Carbon Cycle: 4.3
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
1
New cards
Nutrient cycle
\
The circular movement and exchange of matter through an ecosystem, from abiotic to biotic and back.
The circular movement and exchange of matter through an ecosystem, from abiotic to biotic and back.
2
New cards
Nutrients
chemicals that are needed for the maintenance of life
3
New cards
Steps of nutrient cycle
1. Nutrients enter biotic from abiotic through autotrophs
2. Within biotic, heterotrophs transfer nutrients from organism to organism via feeding
3. Nutrients return to abiotic from biotic e.g. CO2 from cell respiration moves back into the atmosphere
4
New cards
Carbon Cycle
Exchange of carbon among the biosphere, pedosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere & atmosphere of Earth.
5
New cards
Carbon cycle: Pools
Location or system that can store or release carbon.
6
New cards
Pools: (1) Atmosphere
Carbon is found in the form of CO2 and Methane therefore presence of carbon in the atmosphere influences greenhouse effect & climate change.
7
New cards
Pools: (2) Pedosphere
Carbon is found in the form of soil which is a mixture of organic matter, minerals that support life
8
New cards
Pools: (3) Biosphere
portion of the Earth with living material which stores carbon within biological molecules where living matter includes plants, animals, & microorganisms
9
New cards
Pools (4) Hydrosphere
\
Dissolved inorganic carbon in the Earth’s water, mostly in the oceans.
Dissolved inorganic carbon in the Earth’s water, mostly in the oceans.
10
New cards
Pools: (5) Geosphere
Lithosphere where carbon is stored as sedimentary rocks within the planet’s crust. Rocks are derived from hardening mud, CaCO3 particles, or shells into limestone
11
New cards
Pools: (6) Fossil Fuels
A "fossil" store of **organic** matter e.g. coal, oil, natural gas, formed over millions of years. Through human actions this carbon is introduced into the other carbon pools unnaturally.
\
\
12
New cards
Flux
Process that exchange carbon between pools. Where even a single carbon pool may have multiple fluxes adding and removing carbon simultaneously.
13
New cards
Flux: (1) Photosynthesis
Autotrophs photosynthesise, removing carbon and using it within plants, moving it to the biosphere. Transfer From **atmosphere/hydrosphere to biosphere**.
14
New cards
Flux: (2) Respiration
All organisms in biosphere or pedosphere release carbon dioxide into the atmosphere through cell respiration. Therefore **pedosphere/biosphere to atmosphere**
15
New cards
Flux: (3) Decomposition
CO2 released from the biosphere into the atmosphere by cell respiration by decomposers. Breakdown of complex compounds such as faeces & dead orgs into simpler carbon compounds transfers from **biosphere to pedosphere/atmosphere.**
16
New cards
Flux: (4) Diffusion
Inorganic compounds are absorbed and released within the **hydrosphere and atmosphere** through diffusion.
17
New cards
Flux: (5) Lithification
process in which sediments compact under pressure, expel fluids, and gradually become solid rock. Transfers carbon from **pedosphere/biosphere (shells) to the geosphere**
18
New cards
Flux: (6) Combustion
Forest fires & fossil fuel combustion release CO2, moving carbon from the **biosphere to the atmosphere.**
19
New cards
Flux: (7) Fossilisation
Dead organisms decay minimally in anaerobic conditions, when they build up over millions of years, they form fossil fuels. Carbon moves from **pedosphere/biosphere to geosphere**
20
New cards
Flux: (8) Feeding - Technically not
\
heterotrophs moves carbon within biological molecules along the food chain through eating, within the biosphere
heterotrophs moves carbon within biological molecules along the food chain through eating, within the biosphere
21
New cards
Carbon Cycle Diagram, draw then check
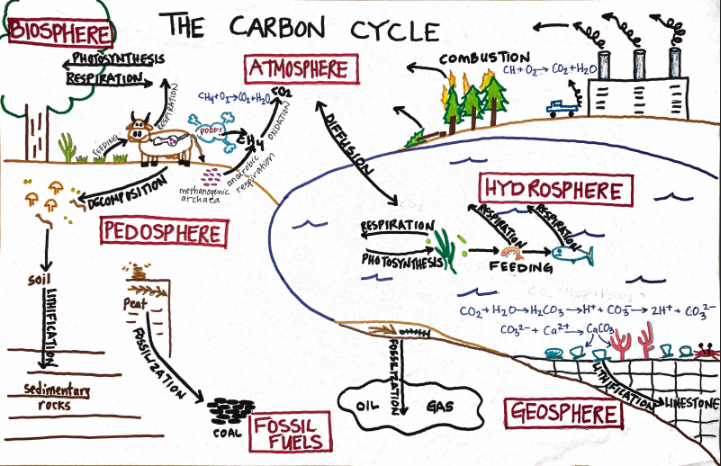
22
New cards
Carbon flux values are:
1. Measured directly
2. Extrapolated from data using mathematical models
23
New cards
Outline how data on the concentration of atmospheric carbon dioxide and methane are collected. (3 points)
Scientists measure the amount of carbon based gases through:
1. satellites measuring amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere
2. collect air samples from specific regionsto examine in a lab
3. Analyse prehistoric atmospheric CO2 content trapped in ice bubbles such as in Greenland or Antarctica.
1. satellites measuring amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere
2. collect air samples from specific regionsto examine in a lab
3. Analyse prehistoric atmospheric CO2 content trapped in ice bubbles such as in Greenland or Antarctica.
24
New cards
\
**Explain why accurate measurements of carbon dioxide and methane in the atmosphere are important.**
**Explain why accurate measurements of carbon dioxide and methane in the atmosphere are important.**
1. It is important to make observations and collect data regarding carbon based gas levels such as **CO₂ and CH4**
2. The information helps scientists understand:
* natural processes
* monitor human impact
* test whether actions to reduce greenhouse gas emissions are working
25
New cards
FF Formation: Coal (4)
\
* hard sedimentary rock
* can be burned as fuel
* C, O, N, S
* formed from peat through heat & pressure
* hard sedimentary rock
* can be burned as fuel
* C, O, N, S
* formed from peat through heat & pressure
26
New cards
FF Formation: Oil & Natural Gas (6)
* prehistoric orgs held carbon in their bodies
* when they died they sank to bottom of sea
* millions of years, sediment formed but lipid kerogen remained
* deeper they sank, more heat & pressure
* amount of pressure, heat, and type of biomass determines gas or oil.
* oil or gas then accumulates in pores around rock in process **lithification**
* when they died they sank to bottom of sea
* millions of years, sediment formed but lipid kerogen remained
* deeper they sank, more heat & pressure
* amount of pressure, heat, and type of biomass determines gas or oil.
* oil or gas then accumulates in pores around rock in process **lithification**
27
New cards
Methanogenic Archaea Examples
* occupy landfills and other soils, & ruminants e.g. cow
* sediments below the seafloor and the bottom of lakes.
* Rice fields also generate large amounts of methane during plant growth
* sediments below the seafloor and the bottom of lakes.
* Rice fields also generate large amounts of methane during plant growth
28
New cards
Methanogenic Archaea - DEF
1. prokaryotic cells in the domain Archaea
2. produce methane as a byproduct of their anaerobic respiration
3. Methane is oxidized in the atmosphere to form CO2 and H2O.
29
New cards
Seasonal CO2 Fluctuations
* result of photosynthetic activity by plants
* Decrease in CO2 is due to high photosynthetic activity by plants in spring & summer
* Increase in CO2 is due to plant dormancy and less photosynthesis in winter, and increased respiration by other orgs.
\
* Decrease in CO2 is due to high photosynthetic activity by plants in spring & summer
* Increase in CO2 is due to plant dormancy and less photosynthesis in winter, and increased respiration by other orgs.
\
30
New cards
Ocean Acidification Reaction
1. CO2 diffuses into the ocean, reacting with H2O to form carbonic acid (H2CO3)
2. Carbonic acid dissociates to form bicarbonate ions and hydrogen ions
3. Then bicarb ions dissociate further to form CO3 & H+
31
New cards
OA: CaCO3
1. coral and molluscs absorb CO3- and Ca+ ions to form CaCO3
2. They use it to build shells and exoskeletons
3. Can also form limestone
32
New cards
Oxidation of Methane
1. Methane is released by organisms and is burned as a fossil fuel
2. When CH4 enters the atmosphere it reacts with oxygen
3. CH4 + 2O2 → 2H2O + CO2
4. This releases CO2
33
New cards
Peat
* heterogenous mixture of dead organic material, moss and histosol
* anaerobic conditions created due to high levels of water, non-decomposed material accumulates
* pH very acidic, and takes hundreds of years to form
* non-renewable
* anaerobic conditions created due to high levels of water, non-decomposed material accumulates
* pH very acidic, and takes hundreds of years to form
* non-renewable
34
New cards
Peat as a fossil fuel
1. peat is dried out to reduce high levels of humidity
2. cut into slabs, granules, or blocks
3. burned
35
New cards
Biosequestration
process of removing carbon from the cycle/environment then trapping carbon within limestone, such as the tiny shells of foraminifera. However this limestone is used in cement, and when used releases CO2 back into the atmosphere