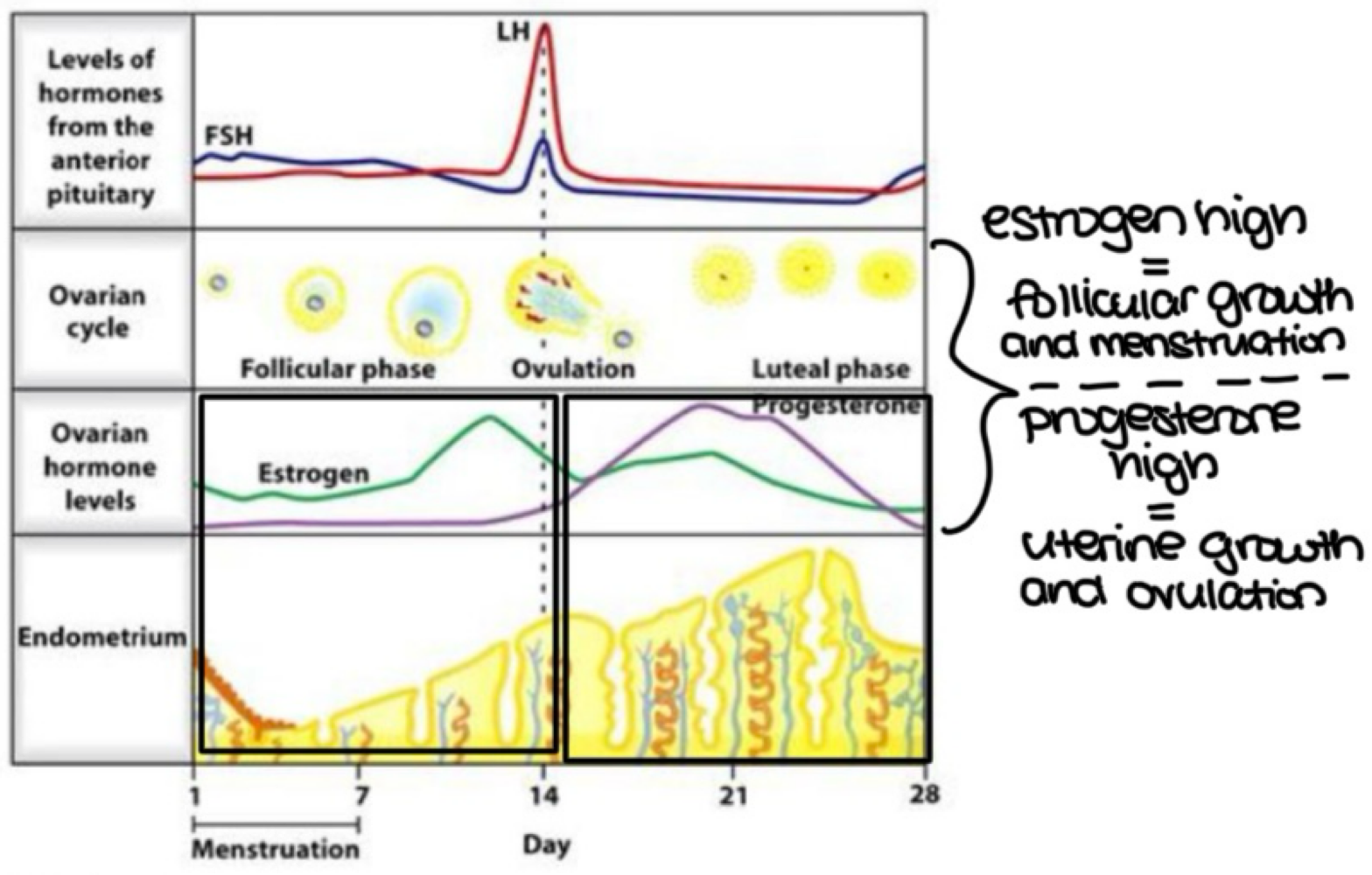
during which ovarian cycle phase does the following occur? (early follicular, late follicular, ovulation, early luteal or late luteal):
LH is at its highest
an egg is released form the corpus luteum
ovulation
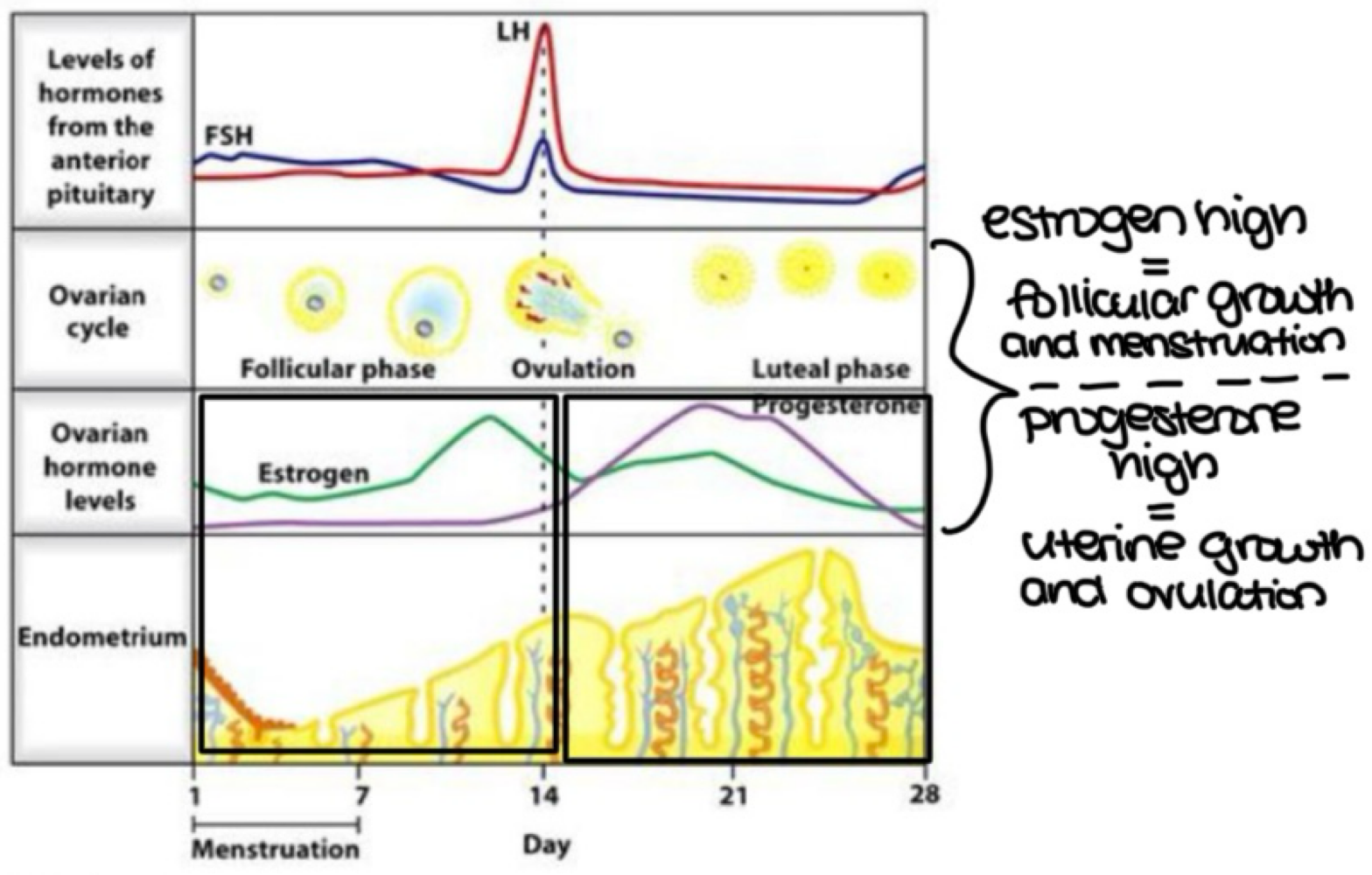
during which ovarian cycle phase does the following occur? (early follicular, late follicular, ovulation, early luteal or late luteal):
the corpus luteum forms and secretes estrogen and progesterone
FHS and LH decrease
the endometrium gland secretion increases
early luteal
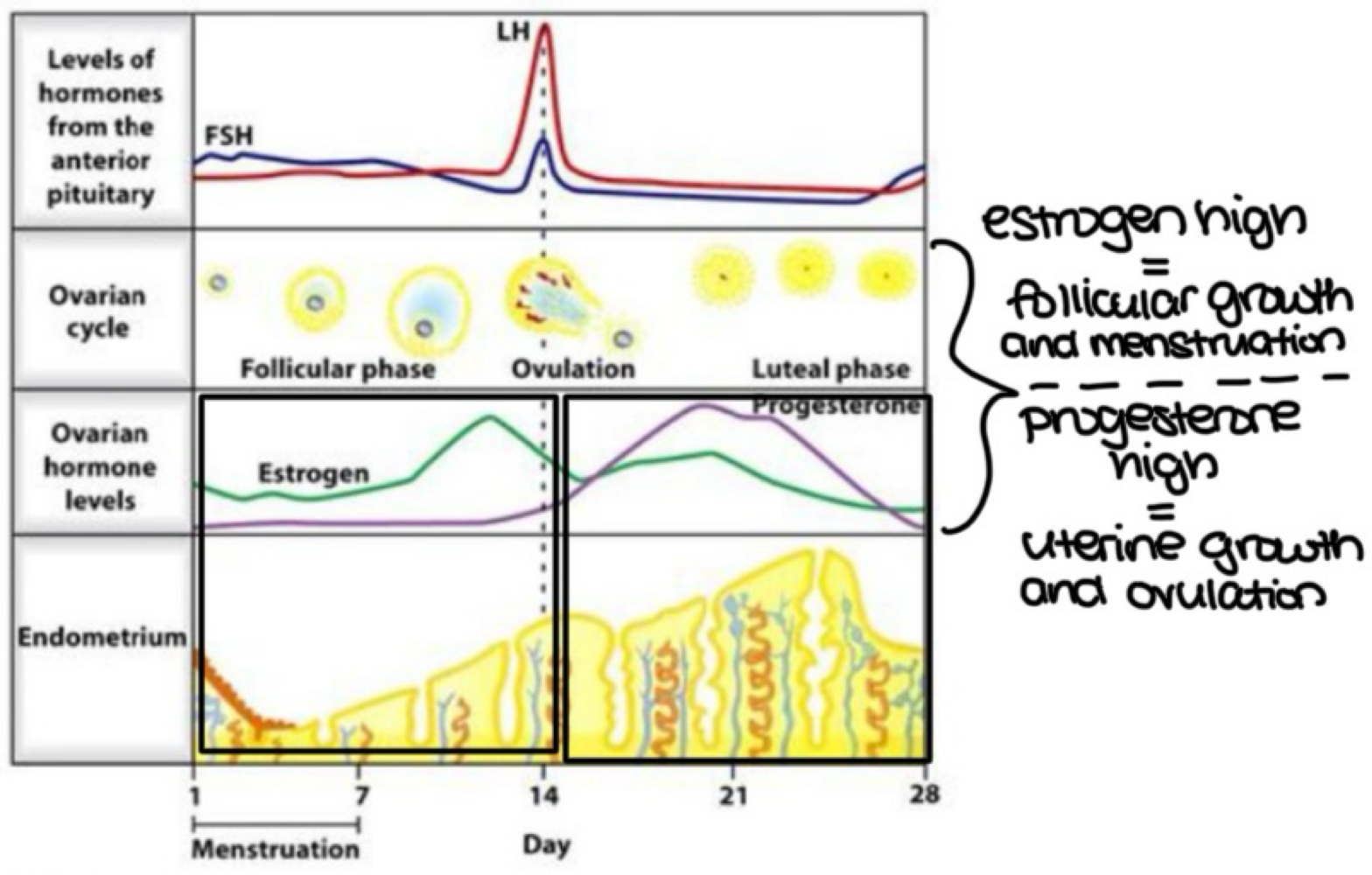
during which ovarian cycle phase does the following occur? (early follicular, late follicular, ovulation, early luteal or late luteal):
estrogen and progesterone drop if the corpus luteum degenerates
FSH and LH increase
late luteal
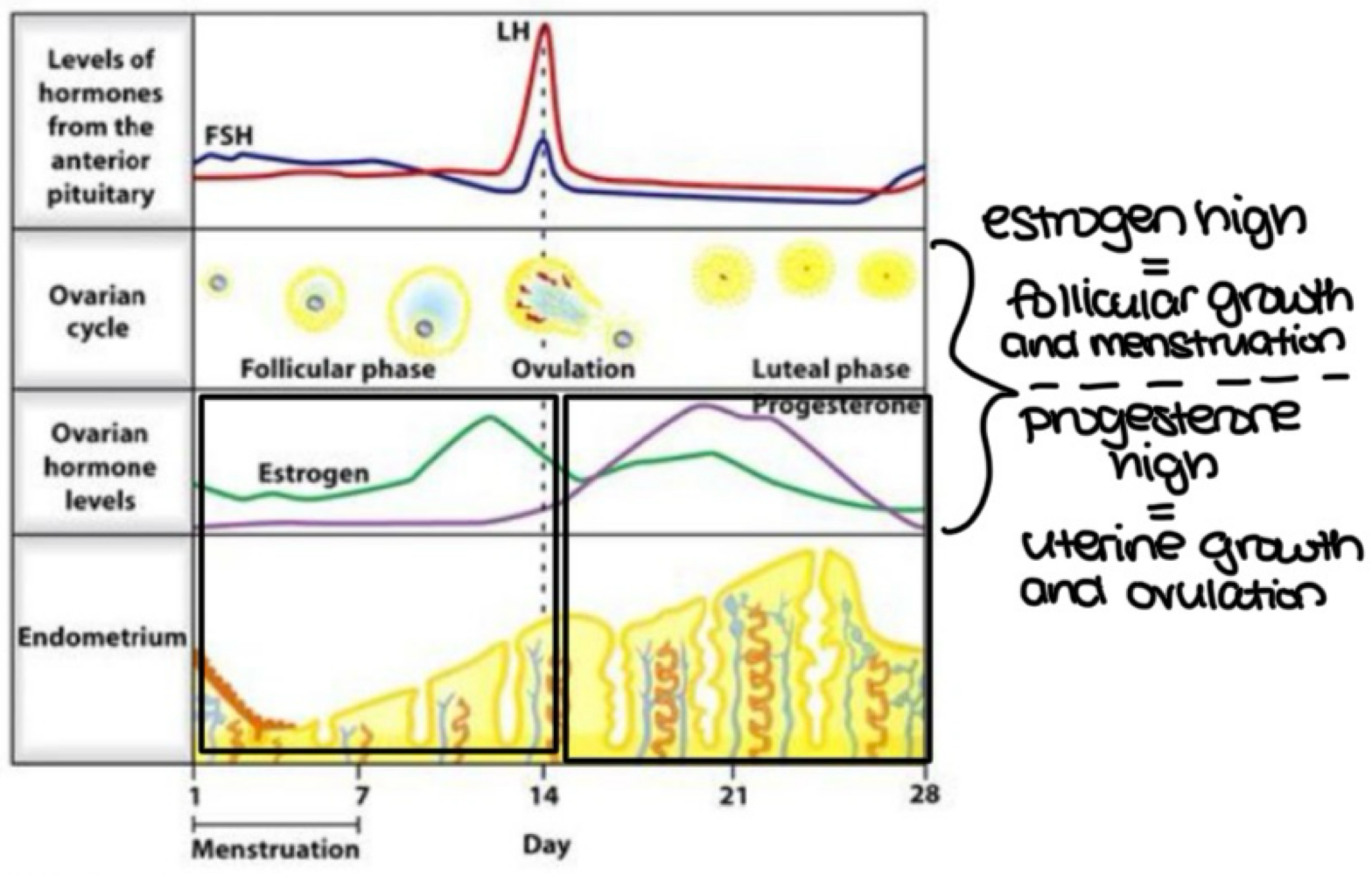
what are three distinct differences in hormone secretions between the sexes? (think about when gametes are present and for how long, and what kind of hormone feedback mechanisms are present)
only females gave gametes before puberty
females have both positive and negative feedback; men only have negative feedback
at some point, females stop producing eggs; males usually always produce sperm
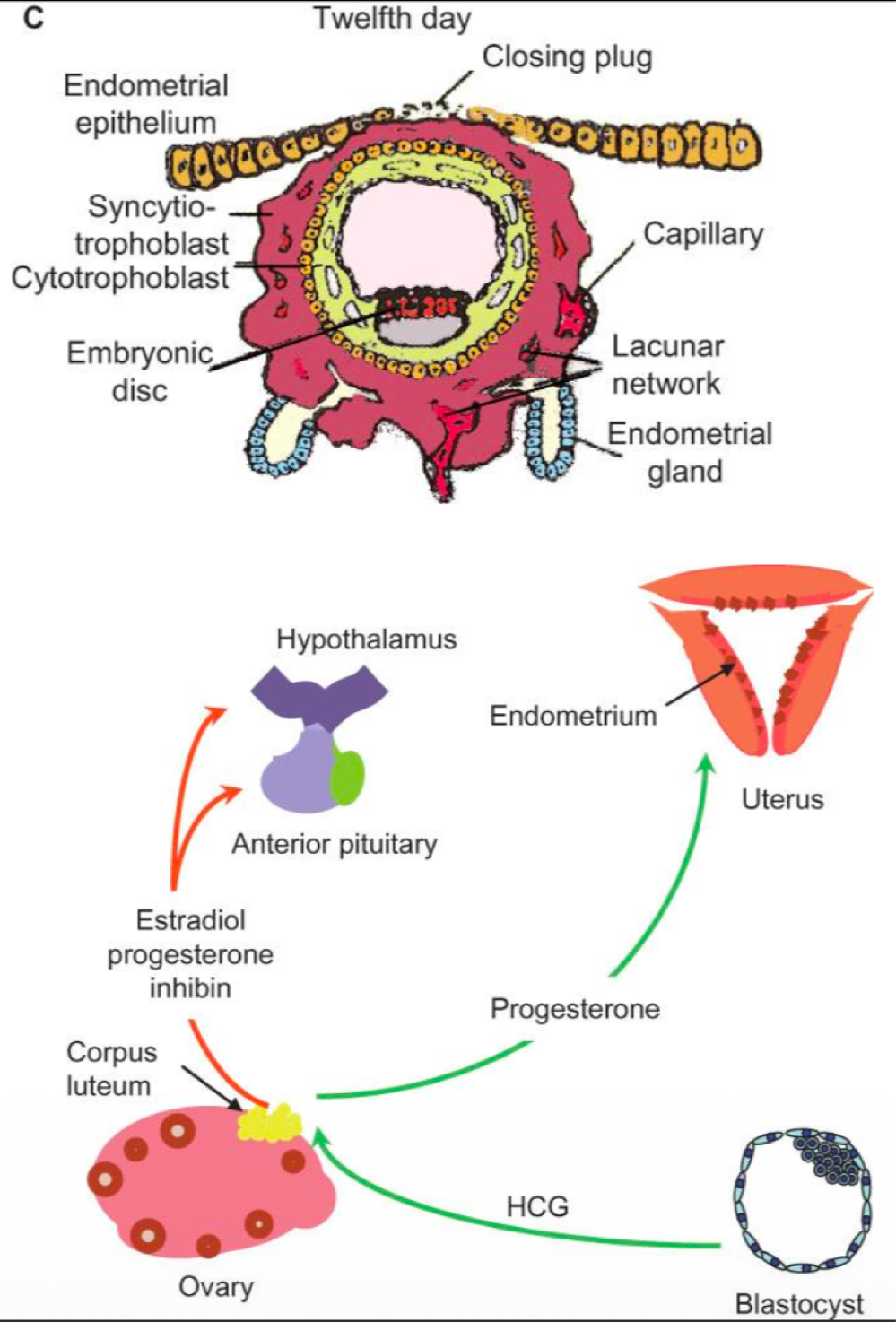
the placenta releases _______, which continues functions of the corpus luteum
human chorionic gonadotropin hormone (hCG)