Human A&P1 , Chapter 11
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
Functions of the nervous system
- Gathers sensory input
- Integrate sensory input
- Causes response or motor output (activates effector organs)
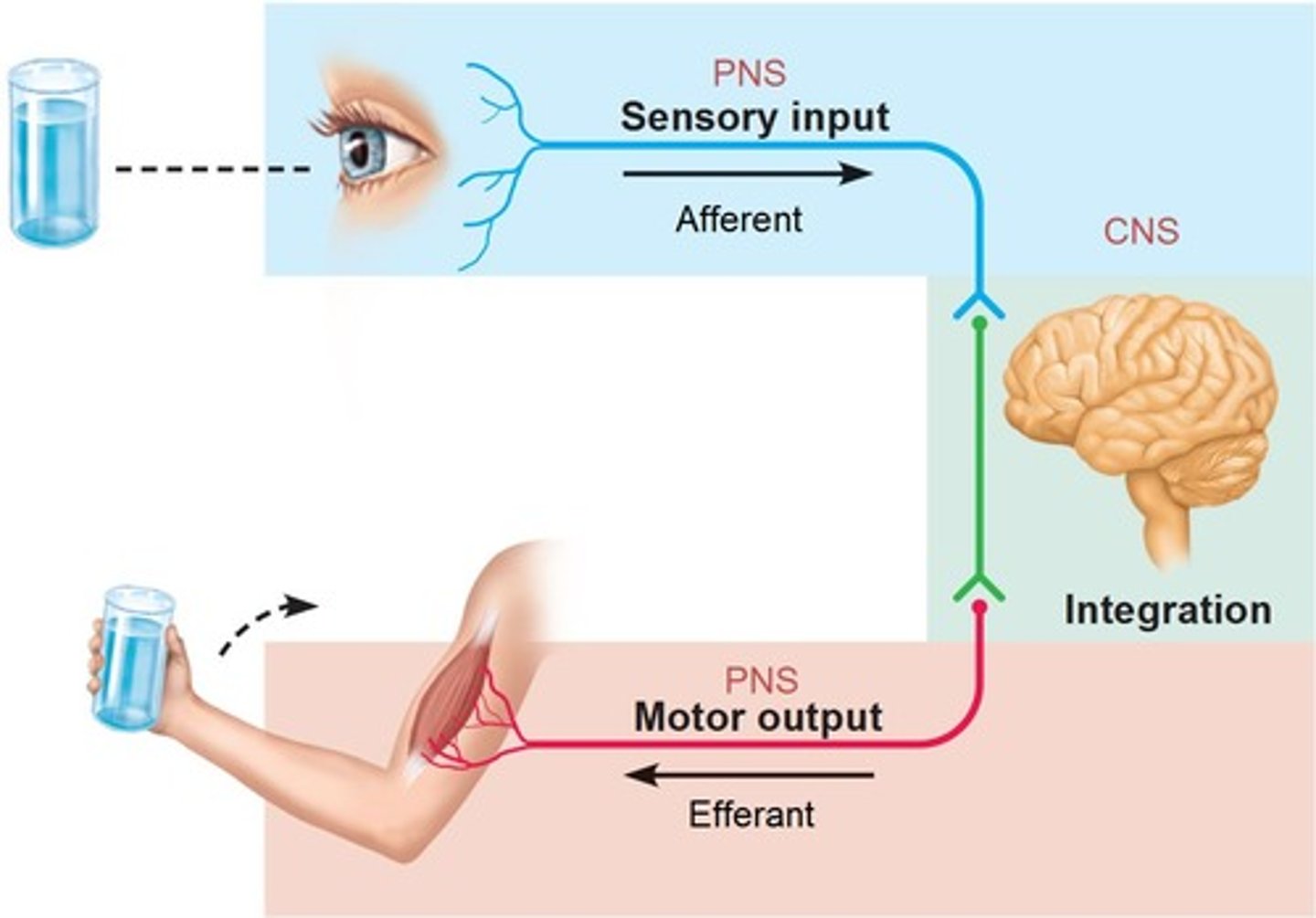
Organization of the Nervous System
Central Nervous System (CNS) and Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) -> sensory + motor division -> somatic + autonomic -> sympathetic + parasympathetic divisions
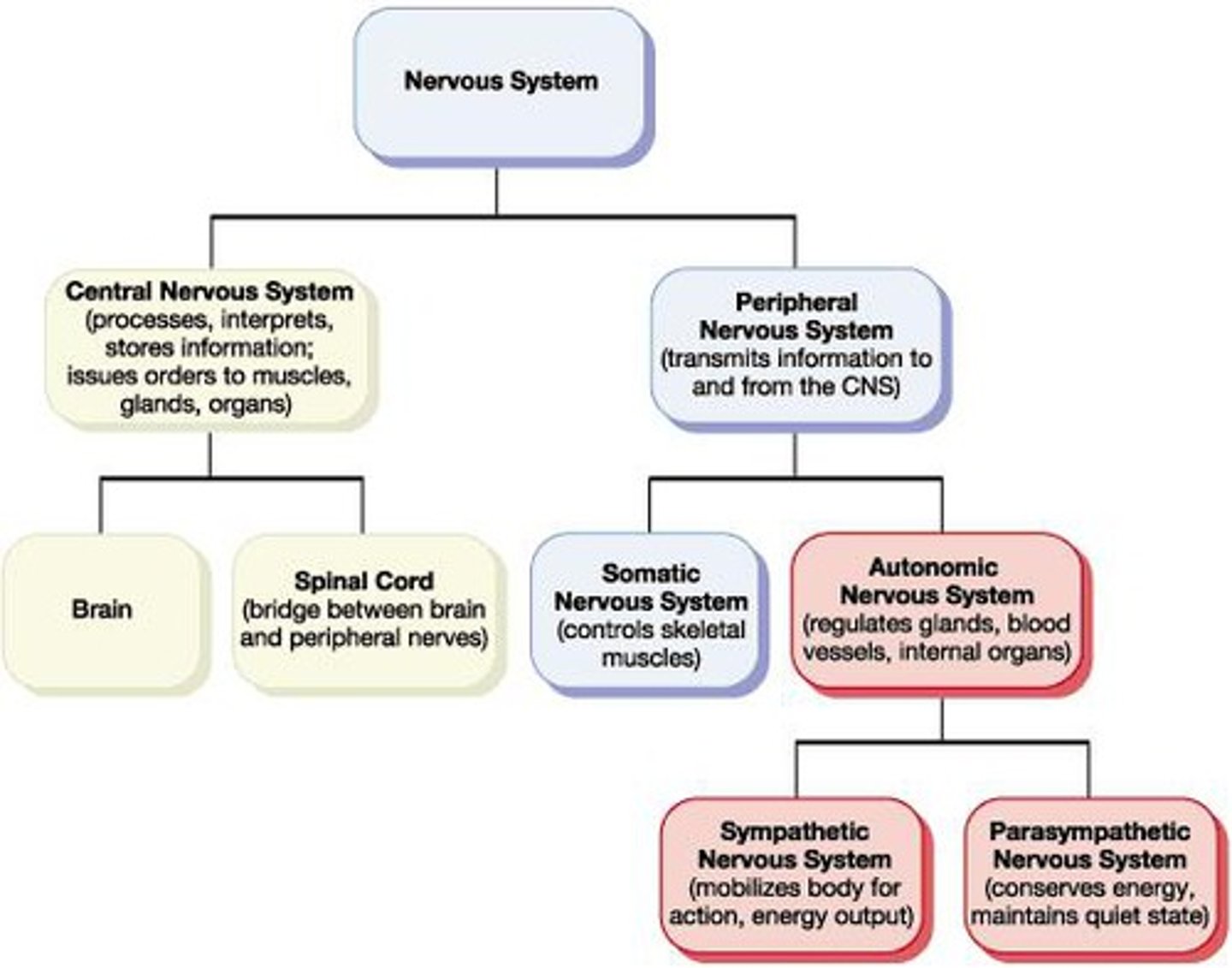
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Control center for interpreting sensory input and motor output
Brain + Spinal Cord
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Communication lines between CNS and rest of body
Nerves and ganglia OUTSIDE the CNS
Visceral organs, Skin, Skeletal muscles
Sensory (afferent) division
Division of PNS
Has somatic (skin) and visceral (heart) sensory fibers
Conducts impulses from receptors TO the CNS
Motor (efferent) division
Division of PNS
Has Motor nerve fibers
Conducts impulses FROM the CNS to effectors (muscles + glands)
Somatic nervous system
Division of motor division
Somatic (voluntary) nerve fibers
Conducts impulses FROM the CNS to skeletal muscles
Autonomic nervous system (ANS)
Division of motor division
Visceral (involuntary) nerve fibers
Conducts impulses FROM the CNS to cardiac muscle, smooth muscle and glands
Sympathetic division
Division of ANS
Mobilizes body systems during activity
Parasympathetic division
Division of ANS
Conserves energy, promotes house-keeping functions during rest
2 major cell types
- Supporting cells
- Neurons
Supporting cells
“Nerve glue” surround and wrap neurons, called neuroglia or glial cells
Help the neurons
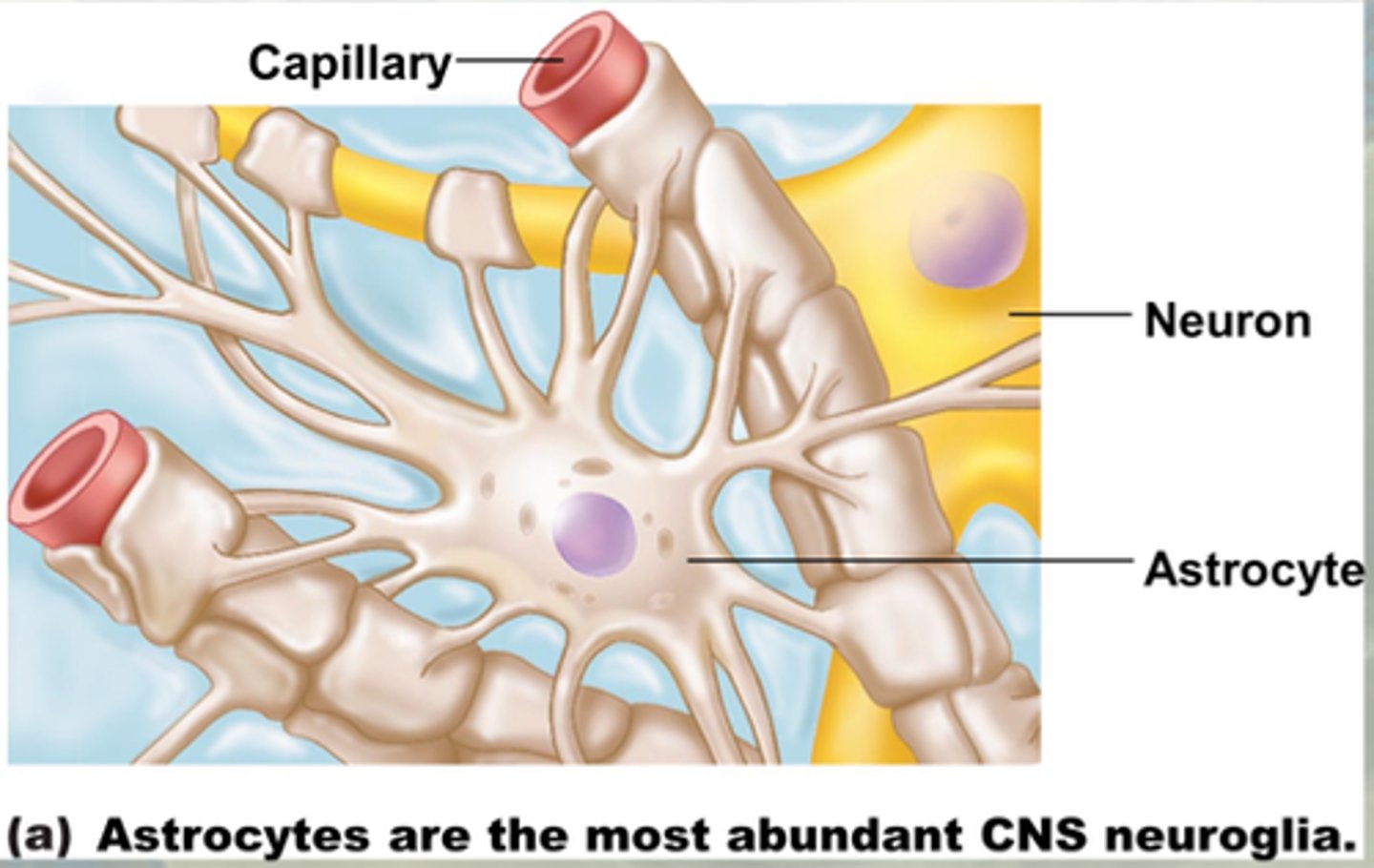
Astrocytes (Supporting cell of CNS)
- Star-shaped, wrap around neurons, blood/brain barrier
- Anything that goes to the neuron goes through the astrocyte
- Most abundant
- Support neurons; anchor to capillaries
- Mop up leaked K+ and recycle neurotransmitters (ACh, etc.)
Microglia (supporting cells of CNS)
- Transform into a macrophage (which phagocytize neural debris + microorganisms)
- Lying in wait for a breach in the nervous tissue; are protective
Ependymal cells (supporting cells of CNS)
- Line cavities of CNS, brain and spinal cord
- Many have cilia facing fluid-filled cavity
- Beat their cilia to circulate CSF (cerebrospinal fluid) cavities
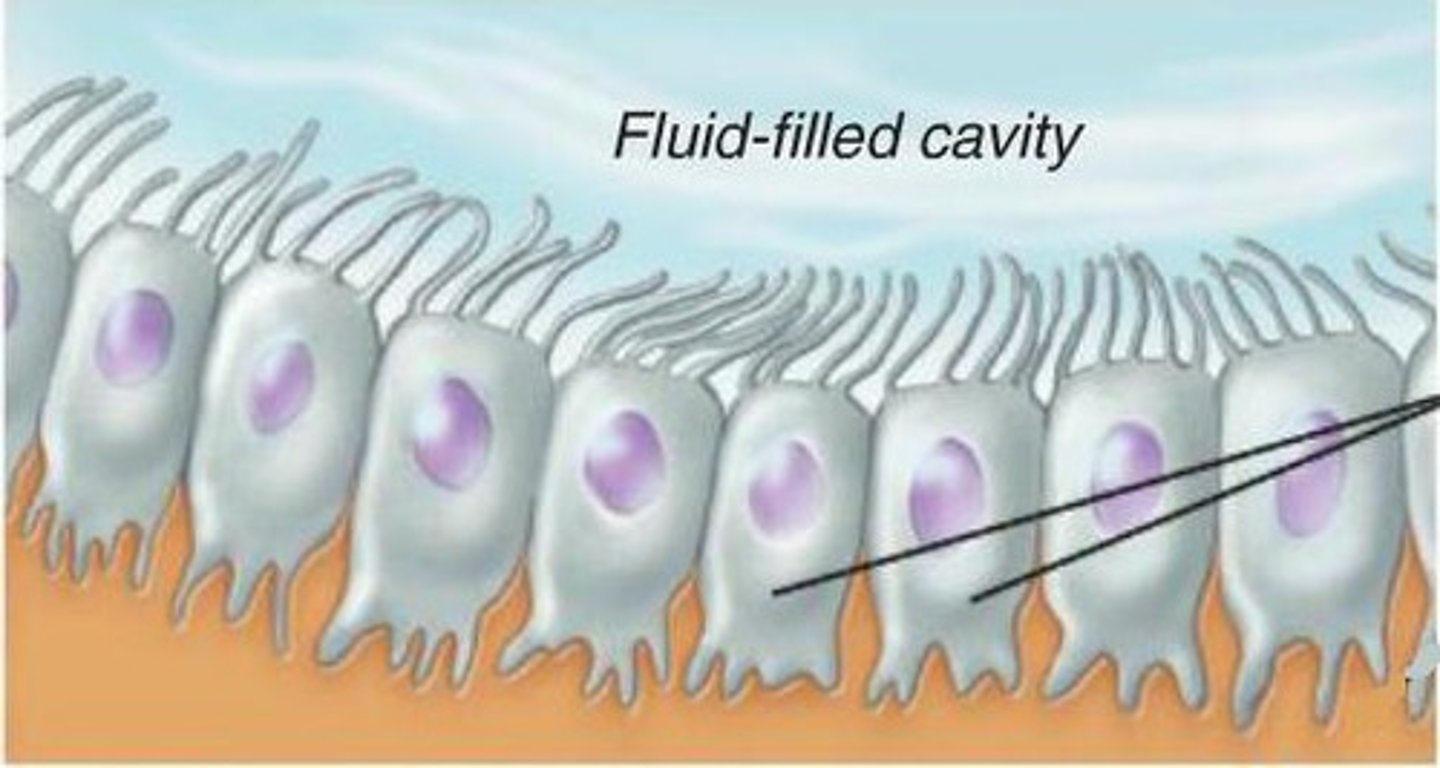
Cerebrospinal Fluid Functions
Protect and cushion the brain and spinal cord, has nutrients
Oligodendrocytes (supporting cells of CNS)
- One of two cell types that make a myelin sheath; is INSIDE THE CNS
- Line up along thicker CNS neurons and wrap them with cytoplasmic extensions
- Produce insulating layers (myelin sheaths, increasing the speed of an action potential)
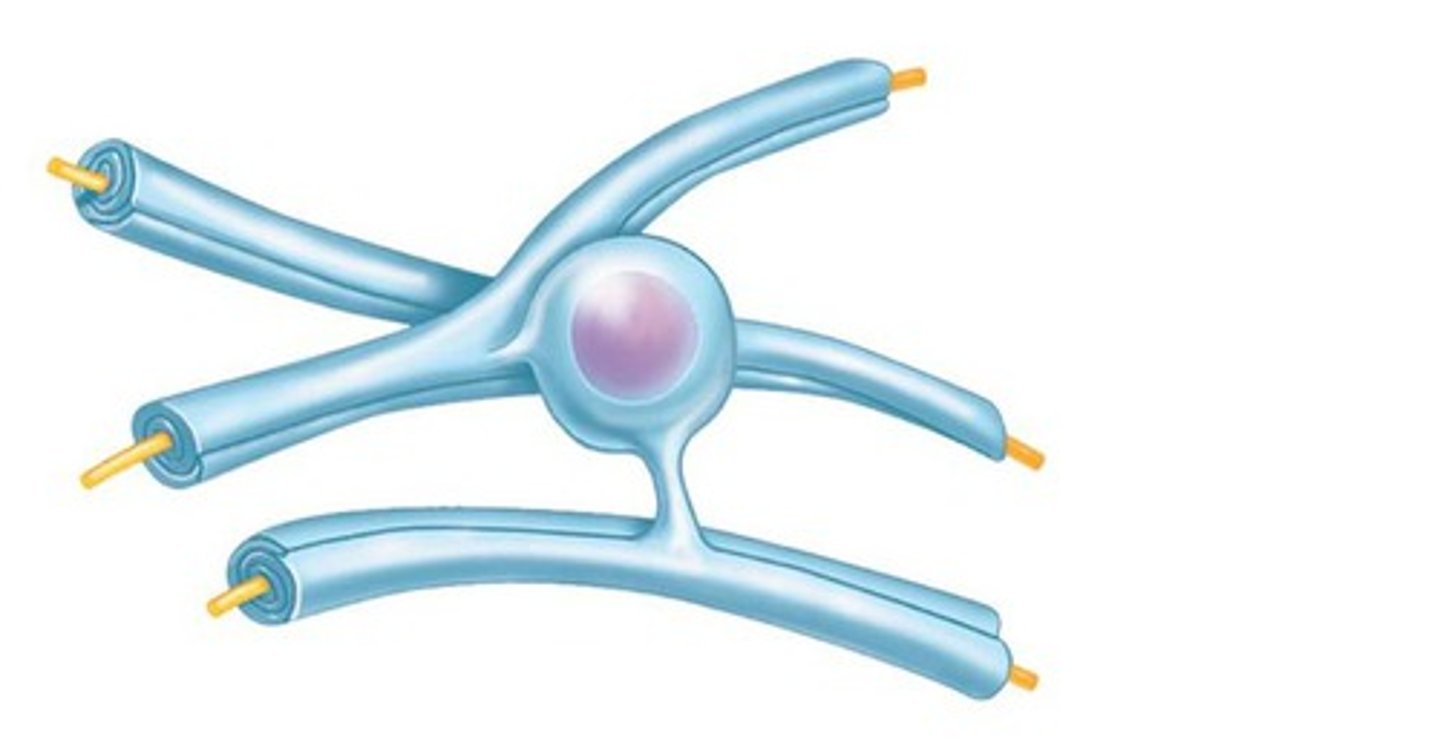
Satellite cells (Supporting cells of PNS)
- Surround the neuron cell bodies within ganglia
- Function unknown
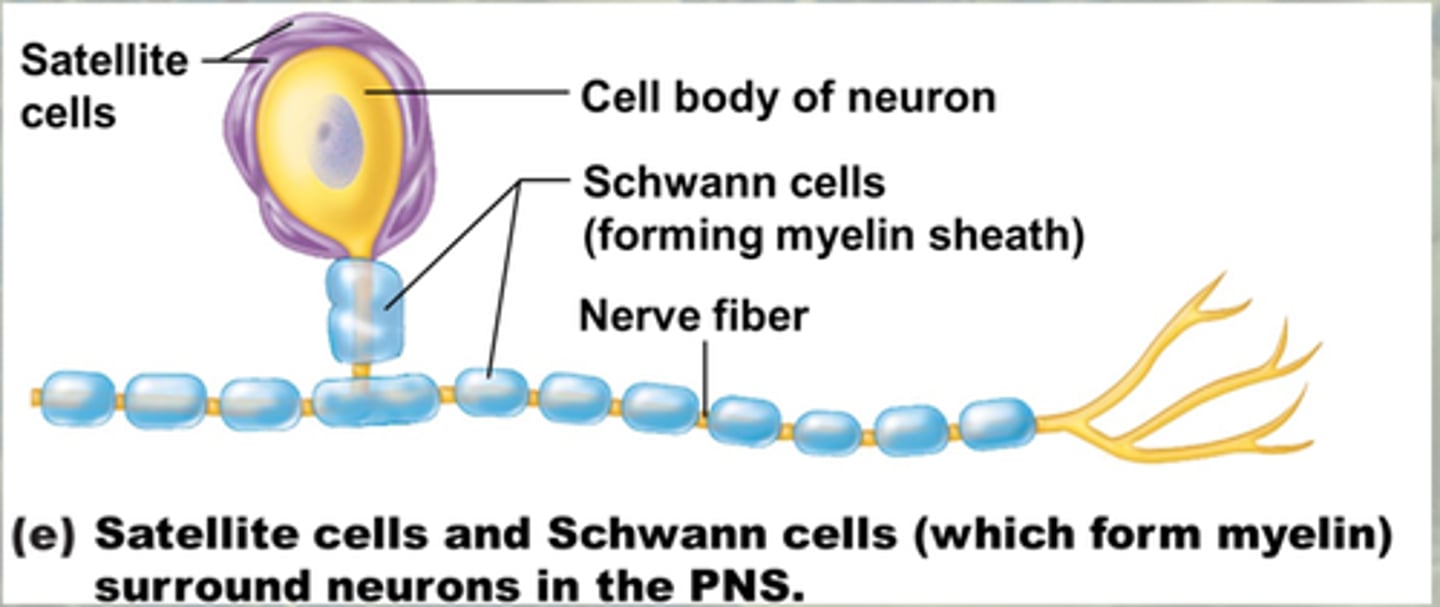
Schwann cells (supporting cells of PNS)
- Also called neurolemmocytes
- Surround nerve fibers and form myelin sheath in the PNS
- Vital for peripheral nerve fiber regeneration
Neurons (nerve cells)
Excitable nerve cells that transmit signals
- Conduct nerve impulses
Characteristics of nerve cells
- Extreme longevity (lasts long)
- Amitotic (cannot divide, hard to replace)
- High metabolic rate (need LOTS of oxygen and glucose)
Cell body of a neuron (soma)
- Mostly in CNS
- Contains nucleus and cytoplasm
- Is the Biosynthetic/metabolic center + receptive region
Structures in Cell body
Protein and membrane-making machinery (rough ER (chromatophilic substance), ribosomes, golgi apparatus)
Cytoskeletal elements - Maintain cell shape/integrity (microtubules and neurofilaments)
Pigment inclusions - changes color (black melanin, lipofuscin)
Biosynthetic center
In soma, has the rough ER, is most active of any cell, no centrioles, makes protein
Processes of a neuron
Dendrites and axons
Dendrites
Branchlike parts of a neuron that are specialized to receive information, large surface area, convey short-distance signals (graded potentials) TOWARD the cell body
Receptive region
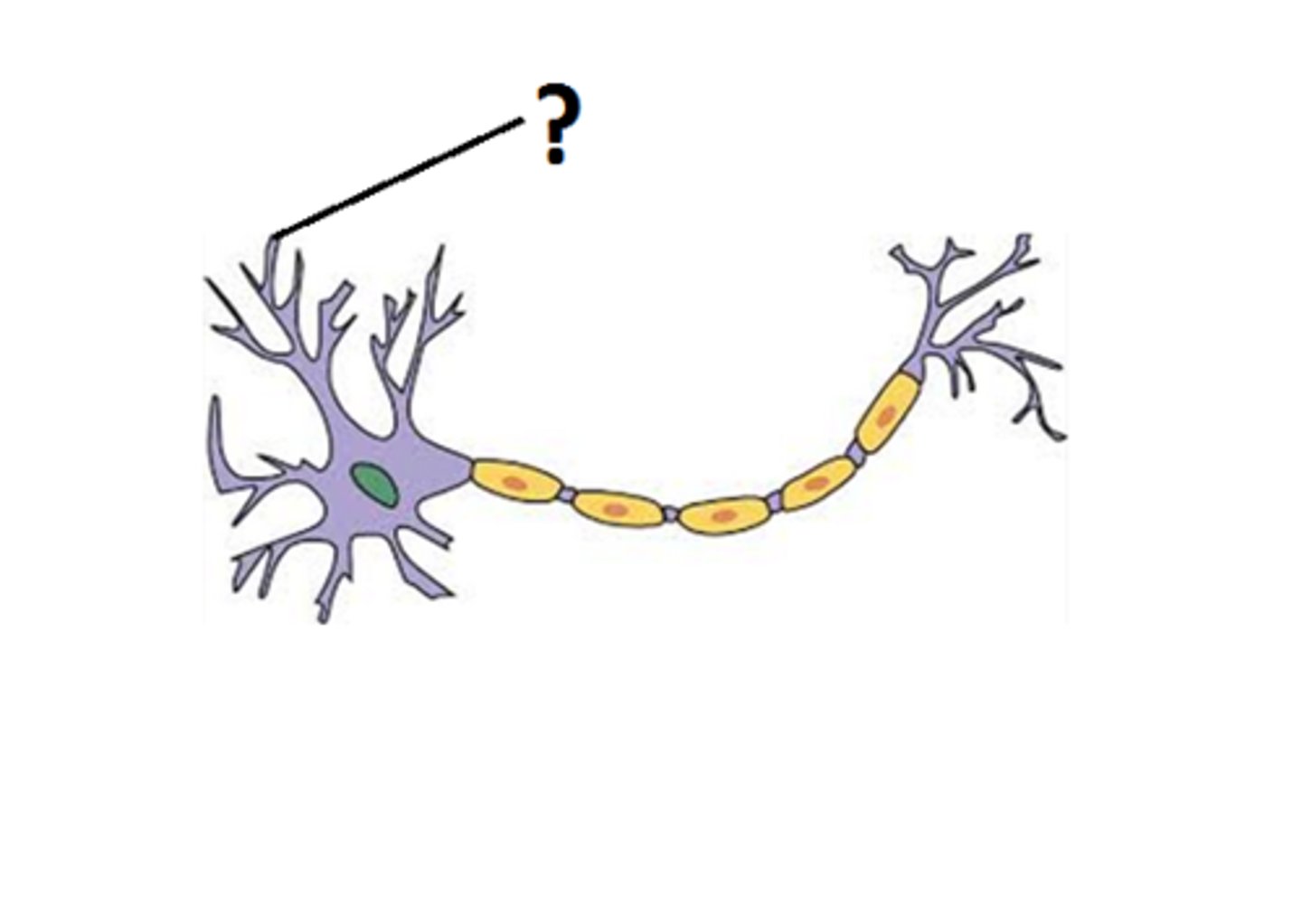
Axon
- Generates nerve impulse AWAY from cell body, starts at axon hillock
- Each neuron has a single axon that relies on cell body
- Ends in terminal branches (have endings called synaptic knobs (boutons)) that release neurotransmitters
- Tracts in the CNS, nerves in the PNS
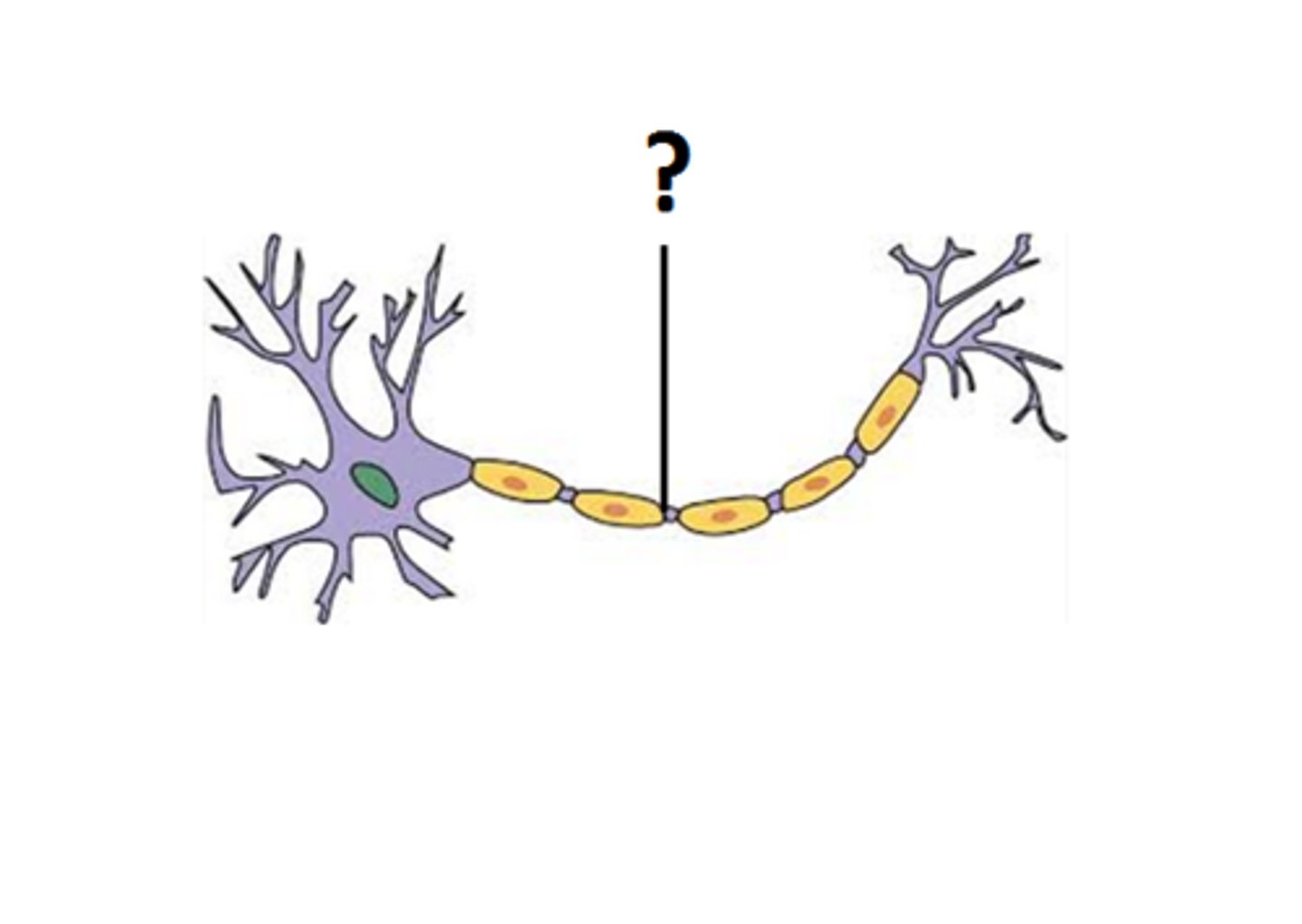
Boutons
Synaptic knobs in the axon that release neurotransmitters
A tract
Bundle of axons in the CNS
A nerve
Bundle of axons in the PNS
Nuclei
Clusters of cell bodies INSIDE CNS
Ganglia
Cell bodies that lie along nerves in PNS (OUTSIDE CNS)
Axonal transport
Anterograde (away from body), retrograde (toward body)
- Uses ATP dependent motor proteins
Regions of a neuron
Receptive (dendrite and body)
Conducting (axon)
Secretory (axon terminals)
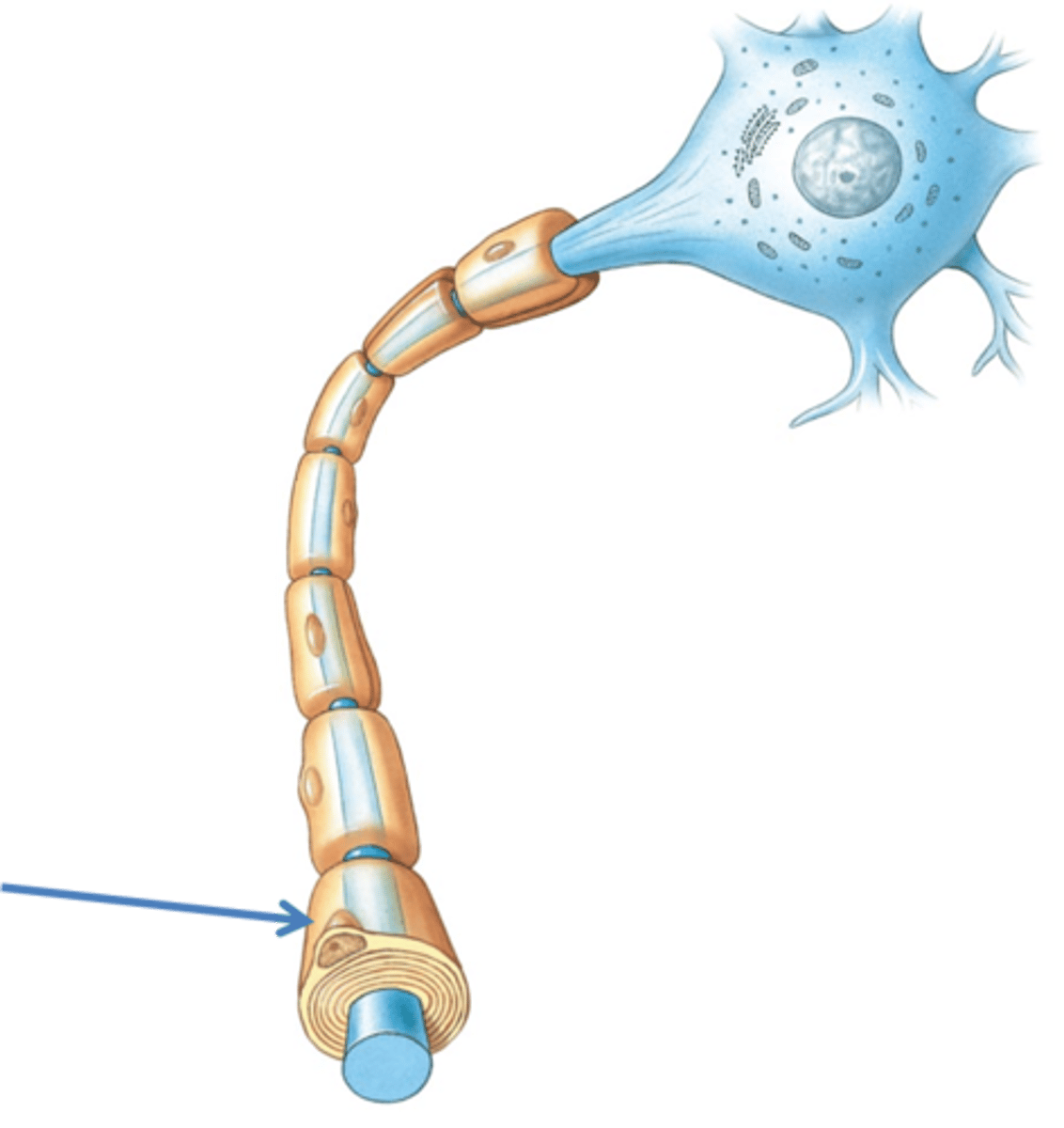
Myelin sheaths
Insulating, whitish/fatty cover that wraps tightly around, protects, and insulates nerve fibers (mostly in CNS)
Formed by Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system, oligodendrocytes in the CNS, with gaps known as myelin sheath gaps (nodes of Ranvier) between cells
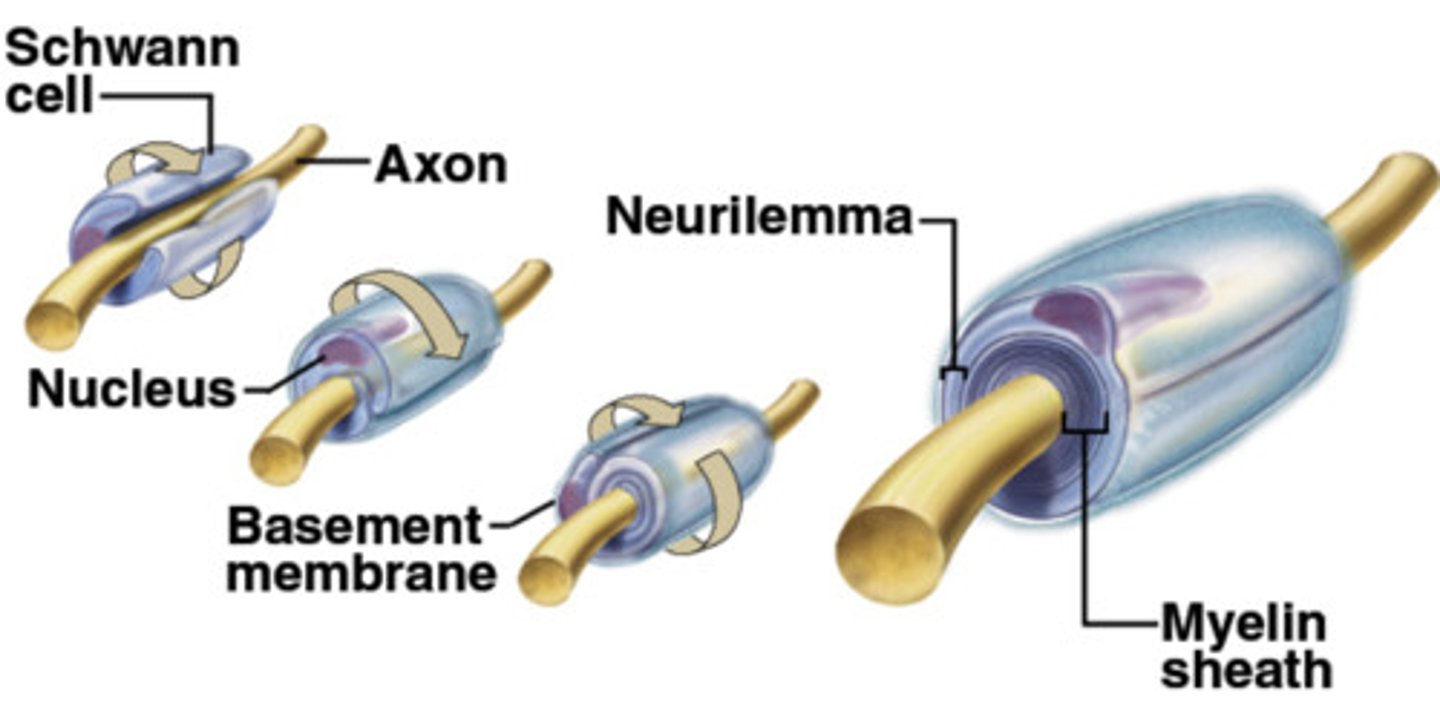
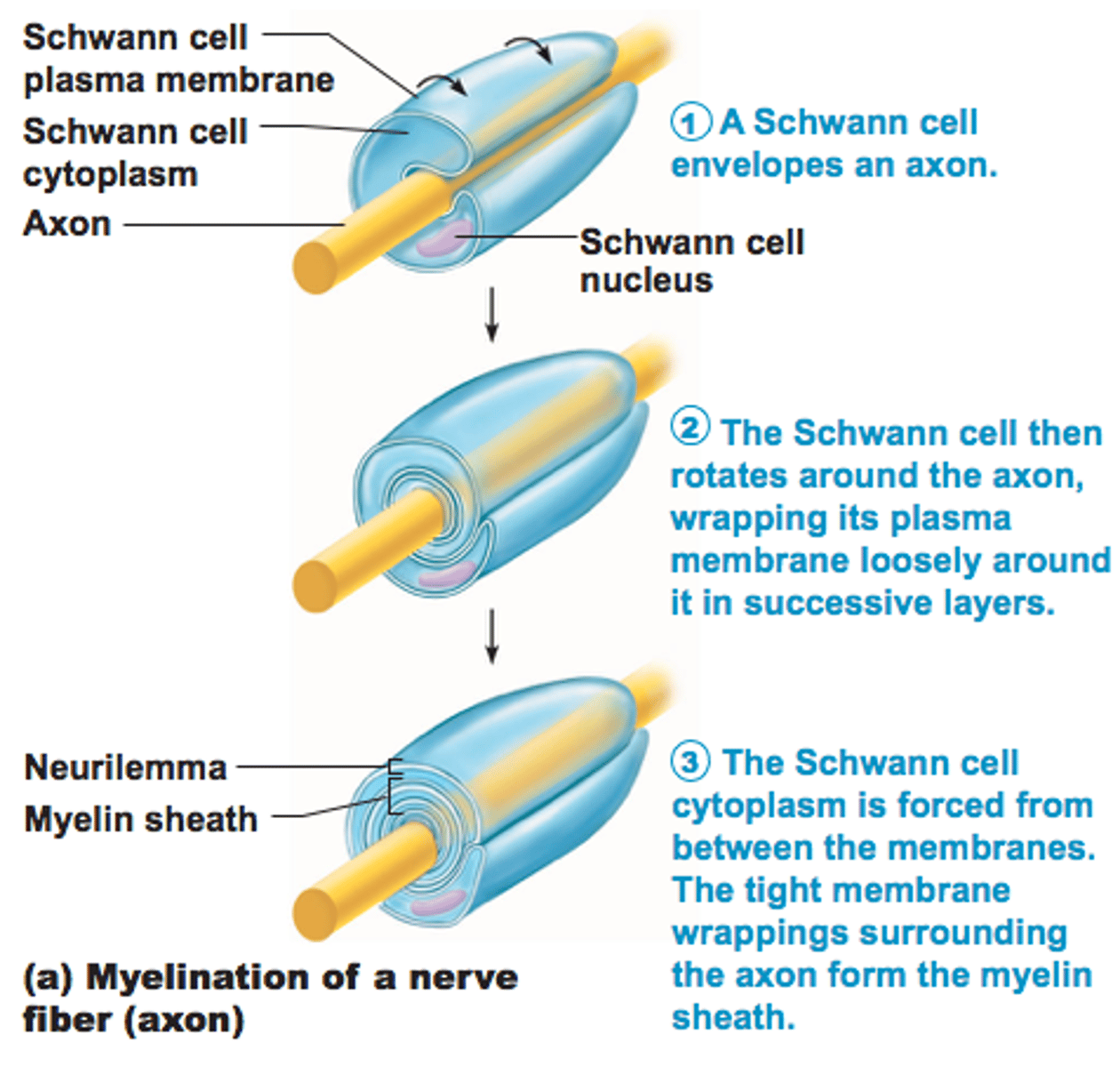
Myelin sheath formation in PNS
- Formed by Schwann cells, wrap around axon in "jelly roll" fashion
-Schwann envelops then rotates, squeezing out cytoplasm
- Adjacent Schwann cells along axon don't touch
Myelin sheath formation in CNS
- Oligodendrocytes, nodes of Ranvier more widely spaced, CNS myelin sheaths lack an external lamina
- Oligodendrocytes can wrap multiple different axons at the same time
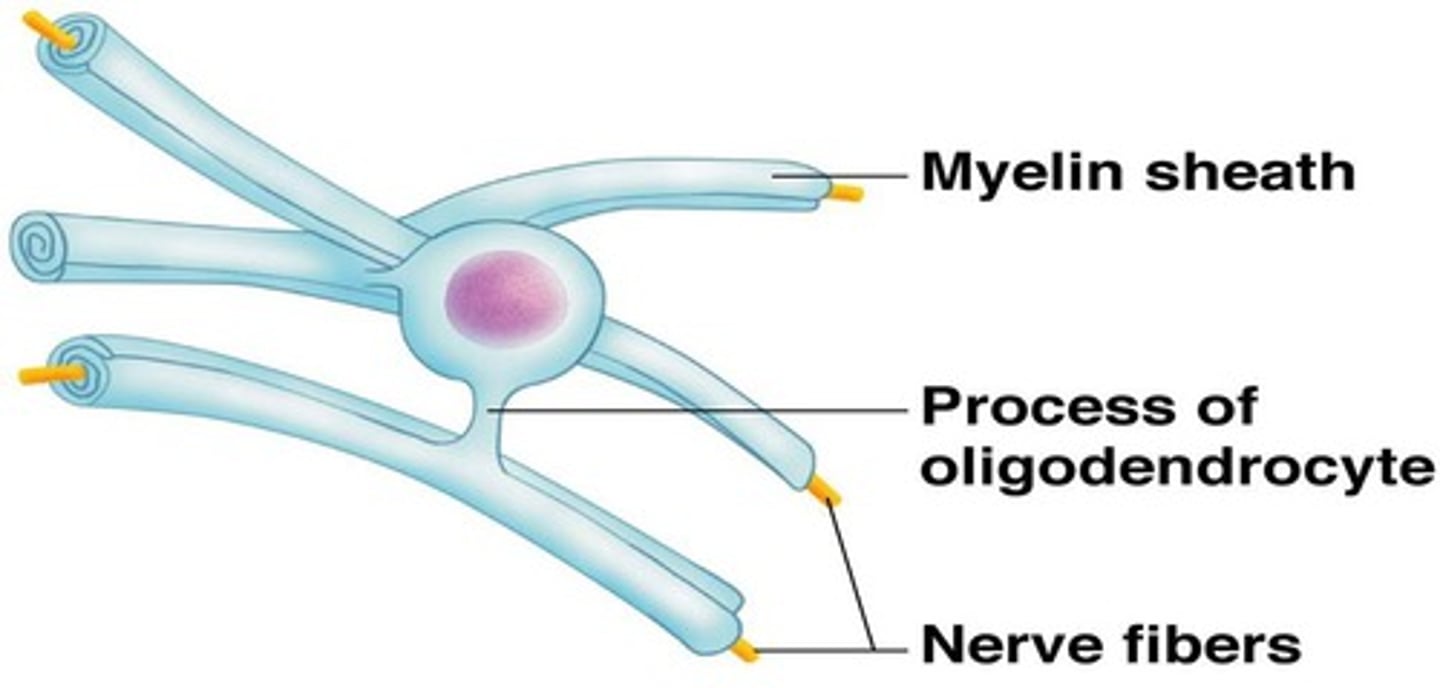
White matter (fiber tracts)
CNS regions containing collections of myelinated fibers
Gray matter
CNS regions of nerve cell bodies and unmyelinated fibers
Classification of neurons by processes
Number of processes extending from body
Multipolar, bipolar, unipolar
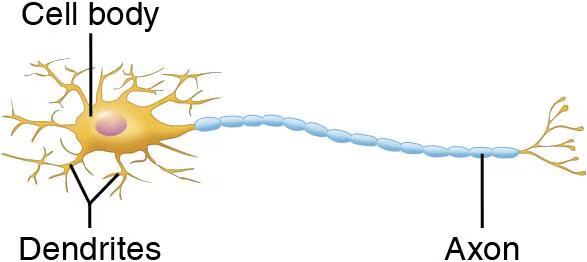
Multipolar
3 or more processes (1 axon and many dendrites)
99% of neurons
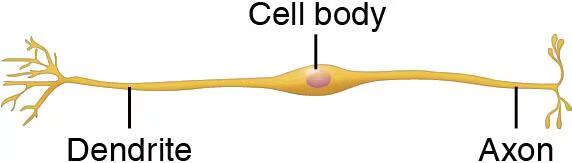
Bipolar
Rare, 2 processes (1 axon and 1 dendrite)
Ex: receptors of the retina and olfactory mucosa
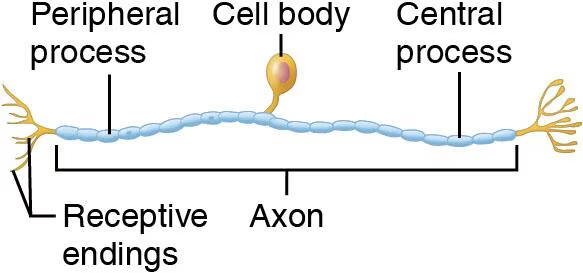
Unipolar (pseudounipolar)
Single, short process divides of cell body into proximal and distal branches
In ganglia of PNS (sensory neurons)
Classification of Neurons
The functional direction the impulse travels
Sensory (afferent), Motor (efferent), Interneurons (association neurons)
Sensory (afferent) neurons
Classification of neuron
From skin/organs to CNS, mostly unipolar
Cell bodies OUTSIDE CNS
Motor (efferent) neurons
Classification of neuron
Carry impulse FROM CNS to the effector organs (muscles + glands), usually multipolar
Cell bodies INSIDE CNS
Interneurons (association neurons)
Classification of neuron
Lie between sensory and motor neurons, shuttle signals through CNS, often multipolar
99% of neurons
Part of Neurophysiology
- When a neuron is stimulated, electrical impulse conducted along length of axon
- Potential energy
Ex: stored potential energy in a battery, complete circuits
Potential energy of neuron
Generated by separated electrical charges of opposite sign
The greater the distance, the greater the voltage
Resting Membrane Potential
The potential difference across a membrane in a resting (polarized) neuron
Measured by a voltameter (-70 mV)
Voltage
-Measure of potential energy difference generated by separated charge
- Volts or millivolts
- Measures between two points (inside and outside)
Current
A flow of electric charge from one point to another, flows through fluids when voltage changes
Sodium and Potassium flow
Resistance
- Hinderance to charge flow
- Insulators and conductors
- Plasma membrane provides resistance to current flow
Insulators
Have a high electrical resistance
Conductors
Have a low electrical resistance
Ohm's Law
Current (I) = Voltage (V) / Resistance (R)
Current is directly related to voltage and inversly related to resistance
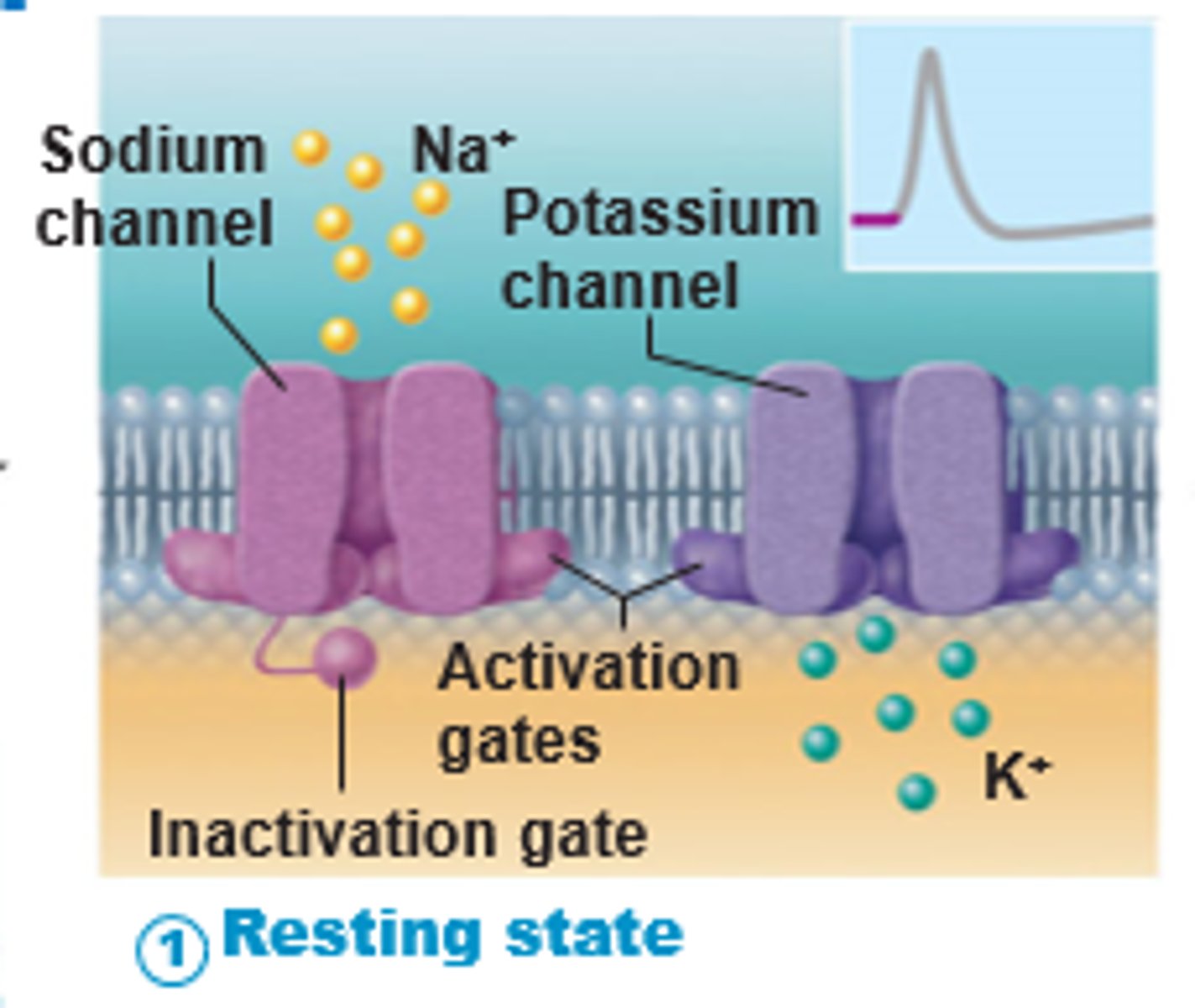
Nongated channels
Leakage channels, are always open
Types of gated ion channels
Voltage gated, chemically gated, mechanically gated
Chemically (ligand) gated
Open in response to binding of the appropriate neurotransmitter
Voltage gated
Normally wide open, are waiting for an electrical response to changes in membrane potential
Initially activated by local (graded) potentials along the dendritic body/soma membranes
Mechanically gated
Open in response to physical deformation of the receptor
Ex. sensory receptors for touch and pressure
Electrochemical gradient
Concentration (higher to lower concentration) and electrical (toward area of opposite charge) gradient
Ions flowing across membrane create currents and voltage
Maintaining RMP
Concentration of Na+ and K+ inside and outside cell
Selective permeability of the membrane (K+ leaks out more than Na+ leaks in)
Na+/K+ Pump (3 Na+ out, 2 K+ in)
Action potential (nerve impulse)
Long-distance signals of axons with consistent strength; brief switch of RMP
Do not decay
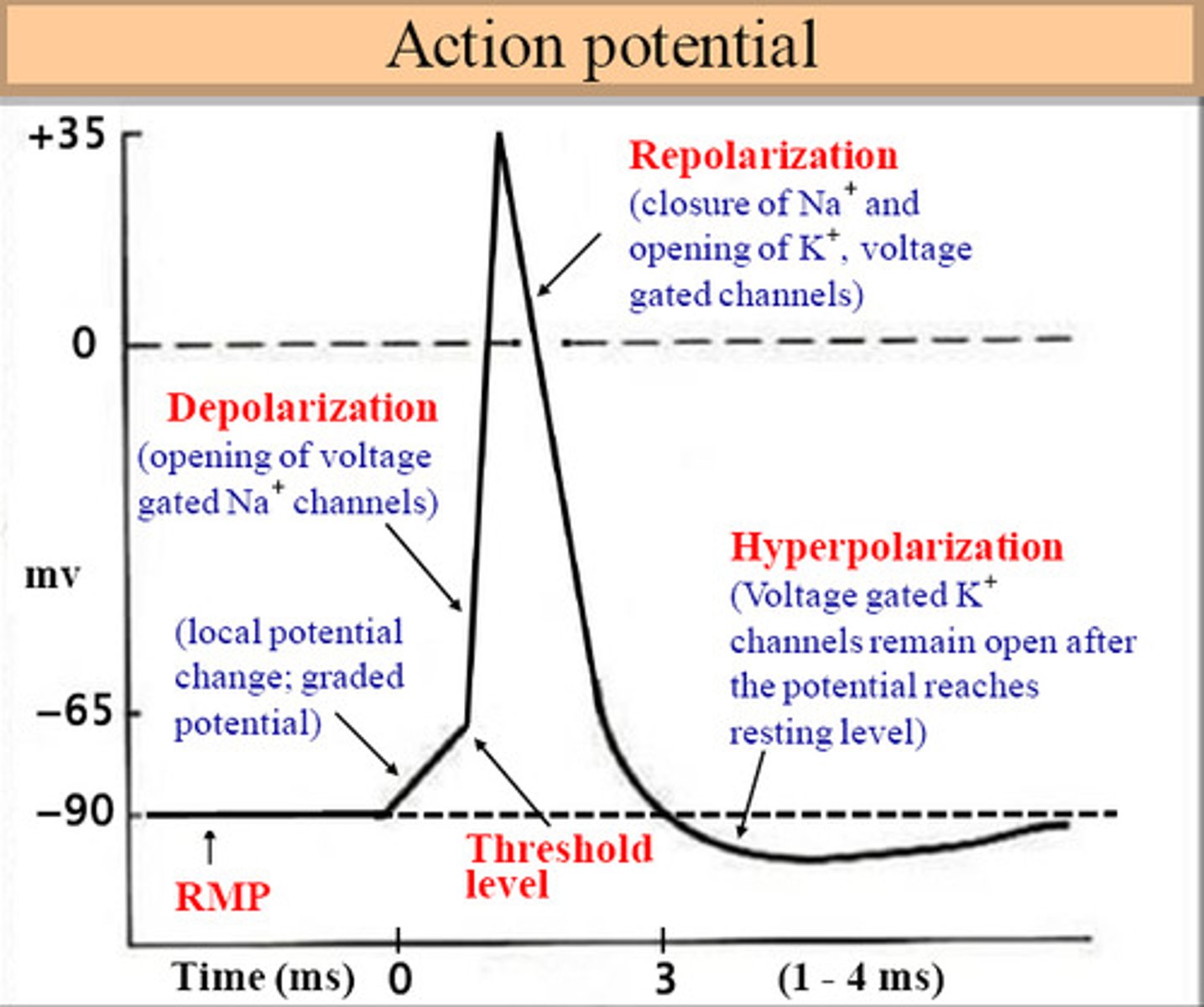
Action Potential generation
Resting state, depolarization
Generated by influx of Na+ (depolarization)
Action Potential propagation
Axonal hillock regulates the generator potential, and it must rise to the threshold, when it reaches the threshold it fires.
The entire AP must be propagated along the entire axon for a nerve impulse. After depolarization, AP is self-propagating down the axon due to voltage-gated channels opening
Resting state
The state in which there is a negative electrical charge of about -70 millivolts within a neuron
All gated Na+ (two gates) and K+ (one gate) channels are closed.
Depolarization
Decrease in membrane potential where the inside of the membrane becomes less negative/more positive (closer to zero); outside is occupied with more negative ions instead
Na+ channels open during depolarization
Repolarization
Sodium efflux (out), return of the cell to resting state, caused by reentry (influx) of potassium into the cell while sodium exits the cell.
Na+ stops rushing in, K+ rushes out
Hyperpolarization
The inside of the membrane becomes more negative, RMP dips lower than normal but are corrected
Some K+ channels remain open, and Na+ channels rest.
Threshold Point
The membrane potential at which the outward current of Na+ is equal to the inward current of K+, reached when depolarization occurs
Subthreshold stimuli
Brief weak stimuli produce subthreshold depolarizations that do not translate into nerve impulses
Depends on amount of current
Threshold stimuli
Stronger stimuli produce depolarizing currents that push the membrane potential toward and beyond the threshold voltage
Depends on amount of current
Local (graded) potential
Short-lived, localized changes in membrane potential, typically occurring in dendrites or the cell body.
-Excitatory or inhibitory (depolarization or hyperpolarization)
-Magnitude varies directly with stimulus strength
-Triggered by a change in the neuron's environment
Receptor generated potential
Sensory receptor is excited by stimuli such as light, pressure, or chemicals
Postsynaptic potential
Stimulus is a neurotransmitter that is released by another neuron
Neurotransmitter is released into a fluid-filled gap called a synapse and influences the neuron beyond the synapse
Absolute Refractory period
Period from the opening of the Na+ channels until the channels begin to reset to their original state. Ensures each AP is separate and enforces one-way transmission of AP.
Cannot respond to another stimulus, one end of axon to the other
Relative Refractory period
Interval following the absolute refractory period where most Na+ channels have returned to resting state,
Some channels still open and repolarization is occurring. Axons threshold for AP generation is elevated
Generator potential
Local depolarization initiated by some form of energy
Pre-synaptic neuron
houses vesicles filled with neurotransmitter in its synaptic knob
Post-synaptic neuron
contains proteins that function as receptors and ion gates
Neurotransmitter receptor
Specialized protein, often embedded in the cell membrane, that selectively senses and reacts to molecules of a corresponding neurotransmitter or hormone
Synaptic cleft
Separates the pre and post synaptic membranes, filled with fluid.
Conduction Velocity
How fast AP is propagated
Depends based on axon diameter and myelination
Continuous conduction
Occurs in nonmyelinated axons where voltage-gated channels are adjacent. Relatively slow
Saltatory conduction
In myelinated fibers, depolarizing current jumps from one myelin sheath gap to next, 30 times faster
Axodendritic synapse
Occur between the axon endings of one neuron and the dendrites of another neuron.
Axosomatic synapse
Occur between the axon endings of one neuron and the cell body (soma) of another neuron.
Axoaxonal synapse
Occur between the axon of one neuron and the axon endings of another neuron
Electrical synapse
Allow direct passage of ions and signaling molecules through gap junctions, enabling rapid and synchronized communication (Direct ion movement between neurons)
Chemical synapse
Use neurotransmitters to transmit signals across a synaptic cleft, allowing for more complex and modifiable communication (Involves neurotransmitter release, diffusion, and receptor binding, resulting in unidirectional communication.)
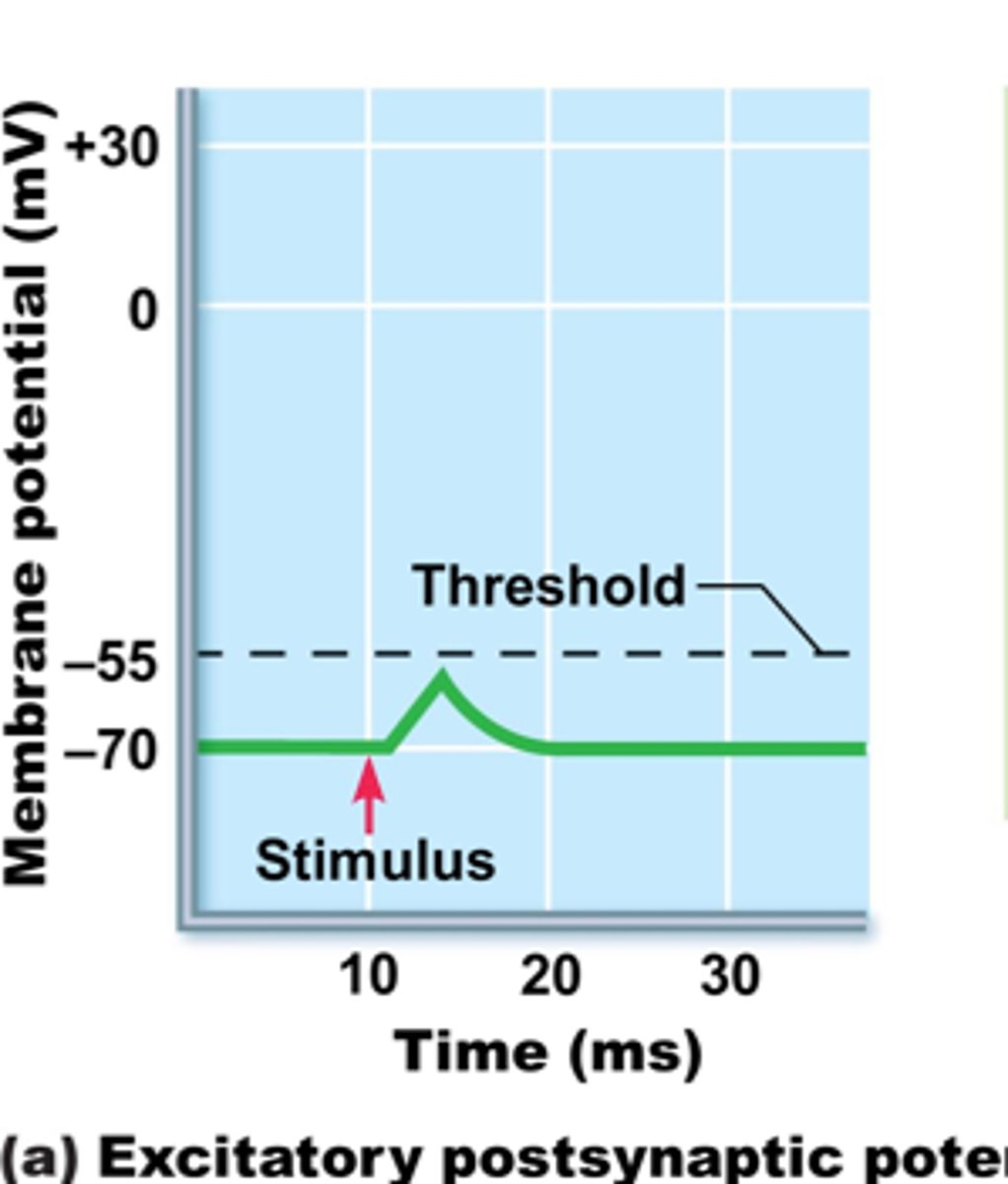
EPSP (Excitatory postsynaptic potential)
- Causes a depolarization
- Likely to reach threshold on a postsynaptic neuron, TOWARD threshold
- “Fire!”
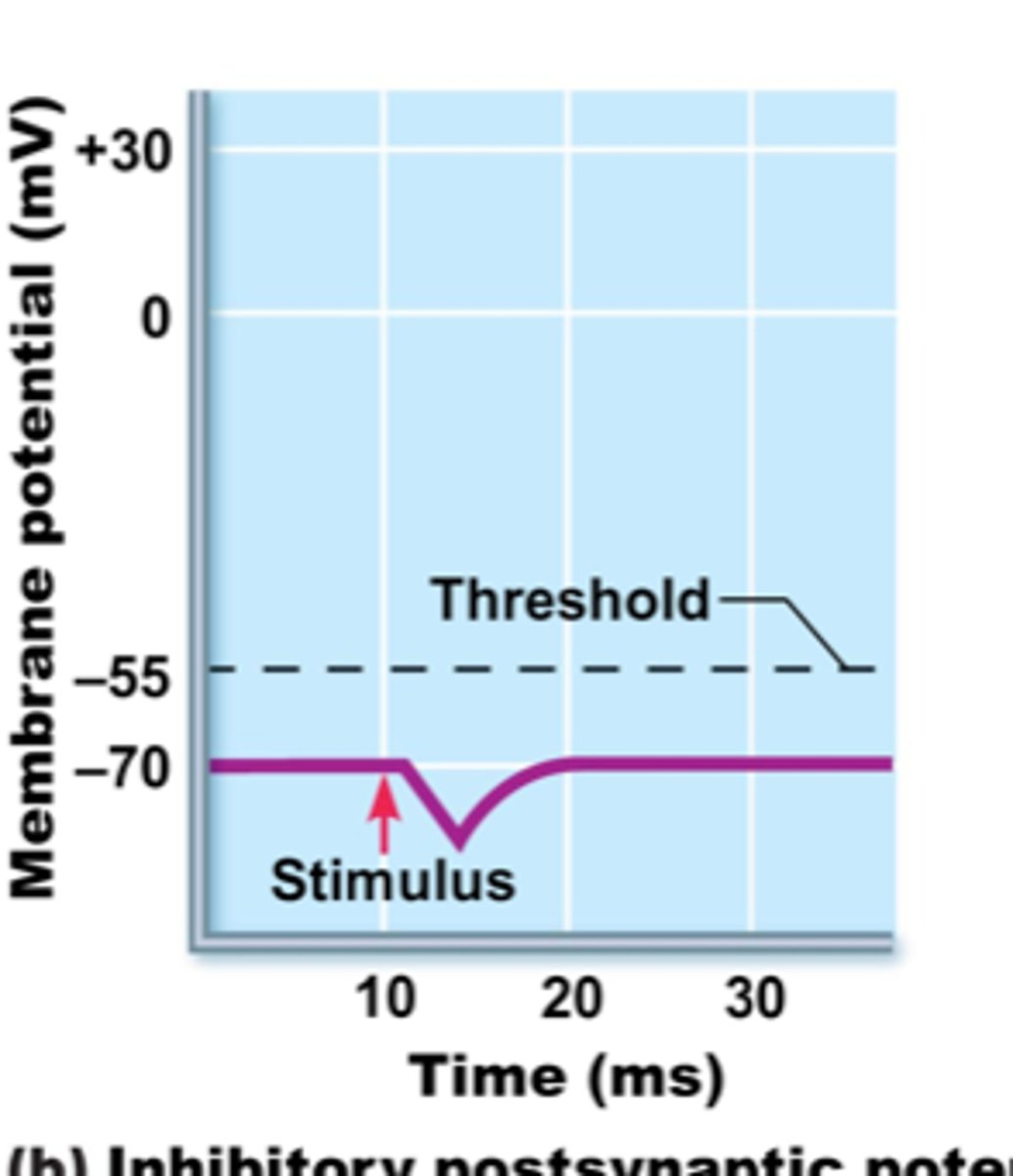
IPSP (Inhibitory postsynaptic potential)
- If a neurotransmitter causes the postsynaptic membrane to hyperpolarize (down)
- AWAY from threshold
- “Don’t fire!”
Neuronal integration
Information-processing, decision-making, and memory mechanisms of neurons
No summation, temporal summation, spatial summation, spatial summation of EPSPs and IPSPs
No summation
- Two ESPS's separated in time, don't add together
- Fire... Fire... Fire...
Temporal summation
- Rapidly firing presynaptic potential causes ESPS's that are close in time
- FireFireFire
Spatial summation
- More than one presynaptic neuron fires at the same time, generated at different locations on the neuron
- Three people saying “Fire!” at the same time
Spatial summation of EPSPs and IPSPs
An EPSP can be overridden by an IPSP
- One saying “Fire!” and one saying “Don’t Fire!”
- Do not reach threshold
Nerve fiber regeneration
- Peripheral nerve fibers (in PNS) can sometimes be regenerated if the soma (cell body) isn't damaged and some of the neurilemma is intact
1. Neurilemma forms a regeneration tube, a new axon goes through it, reestablishes its original connection
2. Regeneration occurs due to reestablished connection
- Muscle cell may atrophy if no innervation