BUSINESS STUDIES PRELIM
1/377
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
378 Terms
Business
An organisation that produces/sells goods and/or services in order to make a profit.
Functions of a business (WIPES ICE Q)
Wealth, Income, Profit, Employment, Goods and services, Innovation, Choice, Entrepreneurship and Risk, Quality of Life
Wealth
Successful business creates wealth for all stakeholders. Increase GDP
Income
Amount of money a person receives for their labor (wage/salary).
Profit
Sales revenue - expenses
Employment
Businesses need employees to run their business --> generate production, revenue
Dividend
A distribution of a company's profits (either yearly or half-yearly) to shareholders that is calculated as a number of cents per share.
Services (& goods)
Things done for you and items that can be seen or touched.
Innovation
Development of new products or improvement to existing products.
Research and Development (R&D)
The creation of new products, services or processes, or the improvement of existing ones
Choice
The act of selecting among alternatives.
Entrepreneurship and Risk
People who transform their ideas into a business, prepared to take the risk of starting and operating a business in an untapped market.
Quality of Life
Overall well-being of an individual, combination of non/material benefits.
Classification of business
Size, geographic spread, industry sector and legal structure
Qualitative business size
Management, advertising, market control
Quantitative business size
Number of employees and owners
Small business characteristics
5-19, sole trader, partnership, owner savings or loan, small local market share
Medium business characteristics
20-199, private company, partnership, owner savings/loan or shareholders, medium market dominance
Large business characteristics
200+, public company, retained profit, share sales, loans, large market dominance
Local geographical spread characteristics
Small to medium in size, restricted, used by local consumers
Local geographical spread example
Newsagent, Corner store, Hairdresser
National geographical spread characteristics
Medium to large in size, operates in one country
National geographical spread example
Cotton On
Global geographical spread characteristics
Business expands internationally, multinational corporation
Global geographical spread example
Mcdonalds, Apple
Industry sector
Businesses involved in similar types of production
Primary industry (60% of exports)
Businesses involved in the collection of natural and raw materials
Primary industry example
Mining, fishing, farming
Secondary industry
Secondary industry example
Iron ore, coal turned into steel - used to produce cars
Tertiary industry
Involves people performing a vast range of services for others
Tertiary industry example
Retailers, dentists, soliciters, banks, health workers
Quaternary industry
Services that involve the processing of information and knowledge
Quaternary industry example
Finance, computing, education
Quinary industry
Services traditionally performed in the home
Quinary industry example
Childcare, hospitality, tourism
Legal structure
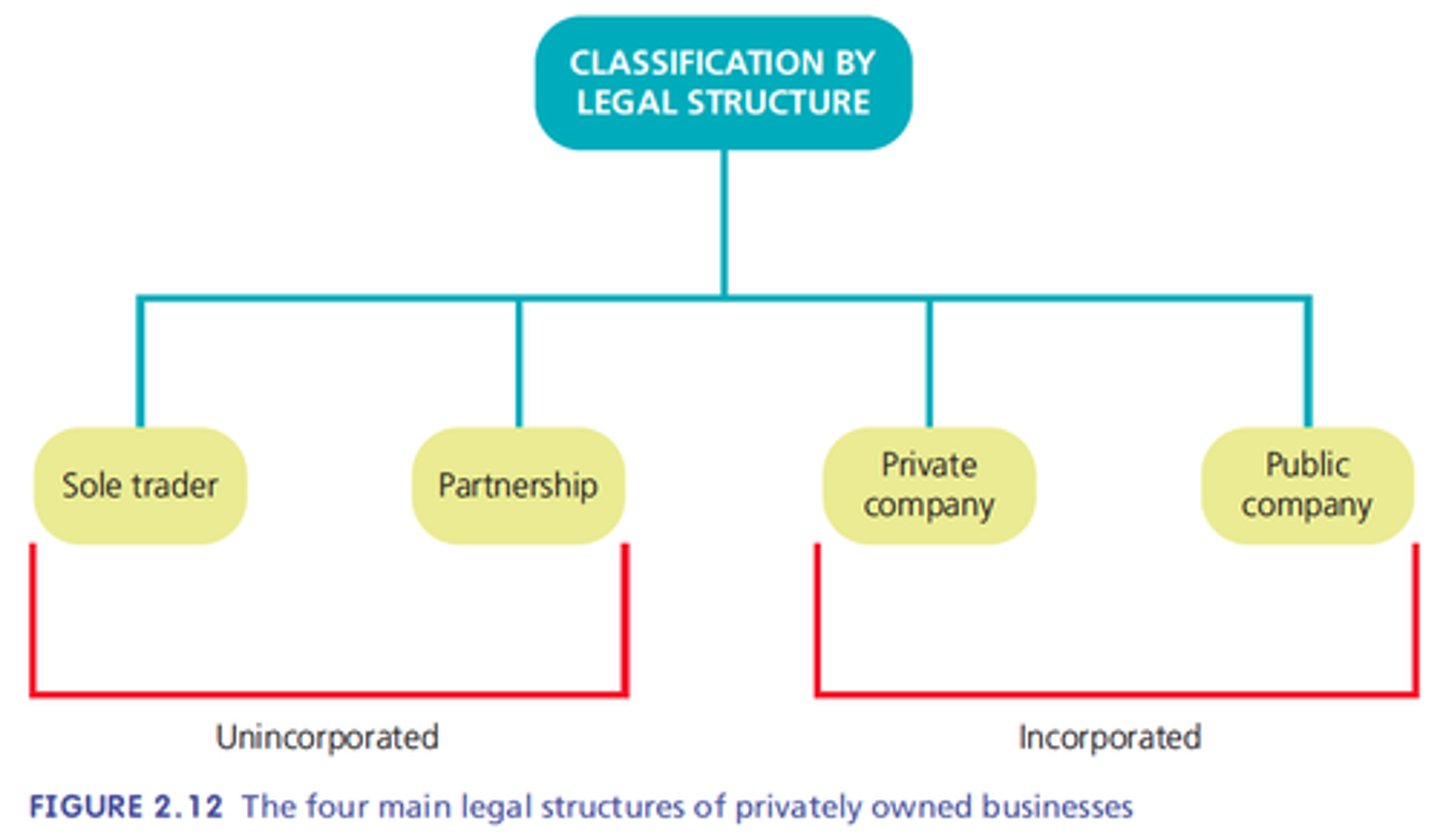
Unincorporated
Not separate legal entity from owners
Sole trader, Partnership
Unlimited liability
Incorporated
Business separate entity from owners
Public, private company
Limited liability
Limited Liability
Only liable for the amount invested in the business.
Unlimited Liability
Owner is personally responsible for all the business's debt
Sole trader
- Unincorporated
- unlimited liability
- sued personally
- income tax
Sole trader advantages
- low operation costs
- no disputes
- keep profits
- less government regulations
Sole trader disadvantages
- unlimited liability
- business ends when owner dies
- burden of management
- difficulty in raising finance for expansion
Partnership
- unincorporated
- unlimited liability
- 2-20 owners
Partnership advantages
- low start up costs
- less costly than company
- shared workload
- minimal gov regulations
Partnership disadvantages
- liability for all debts including partners
- possibility of disputes
- divided loyalty
Companies
- Incorporated
- Limited liability
- Seperate legal entities
- Perpetual succession
- Are regulated by ASIC (Australian Securities and Investment Commission) and the Corporations Act 2001
Private company
- Pty ltd (proprietary limited)
- private shareholders
- company tax
- ASIC regulations
Public company
- Ltd (limited)
- 1 + public shareholders
- listed on ASX (Australian Securities Exchange) → attract customers through a prospectus
Government Business Enterprise (GBE)
The government or public sector have created businesses which act in the interests of the community e.g Australia Post
Privatisation
The process of transferring the ownership of a government business to the private sector
Public vs private sector
Public- government enterprises e.g sydney water
Private - owned by private individuals (shareholders)
Factors influencing choice of legal structure
Size, ownership, and finance influence the selection of a legal structure.
Size (influencing choice of legal structure)
Growing business may want to choose a smaller legal structure to gain finance, skills and expertise
Ownership (influencing choice of legal structure)
Owner may not want to share ownership
Finance (influencing choice of legal structure)
Gaining investors from switching legal structures could help success of the business
Business environment
Refers to the surrounding conditions in which the business operates (external and internal)
External influences - business has very little control (MC PIGS LEFT)
Markets, Competitive situation, Political, Institutional, Geographic, Social, Legal, Economic, Financial, Technological
Markets external influence
Include labor market, financial market, and consumer markets.
Labour market
Flow of capital/workers between countries
Financial market
Heavily impacted by interest rates
Consumer markets
People buying products
Monopoly
No competitors e.g Sydney Water
Oligopoly
Small number of large firms that dominate the market e.g banks, Woolworths
Monopolistic competition
Large number of buyers and sellers sold by differentiating e.g cafes
Perfect competition
Large number of small businesses selling same product competing through price e.g fruit and veg growers
Competitive situation external influence
Influenced by market concentration, types of markets include monopoly, oligopoly, monopolistic competition, and perfect competition.
Political external influence
Government policies impacting upon the business environment
e.g tax, environmental regulations, social reforms e.g paid parental leave
Institutional external influence
Regulating bodies (e.g ACCC), government (State), and other entities (Trade Unions) that impact businesses.
Geographic external influence
- Australia's location within Asia-Pacific region
- Changes in demography = changes in product demand
Globalisation
Allowance of global trade, increase of wider competition due to exporting opportunities
Social external influence
Rapid identification and response to changes in tastes, fashions, and culture can lead to sales and profit opportunities and business growth.
Legal external influence
Regulations and legal framework within which a business must operate
ACCC (Australian Competition and Consumer Commission)
Operates nationally for the enforcement and administration of competition and consumer protection laws
The Competition and Consumer Act 2010
Administered by the ACCC
→ a breach can result in the ACCC taking criminal proceedings against the business
Economic external influence
Fluctuations in economy due to varied levels of consumer spending
Economy is strong = consumer confidence
Government policies to influence economy
Monetary and fiscal policy
Business/economic cycle
Change in consumer and business spending over time
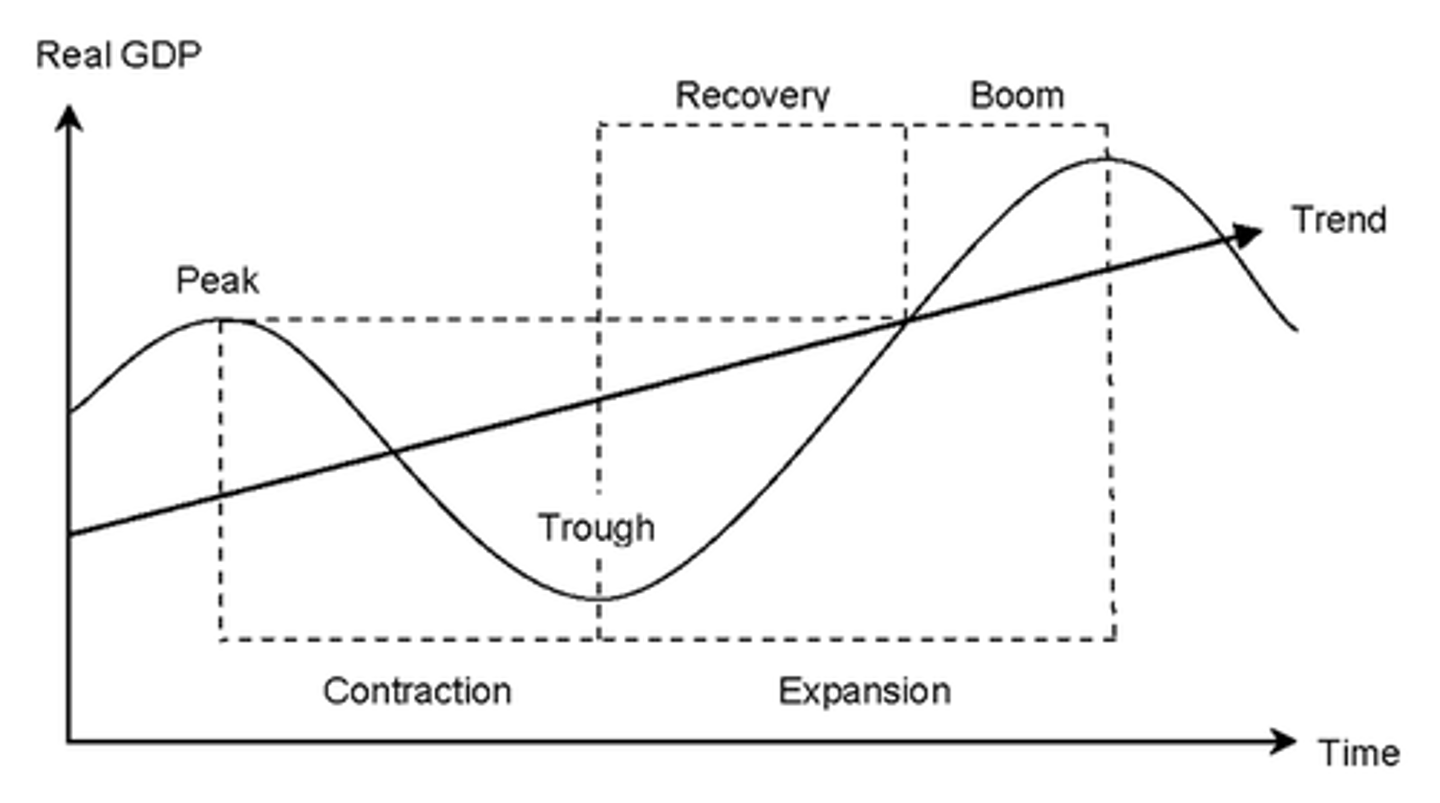
Financial external influence
- A major source of finance for business is debt finance (borrowings from external sources. E.g. bank loans), which is influenced by interest rates (cost of borrowing)
- Changes in global and domestic financial markets affecting borrowing costs and investment levels.
Deregulation
The removal of government regulations with the aim of increasing efficiency and improving competition.
Interest rates
As interest rates are the cost of borrowing money, increases in interest rate levels may reduce the amount of debt finance undertaken by a business.
Debt finance
Money borrowed that needs to be payed back (from a bank)
Equity finance
Money provided by owners (capital or buying shares)
Technological external influence
- Increase communication and productivity
- R&D
Sustainable competitive advantage
The ability of a business to develop strategies that will ensure it has an 'edge' over its competitors for a long period of time
Internal influences on Businesses (PLMBR) - business has control
Products, Location, Management, Business culture, and Resources.
Products internal influence
1. Type of goods and services produced effecting internal operations
2. Type of business (service, manufacturer, retailer)
3. Size of business
Location internal influence factors
- Proximity to customers
- Visibility
- Proximity to suppliers
- Cost
Prime location of business =
Customer convenience + visibility
Proximity to customers (location internal factors)
Retail vs Manufacturing business
Management internal influence
quality of managers, and the functional organisation structure style will either positively or negatively impact the performance of the business
- Classic vs behavioural management approach
Business culture internal influences
The values, ideas, expectations and beliefs shared by the staff and managers of the business.
Resources internal influences
Human: employees
Information: knowledge
Physical: equipment
Financial: Funds used to meet obligations by creditors
Stakeholders
Groups or individuals with an interest or affected by business activities.
Types of stakeholders
Society, Managers, Customers, Environment, Employees, Shareholders
Society (stakeholder)
Expect organisations to be concerned for environment + socially responsible
Managers (stakeholder)
Influence organisation policies and employee productivity
Environment (stakeholder)
Growing pleasure to adopt sustainable/ecological production practices
Customers (stakeholder)
Consider needs of customers = returning/happy experience