Accounting 211
1/53
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
accounts receivable
amounts due from customers for credit sales
direct write-off method
Record bad debt expense when an account is determined to be uncollectible
Allowance method
matches estimated loss from uncollectible accounts receivable against the sales they helped produce
allowance for doubtful accounts
a contra-asset account that reduces accounts receivable. It has a normal credit balance.
note receivable
a promise to pay a specified amount of money at a future date.
principal of a note
amount promised to be repaid
maturity date
day the note must be repaid
Note is honored
cash received in full (with interest)
when a note term runs over two periods
Note is dishonored
accounts receivable and interest recorded
factoring (selling) receivable
Accounts receivable are sold to a bank and the seller is charged a factoring fee
pledging of receivables
Borrowing money by pledging receivables as a security for a loan. Borrower discloses pledging in notes to the financial statement.
cost of plant assets
Normal, reasonable, and necessary costs in preparing an asset for its intended use. If an asset is damaged during unpacking, the repairs are not added to its costs. Instead, they are charged to an expense account.
machinery and equipment
Cost include purchases price, taxes, transportation, insurance, while in transit, installation, assembly, and testing
Building
the costs of a purchased building include its purchase price, real estate fees, taxes, title fees, and attorney fees.
land improvements
additions to land that have limited useful lives. Examples are parking lots, driveways, and lights
land
has an indefinite (unlimited) life and costs include real estate commission,s clearing, grading, and draining
lump-sum purchase
plant assets purchased as a group for a single lump-sum price. We allocate the cost to the assets acquired based on their relative market (or appraised) values.
depreciation
process of allocating the cost of plant asset to expense while it is in use
salvage value
estimate of the assets’ value at the end of its useful life
useful life
length of time a plant asset is to be used in operations
straight-line depreciation
charges the same amount of depreciation expense in each period of the assets’ useful life
asset book value
computed as the asset’s total cost minus accumulated depreciation
units of production formula
deprecation expense= depreciation per unit * units produced in period
double- declining balance depreciation
chargers more depreciation in early years and less depreciation in later years
natural resources
assets that are physically consumed when used. examples are standing timber, mineral deposits, and oil and gas fields
intangible assets
nonphysical assets (used in operations) that give companies long-term rigts, privileges, or competitive advantages
amortization
intangible assets with limited useful lives require amortization it is similar to depreciation and uses the shorter of legal life or useful life of the intangible for straight-line amortization
patent
exclusive right to manufacture and sell a patented item or to use a process for 20 years
copyright
the exclusive right to publish and sell a musical, literary, or artistic work during the life of the creator plus 70 years
franchises or licenses
rights to sell a product or service under specified conditions
trademark or trade (brand) name
A symbol, name, phrase, or jingle identified with a company, product, or service
Goodwill
The amount by which a company’s value exceeds the value of its assets and liabilities (net sales). Goodwill is only recorded when an entire company or business segment is purchased. Not amortized, but tested for impairment.
right-of-use asset (lease)
rights the lessor grants to the lessee under terms of the lease
leasehold improvements
improvements to a leased (rented) property such as partitions, painting, and storefronts. The lessee amortizes these costs over the life of the lease or the life of the improvements, whichever is shorter.
unearned revenues
amount received in advance from customers for future products or services; to record cash received in advance.
short-term note payable
a written promise to pay a specified amount on a stated future date within one year.
gross pay
total compensation an employee earns before deductions such as taxes.
payroll deductions
amounts withheld from an employees gross pay, either required or voluntary
FICA-SOCIAL SECURITY TAXES PAYABLE
withholdings to cover retirement, disability, and survivorship
Employee federal income taxes payable
federal income tac withheld from each employees paycheck
employee voluntary deductions
voluntary withholdings for things such as union dues, charitable giving, and health insurance.
warranty
a seller’s obligation to replace or fix a product or service that fails to perform as expected within a specified period. Warranty expense is a recorded in the period when revenue from the sale of the product or service is reported.
contigent liability
a potential liability that. depends on a future event arising from a past transaction or event. An example is a pending lawsuit.
Types of Intangibles
patents, copyrights, Franchise and Licenses, Trademarks /Tradenames, Goodwill, Right-Use-Asset, Leasehold Improvements, Software, noncompete covenants, customer lists
Interest formula (assumed to have 360 days)
Principle of the note Annual Interest rate * Time in Function
Plant Assets
Machinery and Equipment, Building, Land improvements, Land, and lump-sum purchase
Straight-line deprecation
Depreciation Expense Cost-salvage value/ Useful life
Double declining forumla
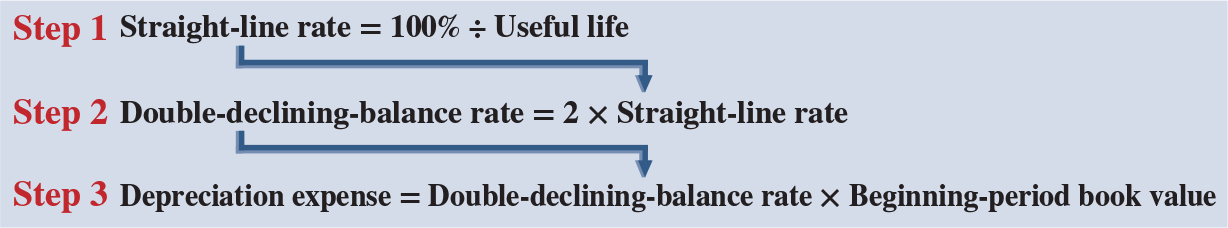
straight line deprication after change in accounting estimate
book value-revised salvage value/ revised remaining useful life
credit card sales
accounts receivable, sales, cash
sales using bank credit card
cash, credit card expense, sales
bad debts forumla
sales * rate
allowance for doubtful accounts formula
Accounts receivable * Rate