3.1G Colored Complexes
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
What are Ligands?
molecules or ions with a lone pair of electrons that can be donated to a transition metal cation
What are complexes?
Coloured compounds as a result of transition elements bonded with ligands.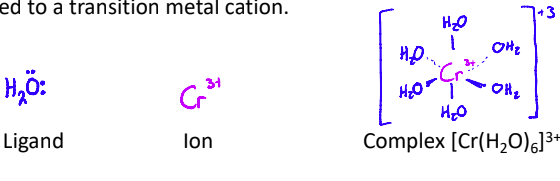
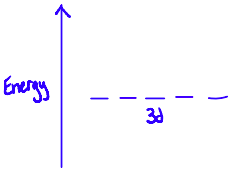
What does it mean if a d-orbital is degenerate? What does this mean for the orbital?
it has no ligands
they are all equal in energy
What happens when a ligand approaches a metal ion?
repulsion between the lone pairs of electrons on the ligand and electrons in the d-orbitals of the transition metal cause the d-orbitals to be split into two sets of differing energies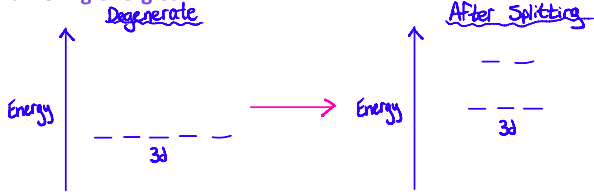
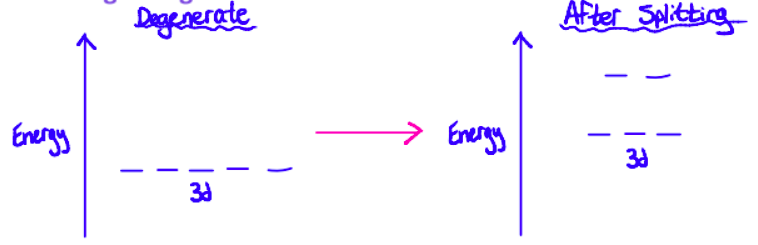
What allows electrons to be promoted to higher energy levels in terms of degenerate d sub-levels? When does this happen?
The differences in energy between the split
this happens when the complex absorbs light with a wavelength that corresponds with the energy gap.
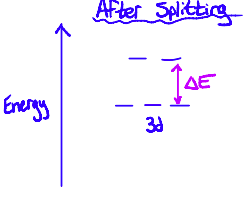
When it comes to the absorbance of light, the observed colour is _____________ to the light that is absorbed
complementary
If red light is absorbed...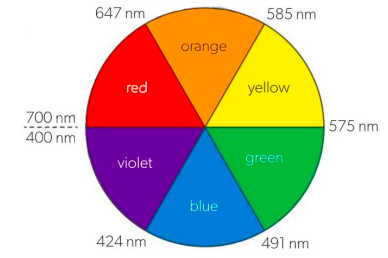
complex appears green!
If yellow light is absorbed...
complex appears violet!
With what equations can we calculate the wavelength of light that would be absorbed for an energy gap (or the other way around)?
E = hf
c = λf
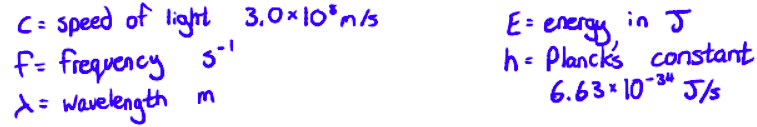
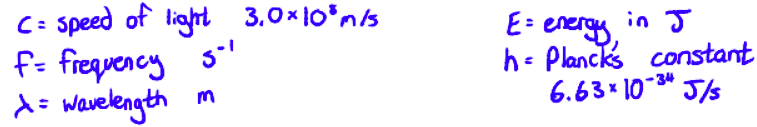
What factors affect the colour of the complex?
Identity of Ligand
The Transition Metal
Why does the identity of the ligand affect the gap between orbitals?
Because ligands that form stronger coordination bonds with the central ion will produce a greater gap between the split d-orbitals.