Chemistry - Functional Groups
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
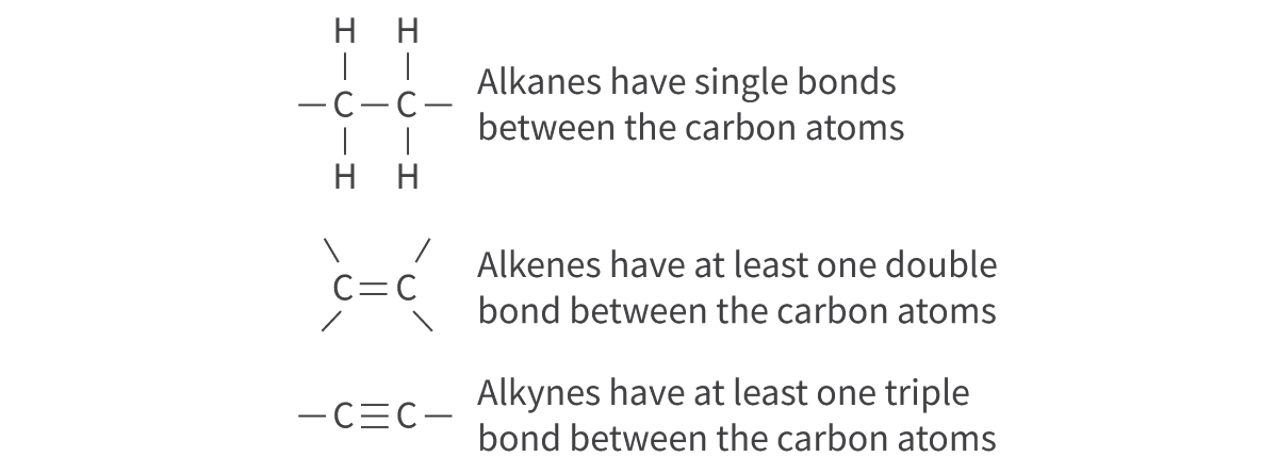
Hydrocarbons: Types
molecules composed of carbon and hydrogen only
ex: alkanes, alkenes, alkynes
Alkanes
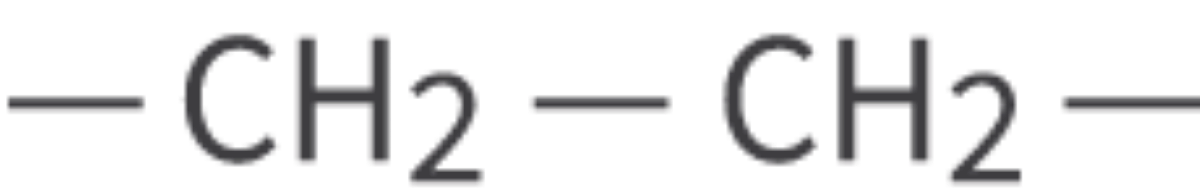
saturated hydrocarbon: single covalent bond between carbon atoms, straight chain

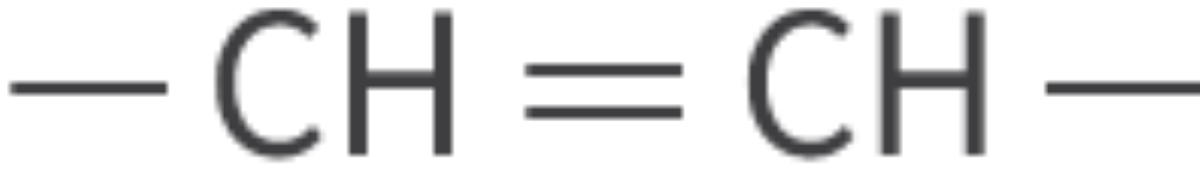
Alkenes
unsaturated hydrocarbon: double bonds between carbon atoms


Alkynes
unsaturated hydrocarbon: triple bonds between carbon atoms


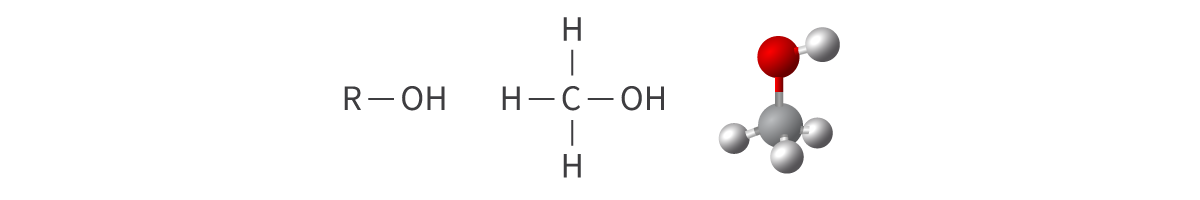
Alcohols
hydroxy functional group: oxygen atom bonded to a hydrogen atom
a single covalent bond
Bond: OH
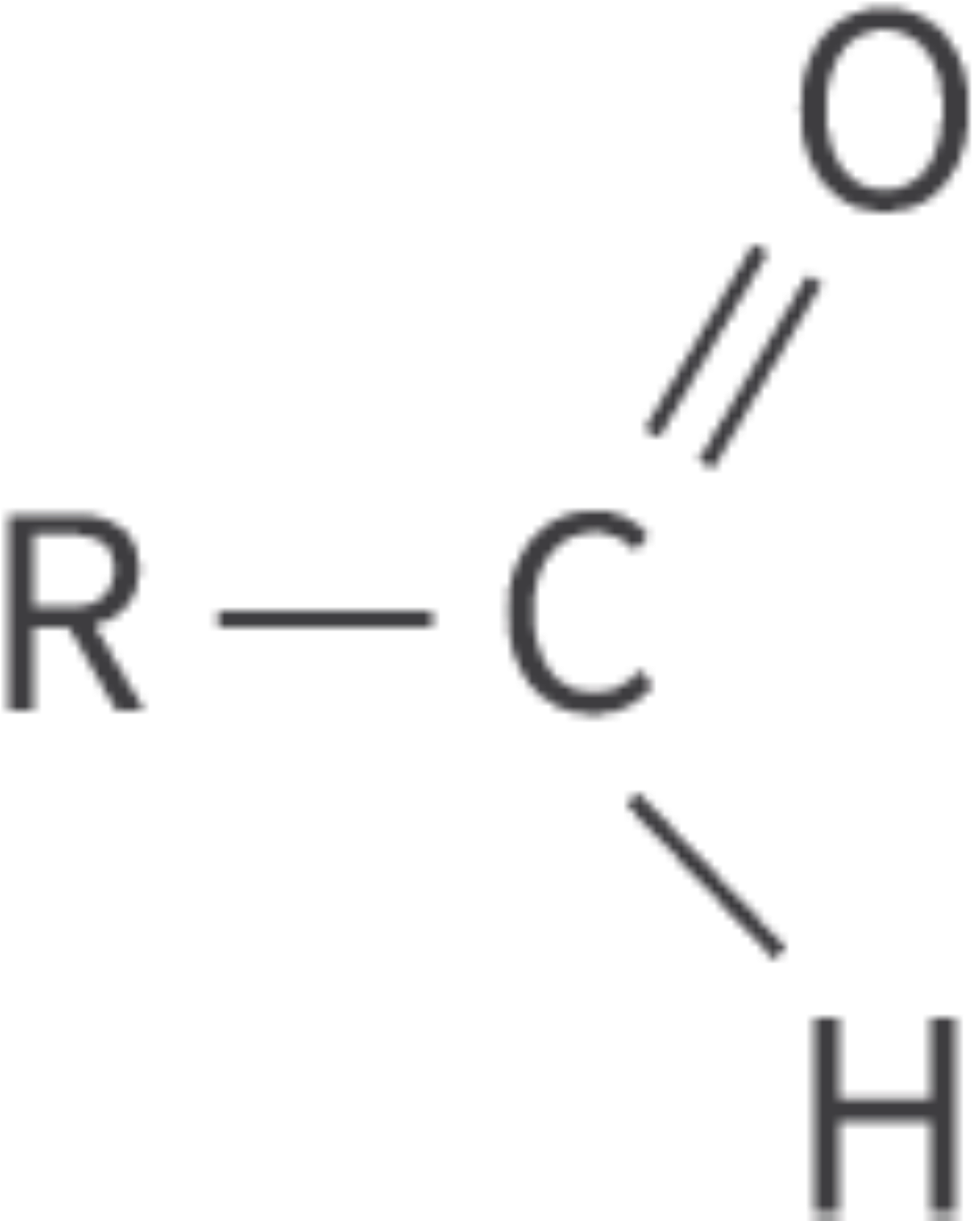
Aldehydes
carbonyl functional group: carbon atom bonded to an oxygen atom
double bond
carbonyl group in terminal position
Bond: C=O at terminal
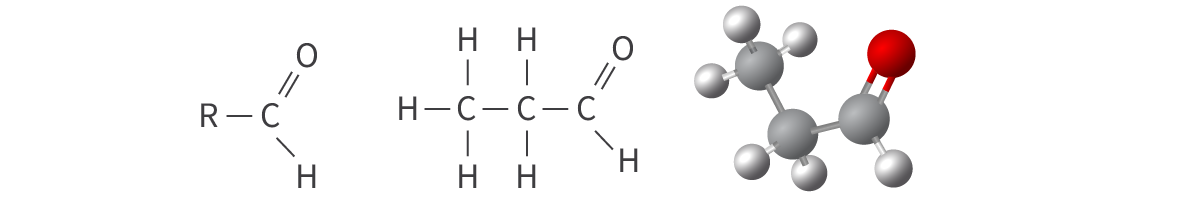
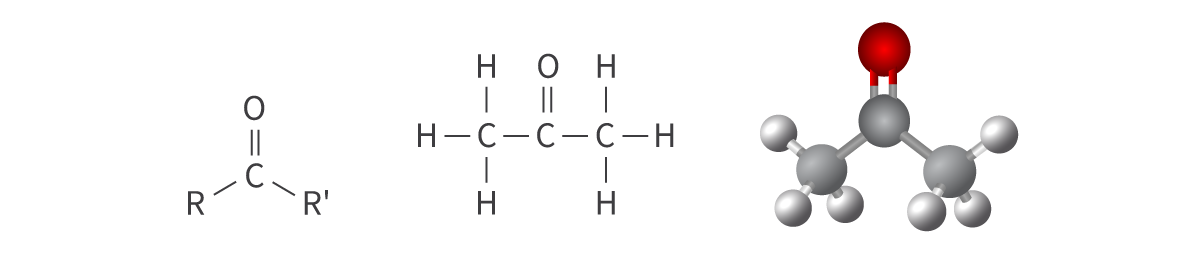
Ketones
carbonyl functional group: carbon atom bonded to an oxygen atom
double bond
Bond: C=O within carbon chain
(also called alkanones)
Carboxylic acids
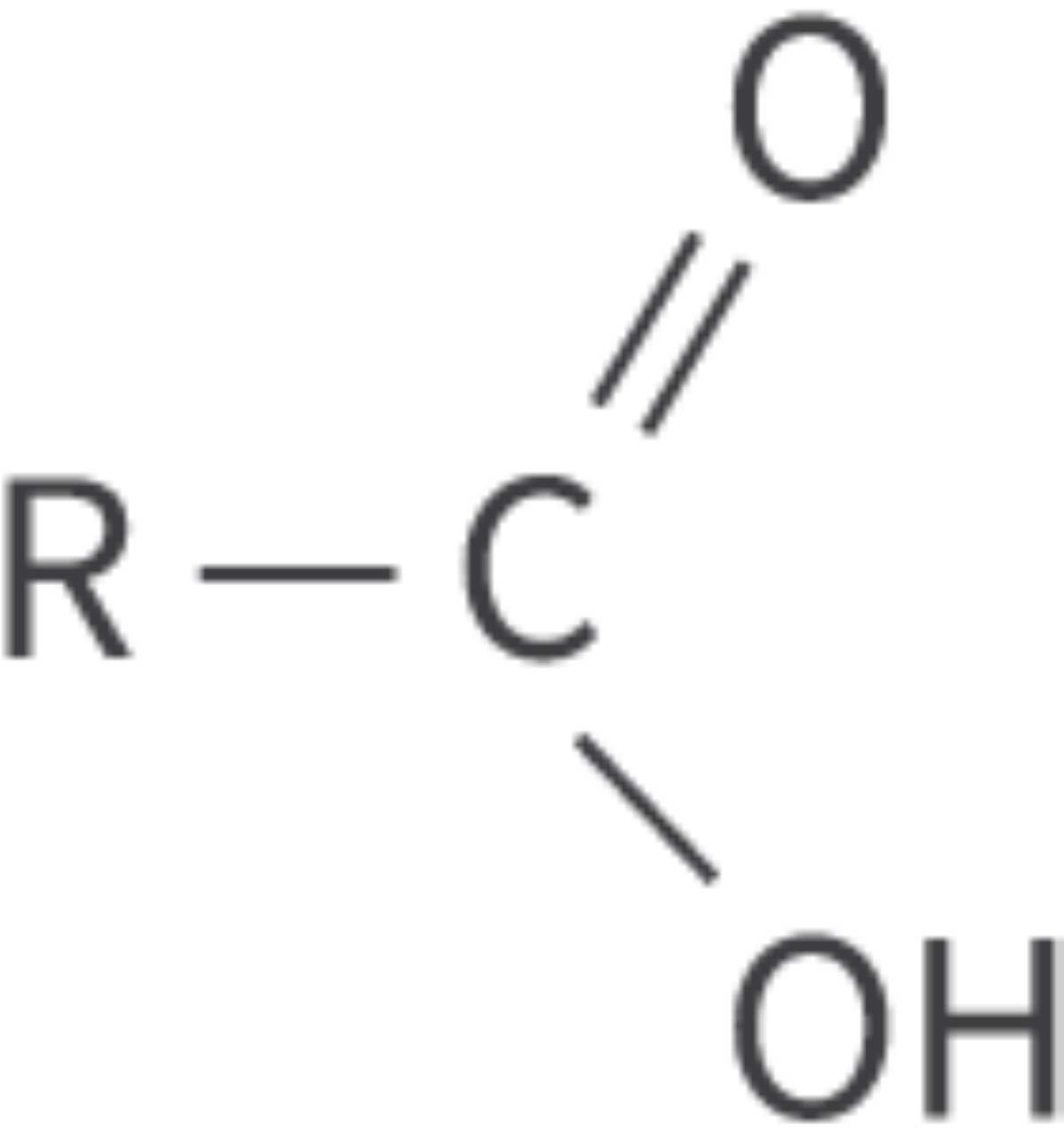
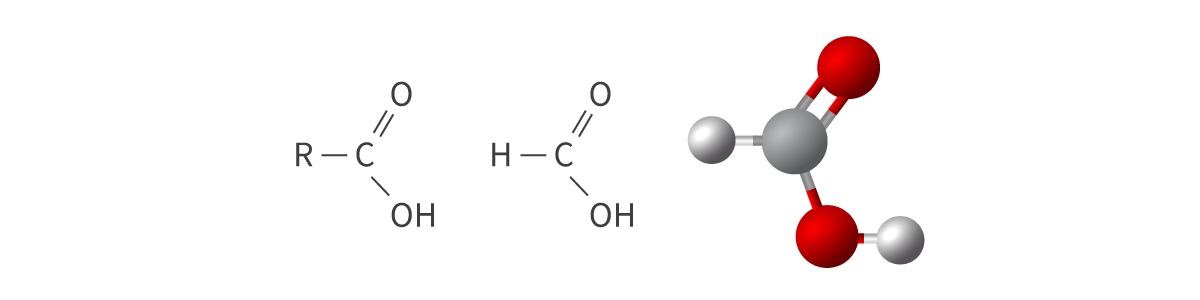
carboxyl functional group (carbonyl group + hydroxyl group)
carboxyl (C=O) + hydroxyl (OH) → COOH or CO2H
Bond: COOH or CO2H
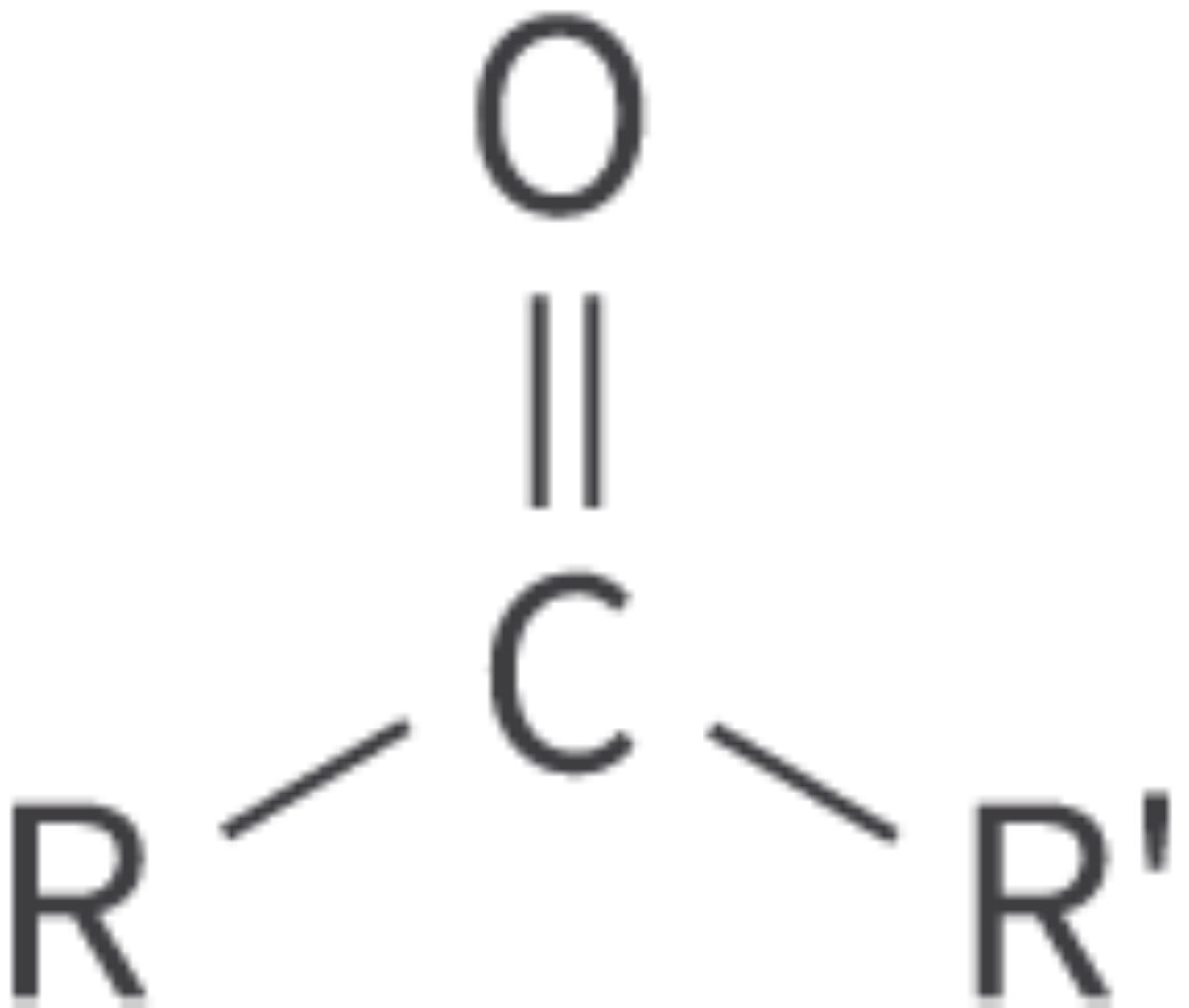
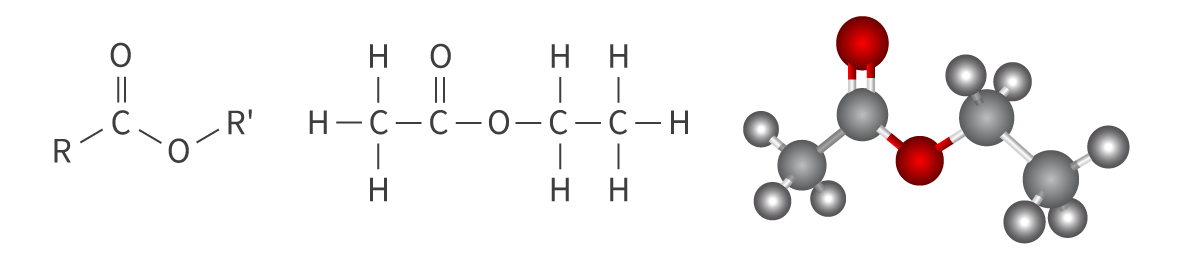
Esters
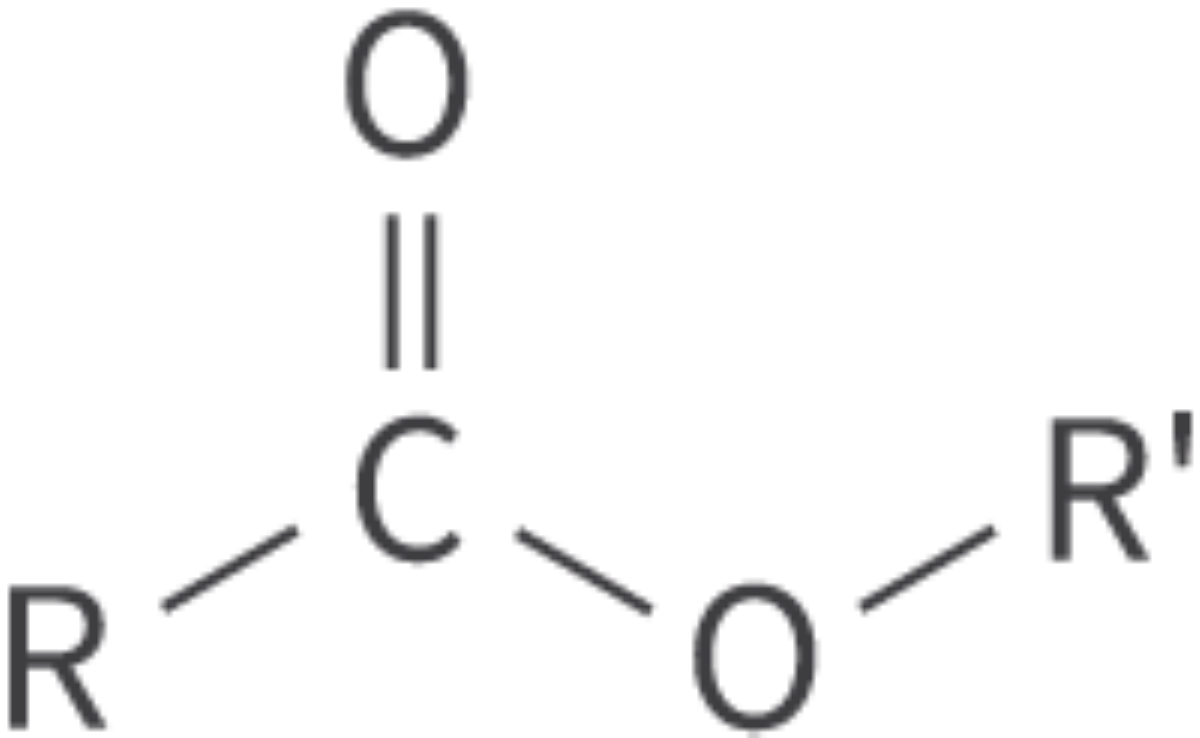
ester functional group
carbonyl group bonded to oxygen atom
single bond, asymmetric
pleasant tastes and smells
Bond: RCOOR'

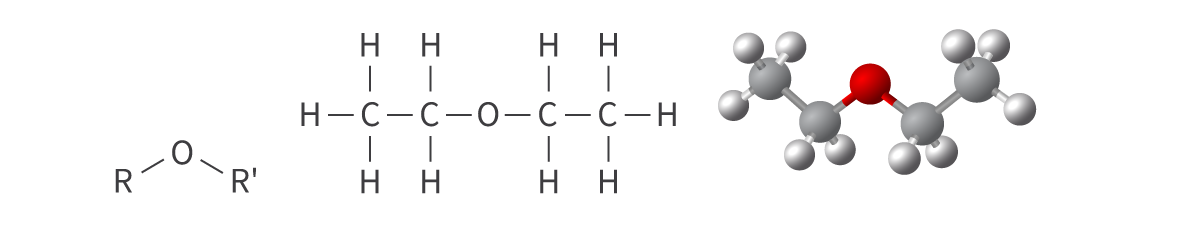
Ethers
alkoxy functional group
oxygen atom bonded to 2 alkyl groups
Bond: R–O–R’
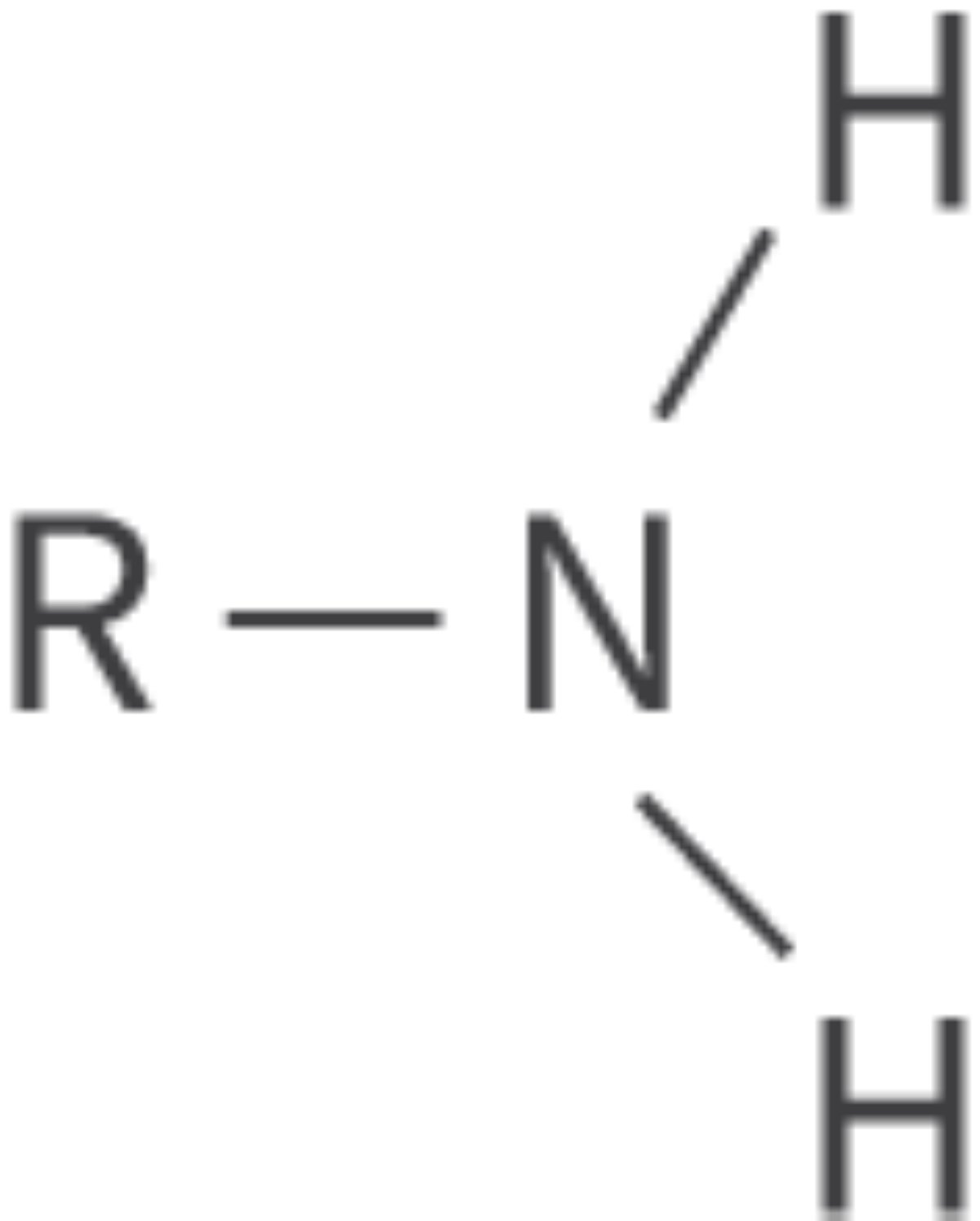
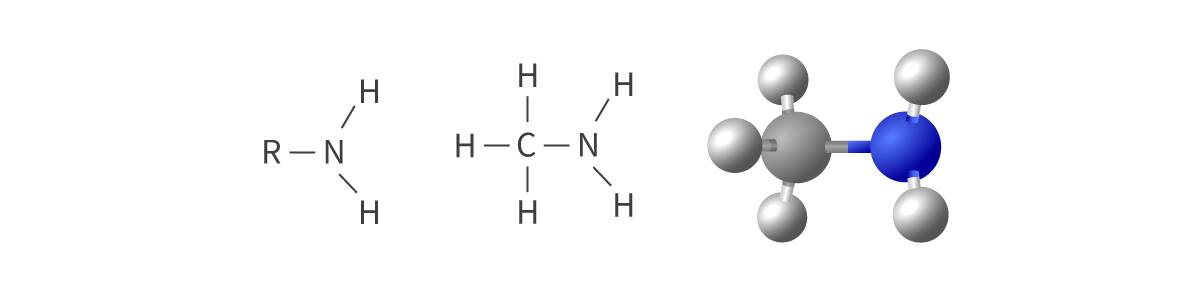
Amines
amino functional group
nitrogen atom bonded to hydrogen atoms or alkyl groups
derivatives of ammonia; can be either primary, secondary, or tertiary
nitrogen atom has a lone pair of electrons
Bond: R–NH2
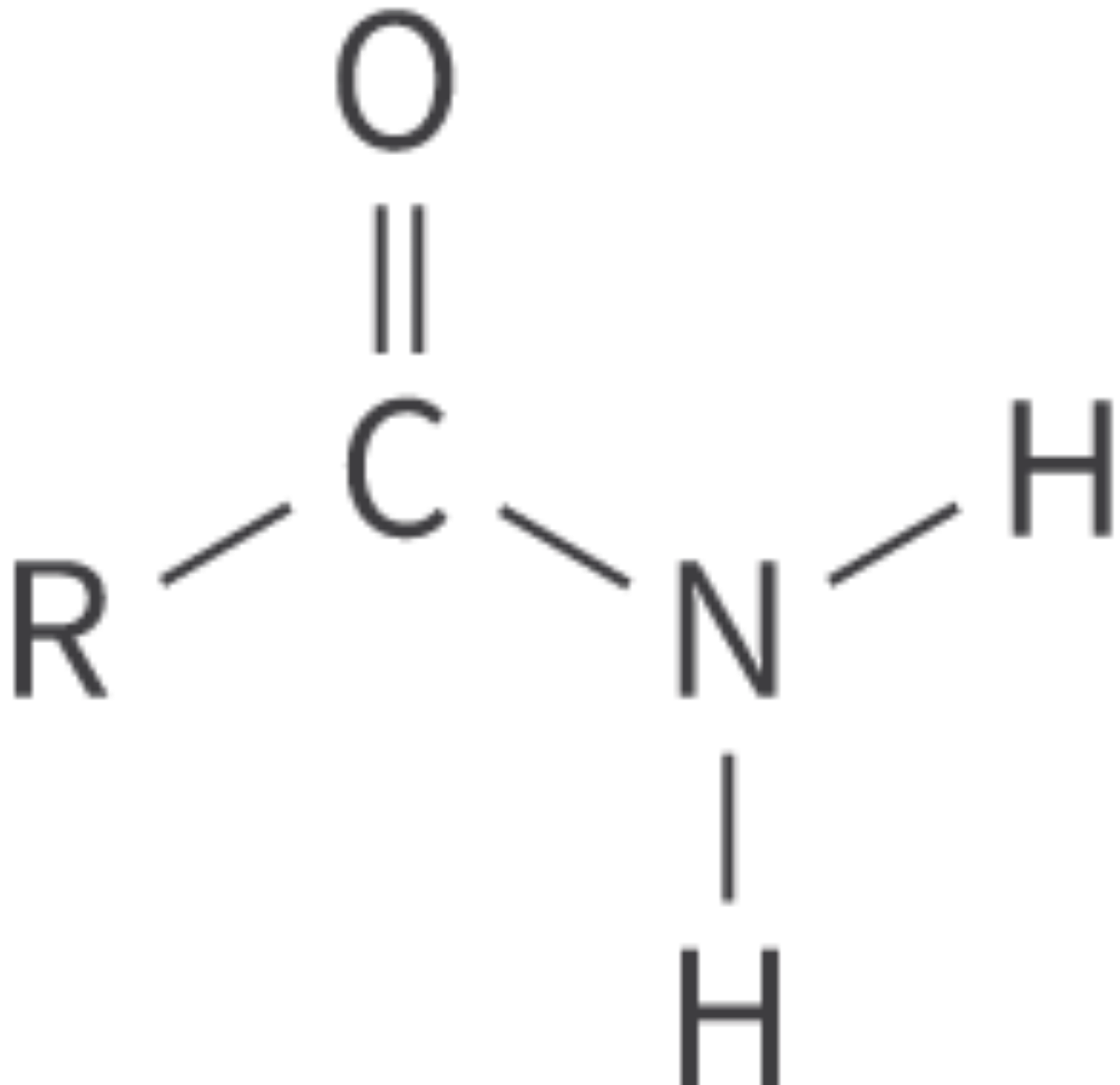
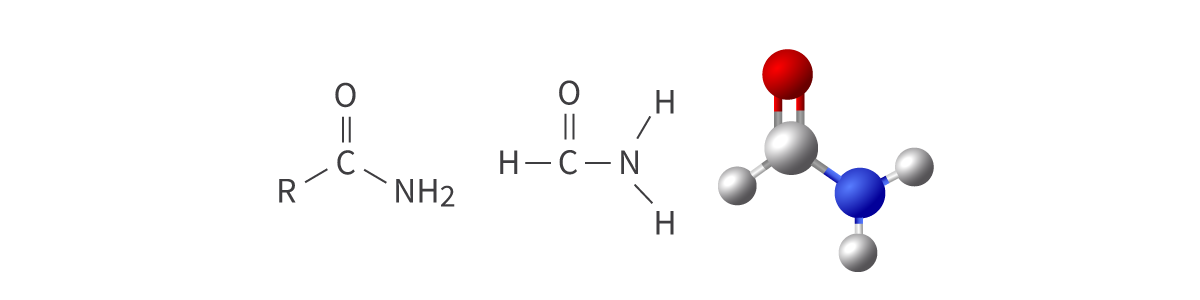
Amides
amido functional group
carbonyl group bonded to amino group
derivatives of ammonia; can be either primary, secondary, or tertiary
Bond: R–CONH2
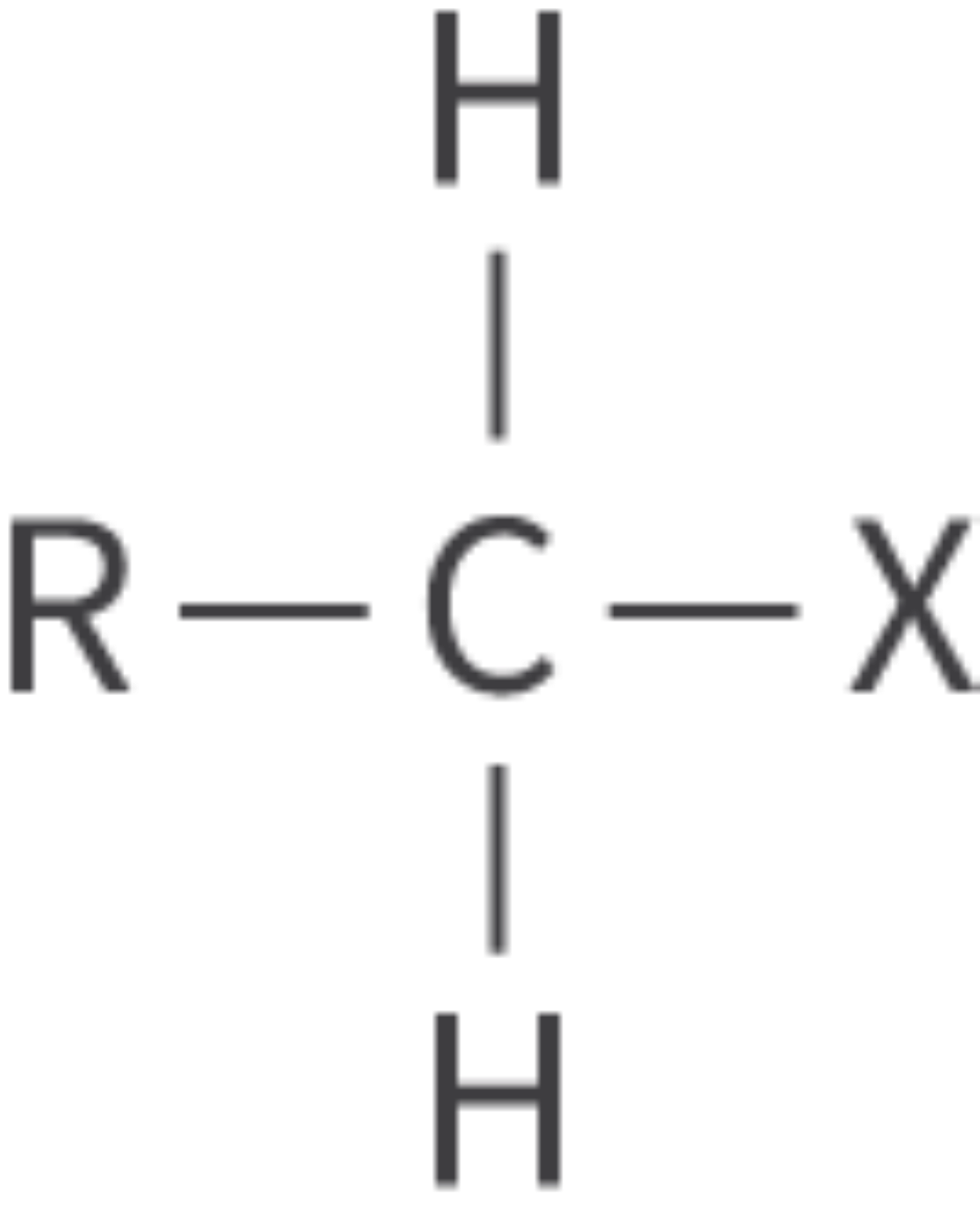
Halogenoalkanes
halogeno functional group
alkanes in which one or more hydrogen atoms are replaced with a halogen atom
fluorine, chlorine, bromine or iodine
Bond: R–X
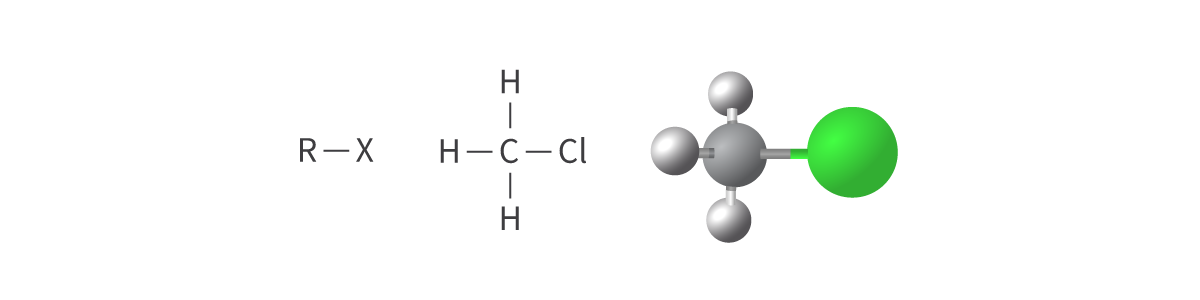
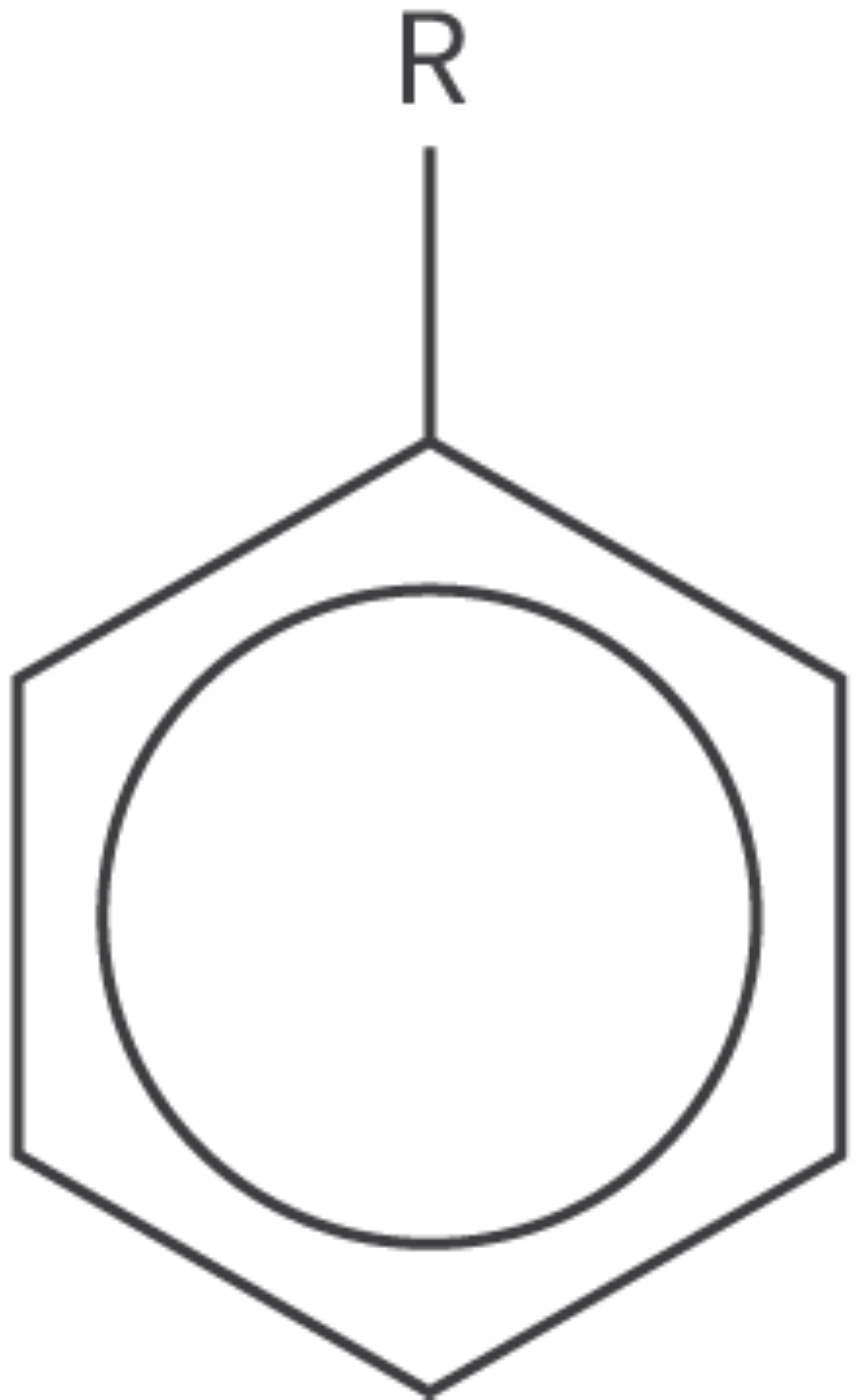
Arene
phenyl functional group
cyclical structure
6 carbon atoms + 5 hydrogen atoms
benzene ring minus hydrogen atom
aromatic hydrocarbons
Primary Alcohol Oxidation
2-step oxidation
aldehyde (carbonyl group): lose 2 hydrogen, C=O double bond
carboxylic acid (carboxyl group)
Secondary Alcohol Oxidation
1-step oxidation
keytone (carbonyl group), C=O bond not in terminal position
Nucleophile
electron-rich species attracted to regions of positive charge (nucleus)
Electrophile
proton-rich species attracted to regions of negative charge (electrons)
Nucleophile Reducing Agents
Hydride ion H- reducing agents:
Sodium Borohydride NaBH4- for aldehyde and ketones
Lithium Aluminium Hydride LiAlH4- for carboxylic acid
explodes in water, reactive, use in low temperature and dry conditions, high yield
2-steps:
Reducing agent or nucleophile, above “→”
H+ (aq) acidified solution, exothermic, below “→”
Oxidizing Agents
Potassium Dichromate(VI) K2Cr2O72-
permanganate ion, MnO4-
Hydrogenation
Chemical reaction between molecular hydrogen (H2) and another compound or element, usually in the presence of a catalyst such as nickel, palladium or platinum
Halogenation with halogens
Bromination with bromine
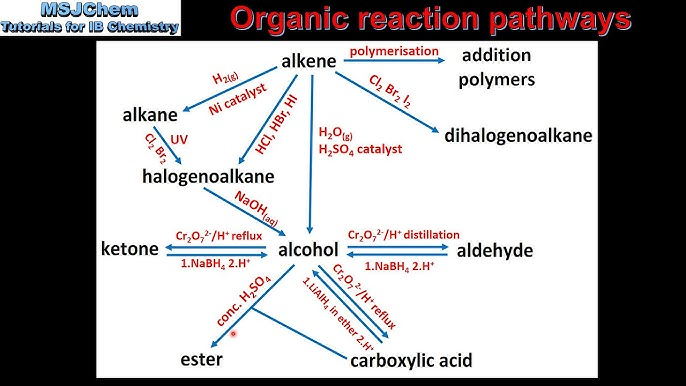
Organic Reaction Pathways