Chapter 8: Rotation II: Inertia, Equilibrium, and Combined Rotation/Translation
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/38
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
1
New cards
Solution
________ ● The minimum coefficient of friction occurs when the object is on the verge of slipping.
2
New cards
Angular momentum
________ is conserved if the external torque is zero.
3
New cards
gravitational force
○ The torque exerted by gravity acts as if the ________ is exerted at the center of mass.
4
New cards
● Tip
________: Once you know the rotational inertia for an axis through the CM, you can use this theorem to find I through a parallel axis.
5
New cards
Linear momentum
________ is conserved if the external force is zero.
6
New cards
axis of rotation
B) The mass density is given to you as a function of the distance from the ________.
7
New cards
Your choice of differential region will be guided by the requirement that every particle of mass in
side the differential region must share a common distance to the axis of rotation
8
New cards
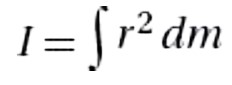
\
**Definition of rotational inertia**
9
New cards
There are two situations concerning these mass densities that you should be able to handle
a) The mass density is uniform
10
New cards
8.2
Parallel Axis Theorem ● The rotational inertia of an object about an axis a distance D from its center of mass (Iparallel axis) is related to the rotational inertia of the object about a parallel axis running through its center of mass (ICM) according to the equation
11
New cards
● Tip
Once you know the rotational inertia for an axis through the CM, you can use this theorem to find I through a parallel axis
12
New cards
8.3
Angular Momentum ● Definition of angular momentum for a point particle
13
New cards
Example 8.3.1 Problem
A person is sitting on a rotating lab stool holding a top that is free to rotate, as shown in Figure
14
New cards
8.4
Rolling Without Slipping Relating Linear and Angular Coordinates for the Center of Mass of an Object that Rolls Without Slipping ● Imagine a spool of thread of radius R that rolls along a surface without slipping, laying down thread ● The translational velocity of the center of mass equals the rate at which thread is laid down, dl/dt
15
New cards
Problem
A cylinder ( ) is at rest on a flat surface
16
New cards
● Now, for the object to roll without slipping, the equation 𝑎 = 𝑅α must be satisfied
𝑐𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑒𝑟
17
New cards
Satisfying 𝐹 = 0
Choose a convenient coordinate system, and sketch all forces acting𝑛𝑒𝑡 on the object
18
New cards
Satisfying τ = 0
The following statements are equivalent if the net force is zero
19
New cards
○ Proof
Consider the torque exerted by gravity about the z-axis on an arbitrary mass distributed along an xy-plane
20
New cards
○ Selection of axis
If we choose the axis to pass through the point where the ladder contacts the ground, the torque due to FN and Ffr will be zero, giving us a simple equation
21
New cards
This is straightforward because of our choice of axis
The last equation can be immediately solved for F′N, which can then be plugged into the first equation to calculate Ffr
22
New cards
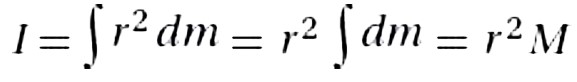
**Rotational inertia** for point masses, rings, and cylindrical shells rotating about their axes
23
New cards
**line segments**
One-dimensional mass ⇒ differential **_________**
24
New cards
**rings**
Two-dimensional mass rotating about an axis perpendicular to its plane ⇒ **_________**
25
New cards
**rectangular strips**
Two-dimensional mass rotating about an axis contained in its plane ⇒ **___________**
26
New cards
**cylindrical shells**
Three-dimensional mass ⇒ **_________** whose axes lies along the axis of rotation
27
New cards
2πr dr
**Area of a ring**
28
New cards
(2πr dr)h
**Volume of a cylindrical shell**
29
New cards
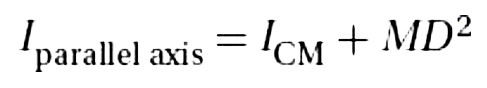
**Parallel Axis Theorem**
30
New cards
L = r x p
Definition of **angular momentum for a point particle**
31
New cards
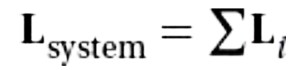
Net angular momentum of a system of particles
32
New cards
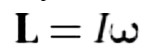
Relationship between angular momentum and angular inertia for an extended object rotating about a symmetry axis
33
New cards
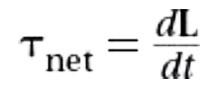
Relationship between net torque and angular momentum
34
New cards
Angular momentum
It is conserved if the external torque is zero.
35
New cards
Linear momentum
It is conserved if the external force is zero.
36
New cards
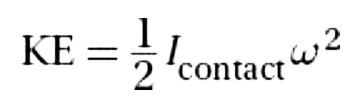
***Object’s Kinetic Energy***
37
New cards
**Equilibrium**
A system that is not accelerating
38
New cards
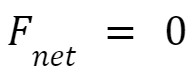
For a point mass, equilibrium is defined by the requirement that __________
39
New cards
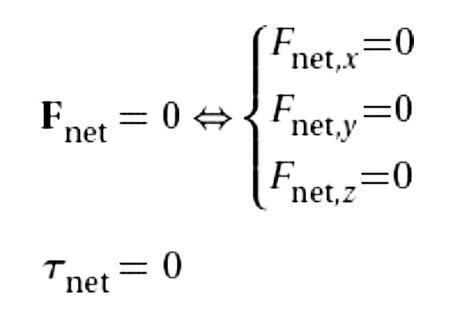
Conditions required for equilibrium