3.5 Cellular Respiration
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Cellular Respiration
cells harvest chemical energy stored in organic molecules and use it to generate ATP
organic molecules + oxygen → CO2 + H2O + energy
starch is the major source of fuel for animals and breaks down into glucose
catabolic breakdown of glucose:
C6H12O6+6O2→6CO2+6H2O+energy(ATP and heat)
the oxidation of glucose transfers electrons to a lower energy state, releasing energy to be used in ATP synthesis
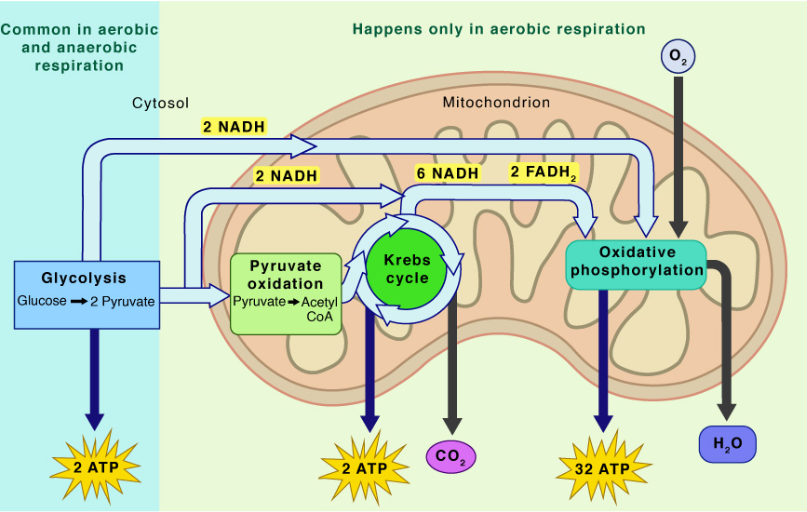
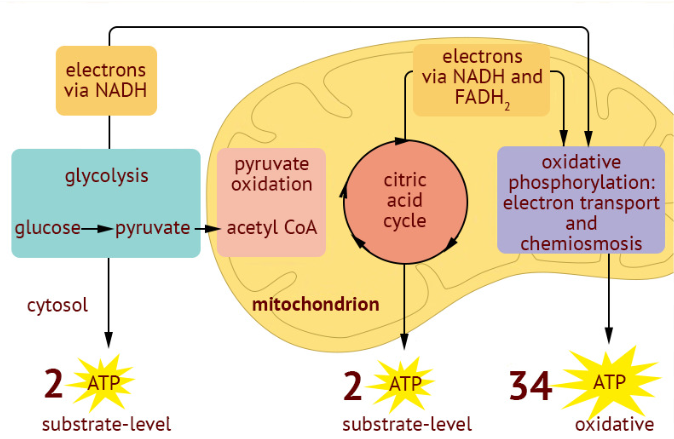
4 stages: Glycolysis, Pyruvate oxidation, Citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle), and oxidative phosphorylation (ETC and chemiosmosis)
total ATP produced: about 30-32 ATP
Glycolysis
starting point of cellular respiration
occurs in the cytosol
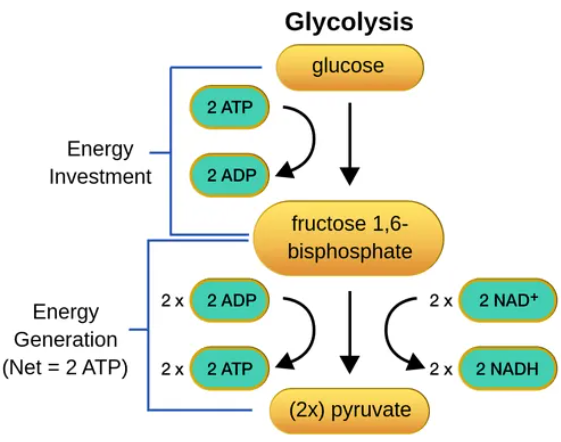
splits glucose (6C) into 2 pyruvates (3C)
2 stages:
energy investment stage- the cell uses ATP to phosphorylate compounds of glucose
energy payoff stage- energy is produced by substrate level phosphorylation
starting materials: glucose, ATP, NAD+, ADP + Pi
end products: pyruvate, 2 ATP, NADH
2 ATP and 2 NADH are produced per 1 glucose
ATP and NADH later used in the ETC
2 pyruvate used in the Citric acid cycle
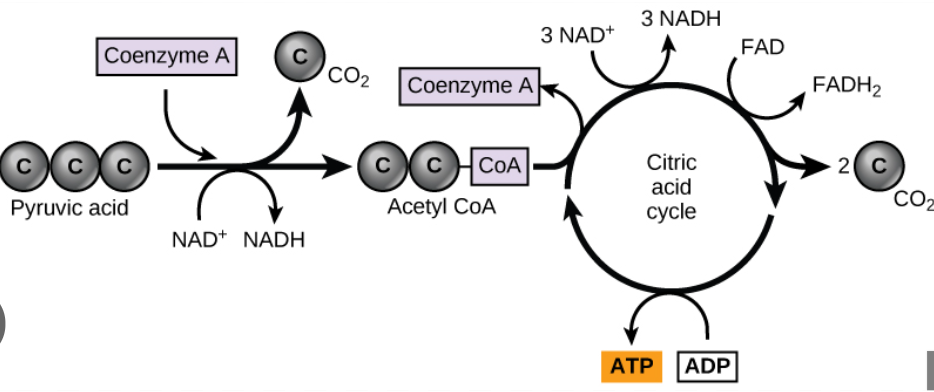
Pyruvate Oxidation
if oxygen is present, the pyruvate enters a mitochondrion (eukaryotic cells)
pyruvate is oxidized into acetyl coA
acetyl coA is used to make citrate in the citric acid cycle
CO2 is released as waste
electrons are transferred to carriers (NADH)
starting materials: pyruvate, coenzyme A, NAD+
end products: acetyl CoA, CO2, NADH
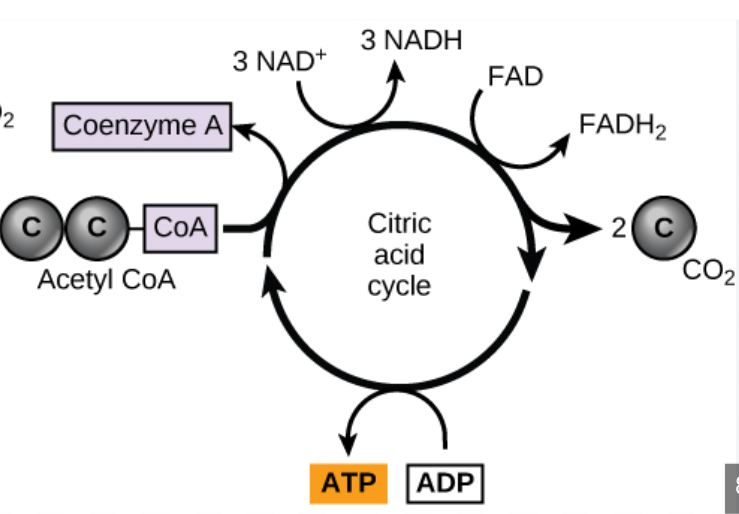
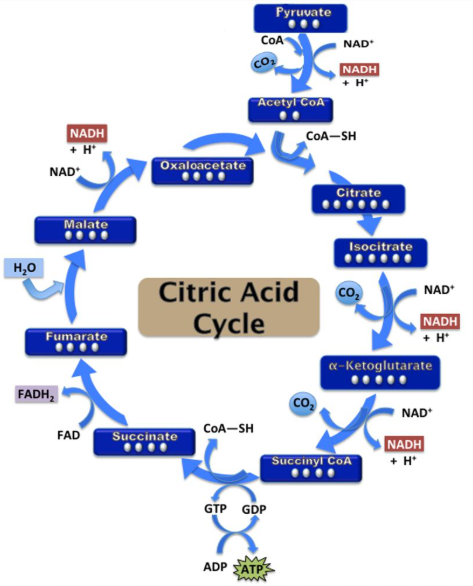
Citric Acid (Krebs) Cycle
occurs in the mitochondrial matrix
turns acetyl CoA into citrate, which:
releases CO2
ATP synthesized
electrons are transferred by NAD+ and FAD
NADH and FADH2 will then carry high energy electrons to the ETC
starting materials: acetyl CoA, NAD+, FAD, ADP + Pi
end products: CO2, NADH, FADH2, 2 ATP
2 ATP produced
Oxidative Phosphorylation
consists of electron transport chain (ETC) and chemiosmosis
starting materials: NADH, FADH2, O2, ADP + Pi
end products: NAD+, FAD, H2O, 26-28 ATP
26-28 ATP produced
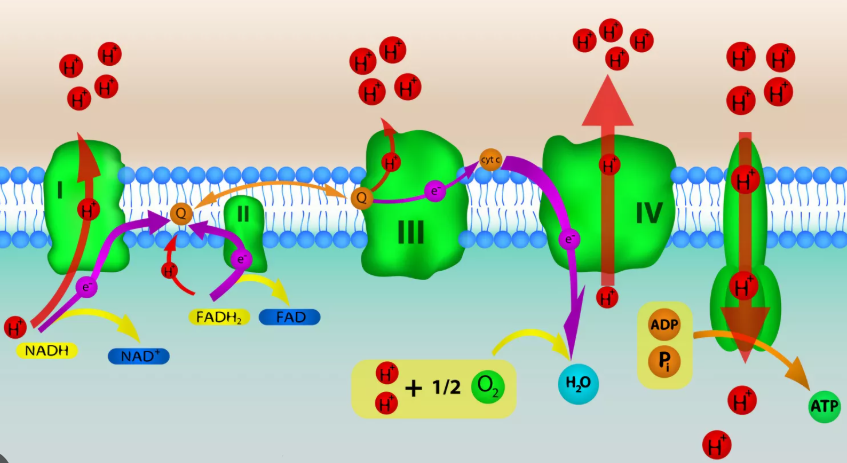
Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
located in the inner membrane of the mitochondria
consists of a collection of electron carriers (proteins) embedded in the membrane
NADH and FADH2 (from the Krebs cycle) bring electrons to the ETC
electrons go down the ETC in a series of redox reactions until they reach the final electron acceptor, oxygen(very important to the process, because if oxygen did not accept the electrons and drive electrons down the ETC, the chain backs up which stops the flow of electrons and prevents the production of large amounts of ATP)
as electrons move through the ETC, they move from a higher to lower energy level
some of the released energy is used to pump H+ into the intermembrane space, forming an electrochemical gradient of protons (H+)
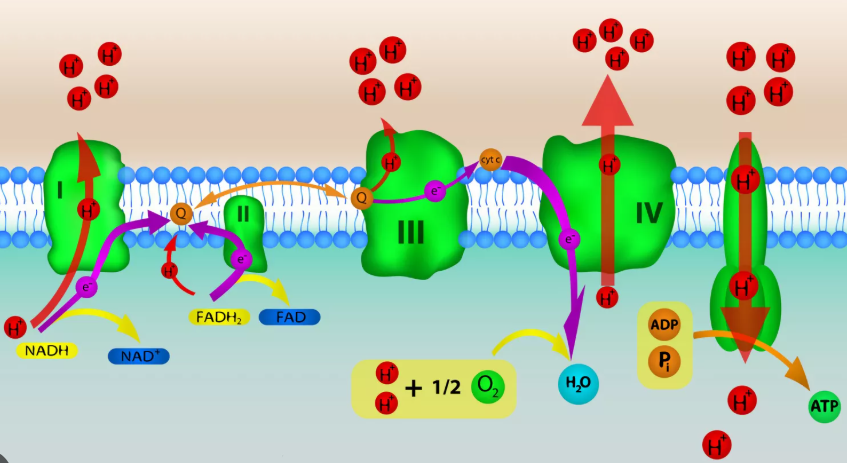
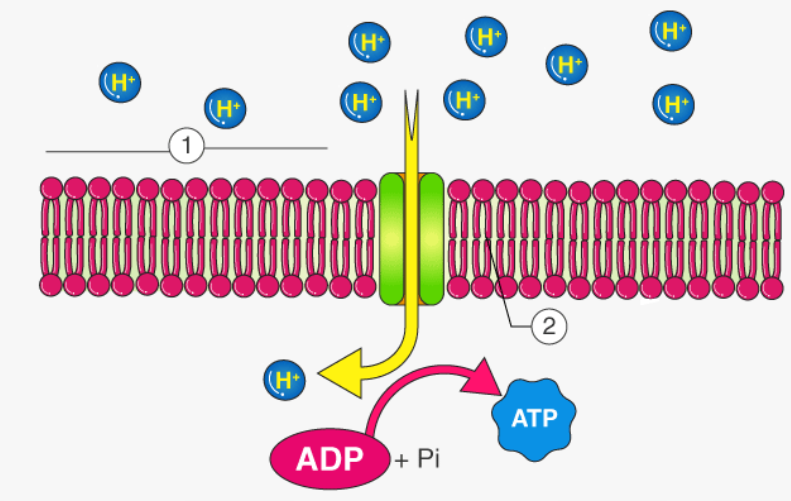
Chemiosmosis
H+ ions flow down their gradient(established due to ETC) back into the matrix through ATP synthase
drives the formation of ATP from ADP + Pi
the cristae increase the surface area for reactions to occur, which allows more ATP to be synthesized
produces about 26-28 ATP per glucose
Anaerobic Respiration
generates ATP using an ETC in the absence of oxygen
takes place in prokaryotic organisms that live in environments with no oxygen
final electron acceptors are sulfates or nitrates
Fermentation
generates ATP without an ETC
extension of glycolysis
recycles NAD+
occurs in the cytosol
NO oxygen
2 types: alcohol fermentation and lactic acid fermentation
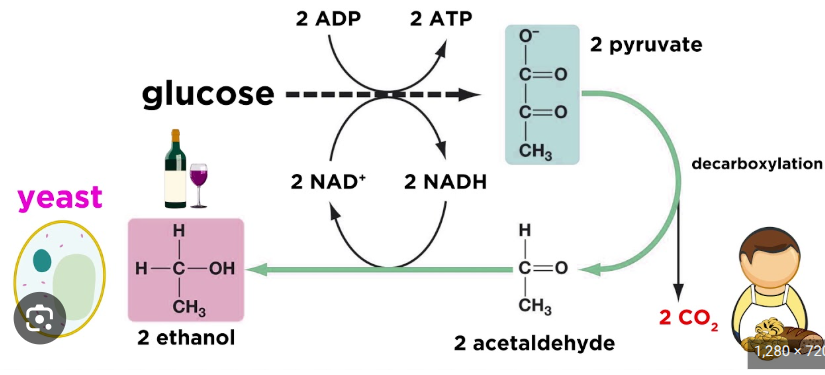
Alcohol Fermentation
pyruvate is converted into ethanol
2 pyruvate→2 acetaldehyde→2 ethanol
ex. bacteria and yeast
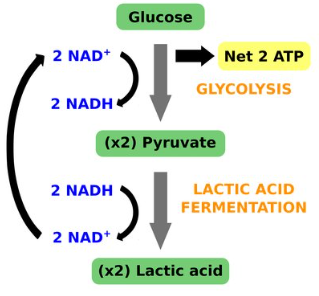
Lactic Acid Fermentation
pyruvate is reduced directly by NADH to form lactate
ex. muscle cells
when muscles run out of oxygen, they can go through lactic acid fermentation to produce ATP
causes the burning sensation you may feel when performing strenuous exercise
breakdown of lactate:
muscles produce lactate, which goes into the blood, and is broken down back to glucose in the liver
when lactate is in the blood, it lowers the pH
if lactate builds up and is unable to be broken down it can lead to lactic acidosis(excess
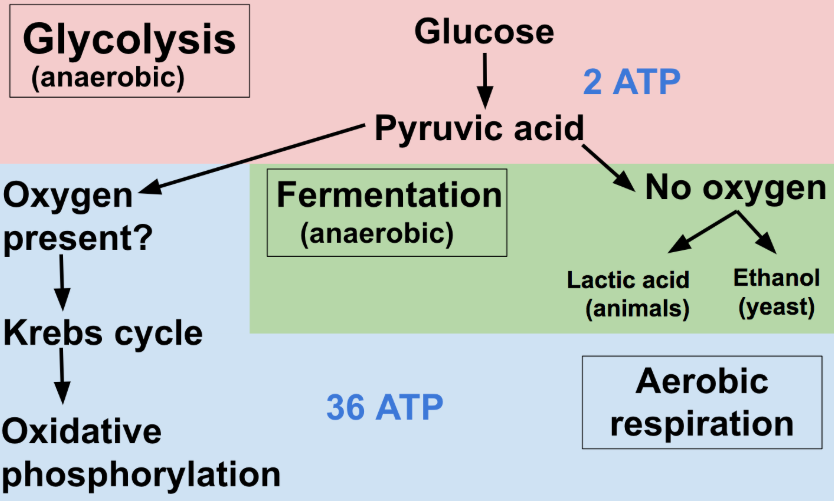
After glycolysis with and without oxygen
With oxygen: typical cellular respiration (glycolysis→pyruvate oxidation→krebs cycle→oxidative phosphorylation)
Without oxygen: Fermentation(anaerobic), Lactic acid fermentation in animals, alcohol fermentation in yeast(glycolysis→lactic acid/alcohol fermentation)