Quantum Mechanics and Wave Phenomena: Key Concepts and Applications
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
What is quantum mechanics?
The branch of physics needed to deal with submicroscopic objects.
What are the main components of atomic structure?
Electrons orbit atoms in discrete shells around a nucleus composed of protons and neutrons.
What does it mean for charges to be quantized?
Charges appear only in certain discrete values and cannot be fractional.
What is blackbody radiation?
Radiation emitted by a non-reflecting surface that can absorb and emit all wavelengths.
How does temperature affect blackbody radiation?
The total intensity of radiation varies as T^4, and the peak shifts to shorter wavelengths at higher temperatures.
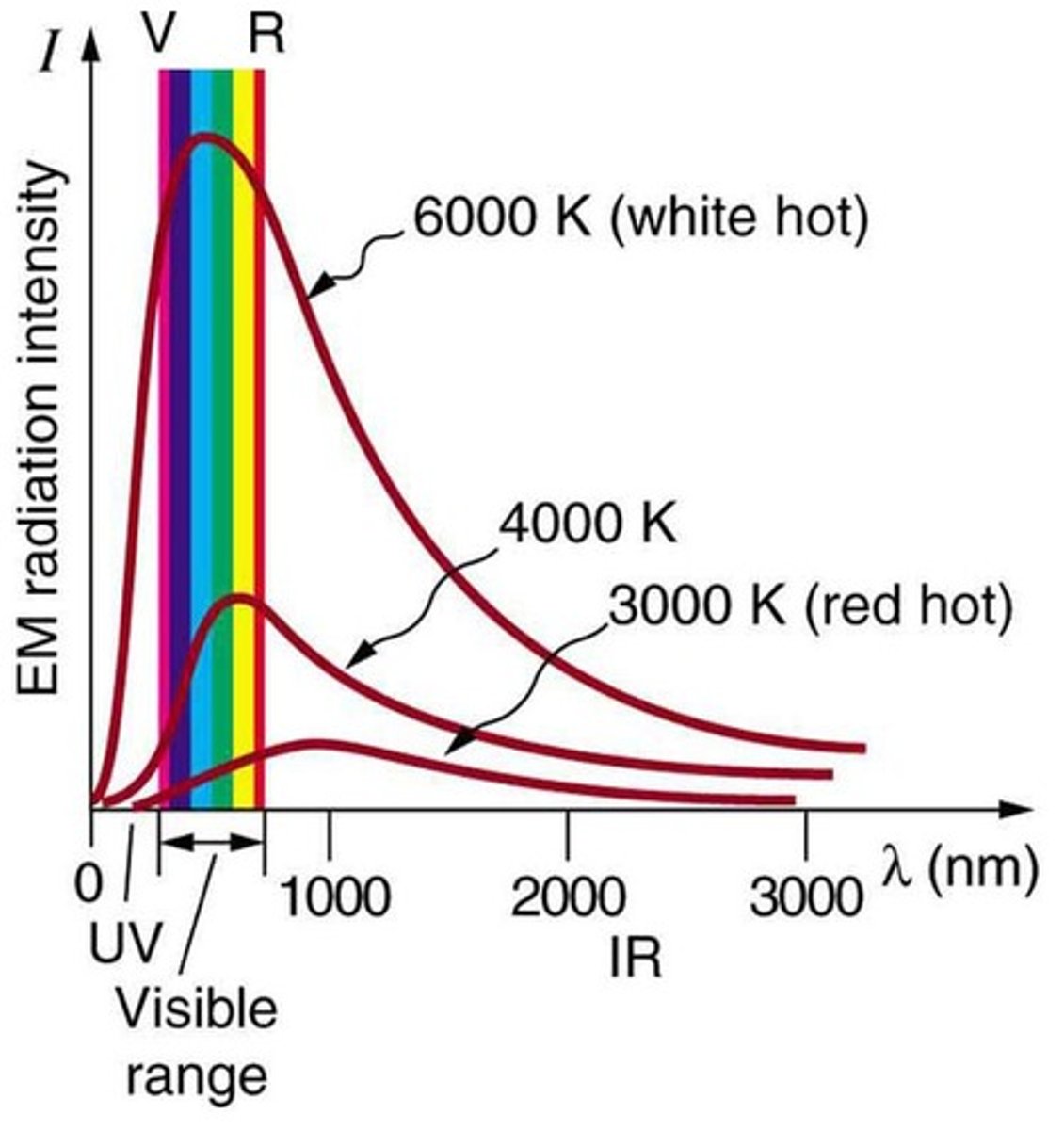
What is the 'ultraviolet catastrophe'?
A problem in classical physics where the predicted intensity of blackbody radiation diverged at short wavelengths.
Who proposed the quantization of energy in blackbody radiation?
Max Planck.
What is Planck's equation for the energy of an oscillator?
E = n h f, where n is a nonnegative integer, h is Planck's constant, and f is frequency.
What is atomic spectra?
The emission of light at specific wavelengths by excited atoms, resulting in a series of colored lines.
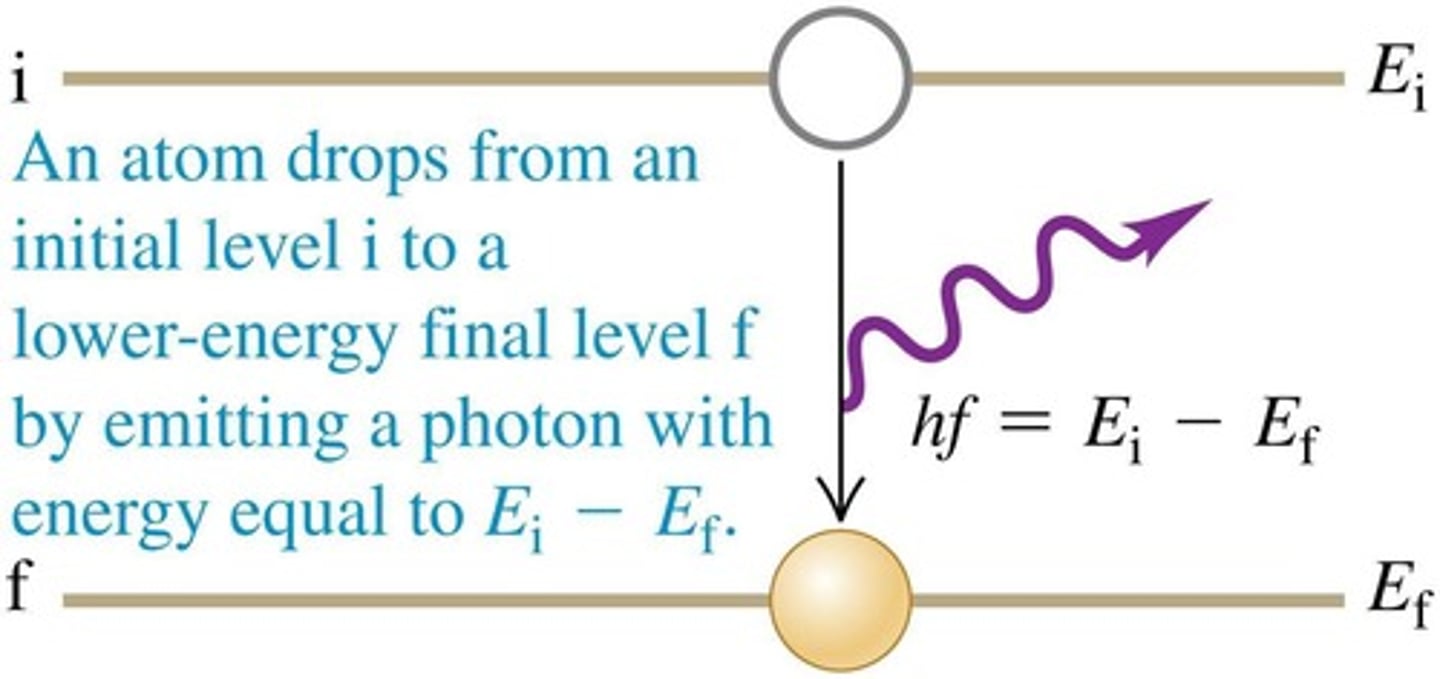
What happens when an atom transitions from a higher to a lower energy level?
It emits a photon whose energy equals the energy lost by the atom.
What is the significance of the hydrogen spectrum?
It shows discrete spectral lines that correspond to quantized energy levels of the hydrogen atom.
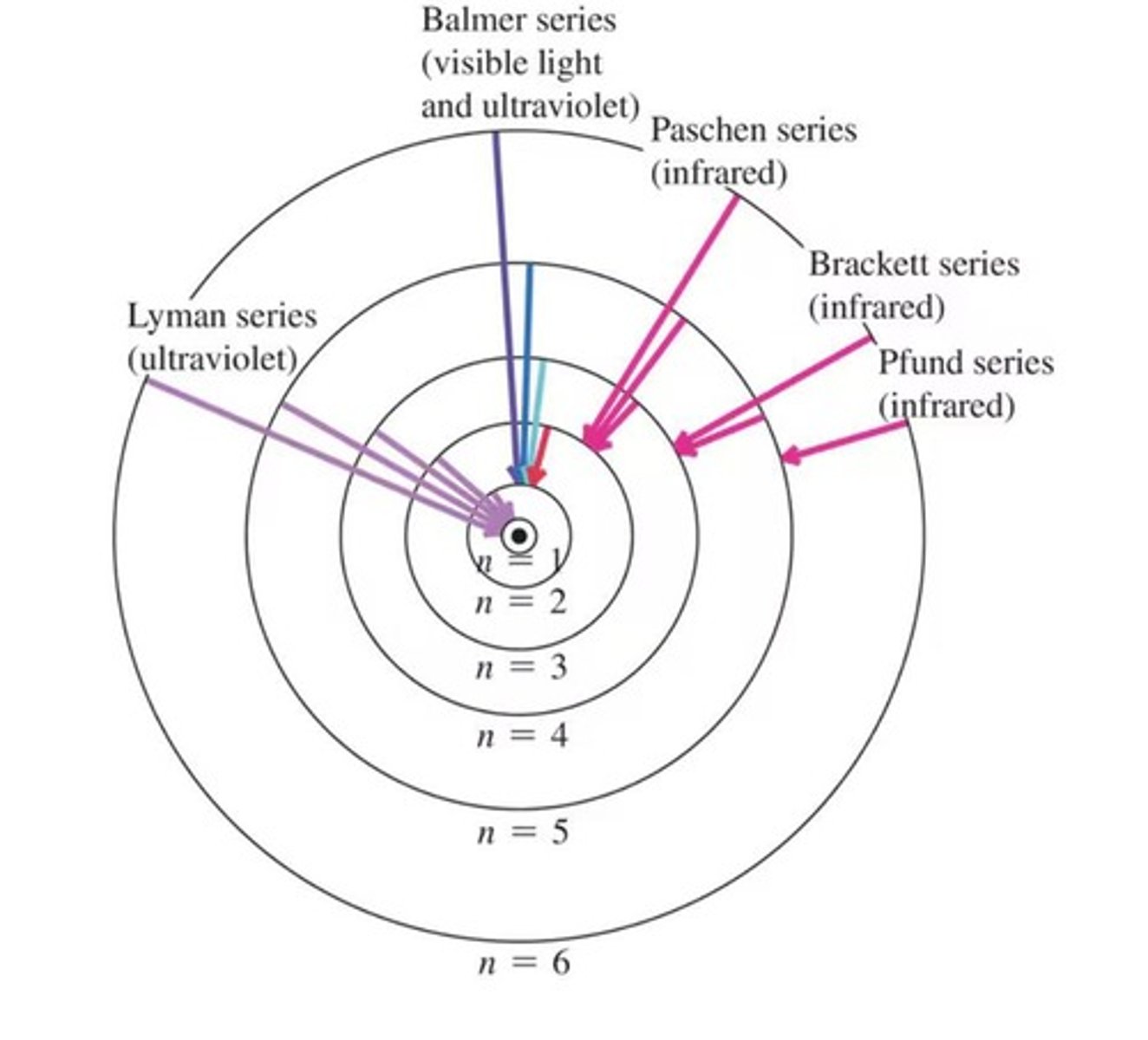
What is Bohr's first proposal regarding electron orbits?
Electrons can only revolve in certain allowed orbits, which are quantized.
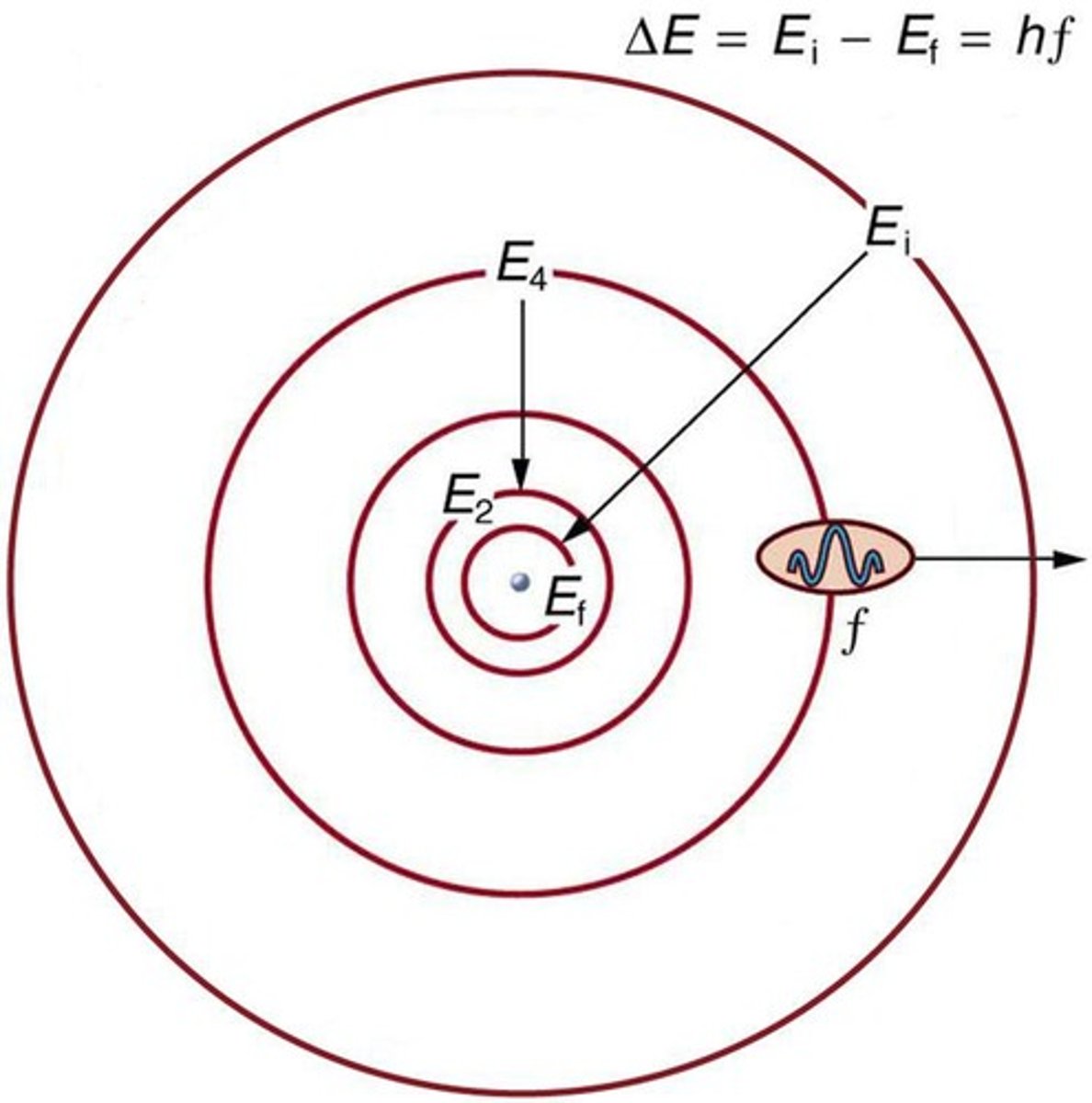
What is the formula for the change in energy between electron orbits?
ΔE = h * f, where ΔE is the change in energy and f is the frequency of the emitted or absorbed photon.
What does Bohr's energy-level diagram represent?
It plots energy states vertically, showing transitions between quantized energy levels.
How can the radii of allowed electron orbits in hydrogen be calculated?
Using the formula r_n = n^2 * a_B, where a_B is the Bohr radius.
What is the ground state energy of hydrogen?
-13.6 eV.
What is the photoelectric effect?
The phenomenon where light can eject electrons from materials.
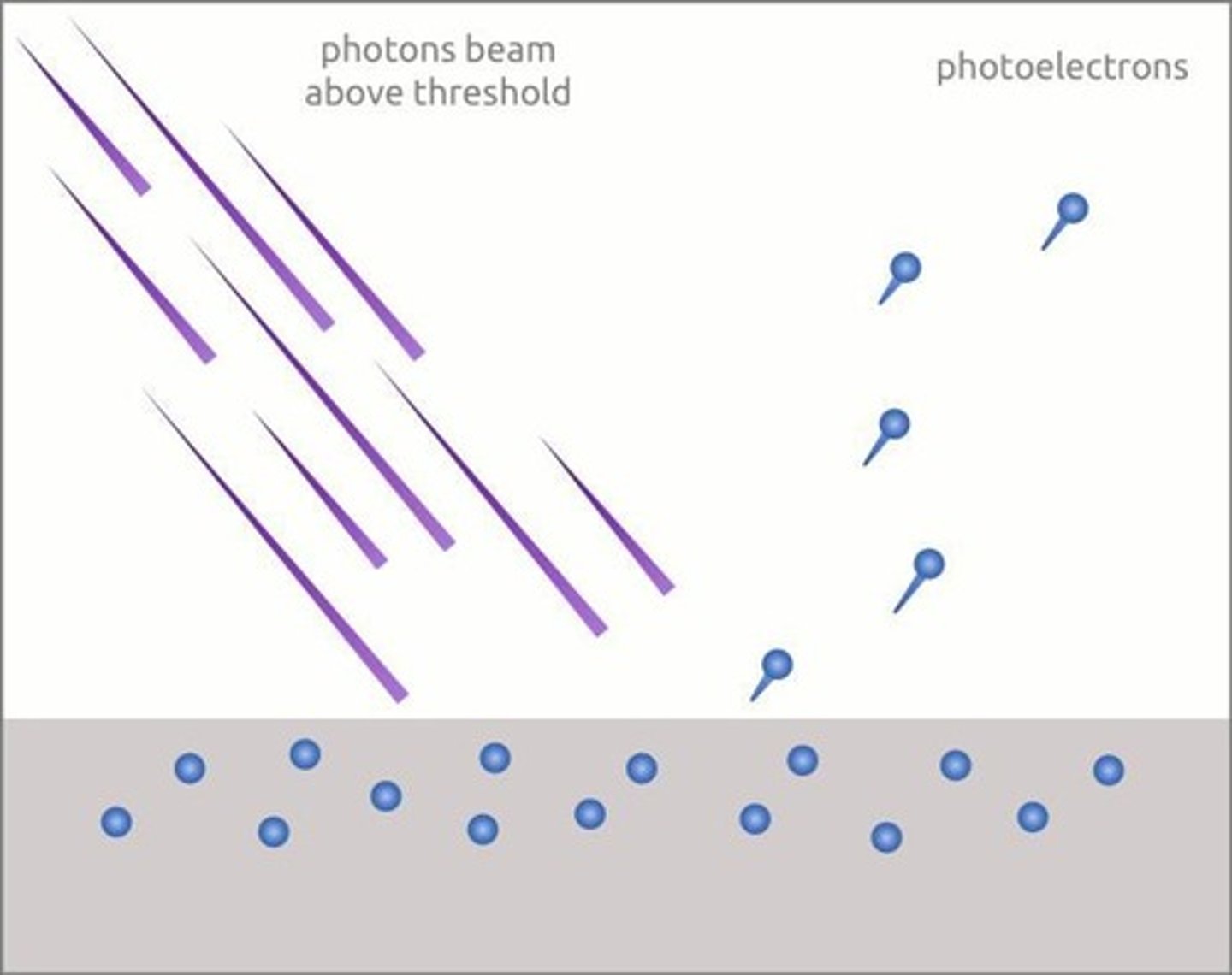
Who explained the photoelectric effect using quantized energy?
Albert Einstein.
What are photons?
Energy quanta that make up electromagnetic radiation.
What is the relationship between energy and frequency in the context of photons?
Energy is directly proportional to frequency.
What is the significance of the emission and absorption spectra?
They provide a unique fingerprint for each element, allowing for identification.
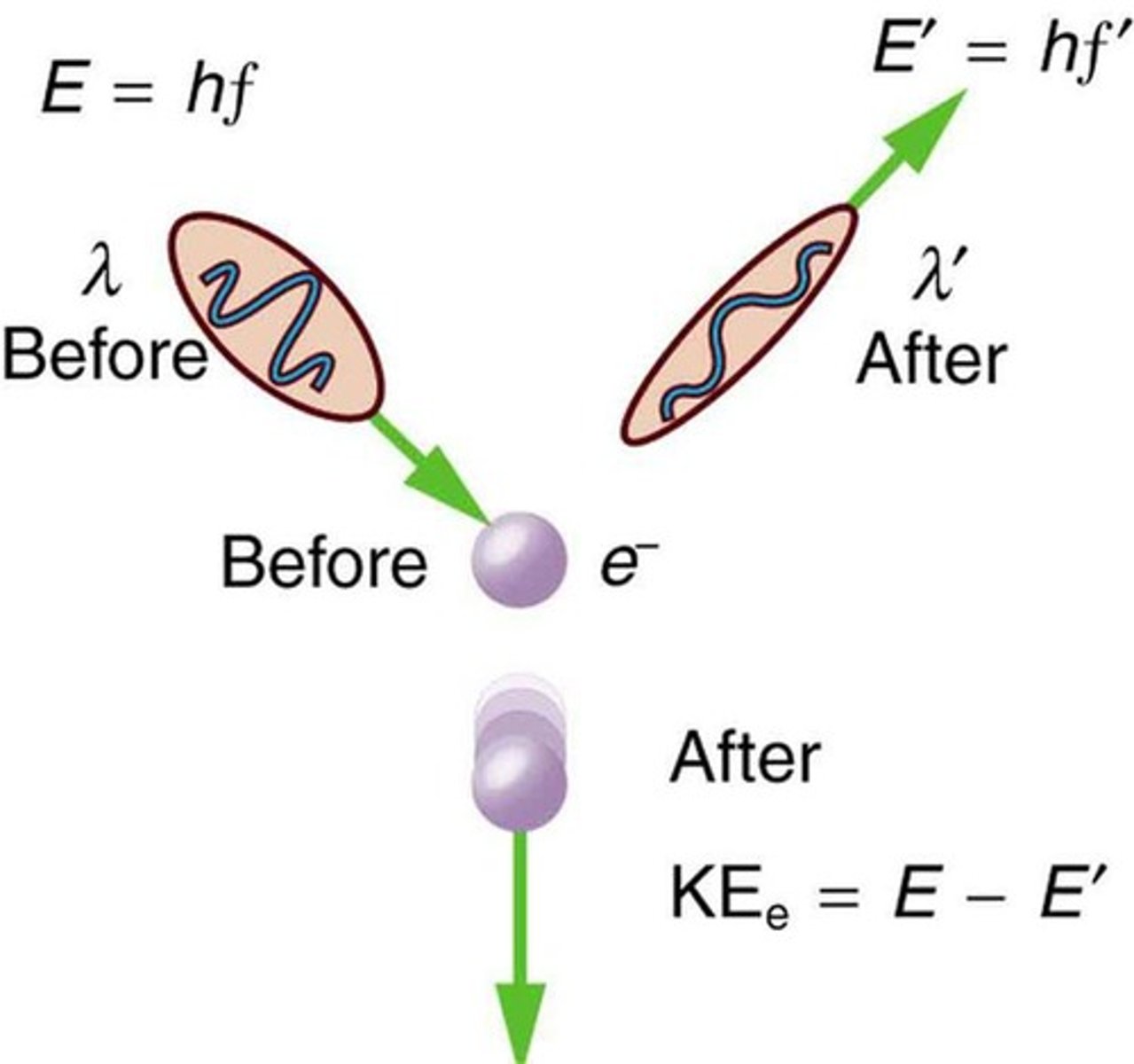
What is the Compton Effect?
The scattering of X-rays by electrons, demonstrating the particle nature of light.
What does wave-particle duality refer to?
The concept that particles, such as electrons, exhibit both wave-like and particle-like properties.
What is de Broglie's wavelength?
A formula that relates the wavelength of a particle to its momentum.
What is Heisenberg's uncertainty principle?
A principle stating that certain pairs of physical properties cannot be simultaneously known with arbitrary precision.
What is Schrödinger's Cat thought experiment?
A scenario that illustrates the concept of superposition in quantum mechanics.
What is a photon?
A quantized unit of energy in electromagnetic radiation.
What is the equation for photon energy?
E = hf, where E is the energy of a photon, h is Planck's constant, and f is the frequency.
What is the threshold frequency (f0) in the photoelectric effect?
The minimum frequency of electromagnetic radiation required to eject electrons from a material.
What happens to electrons when electromagnetic radiation hits a material?
Electrons are ejected without delay.
How is the number of ejected electrons related to the intensity of EM radiation?
The number of ejected electrons per unit time is proportional to the intensity of the EM radiation.
What is the maximum kinetic energy of ejected electrons dependent on?
It is independent of the intensity of the EM radiation.
What is the formula for the maximum kinetic energy of an ejected electron?
KEe = hf - BE, where KEe is the maximum kinetic energy, hf is the photon energy, and BE is the binding energy.
What is Compton scattering?
The phenomenon where x-rays scatter from materials, resulting in decreased energy due to photon-electron collisions.
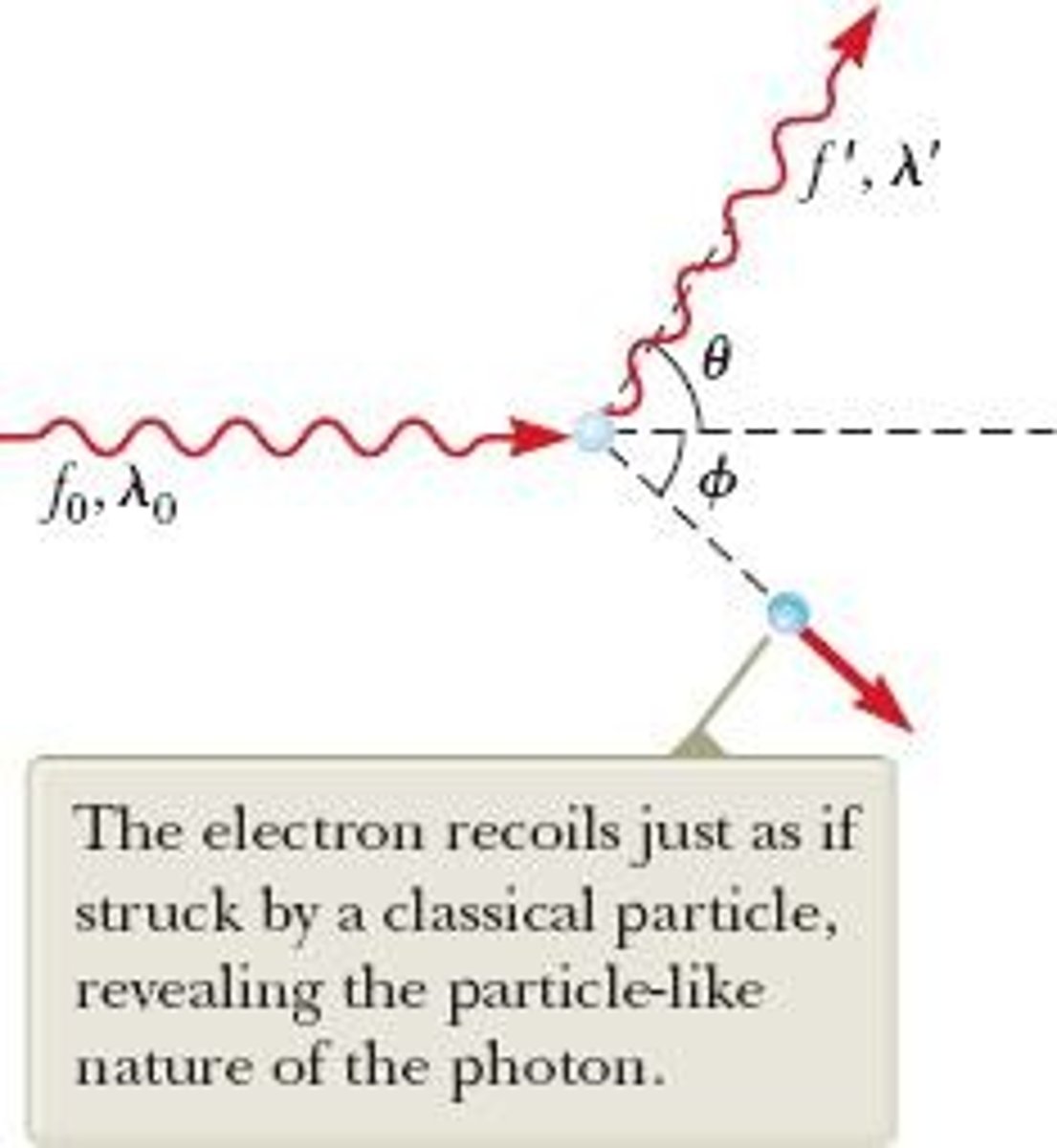
What is the equation for photon momentum in the Compton effect?
p = h/λ, where p is momentum, h is Planck's constant, and λ is the photon wavelength.
What does the Compton shift equation describe?
The change in wavelength of scattered photons: λ' - λ0 = h/(mec)(1 - cos θ).
What is wave-particle duality?
The concept that electromagnetic radiation exhibits both wave-like and particle-like properties.
What is the de Broglie wavelength?
The wavelength associated with a particle, given by λ = h/p, where p is momentum.
What does the equation Δx·Δp ≥ h/4π represent?
The relationship defining the limits of precision in measuring position (Δx) and momentum (Δp).
What is superposition in quantum mechanics?
The ability of quantum systems to exist in multiple states at the same time until measured.
What are orbitals in the quantum model of the atom?
Regions in space where there is a high probability of finding an electron, as opposed to fixed orbits.
What does the square of the wave function (ψ²) represent?
The probability density of finding an electron in a given region of space.
What is the binding energy (BE) in the context of the photoelectric effect?
The energy required to remove an electron from its material, also known as the work function.
What is the significance of Planck's constant (h)?
A fundamental constant that relates the energy of a photon to its frequency.
What happens to the superposition of a quantum system upon measurement?
The superposition collapses into one definite state.
How does the uncertainty in position (Δx) relate to wavelength?
Δx is approximately equal to the wavelength of the particle.
What is the relationship between photon wavelength and uncertainty in momentum?
As photon wavelength decreases, the uncertainty in momentum increases.
What is the role of the radiation detector in Schrödinger's cat thought experiment?
It triggers the release of poison based on the decay of radioactive material, determining the cat's fate.
What does the term 'quantum model of the atom' imply?
Electrons do not follow fixed paths but are described by probabilities and wave functions.
What is the Compton wavelength?
The wavelength associated with a particle, defined as λC = h/(mec), where me is the electron mass.
What is a wave?
A wave is a disturbance that travels through a medium from one location to another.
What is the medium of a wave?
The substance through which waves travel, such as air or water.
What are mechanical waves?
Waves that require a material medium to exist, governed by Newton's laws, like sound and water waves.
What are electromagnetic waves?
Waves that do not require a material medium, such as light waves from stars.
What are matter waves?
Waves associated with particles like electrons and protons.
What is a transverse wave?
A wave where oscillations are perpendicular to the direction of wave travel, like electromagnetic waves.
What is a longitudinal wave?
A wave where oscillations are along the direction of wave travel, like sound waves.
What is the period of a wave?
The time for one complete up and down motion of the wave.
How is frequency defined?
The number of cycles of a wave passing a point per unit time, calculated as f = 1/T.
What is amplitude in wave motion?
The maximum displacement of points on a wave from the equilibrium position.
What is wavelength?
The distance between two successive like points on a wave, represented by the Greek letter lambda (λ).
What is wave velocity?
The speed at which the disturbance moves, calculated as v = fλ.
What is the speed of sound in air dependent on?
The ratio of the pressure of the gas to its density, which depends on temperature.
What is infrasound?
Sound with frequencies less than 20 hertz, inaudible to humans.
What is ultrasound?
Sound with frequencies higher than 20,000 hertz, inaudible to humans.
What is the human audible range?
The range of sound frequencies that a person with good hearing can hear, typically 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz.
What is echolocation?
A method used by some animals to 'see' their surroundings using sound.
What is sonoluminescence?
The production of light from sound waves, a subject of recent research.
Who first suggested the existence of electromagnetic waves?
James Clerk Maxwell, while analyzing the interactions between electricity and magnetism.
What are electromagnetic waves composed of?
A combination of oscillating electric and magnetic fields.
What happens when an oscillating electric field is produced?
It induces an oscillating magnetic field in the surrounding space.
What is the relationship between wave speed, frequency, and wavelength?
Wave speed (v) is equal to frequency (f) multiplied by wavelength (λ), v = fλ.
What is the effect of temperature on the speed of sound in gases?
The speed of sound is proportional to the square root of the temperature in Kelvin.
What is the significance of the Doppler Effect?
It describes the change in frequency or wavelength of a wave in relation to an observer moving relative to the wave source.
What is the Superposition Principle in wave theory?
It states that when two or more waves overlap, the resulting wave is the sum of the individual waves.
What are standing waves?
Waves that remain in a constant position, typically formed by the interference of two waves traveling in opposite directions.
What induces an oscillating magnetic field?
An oscillating electric field.
What is the speed of electromagnetic waves in a vacuum?
300,000,000 m/s (the speed of light, represented by c).
What is the relationship between speed (v), frequency (f), and wavelength (λ) for electromagnetic waves?
c = fλ.
What are the two components of electromagnetic waves?
An electric field wave and a magnetic field wave.
Do electromagnetic waves require a medium to travel?
No, they can travel through a vacuum or matter.
What is the range of wavelengths for electromagnetic waves?
From about 10-15 meters (size of a proton) to almost 4,000 kilometers (for certain radio waves).
What are the categories of the electromagnetic spectrum in order of increasing frequency?
Radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, x-rays, and gamma rays.
What is visible light?
A narrow band of frequencies of electromagnetic waves detectable by human beings.
How do different frequencies of visible light correspond to color?
Lower frequencies are perceived as red and higher frequencies as violet.
What is the Doppler Effect?
The change in frequency of a wave in relation to an observer moving relative to the source of the wave.
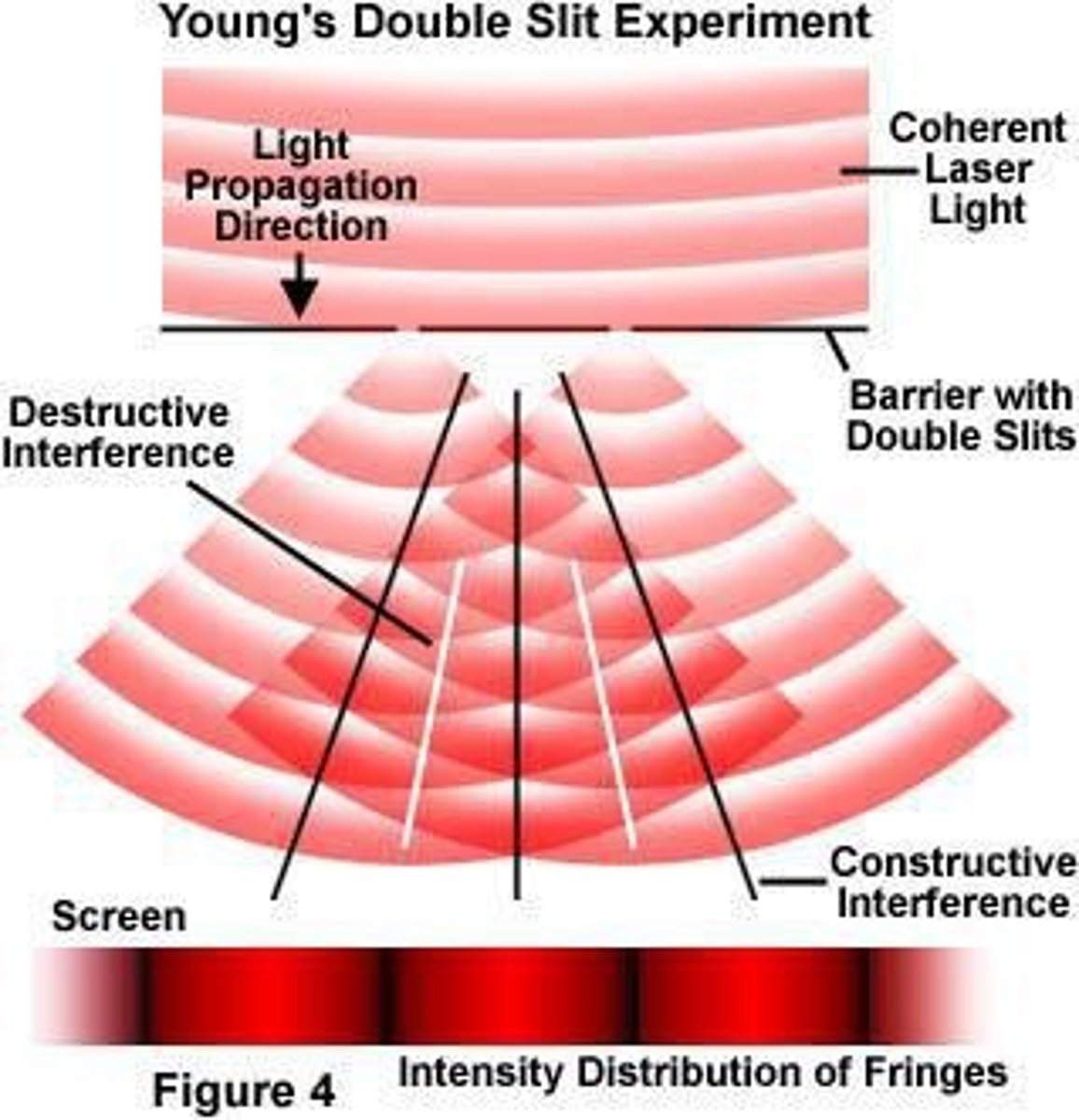
What happens during constructive interference?
Crests of one wave align with crests of another, producing maximum amplitude.
What happens during destructive interference?
The crest of one wave aligns with the trough of another, resulting in a wave amplitude of zero.
What is the principle of superposition of waves?
When two or more waves overlap, they algebraically add to produce a resultant wave.
What demonstrates the wave nature of light?
Young's double slit experiment, which shows bright and dark fringes due to interference.
What is a standing wave?
A wave that appears to be standing still due to the superposition of two waves moving in opposite directions.
What are nodes in a standing wave?
Points that never move, resulting from complete destructive interference.
What are antinodes in a standing wave?
Points that oscillate with maximum amplitude, resulting from complete constructive interference.
What is the fundamental frequency (f1) in standing waves?
The lowest frequency at which a standing wave can form on a given medium.
How is the frequency of the nth harmonic (fn) calculated?
fn = n * f1, where n is the harmonic number.
What is the wavelength of the first harmonic (λ1) in terms of length (L)?
λ1 = 2L.
What is the significance of the amplitude in electromagnetic waves?
It is the maximum value of the electric field strength.
What is the frequency range for red light?
Approximately 4.0-4.8 × 10^14 Hz.
What is the frequency range for violet light?
Approximately 6.7-7.5 × 10^14 Hz.
What type of interference occurs when two waves are perfectly in phase?
Constructive interference.