GCSE EDEXCEL DT: core 1.11 Fibres and textiles
4.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:05 PM on 3/19/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
1
New cards
What are the properties of Fibres and textiles
elasticity resilliance durabily
2
New cards
What are natural fibres ?
From plant sources include cotton, flax, hemp, sisal, jute and coconut. Fibres from animals include silk, wool and mohair.
3
New cards
What are the 2 types of natural fibres
* animal wool
* plant cotton
* plant cotton
4
New cards
Describe Animal wool
From an Animal’s fleece. Made of protein molecules. Produces a short fibre or staple with a crimp or kink which traps air creating warmth.
5
New cards
What are uses of animal wool
Coats, jumpers, suits, blankets, carpets and upholstery.
6
New cards
What are the advantages and disadvantages of animal wool
Advantages
Warm, absorbent, breathable, durable, repels rain, hangs well, creases drop out.
Disadvantages
Dries slowly, susceptible to moth attack, can feel itchy, washes poorly, can shrink and heavy when wet.
Warm, absorbent, breathable, durable, repels rain, hangs well, creases drop out.
Disadvantages
Dries slowly, susceptible to moth attack, can feel itchy, washes poorly, can shrink and heavy when wet.
7
New cards
Describe plant cotton
Machine harvested where saw teeth remove waste from the seed pod and the resulting fibre is called lint. Cellulose makes the fibre strong, durable and absorbent. 20-30 layers of cellulose are coiled in natural springs.
8
New cards
What are uses of plant cotton
Towels, denim, socks, underwear, T-shirts and bedding. Shorter fibres make bandages and insulation
9
New cards
What are the advantages and disadvantages of plant cotton
Advantages
Cool, absorbent, soft, resists abrasion, withstands frequent washing at high temperature, good drape, durable, does not stain easily, static and cling resistant, available in various weights, can be ironed at high temperatures, good colour retention.
\
Disadvantages
Creases easily, burns, shrinks, dries slowly.
Cool, absorbent, soft, resists abrasion, withstands frequent washing at high temperature, good drape, durable, does not stain easily, static and cling resistant, available in various weights, can be ironed at high temperatures, good colour retention.
\
Disadvantages
Creases easily, burns, shrinks, dries slowly.
10
New cards
What are synthetic fibres ?
Artificial fibres are usually made using coal, oil and other petrol-based chemicals. Examples include polyester, acrylic, polyamide (nylon), elastane (lycra) and Kevlar
11
New cards
What are the 2 syntheic fibres ?
polyester
Acrylic
Acrylic
12
New cards
Describe polyester
Simple chemical molecules (monomers) are joined to form polymers by polymerisation. The polymer chains are spun into a yarn.
13
New cards
What are uses of polyester
Raincoats, fleece jackets, children’s nightwear, medical textiles, working clothes.
14
New cards
What are the advantages and disadvantages of polyester
Advantages
Strong when wet or dry, dries quickly, resistant to abrasion, soft, hangs well, durable, crease and stain resistant, easy care, can be recycled, resists bacteria.
\
Disadvantages
Damaged by acids, low warmth, poor absorbency, does not breathe, not environmentally friendly.
Strong when wet or dry, dries quickly, resistant to abrasion, soft, hangs well, durable, crease and stain resistant, easy care, can be recycled, resists bacteria.
\
Disadvantages
Damaged by acids, low warmth, poor absorbency, does not breathe, not environmentally friendly.
15
New cards
Describe acylic
Formed by polymerisation of at least 85% acrylonitrile or vinyl cyanide. The double bond between the first two carbon atoms is broken and the molecules join in a chain.
16
New cards
What are the uses of acrylic
Imitation wool knitwear, upholstery fabrics, sportswear, fleece jackets and blankets
17
New cards
What are the advantages and disadvantages of acrylic
Advantages
Warm, dries quickly, good drape, durable, crease resistant, easy care.
\
Disadvantages
Poor absorbency feels stiff, can irritate skin.
Warm, dries quickly, good drape, durable, crease resistant, easy care.
\
Disadvantages
Poor absorbency feels stiff, can irritate skin.
18
New cards
What are woven textiles
Weaving turns yarns into a fabric on a loom, which has an arrangement of warp (vertical) threads held under tension. The edges where the weft (horizontal) threads loop back form a non-fraying edge (selvedge).
19
New cards
What are the two types of woven textiles
* plain weave: Calico
* Twill weave: Denim
* Twill weave: Denim
20
New cards
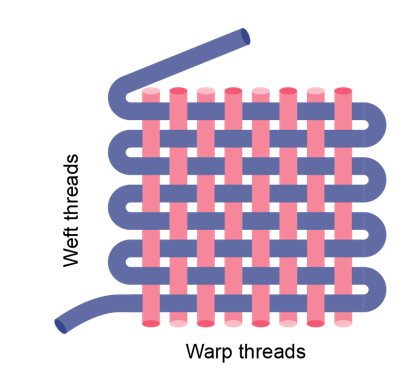
Describe Plain weave: calico
A simple cotton cloth where the warp and weft pass over and under each other forming a criss-cross pattern. Calico (muslin) is naturally grey and can be soft or course.
21
New cards
What are the uses of plain weave-calico
Shirts, bags, bedding and textile crafts
22
New cards
What are the advantages and disadvantages of plain weave :calico
Advantages
Strong, hardwearing, hangs well, same on both sides, cheap to make, creating a good background for printing and applied surface designs.
\
Disadvantages
Firm and varied quality.
Strong, hardwearing, hangs well, same on both sides, cheap to make, creating a good background for printing and applied surface designs.
\
Disadvantages
Firm and varied quality.
23
New cards
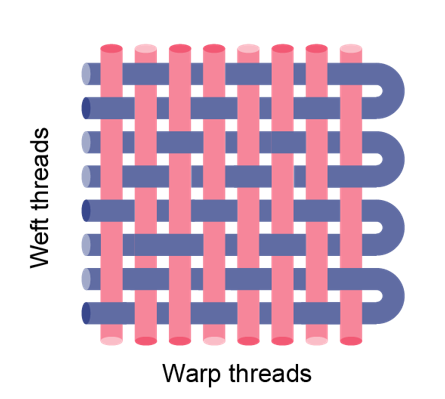
Describe teill weave:Denim
The weft goes over 2 or more warp threads, repeated on the row but steps over one warp thread on the next rows to make a diagonal pattern. Denim is blue in the warp and white in the weft.
24
New cards
What are uses of twill weave:denim
Jeans, jackets, curtains, blankets and soft furnishings.
25
New cards
What are the advantages and disadvantages of twill weave:Denim
Advantages
Hardwearing, strong, hangs well less stiff and more interesting to look at than a plain weave.
\
Disadvantages
Frays, thickness makes it hard to use.
Hardwearing, strong, hangs well less stiff and more interesting to look at than a plain weave.
\
Disadvantages
Frays, thickness makes it hard to use.
26
New cards
What are non-woven textiles ?
Fabrics are layered at different angles to form a web, joined by either felting or bonding. Bonding joins the fibres with heat, solvents or adhesives, so is cheap to produce but not as strong as woven or knitted fabrics
27
New cards
What are the 2 non-woven textiles
* felted wool fabric
* bonded fibres/webs
* bonded fibres/webs
28
New cards
Describe felted wool fabric
Scaly fibres of wool or hair become tangled as they are rubbed together when wet. Heat and pressure is then applied to join them.
29
New cards
What are the uses of felted wool fabric
Pool table surfaces, hats, bags, coats, slippers, applique quilts and wall hangings
30
New cards
What are the advantages and disadvantages of felted wool fabric
Advantages
Resists chemicals and fire, does not unravel or fray, can be repeatedly compressed and released without deforming, excellent sound insulator and environmentally friendly.
\
Disadvantages
Expensive, no drape, not stretchy and deforms when wet
\
Resists chemicals and fire, does not unravel or fray, can be repeatedly compressed and released without deforming, excellent sound insulator and environmentally friendly.
\
Disadvantages
Expensive, no drape, not stretchy and deforms when wet
\
31
New cards
Describe bonded fibres/webs
Does not fray, weaker when wet, can be produced in a range of weights and not very strong.
32
New cards
what are the uses of bonded fibres/webs
Fusible interfacing, wet wipes and disposable overalls.
33
New cards
what are the advantages and disadvantages of bonded fibres/webs
advantages
Does not fray, cheap to produce, stable and retains shape.
\
Disadvantages
Not very strong, does not drape and sometimes weaker when wet.
Does not fray, cheap to produce, stable and retains shape.
\
Disadvantages
Not very strong, does not drape and sometimes weaker when wet.
34
New cards
What are knitted textiles
Knitted textiles are constructed from interlocking loops of yarn and are either warp or weft
35
New cards
What are the types of knitted textiles ?
* warp knitted fabric
* weft - knitted fabric
* weft - knitted fabric
36
New cards
Describe warp - knitted fabric
Formed by vertical loops like a series of chains. It can only be produced on a machine.
37
New cards
what are the uses of warp-knitted fabric
Swimwear, geotextiles, lace, nets and fleece
38
New cards
What are the advantages and disadvantages of warp-knitted fabric
Advantages
Fairly stretchy, retains heat and does not unravel.
\
Disadvantages
Can lose shape and curls at the edges.
Fairly stretchy, retains heat and does not unravel.
\
Disadvantages
Can lose shape and curls at the edges.
39
New cards
What is a weft-knitted fabric ?
A single yarn creates interlocking loops across the fabric. IF a loop breaks, a hole forms and ladders. Made by hand or machine.
40
New cards
What are the uses of weft-knitted fabrics ?
T-shirts, jumpers, tops and socks
41
New cards
What are the advantages and disadvantages of weft knitted fabric
Advantages
Stretchy, comfortable and fast production.
\
Disadvantages
Ladders easily.
Stretchy, comfortable and fast production.
\
Disadvantages
Ladders easily.