MEDI 1101A Kahoot Quiz
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key concepts from the MEDI 1101A lecture, focusing on physiology, pharmacology, and pathology.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
What are the characteristics of the sympathetic nervous system?
Short preganglionic fibers, long postganglionic fibers, key neurotransmitters NA and A. Thoracolumbar
What is supraventricular tachycardia?
A rapid heart rhythm originating above the ventricles. 140+
What are the symptoms of cholinesterase inhibitor poisoning?
Muscle twitching, hypersalivation, nausea, pinpoint pupils, urinary incontinence.
What is the primary characteristic of an antagonist?
Just Affinity
What does the baroreflex respond to? (Basic)
Changes in blood pressure.
What ECG changes are seen during acute myocardial infarction (AMI)?
Pathological Q Waves, T Wave Inversion, ST Elevation, Hyper Acute T wave
What is the first response to loss of IV volume?
Baroreflex
What is the difference between diploid and haploid cells?
Diploid cells have two complete sets of chromosomes (Somatic), haploid cells have one set (Gamete)
When does DNA replication occur in the cell cycle?
During the S phase.
Where does transcription occur in eukaryotic cells?
In the nucleus.
Which vitamins are fat soluble?
K, A, D, E
What does heart sound S1 signify?
Closing of the AV valves.
What type of drug is GTN?
A vasodilator used as a first-line treatment for angina. Nitrate
What type of shock is caused by anaphylaxis?
Distributive shock.
What does the Na:K pump transport?
Pumps 3 Na+ ions out of the cell and 2 K+ ions into the cell, against their gradients.
What role does cholesterol play in the lipid bilayer?
Maintains membrane integrity and fluidity.
What is the predominant buffering system in intracellular fluid (ICF)?
Phosphate buffer.
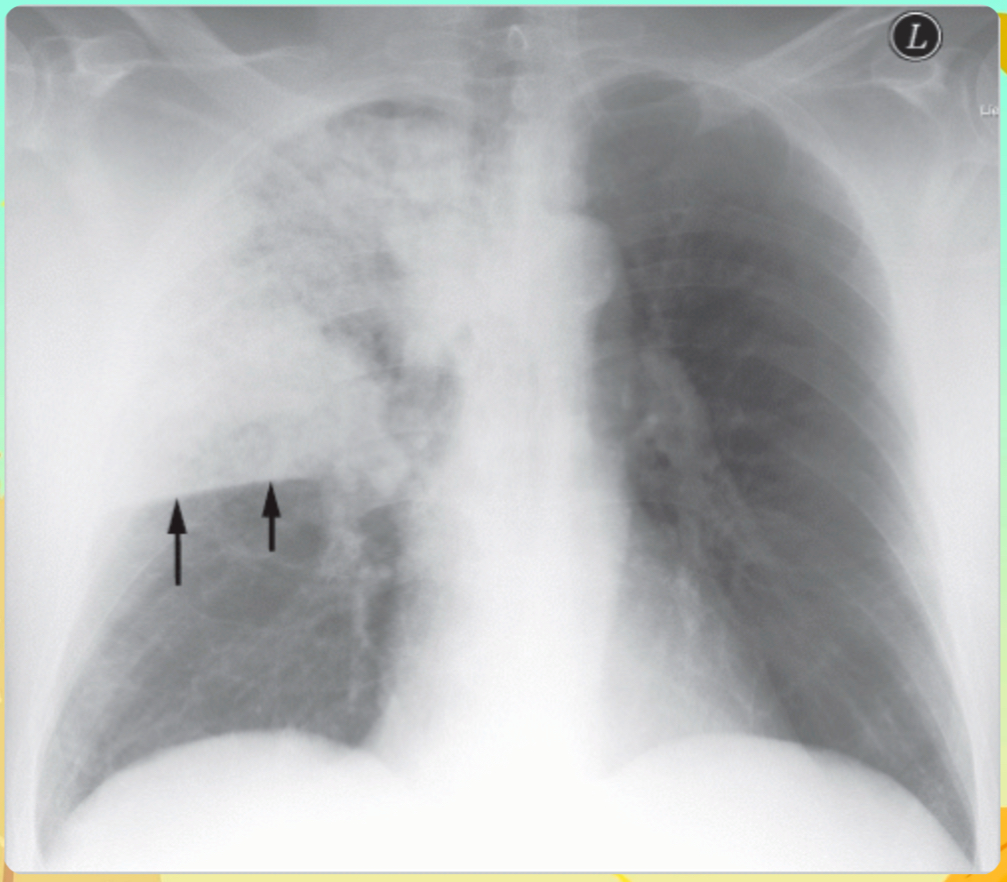
What is the likely diagnosis?
Lobar pneumonia
What does a change of sequence from ATTAGC to ATAAGC represent?
A substitution mutation.
What effect does Nor/adrenaline have on alpha 1 receptors?
Vasoconstriction
What is a key feature of Gram-positive organisms?
A thick peptidoglycan layer.
What is a hallmark of inflammation?
5 cardinal signs
How is CO2 transported in the blood? (Mostly)
HCO3-
In what Tanner Stage does enlargement of the scrotum occur?
Stage 2
Which coronary artery supplies the inferior border of the myocardium
Right Marginal
Phase 4 in a pacemaker cell is caused by what channel?
If Na+
Which Ig is found on mucosal surfaces?
IgA
At what level does the Carotid artery bifurcate?
C3-4
MOA of nitric oxide?
Increases cGMP and inhibits Ca2+ channels
The Bohr effect will cause?
Decreased affinity for O2, therefore increased delivery to tissues
The brain chemoreceptors are more sensitive to changes in?
H+ and C02
Pluripotent cells are able to?
Form many different cells
Cardiac Output =
(EDV-ESV) x HR
What is made in 1 rotation of the TCA cycle?
1 ATP and 3 NADH