Learning Approach - The behaviourist approach
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
what is the behaviourist approach
a way of explaining behaviour in terms of what is observable in terms of learning
what to behaviorist believe about behaviour
behaviour is learned
what is the behaviourist approach interested in
observing behaviour that can be measured
What do behaviorist assume about babies
they describe a baby’s mind as a blank slate that is written on by experiences
why did behaviorist use animals to replace humans as experimental subjects
following Darwin - behaviourist suggested that the basic processes of learning are the same for all species.
who is john B Watson and what did he add to the assumptions of behavioursit
an early behaviorist
who rejected introspection because it involved too many concepts that are vague and difficult to measure
so they try to maintain objectivity within the research - lab studies
what are the two different ways of learning identified by behaviourist?
operant conditioning
classical conditioning
What is classical conditioning ?
This is learning by association and occurs when two stimuli’s are repeatedly paired together
what is the equation for classical conditioning
unconditioned stimuli-=unconditioned response
natural stimuli = unconditioned response
unconditioned stimuli + unconditioned response = unconditioned response
conditioned stimuli = conditioned response
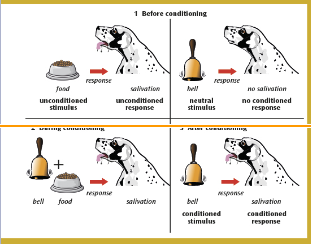
what did Ian Pavlov demonstrate ?
showed how dogs could be conditioned to salivate to the sound of a bell.
if that sound was repeatedly presented at the same time as the food they were given then the dogs would associate the bell (stimulus) with food. = would produce the salivation response
showing that a neutral stimulus = bell can elicit a new response through association
What did B.F Skinner suggest ?
that learning is an active process whereby humans and animals operate on their environment behavior is shaped by experiences
what is positive reinforcement?
is receiving a reward when a certain behaviour is performed
this could be praise
what is negative reinforcement ?
occurs when an animal avoids something unpleasant the outcome is a positive experience - handing in an essay to not get told off
what is punishment ?
it is an unpleasant consequence of a behaviour
what do both positive and negative behaviour have in come
they increase the likelihood of the behaviour while punishment decreases the likelihood of a behaviour
exlpain the Skinner box experiment A
conducted an experiment with rat and pigeons in a specially designed cage known as skinner’s box
every time the rat activated a lever (pecked disc in the case of a pigeon ) within the box it was rewarded with a food pellet
from then on the animal would continue to perform this behaviour
explain skinners box B
Skinner showed how rats and pigeons could be conditioned to perform the same behaviour to avoid unpleasant shock.