UNIT 6 BIOLOGY
1/110
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
111 Terms
biomass
total dry weight of organic matter in organisms or ecosystems
abiotic factor
non living factor eg) rocks, soil, light
biotic factor
living factor eg) other organisms
habitat
place where an organism or group of organisms lives and interact with its surrounding
Ecosystem
biotic and abiotic factors and their relationships with the area
Marram grass adaptations: tolerance to drought
deep roots allow access to water and nutrients during long periods of drought
Marram grass adaptations: tolerance to salt
high levels of salt in sand
Marram grass adaptations: root
strong or anchoring to resist erosion from wind or waves
Marram grass adaptations: leaf
strong and leathery rolled shape stomata tucked in curved side reducing water loss (transpiration)
Marram grass adaptations: sandbinding
traps sand particles in roots and stems to prevent erosion
Marram grass adaptations: Rhizomes
horizontal underground stems that grow bellow surface allows anchor and spread access water and nutrients and stabilise dune
Mangrove adaptations: Salt Tolerance
can tolerate high salinity levels in its habitat. leaves have mechanisms to excrete excess salt, preventing damage to sensitive tissues.
Mangrove adaptations: Aerial Root Systems
Roots emerge from the base of the trunk and extend above the water. Allow plant to breathe in oxygen even when submerged during high tides. helps it survive in the anaerobic conditions of mangrove swamps
Mangrove adaptations: Viviparous Propagules
develops green, cigar-shaped propagules within the calyx of its flowers. These propagules grow into new plants while still attached to the parent tree. Ensures successful reproduction in the challenging intertidal environment.
Mangrove adaptations: Bird-Pollinated Flowers
Large, pale yellow-green to pinkish-orange flowers attract birds. When probed by a bird, the petals release pollen explosively over the bird’s head, aiding in cross-pollination and reproductive success
Adaptations of Plants: Light
insufficient light: ferns and shade tolerant trees grow larger and thinner leaves and increase chlorophyll content to maximise light absorption
Adaptations of Plants: Light 2
too much light: succulents and cacti have thicker waxy skin that helps them retain water and reflect sunlight
Adaptations of Plants: temperature
extreme high: tomato plants have developed heat stock proteins to protect agains high temps
Adaptations of Plants: water
inadequate supply: during drought rice plants reduce water loss by closing their stomata
Adaptations of Plants: Soil
poor soil quality: legumes have developed symbiotic relationships with nitrogen fixing bacteria to obtain nitrogen from air
Adaptations of Animals: Temperature
extreme temps: polar bears + penguins have thick layers of fur or blubber to insulate from extreme cold
Adaptations of Animals: water
fluctuations in water level: camels + kangaroo rats store water in their bodies to survive dry environments
Adaptations of Animals: light intensity
changes in light: bats and owls are active at night to avoid predators and to take advantage of night active prey
Adaptations of Animals: Food
changes in food supply: herbivores adapted to have specialised teeth or digestive systems to extract nutrients from tough plant
Adaptations of Animals: Climate
climate patterns: bats + ground squirrels hibernate during winter months to conserve energy and survive colder temps
Type of Transect: REA
Rapid ecological assessments —> used to quickly document what species are present at a specific location
Type of Transect: BLT
Belt transects —> mainly used to count high numbers of small and abundant fish
Type of Transect: SPC
Stationary Point Counts —> used to count larger (<25cm total length) and more active fish species
Type of Transect: TDVS
Towed-Driver video Surveys —> used to count larger (<50cm total length) and more active fish species
Conditions for Coral Reef Formation: Water depth
light only penetrates to relatively shallow depths, zooxanthellae are photosynthetic
Conditions for Coral Reef Formation: Water temp
corals only survive in narrow range of water temps. Global warming is resulting in temperature that are too warm for corals to tolerate when too warm corals expel zooxanthellae —> coral bleaching
Conditions for Coral Reef Formation: Salinity
corals need correct amount of salt water around them, areas with freshwater run-off may not be of correct salinity.
Conditions for Coral Reef Formation: Water clarity
water needs to be clear for light to pass through, if there is a lot of sediment or pollution in the water the clarity decreases and zooxanthellae may not receive enough light
Conditions for Coral Reef Formation: Water pH
increased CO2 from fossil fuel emissions is being absorbed into ocean water resulting in a lowered pH that is detrimental to coral growth, acidification results in less calcium carbonate compounds being available in water from corals to use when building reefs
Zooxanthellae
algae that live in corals and provides nutrients - mutualistic relationship with coral
Biomes
large geographical area that contains communities of plants and animals that are adapted to living in that environment
Life in Hot Deserts: Plant Species
Saguaro Cactus: native to Sonoran desert in southwestern United States
Adaptations:
thick waxy skin (waterproof)
bristles for defence
single long taproot to collect water when available
water stored in sponge like material
Life in Hot Deserts: Animal Species
Fennec Fox: native to desert areas of Sahara North America
Adaptations:
very large eats, highly vascularised to help remove heat and to help locate small prey animals underground
nocturnal hunters
spend day in underground dens (for shade)
kidneys reabsorb most of water that passes through and rarely urinates
Life in Rainforest: Plant Species
Kapok tree: located in Costa Rica and the Amazon
Adaptations:
competition for rain water and sunlight is high in rainforests
grow very tall and create part of canopy layer
large buttress roots form strong foundation for rapid growth of tall trunk or shallow soil
Life in Rainforest: Animal Species
Harpy Eagle: native to Central and South America
Adaptations:
binocular vision allows accurate judge of distances and tracking of fast moving prey
strong and sensitive hearing allow detection of sound of prey moving
sharp beak allows capture and feeding on large prey
broad strong wings enable movement through dense forest canopy with ease and glide through air silently
strong talons to crush skulls of prey
Niche Paritioning
process by which competing species use the environment differently in a way that helps them coexist (may be spatial or temporal)
Competition
occurs when two or more organisms fight for the same limited resource (such as food, space, light, or mates) in an ecosystem.
Intraspecific Competition
within the same specie
Interspecific Competition
between different species
Predation
biological interaction where one organism, the predator, hunts, kills, and eats another organism, the prey. This interaction benefits the predator but is fatal for the prey. Killing + eating prey or eating something that has recently died (scavenging)
Mutualism
2 species providing food or other resources where both benefit
Parasitism
Symbiotic relationship where one organism, the parasite, lives on or in a host organism and derives its nutrients at the host's expense. The parasite benefits, while the host suffers harm, though it is usually not immediately killed.
Obligate Anaerobes
single celled organisms that have no tolerance in the presence of O2, live in places like soil, deep water, animal intestines, use alternative elements for electron acceptor
Facultative Anaerobes
carries out both anaerobic and aerobic respiration, can switch depending on availability of O2
Obligate Aerobes
require oxygen and cannot convert food nutrients into energy without it —> fish
Autotrophs
produce their own food through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis
Heterotrophs
consume food source
Holozoic nutrition
ingesting all or part of an organism, type of Heterotrophic nutrition
Mixotrophic Nutrition
Can make and ingest their own food, type of Heterotrophic nutrition
Faculative Mixotrophs
can survive in 1 system but use other as supplement
Obligate Mixotrophs
need both auto and heterotroph systems to thrive
Saprotrophic Nutrition/Saprotrophs
secrete digestive enzymes and then absorb the products of digestion, capable of breaking down dead organic material, decomposers
chemosynthesis
generating energy from reactions involving chemical compounds (chemoautotrophs)
Incisors
cut into food
Canines
used for ripping and tearing tougher materials
Premolar
crushing or slicing food
Molar
grinding food and reducing it to a paste before swallowing
Adaptations of Predators: Chemical
some predators inject chemicals into their prey while others use chemicals to attract prey to their hunting grounds
Black mamba: injects prey with paralysing neurotoxins
Orb-weaver Spiders: release a chemical that mimics sex pheromones of moths then wait for prey to arrive
Adaptations of Predators: Physical
predators have adapted sensory organs that provide advantages to catching prey
Owls: low light vision for night hunting
Bats + Dolphins: echolocation
Vultures: keen sense of smell
Sharks: organs called ampullae of Lorenzini register electromagnetic fields for finding prey
Adaptations of Predators: Behavioral
Ambush predators: hiding and waiting for prey then attacking, web building spiders, angler fish with illicium
Pack hunting: teamwork to attack prey often larger than predator, wolves must have a leader to create trust, wasps, ants, bees, termites
Pursuit predator: rely on speed to outrun prey, cheetah
Persistence hunting: pursuing prey for several hours until they fatigue, humans living as hunter gatherers
Adaptations of Prey: Chemical
prey may produce chemicals to deter a predator such chemicals taste bad or are toxic, poison dart frogs secrete an alkaloid on their skin that interferes with muscle function, including the heart which can lead to death
Adaptations of Prey: Physical
Camouflage: taking on the appearance of the organism’s surroundings, some octopi can change their colour and skin texture
Aposematism: coloration that warns predators of prey’s danger, poison dart frogs bright colours, non-venomous king snakes look like venomous coral snakes
Adaptations of Prey: Behavioural
fleeing at the sight of a predator
Staying in Large Groups: when attacked by predators elephants form a tight group with smaller elephants in the middle and large elephants on the outer edge
Canopy
most of the crowns (tops) of trees are found. trees position leaves far from ground to gain maximum exposure
Understory
shorter trees
Shrub layer
shortest trees and shrubs
Forest floor
small non-woody plants often has full shade
Harvesting light from: Lianas
are vines that cannot build trunks large enough to reach the canopy
use trees to climb and reach canopy
seedlings are attached to shade and are drawn towards tree for support
roots in soil
eg) Kudzu
Harvesting light from: Epiphytes
use tree for support and access to sun
roots are not in soil
eg) orchids
Harvesting light from: Shade-tolerant shrubs
grow on forest floor
absorb remaining light after passing through other leaves
Herbaceous plants (no woody stem) are often shade tolerant
eg) bananas
population
a group of organisms of the same species living in the same geographical area at the same time and are able to interbred
Systematic Sampling
when a line or grid is set up and measurements or counting are carried out as specific and regular intervals
Random Sampling
Arbitrary chosen areas of the population are selected for sample, removes bias from selecting particular areas
Sampling sessile organisms
random sampling
sessile organisms: plants, coral
quadrant sampling: square of particular dimension maintains consistent surface area for fair comparison
Sampling motile organisms
CMRR method
sampling technique allows an estimate of animals in ecosystem
Capture, Mark, Release, Recapture method
capture some individuals in a given space
mark them
release them back into the ecosystem
wait a given amount of time
capture a second sample
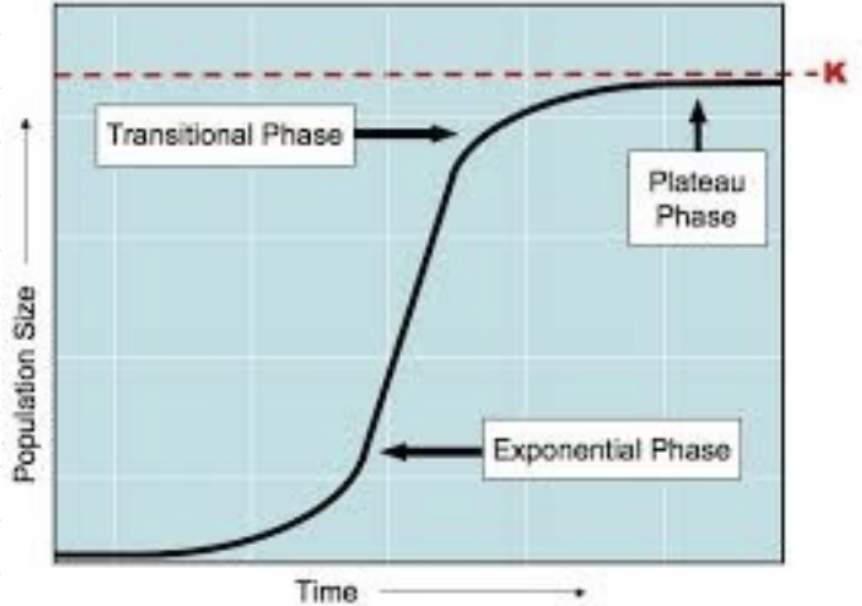
Carrying Capacity = K
maximum number of individuals that a particular habitat can support —> environments can only allow a population to get so large before resources result in established population size
Limiting Factor
Limiting factors are those that prevent a population from getting bigger or reduce a population’s size. density dependent + density independent
Positive feedback systems
Something increasing the population that the system encourages - more of the same
Negative feedback systems
prevents system from going too far in 1 direction leads to carrying capacity
Population growth curves
exponential phase: number of individuals increases at a increasingly faster rate
transitional phase: growth rate slows down considerably but still increases
plateau phase: stationary phase number of individuals stabilises no more growth
Community
a group of populations in an area including plants, animals, fungi and bacteria living and interacting with each other in an area
herbivory
eating plant material
Pathogenicity
ability of microbes such as bacteria and viruses to cause disease in other species
Endemic
a species found only in one location in the world
Invasive
introduced into a new area from a distant origin and their populations grow so well they cause problems for the species already living their
Top-down controls (of Population)
seen when a species can be reduced by other species feeding on it. herbivory for plant populations - the more eaten the smaller the population
Bottom-up controls (of Population)
seen when a species population can be decreased by lack of resources eg) food, sunlight, or minerals
Allelopathy
production of secondary metabolites that influence growth and success of other organisms
primary metabolites
molecules needed for basic functions
secondary metabolites
molecules produced to impede or kill competitors
photoautotrophs
producers that use sunlight as their energy source
chemoautotrophs
producers that use chemosynthesis for their energy source usually found in ecosystems with no light
trophic levels
indicate how many organisms the energy in a system has travelled through — a method of classification of organisms based on its feeding relationship with other organisms
food chains
linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass as one organism eats another