bio99 midterm 3
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
which of the following DNA/RNA
RNA uses Uracil as one of its bases, DNA uses Thymine
RNA has a hydroxyl group on it’s 2’ carbon, DNA does not
RNA has a hydroxyl group on it’s 3’ carbon, DNA does not
DNA has a phosphate group on it’s 5’ carbon, RNA does not 8
RNA uses Uracil as one of its bases, DNA uses Thymine
RNA has a hydroxyl group on it’s 2’ carbon, DNA does not
Where is the beginning of this transcript?
5’
What end is the polymerase progressing towards?
3’
What is the last base to be transcribed?
3’
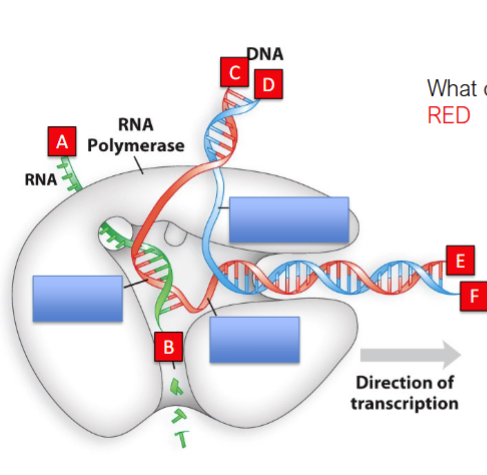
Which letter corresponds to
1) 5’ end of transcript?
2) 5’ end of coding strand?
3) 5’ end of template strand?
a
d
e
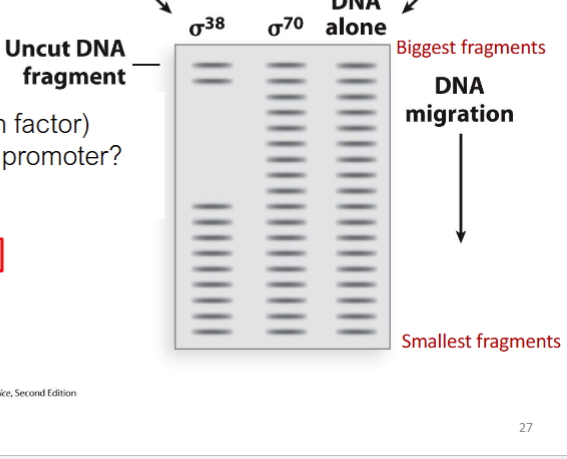
Which σ factor (txn factor)
binds to the osmY promoter?
A. Neither
B. σ38
C. σ70
D. Both
B
What are correct terms for the three steps of bacterial transcription
A. Initiation, extension, cessation
B. Initiation, elongation, termination
C. Binding, primer addition, extension
D. Binding, extension, cessation
B. Initiation, elongation, termination
What does the nucleophilic attacking?
A. Mg2+
B. Asp
C. The α-phosphate of the incoming NTP
D. The 3’OH of the attached NTP
D. The 3’OH of the attached NTP
Which have occured when transcription initiation completes?
A. Sigma factor no longer blocks the exit channel
B. The polymerase clears the promoter
C. 10 nucleotides are added to the transcript, stabilizing it
D. Sigma factor detaches from the RNA polymerase
E. All of the above
E. All of the above
What does the pin region of the RNA polymerase do?
A. Melts the DNA
B. Kicks out the sigma factor from the exit channel
C. Stabilizes the open state of the DNA
D. Helps the two strands to reform
C. Stabilizes the open state of the DNA
Which type of proofreading is essentially the reverse of the polymerase
reaction?
A. Kinetic Proofreading
B. Nucleolytic Proofreading
A. Kinetic Proofreading
What sequence is NOT essential for rho-independent
transcription termination?
A. The termination sequence
B. The AAA sequence
C. The rut sequence
C. The rut sequence
Which transcription factor is used by all three Pol promoters?
A. TFIID
B. UBF
C. TBP
D. TFIIIB
C. TBP
What feature of Pol I promoters makes it similar to Bacterial promoters?
A. UCE and core promoter basic structure
B. SL1
C. UBF
D. TBP
A. UCE and core promoter basic structure
What is a similarity between Pol II and Pol III promoters?
A. Both use TFIID
B. Both use TFIIIB
C. Both have transcription factors bind to regions downstream of
the start site
D. Both use BRE
C. Both have transcription factors bind to regions downstream of the start site
In which of the following steps of transcription is the C-terminal domain
of RNA polymerase II first phosphorylated?
A. assembly of the preinitiation complex
B. initiation
C. elongation
D. termination complex formation
E. after termination
B. initiation
Which of the following is NOT true about the role of Mediator complex
in transcription initiation?
A. Mediator binds to RNA polymerase II.
B. Mediator binds to specific DNA sequences.
C. Mediator binds to general transcription factors.
D. Mediator binds to transcription activators.
E. Mediator increases the rate of the assembly of the preinitiation
complex.
B. Mediator binds to specific DNA sequences.
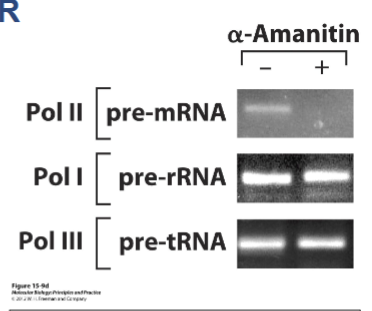
α-How do you interpret this data?
A. α-amanitin is needed for pre-rRNA and tRNA synthesis
B. Pol I and Pol III synthesis is a more rapid process than Pol II
C. α-amanitin blocks Pol II transcription, but not Pol I or Pol III
D. Pol II cannot make DNA in the presence of α-amanitin
E. More than 1 of the above is true
C. α-amanitin blocks Pol II transcription, but not Pol I or Pol III
A. Northern Blot
B. qRT-PCR
C. RNA Sequencing
D. 2 of the above
E. All of the above
1) Quantifying gene expression changes of a specific target gene
between a wild-type sample and a mutant sample
2) Quantifying gene expression changes of a specific target gene
between a wild-type sample and a mutant sample if you have very
little RNA to work with, and a small budget
3) Looking for global changes in gene expression between a wild-type
sample and a mutant sample
4) Estimating the length of an RNA transcript for a specific gene
E
B
C
A
Which is NOT true about 5’ capping?
A. The cap is generated by guanylyltransferase
B. The cap is a GTP added backwards to the 5’ phosphate of the first
rNTP
C. The cap is methylated at the 7 position
D. A protein called CBC binds to the cap, tethering it to the CTD
E. All are true
E. All are true
The poly(A) tail protects the RNA from what?
A. Evil spirits
A. Evil spirits
B. 3’ – 5’ nucleasesS
C. 5’ – 3’ nucleases
D. Xrn nuclease
A. Evil spirits
B. 3’ – 5’ nucleasesS
The nucleophile of the first step of spliceosome-mediated pre-mRNA
splicing is the:
A. 2’ OH of the branch point adenosine.
B. 3’ OH of a free guanine nucleotide.
C. 3’ OH of the 5' splice site exon.
D. 2’ OH of the 3' splice site intron.
A. 2’ OH of the branch point adenosine.
Which part of the intron involved in the last step of splicing?
A. 5’ splice site
B. 3’ splice site
C. Branch point
nt
B. 3’ splice site
Which process occurs last?
A. Capping
B. Polyadenylation
C. Splicing
B. Polyadenylation
The transport receptor, exportin, transports:
A. mRNA to the nucleus when associated with GDP-bound Ran
protein.
B. noncoding RNA to the cytoplasm when associated with GTP-
bound Ran protein.
C. noncoding RNA to the nucleus when associated with GDP-bound
Ran protein.
D. mRNA to the cytoplasm when associated with GDP-bound Ran
protein.
B. noncoding RNA to the cytoplasm when associated with GTP-
bound Ran protein.
Which proteins are bound at the exon-exon borders and facilitate
transport of the spliced mRNA from the nucleus to the cytoplasm?
A. exportins
B. importins
C. EJC proteins
D. Ran-GTP complex
E. U1
C. EJC proteins