Alimentary 2: Stomatides and Oral Tumors
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
What are the 5 viral causes of Vesicular Stomatitides?
FMD
Vesicular Stomatitis
Swine Vesicular Disease
Vesicular Exanthema
Senecavirus A
Why is FMD also known as Apthous fever?
It is caused by a apthovirus
Which animal is a disease indicator for FMD? What is a disease indicator animal?
Cattle
It means they are the species we the disease in the most
Which species is the Amplifying host of FMD?
Pigs
They excrete large quantities of virus
How does FMD affect horses, if at all?
FMD doesn’t affect equids
How does FMD affect sheep/goats, if at all?
They are maintenance hosts
They show little to no C.S
They will spread the disease without showing it
T/F: FMD has a high morbidity and mortality
False, just a high morbidity (“on of the most infectious animal diseases in the world“)
FMD affects which animals the most?
Ruminants and pigs
What are the Clinical Signs of FMD?
Vesiculoulcerative skin/oral lesions
Oral Lesions
Profuse salivation/drooling
Foot Lesions
Lameness
Stamping of feet
Walking weird
Teat Lesions
Decrease in milk production
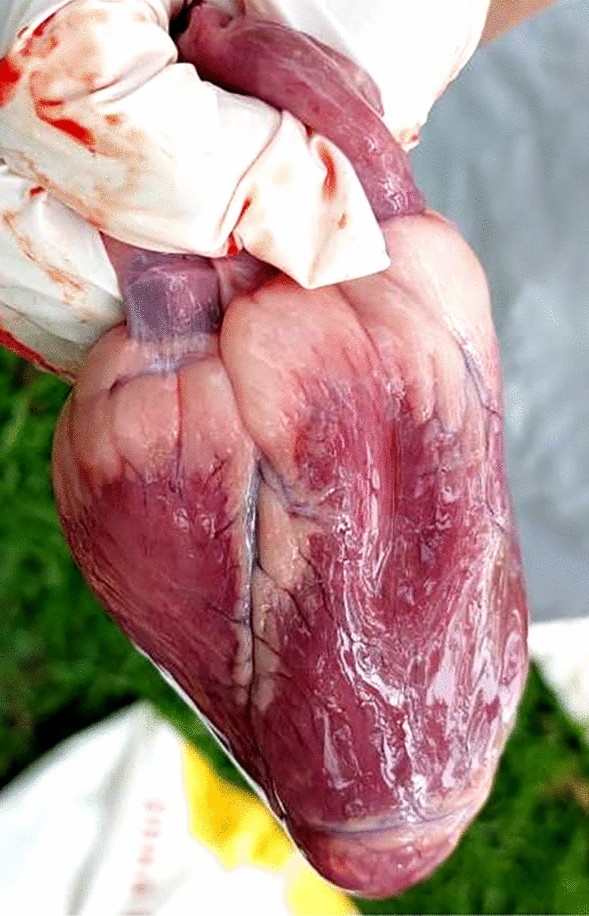
Heart Lesions
Sudden death in young calves (neonate/calves only)
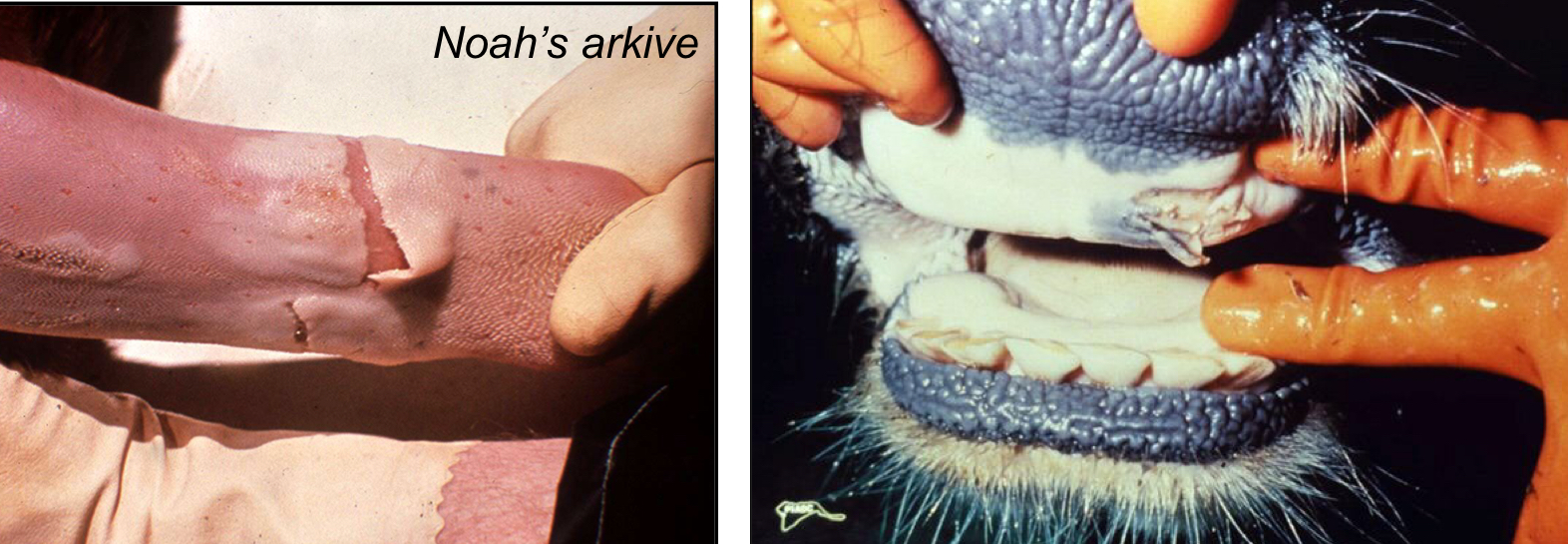
What additional C.S of FMD can only be seen in infected neonates?
Myocardial degeneration/Myocarditis → Acute Heart Failure
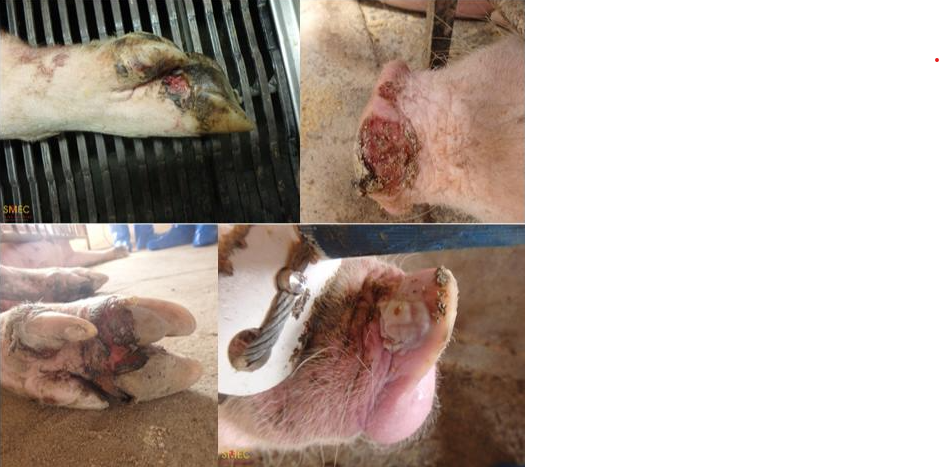
A common complication of FMD is _____ separration
Hoof Separation (the result of rupture of vesicles on the hoof)
T/F: Vesicular stomatitis is always indistinguishable from FMD
False and True
True in ruminants
False if a horse is infected, FMD cannot infect horses but vesicular stomatitis can!
T/F: All vesicular diseases should be assumed to be FMD until proven otherwise
True
How is Swine Vesicular Disease (SVD) different from Vesicular Exanthema (VE) or Senecavirus A (SVA)?
Swine Vesicular Disease (SVD)
Only infects pigs
Vesico-ulcerative lesion on the feet, less often in other areas
Exanthema (VE)
Only infects pigs
Eradicated (historic importance)
Senecavirus A (SVA)
Only infects pigs
Key distinction: can cause severe neonatal mortality (up to 30–70%) with vesicles sometimes absent in piglets
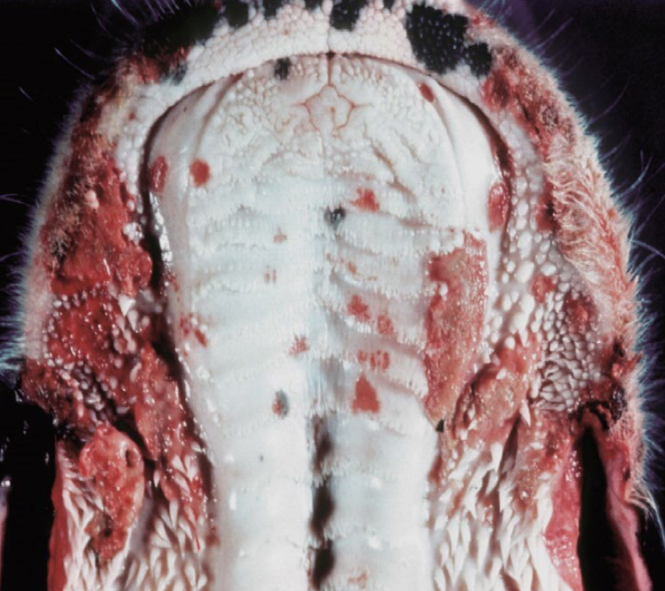
What is the difference between an Ulcer and an Erosion?
Ulcer
Penetrates the epidermis and affects the dermis too
Erosion
Damage just in epidermis
T/F: For erosive and ulcerative stomatitides, ulcers will often develop without first being a vesicle
True
Bovine ______ ______ causes erosive/ulcerative stomatitides
Bovine Viral Diarrhea
T/F: Renal issues can result in the development of oral ulcers
True, they’re called uremic ulcers
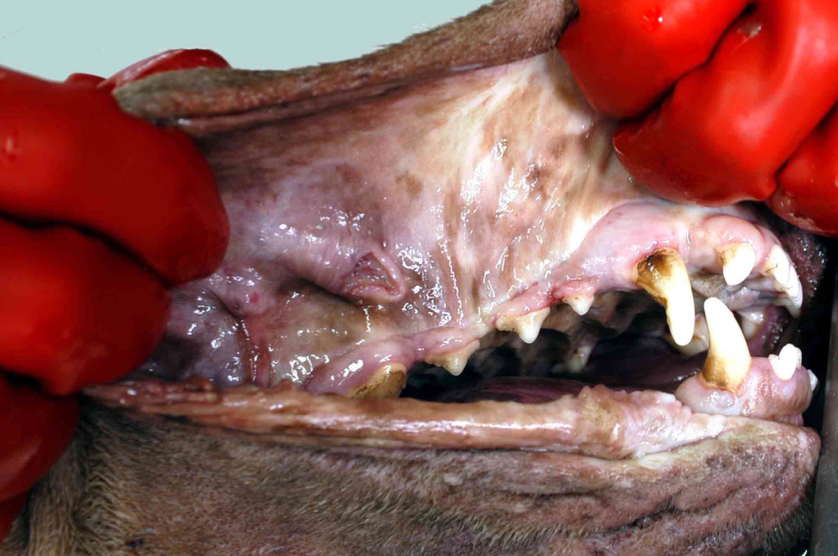
What causes Uremic Ulcers in the oral cavity (more specific than just kidney issues)?
High BUN → thrombosis → ischemia → infarction → ulceration
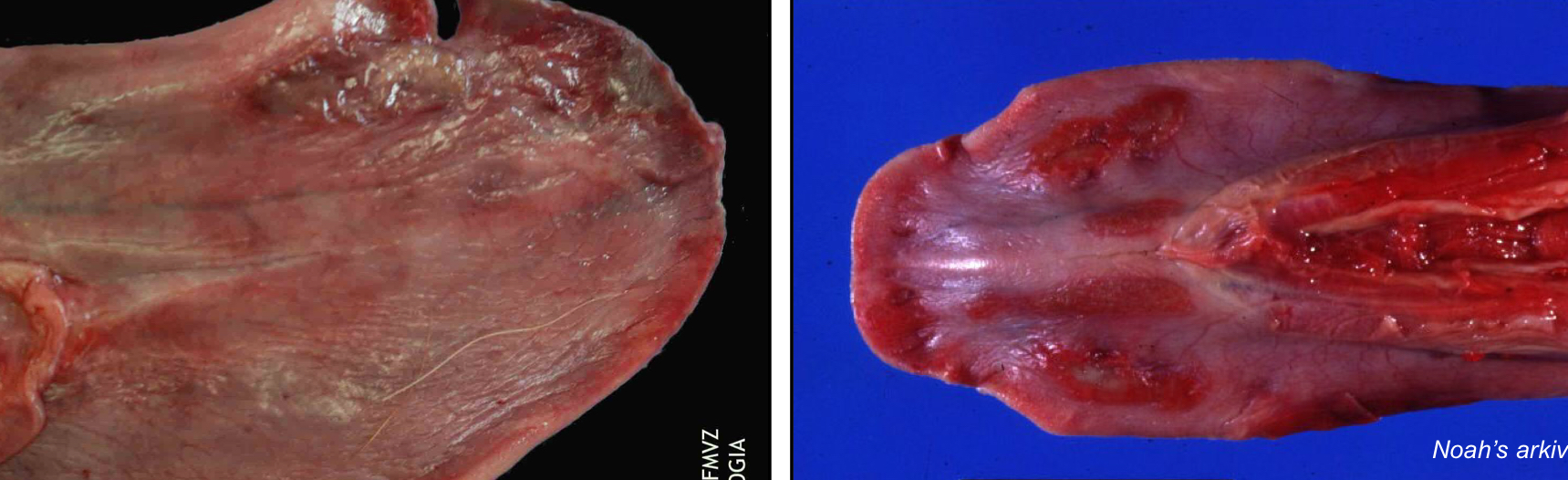
T/F: FMD can cause ulcerative stomatitis
True, it can cause vesicular/ulcerative stomatitis
What genus of virus causes Papular Stomatitis? What are the 2 examples of these viruses that we discuss?
Parapoxviruses
Contagious ecthyma (orf)
Bovine Papular Stomatitis
What is a papule?
Elevated dome shaped/flat topped lesion 1cm or less across
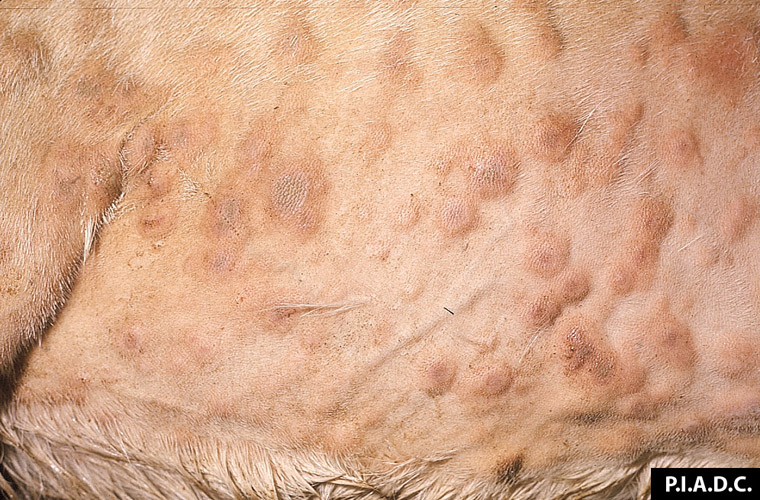
Papules are cases of chronic proliferative and _______ lesions
Proliferative and Necrotizing
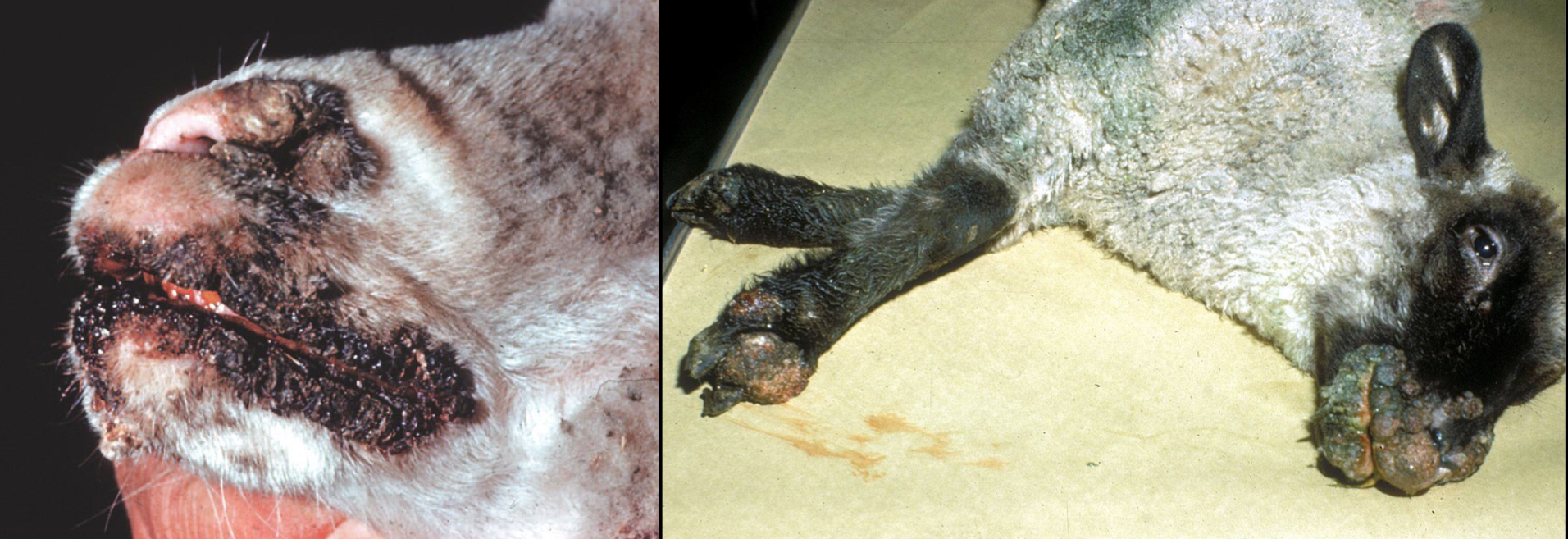
What condition is this?
Contagious ecthyma (orf)
Causes papular stomtitis or pustular dermatitis
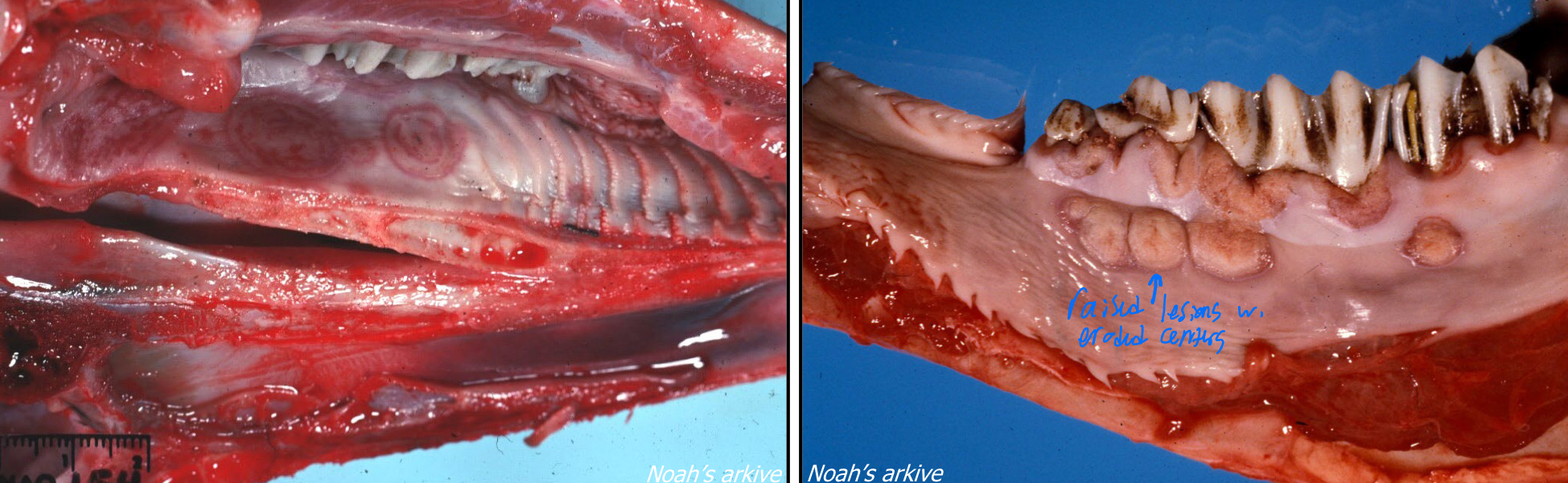
What disease is this most likely?
Bovine papular stomatitis
What is the difference between Ulcerative stomatitis and Necrotizing stomatitis?
Ulcerative
Lesions in which the damage extends through the epidermis and into the dermis
Necrotizing
Penetration of the mucosa and invasion into deeper tissues
Results in chronic inflammation → Abscess, granulomas
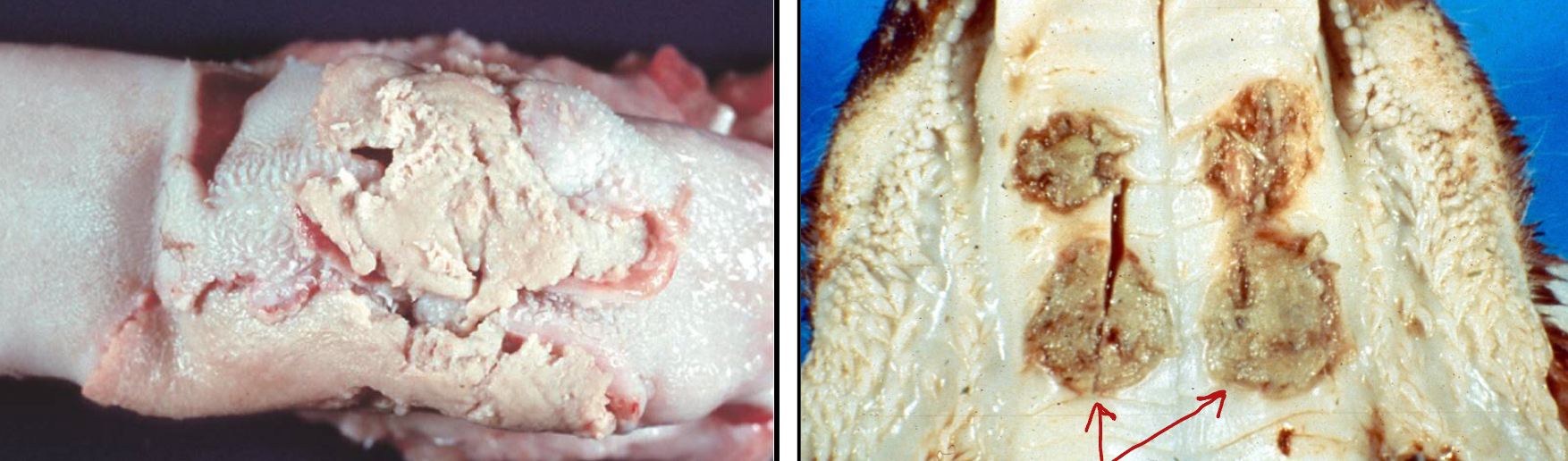
What is the etiology of Oral necrobacillosis (Calf Diphtheria)?
Fusobacterium necrophorum
The trademark appearance of Calf Diphtheria is ______/_______ that are often covered by a yellow-grey _________
Ulcers/erosions
Pseudomembranes
a false membrane-like layer of inflammatory material, typically consisting of mucus, dead cells, and inflammatory cells, that forms on a mucous membrane or skin surface
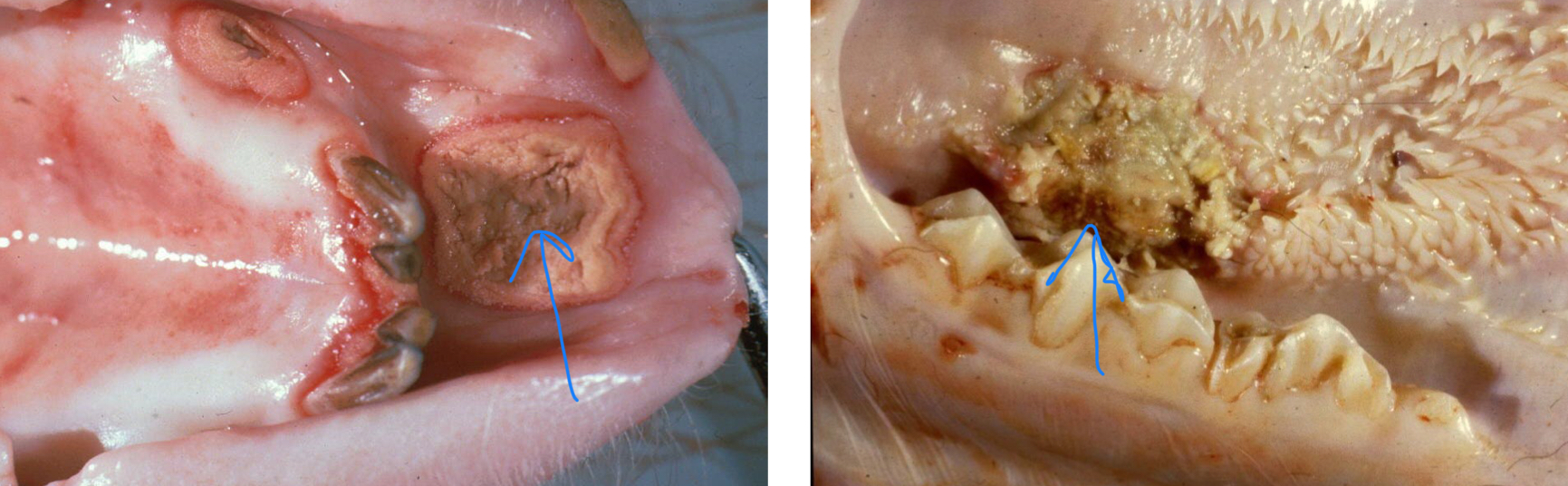
What are some predisposing factors to Calf Diphtheria?
Eruption of teeth
Rough feed
Poor use of Dosing gun
Intercurrent disease
Essentially anything that can damage the oral mucosa and provide F. necrophorum an entrance
A cow presents with chronic granulomatous glossitis, what is your initial ddx (include etiology)?
Oral Actinobacillus (Wooden Tongue)
Actinobacillus lignieresii
Don’t confuse with A. bovis
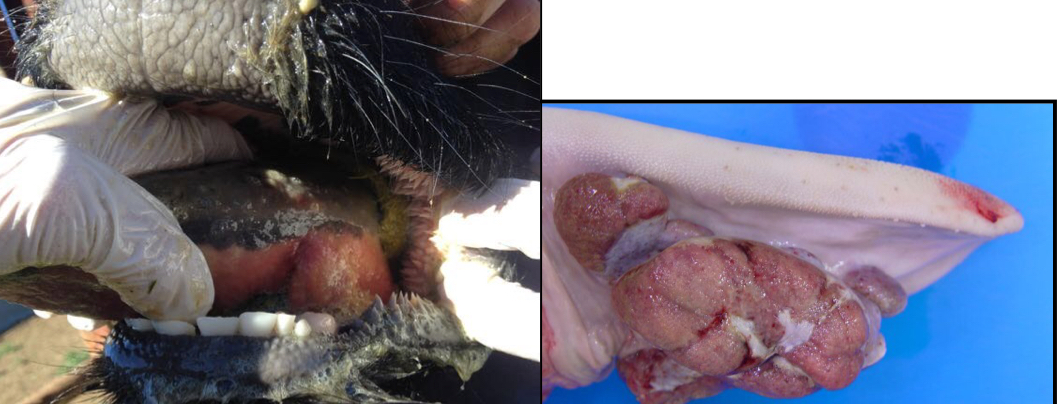
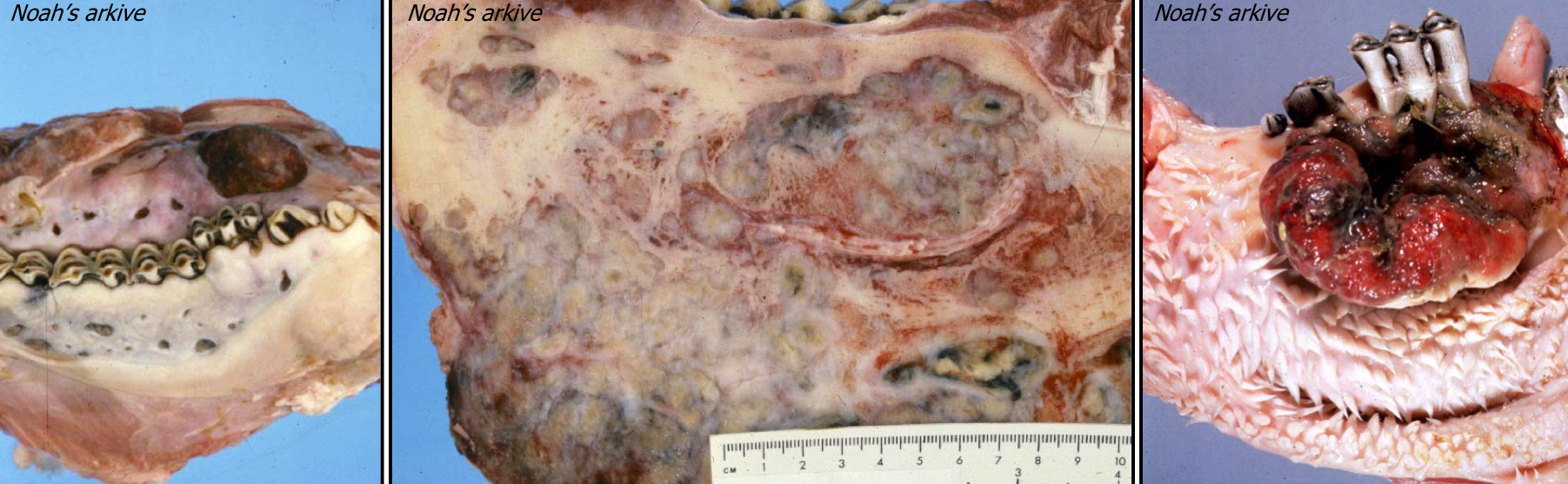
What bacteria cause lumpy jaw in cattle?
Actinobacillus bovis
What is a good way to remember the difference between oral actinomycosis and oral actionbacillus?
Actinomycosis → M = Mandible → causes Lumpy Jaw
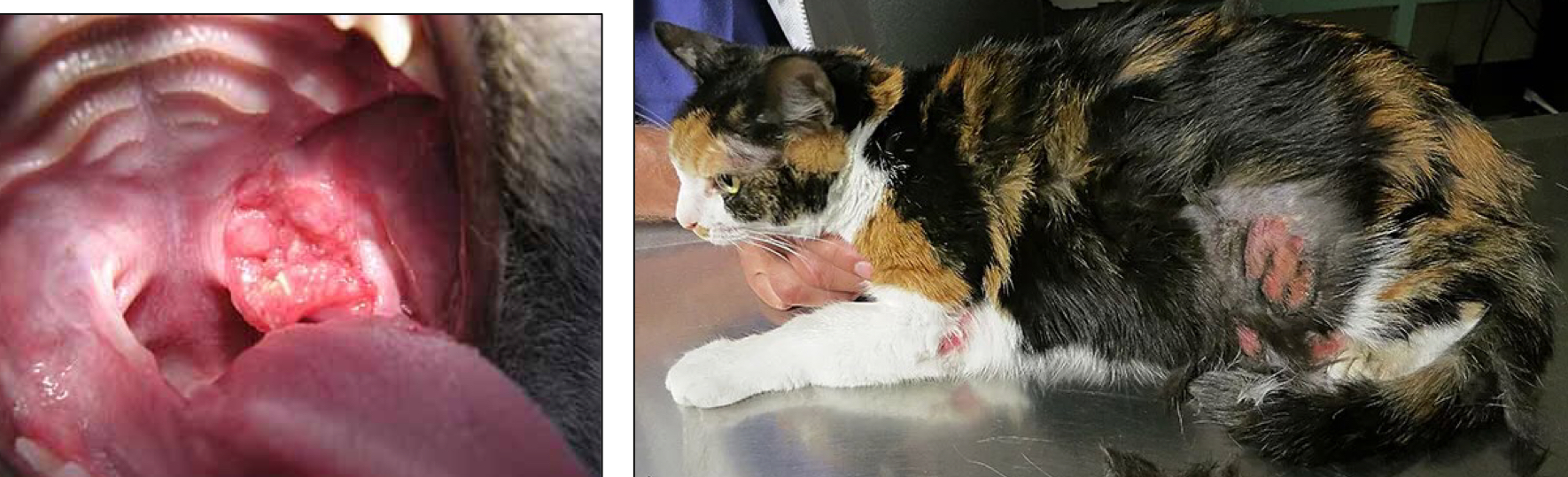
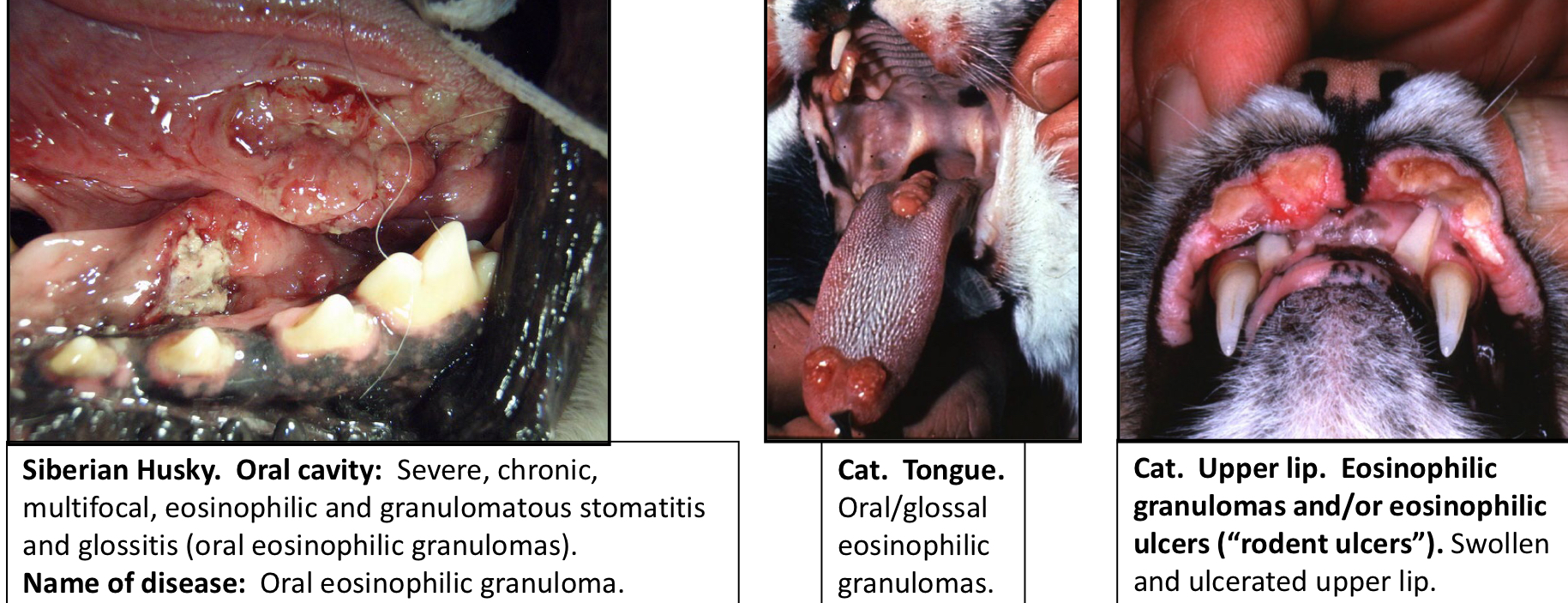
A cat presents with what appears to be an ulcerated mass in its mouth, you do an FNA on it, and you see numerous eosinophils and eosinophil degranulation, you also notice that the cat has cutaneous ulcers as well, what is your main ddx?
Eosinophilic Stomatitis (Part of Feline Eosinophilic Granuloma Complex Cutaneous and/or oral ulcers)
This complex can result in the formation of cutaneous and or oral ulcers
What type of disease does Eosinophilic Stomatitis cause?
Affects cats mostly (sometimes Huskies)
aka Oral eosinophilic granulomas and/or eosinophilic ulcers
Appears like an ulcerated tumor
How does Lympoplasmacytic Stomatitis/Gingivitis present?
Ulcerative/raised and proliferative erythematous (reddened) lesions
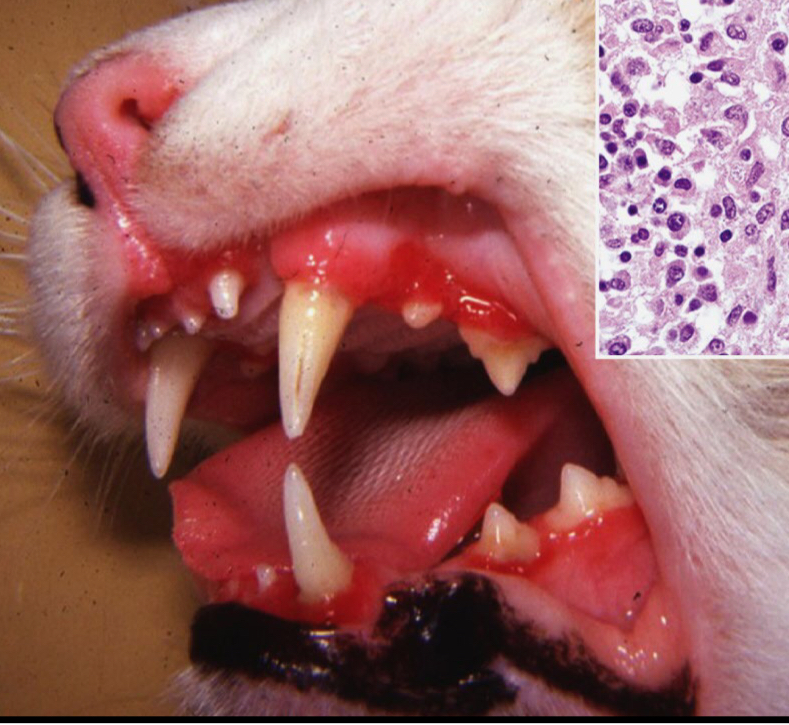
WHat is the cause of Lympoplasmacytic Stomatitis/Gingivitis
It’s Idiopathic
T/F: You can often differentiate oral growths (Hyperplasia/neoplasia) visually
False, their gross appearance is often too similar