Chem Basic Review
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/34
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
1
New cards
Base units
length: meter
mass: gram
volume: liter
time: second
temperature: celcius
mass: gram
volume: liter
time: second
temperature: celcius
2
New cards
Kilo compared to base unit
1000x larger
1x10^3
abbreviation, k
1x10^3
abbreviation, k
3
New cards
Centi compared to base unit
100x smaller
1x10^-2
abbreviation, c
1x10^-2
abbreviation, c
4
New cards
milli compared to base unit
1000x smaller
1x10^-3
abbreviation, m
1x10^-3
abbreviation, m
5
New cards
micro compared to base unit
1,000,000x smaller
1x10^-6
abbreviation, Greek letter mu
1x10^-6
abbreviation, Greek letter mu
6
New cards
nano compared to base unit
1,000,000,000x smaller
1x10^-9
abbreviation, n
1x10^-9
abbreviation, n
7
New cards
Sig fig rules
* All non-zero digits are significant
* When writing a number in scientific notation, only digits in decimal portion are significant
* Captive zeros (zero between nonzeros) are significant
* Leading zeros (to the left of nonzeros) aren’t significant
* Trailing zeros (to the right of nonzeros) are significant
* When writing a number in scientific notation, only digits in decimal portion are significant
* Captive zeros (zero between nonzeros) are significant
* Leading zeros (to the left of nonzeros) aren’t significant
* Trailing zeros (to the right of nonzeros) are significant
8
New cards
When doing multiplication/division with sig figs…
Round to the fewest number of sig figs
3\.951 x 0.710 x 21.9837645 = 61.66907601 = 61.1 (3 sig figs)
3\.951 x 0.710 x 21.9837645 = 61.66907601 = 61.1 (3 sig figs)
9
New cards
When doing addition/subtraction with sig figs…
Round to the lowest common decimal place
21\.9837645 + 3.951 + 0.710 = 26.447645 = 26.644 (common in 1000th place)
21\.9837645 + 3.951 + 0.710 = 26.447645 = 26.644 (common in 1000th place)
10
New cards
How to write names of ionic compounds from ionic formulas
Ex: Sn(NO₃)₂
1. Determine the formulas and charges of the ions, write the cation first.
1. Tin is cation so it could be +2 or +4, nitrate is anion, charge is -1
2. Use subscripts to find total positive and negative charges
1. Total negative charge= -1 since 2 nitrates. So positive is +2
3. Find name of ions
1. Tin 2 and nitrate
4. Write name of compound, cation is always first
1. Tin 2 nitrate
1. Determine the formulas and charges of the ions, write the cation first.
1. Tin is cation so it could be +2 or +4, nitrate is anion, charge is -1
2. Use subscripts to find total positive and negative charges
1. Total negative charge= -1 since 2 nitrates. So positive is +2
3. Find name of ions
1. Tin 2 and nitrate
4. Write name of compound, cation is always first
1. Tin 2 nitrate
11
New cards
How to write ionic formulas from compound names
Ex: Aluminum sulfate
1. The name gives you the 2 ions, find formula and charges
1. Alumininum =Al³⁺ and Sulfate=SO₄²⁻
2. Decide how many of each ion is needed to neutralize charge
1. 2 Aluminums and 3 Sulfates
3. Write formula using subscript and parenthesis
1. Al₂(SO₄)₃
1. The name gives you the 2 ions, find formula and charges
1. Alumininum =Al³⁺ and Sulfate=SO₄²⁻
2. Decide how many of each ion is needed to neutralize charge
1. 2 Aluminums and 3 Sulfates
3. Write formula using subscript and parenthesis
1. Al₂(SO₄)₃
12
New cards
Notes about formula and nomenclature of ionics
* No charges are written in final formula
* Cation is first
* Parenthesis aren’t used on monatomic ions
* Parenthesis aren’t used on polyatomic ions if there’s only 1
* Parenthesis only used if there’s more than 1 polyatomic ion
* Cation is first
* Parenthesis aren’t used on monatomic ions
* Parenthesis aren’t used on polyatomic ions if there’s only 1
* Parenthesis only used if there’s more than 1 polyatomic ion
13
New cards
Binary inorganics
* Similar to naming ionics, say the name of the first element and the second element is named by adding “ide” to the root
* Use Greek prefixes to denote number of atoms of each element
* Don’t use “mono” for first element
* Use Greek prefixes to denote number of atoms of each element
* Don’t use “mono” for first element
14
New cards
Prefixes used in naming inorganic molecular compounds
1. mono
2. di
3. tri
4. tetra
5. penta
6. hexa
7. hepta
8. octa
9. nona
10. deca
15
New cards
What are the 7 diatomic molecules
H₂, O₂, N₂, F₂, Br₂, Cl₂, I₂
16
New cards
What is an acid
A substance that yields hydrogen ions (H⁺) when dissolved in water
* Could go by their inorganic name or acidic name depending on its state
* Could go by their inorganic name or acidic name depending on its state
17
New cards
What is an oxoacid
Acids that contain hydrogen, oxygen, and another element
18
New cards
ide
hydro…ic acid
19
New cards
Hypo…ite
hypo…ous acid
20
New cards
ite
…ous acid
21
New cards
ate
…ic acid
22
New cards
per…ate
per…ic acid
23
New cards
Hydrocarbons
Only contain carbon and hydrogen
24
New cards
Alkanes
Saturated hydrocarbons contain carbon atoms that each form single bonds
25
New cards
Alkenes and alkynes
Unsaturated hydrocarbons have a double(alkene) or triple(alkyne) bond
* They’re much more reactive than alkanes
* They’re much more reactive than alkanes
26
New cards
How to name organic molecules (alkane, alkene, alkyne)
1. meth…
2. eth…
3. prop…
4. but…
5. pent…
6. hex…
7. hept…
8. oct…
9. non…
10. dec…
27
New cards
How to name isomers (chains)
The longest carbon chain is numbered and the name starts with the number where the bond is
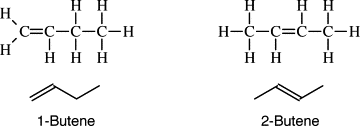
28
New cards
Cyclic hydrocarbons
Carbons arranged in rings, can be alkanes, alkenes, or alkynes
* The prefix “cyclo” is added to the name to indicate it’s a ring
* The prefix “cyclo” is added to the name to indicate it’s a ring
29
New cards
Alcohols
have the hydroxyl functional group (OH)
* Not hydroxide (OH⁻)
* Covalently bonded to a carbon molecule
* Gives polarity to an otherwise nonpolar molecule
* Put ending “OL” onto the name of the hydrocarbon with a number to show which carbon has the OL (similar to double/triple bond)
Ex: Methanol = CH₃OH
Ex: 1 propanol = CH₃CH₂CHOH
Ex: 2 propanol = CH₃CHOHCH₃
* Not hydroxide (OH⁻)
* Covalently bonded to a carbon molecule
* Gives polarity to an otherwise nonpolar molecule
* Put ending “OL” onto the name of the hydrocarbon with a number to show which carbon has the OL (similar to double/triple bond)
Ex: Methanol = CH₃OH
Ex: 1 propanol = CH₃CH₂CHOH
Ex: 2 propanol = CH₃CHOHCH₃
30
New cards
Double replacement reactions
Ex: 3 CoCl₂ + 2 Na₃PO₄ →Co₃(PO₄)₂ + 6 NaCl
* 2 ionic reactants, 2 ionic products (cations trade anions)
* 2 ionic reactants, 2 ionic products (cations trade anions)
31
New cards
Single replacement reaction
Ex: 2 HCl + Mg → MgCl₂ + H₂
* 2 products (1 ionic, 1 element), 2 products (1 ionic, 1 element)
* considered a redox reaction
* 2 products (1 ionic, 1 element), 2 products (1 ionic, 1 element)
* considered a redox reaction
32
New cards
Synthesis reaction
Ex: 2 Mg +O₂ →2MgO
* Multiple reactants (elements or molecules), 1 product
* Often a redox reaction
* Multiple reactants (elements or molecules), 1 product
* Often a redox reaction
33
New cards
Decomposition reaction
Ex: 2 H₂O₂ →2H₂O + O₂
* 1 reactant, multiple products
* Often a redox reaction
* 1 reactant, multiple products
* Often a redox reaction
34
New cards
Combustion reaction
Generic: CxHy + O₂ →CO₂ +H₂O
* 2 CH₃OH + 3 O₂ →2 CO₂ + 4 H₂O
* Something organic (C, H, O?) reacts with O₂, products are CO₂ and H₂O
* Also redox
* 2 CH₃OH + 3 O₂ →2 CO₂ + 4 H₂O
* Something organic (C, H, O?) reacts with O₂, products are CO₂ and H₂O
* Also redox
35
New cards
Redox (oxidation and reduction)
Mg + 2 Ag⁺ →2 Ag + Mg²⁺
Mg + 2 AgNO₃ → 2 Ag + Mg(NO₃)₂
* OILRIG (oxidation is loss, reduction is gain)
* Any reaction that involves the movement of electrons
Mg + 2 AgNO₃ → 2 Ag + Mg(NO₃)₂
* OILRIG (oxidation is loss, reduction is gain)
* Any reaction that involves the movement of electrons