Groups in Periodic Table
1/14
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
What is a periodic table?
A list of elements arranged in order of increasing atomic number.
What are metals and non-metals?
Elements can be classified based on their properties, with metals typically being shiny, malleable, and forming bases, while non-metals form acids.
Define alkali metals.
Group 1 elements in the periodic table with properties like silvery appearance, low density, and reactivity with water to form metal hydroxide and hydrogen.
Define Halogens.
Group 7 elements in the periodic table, non-metals occurring as diatomic molecules, with trends of increasing color darkness and melting/boiling points down the group.
Define noble gases.
Group 8 elements in the periodic table, inert gases with full valence shells, unreactive due to their stable electron configuration.
What are Physical Properties of grp 1 metals?
Silvery/shiny when freshly cut
Soft (easily slice with a knife) – become softer as you move down the group
Low density – float on water
Conduct electricity
Chemical properties of group 1 metals.
They react with water to give a metal hydroxide and hydrogen
They become more reactive with increasing atomic number (as you go down the group)
Why is there a similarity in chemical properties within a group?
due to all members having the same number of electrons in the outer shell.
Li + H2O
2Li(s) + 2H_2O(l) → 2LiOH + H_2(g)
Na + H2O
2Na(s) + 2H_2O → SNaOH(aq) + H_2(g)
K + H2)
2K(s) + 2H_2O(l) → 2KOH(aq) + H_2(g)
Trend of reactivities of halogens.
They become less reactive as you go down the group
Trends of physical property in group 7
They become darker in color
Their melting point/ boiling point increases (hence the gradual change in state at room temperature from gas to liquid to solid)
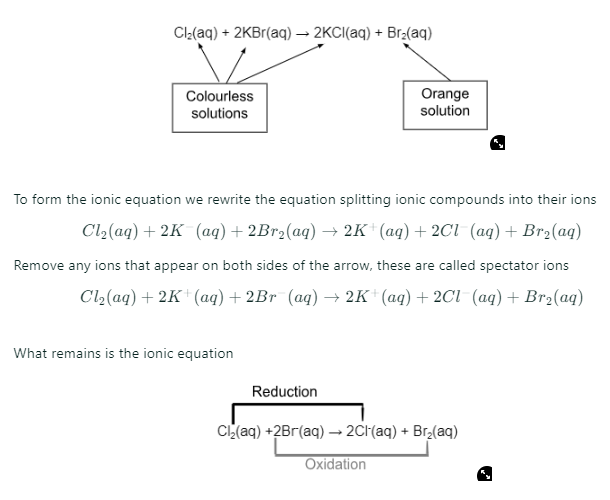
Chlorine + Potasssium Bromide
Why are group 8 elements unreactive?
They are very unreactive because they all have full valence shells and hence have a valency of 0.