Gastrointestinal Histology - Dr. Schreeg
1/218
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
219 Terms
Three embryologic tissue layers:
1.) ectoderm
2.) endoderm
3.) mesoderm
Endoderm
forms mucosa, or the tissues that line the GI tract and lungs (gut, liver, and lungs)
Mesoderm
forms the connective tissues and muscle that form the outer layer of GI tract (forms muscle, bones, kidneys, blood, gonads, and connective tissue)
Three embryological origins of GI tract organs:
1.) foregut
2.) midgut
3.) hindgut
The foregut will develop into (6)
1.) esophagus
2.) stomach
3.) proximal duodenum
4.) liver
5.) pancreas
6. (lungs)
The midgut will develop into (3)
1.) remaining small intestine
2.) cecum
3) proximal colon
The hindgut will develop into (2)
1.) distal colon
2.) rectum
What structure sets the boundary of the cranial aspect of developing embryo?
oropharyngeal membrane
oropharyngeal membrane
dissolves during development to become the mouth
What structure sets the boundary of the caudal aspect of developing embryo?
cloacal membrane
cloacal membrane
dissolves during development to become the urogenital and anal orifices
Main vessel that supplies the foregut
celiac artery
Main vessel that supplies the midgut
cranial mesenteric artery
Main vessel that supplies the hindgut
caudal mesenteric artery
Across multiple species, GI anatomy is the same EXCEPT when it comes to the: (3)
1.) stomach
2.) ascending colon
3.) cecum
Across multiple species, GI histology is the same EXCEPT in:
the stomach
Four upper GI tract sections:
1.) oral cavity
2.) tongue
3.) esophagus
4.) salivary gland
What upper GI tract structures are lined by stratified squamous epithelium? (3)
1.) oral cavity
2.) tongue
3.) esophagus
Function of stratified squamous epithelium of the upper GI tract
protection
Which part of the oral cavity may be keratinized?
gingiva
What regions of the oral cavity may contain skeletal muscle? Why?
soft palate; it is mobile
What lies below the epithelium of the upper GI tract?
lamina propria
Describe the lamina propria under the epithelium of the upper GI tract
Deep connective tissue that’s vascular and collagen-rich
The tongue is lined by what epithelium?
Stratified squamous epithelium that may be keratinized
Two special features of the tongue histology:
1.) dorsal surface forms papillae or exophytic projections
2.) skeletal muscle forms core of tongue
What does the dorsal surface of the tongue form?
Papillae or exophytic projections
What is the purpose of papillae found on the dorsal surface of the tongue?
Serves different functions, including grooming and chemoreception (taste buds!)
What forms the core of the tongue?
Skeletal muscle
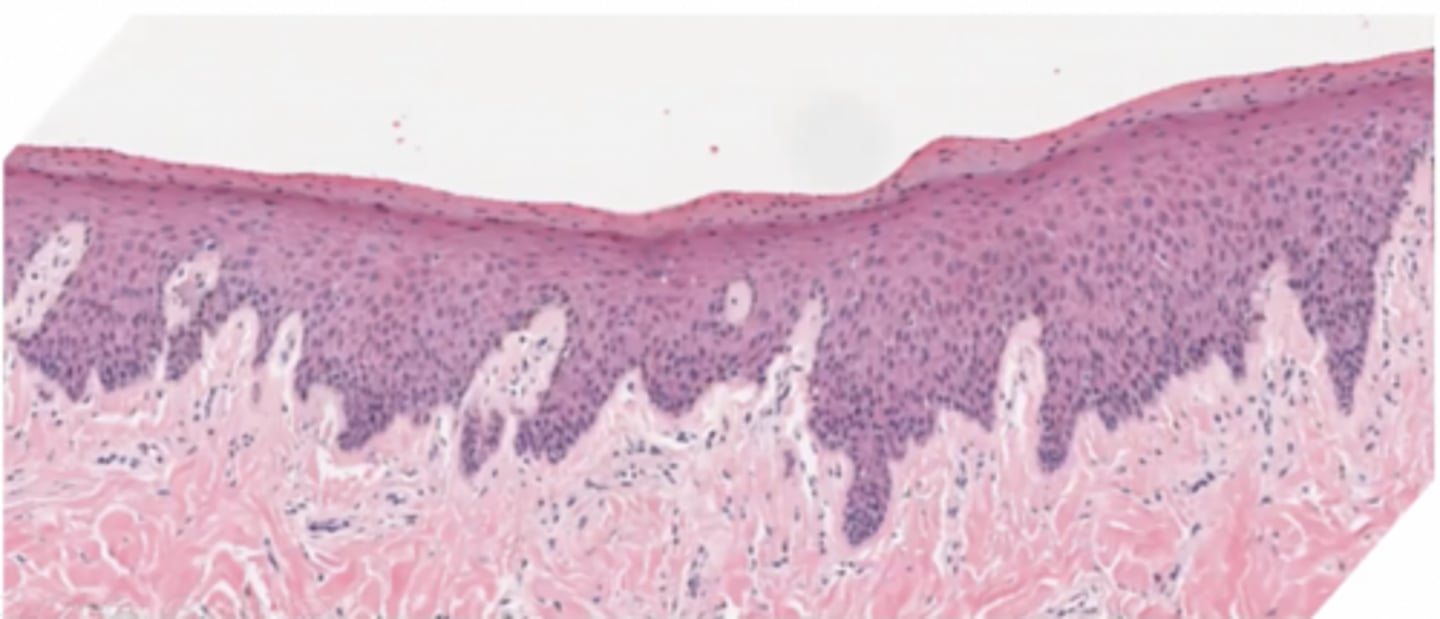
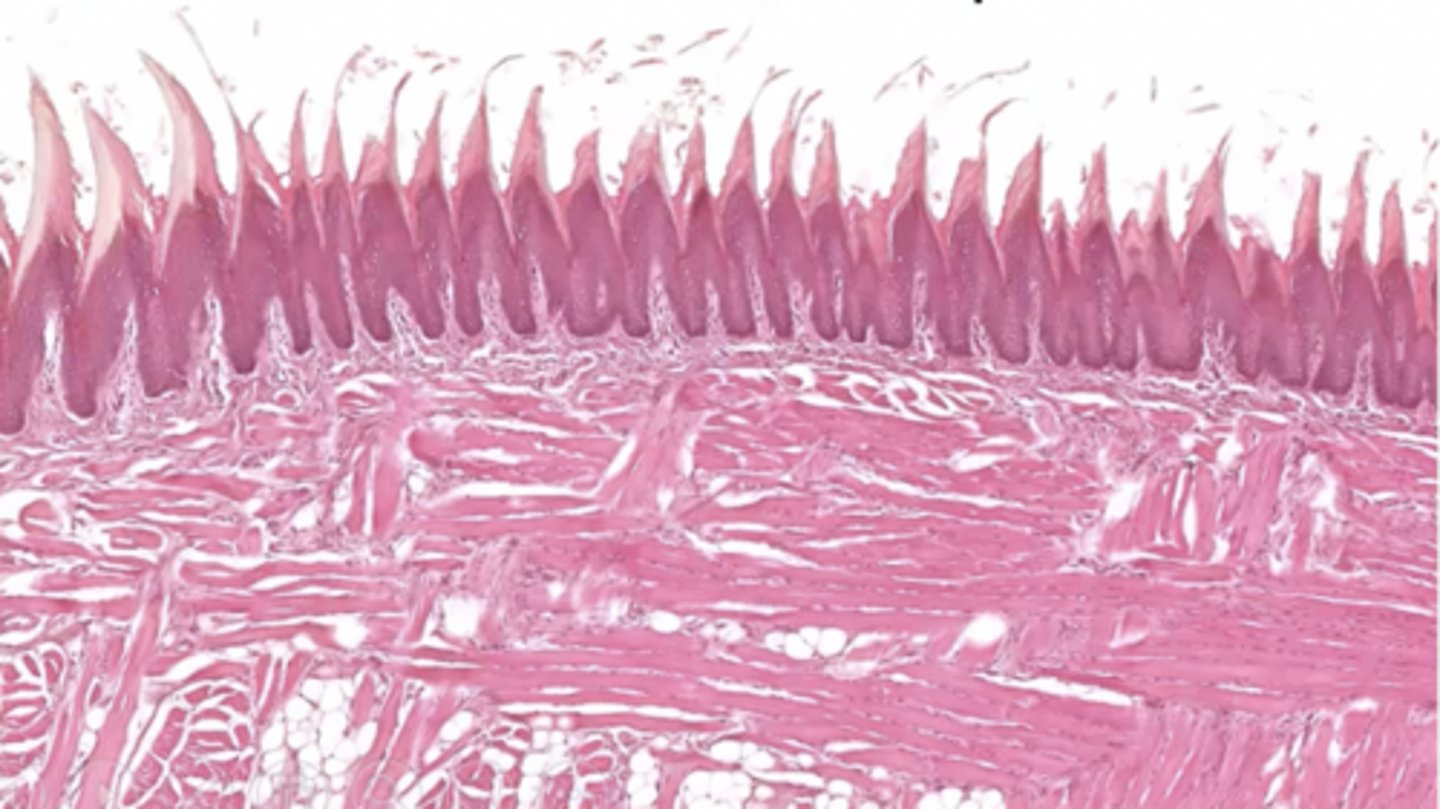
What type of epithelium is this?
keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
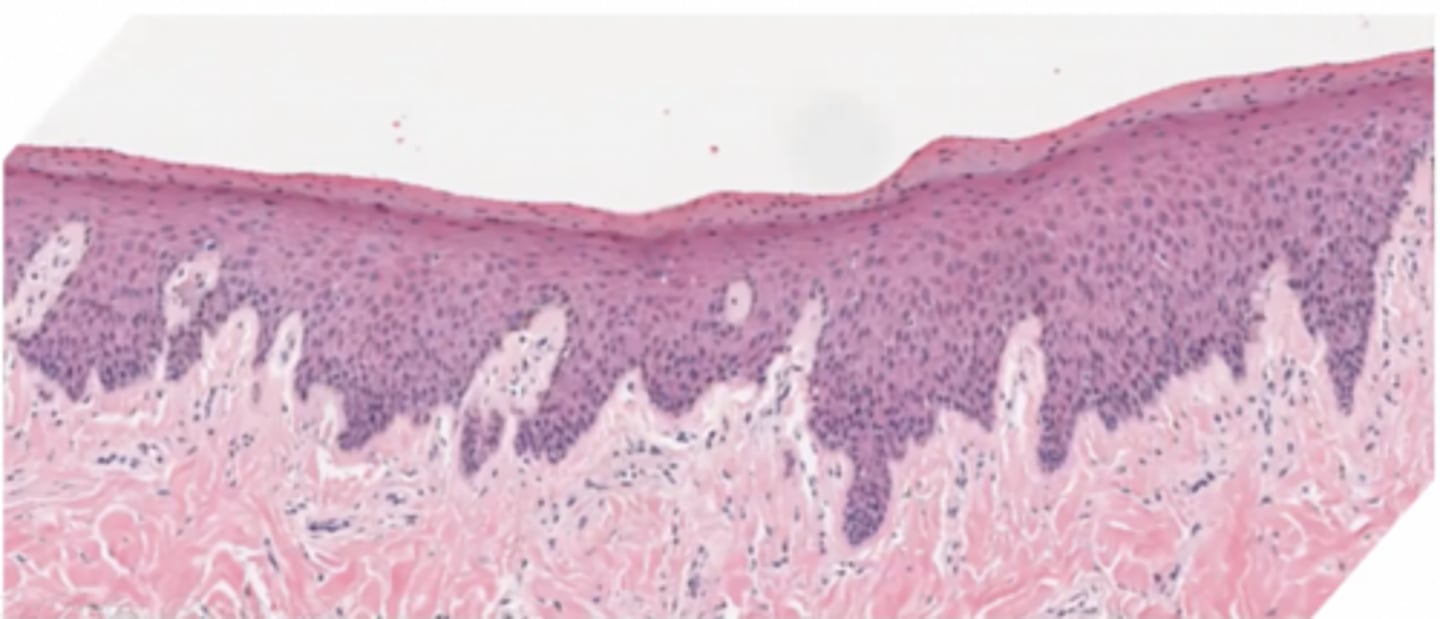
Where might this epithelium be found?
oral cavity
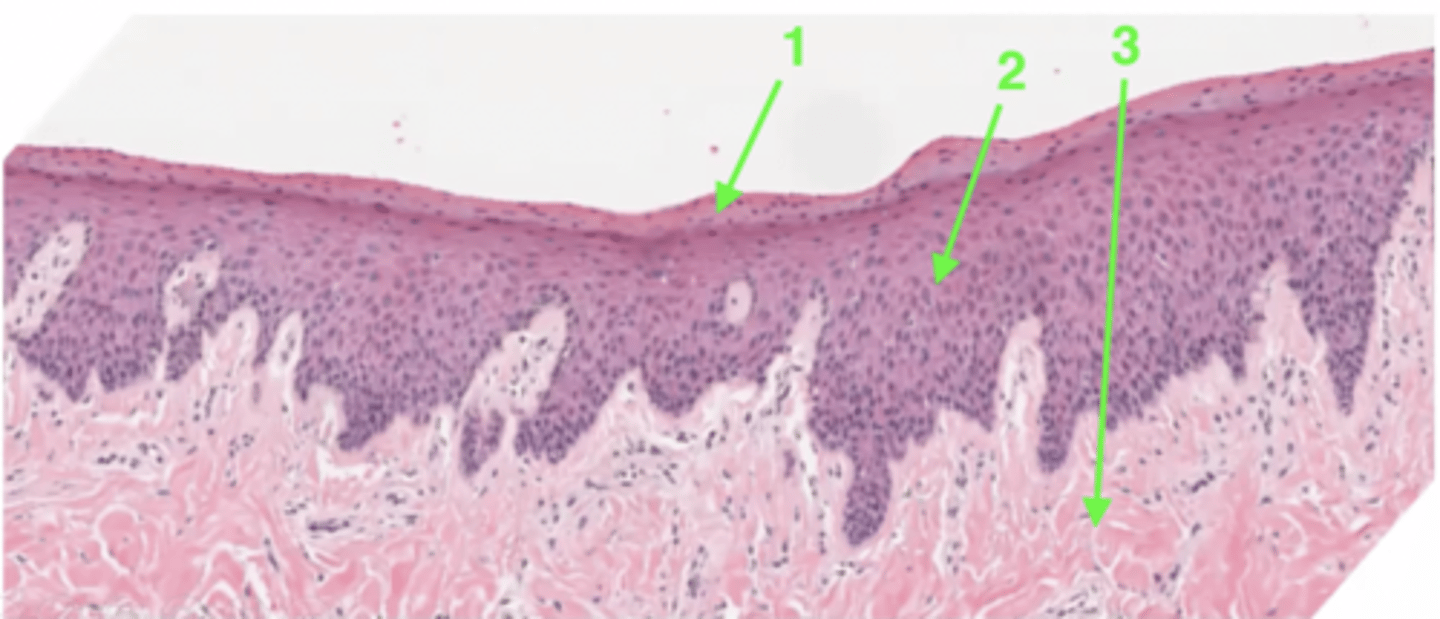
1
keratin layer
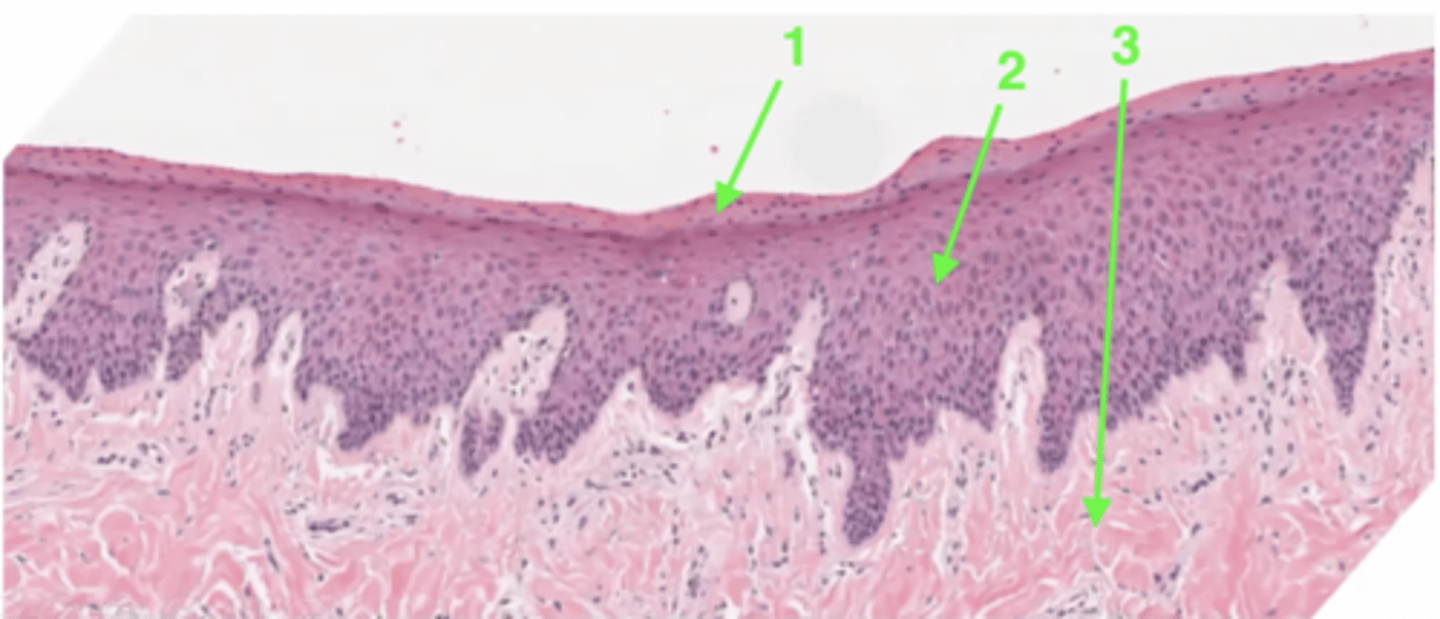
2
stratified squamous epithelium
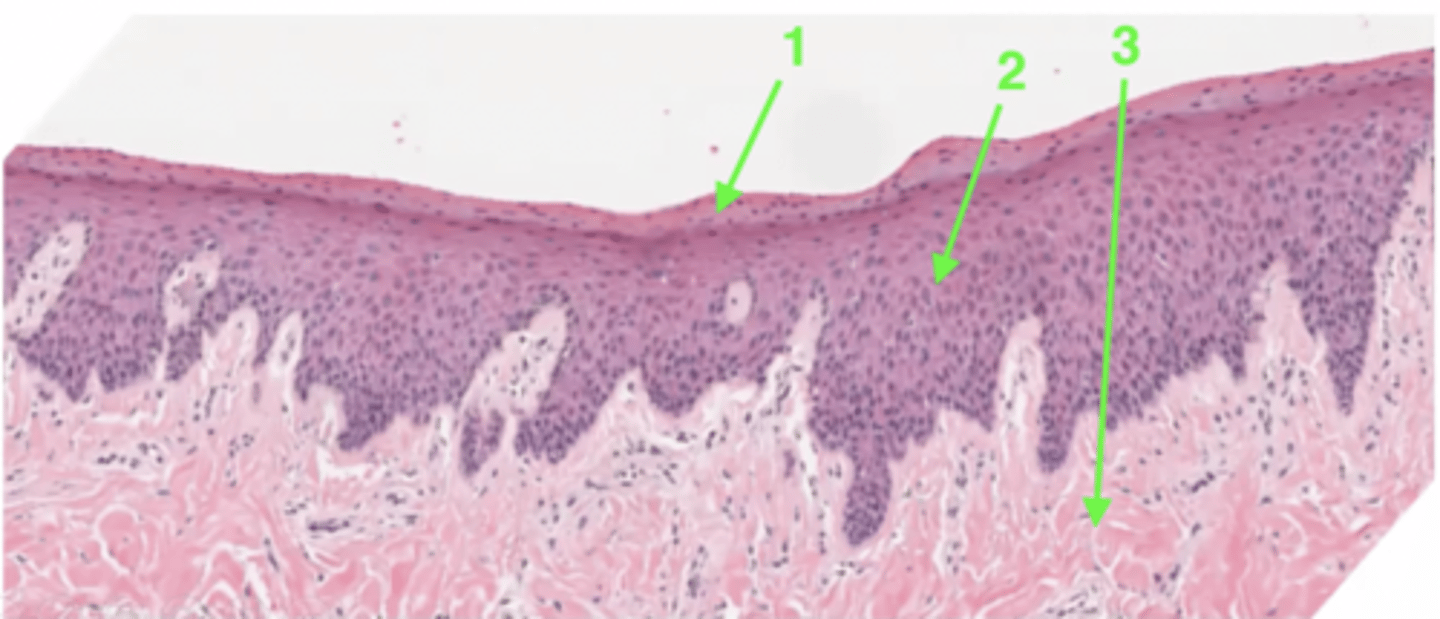
3
lamina propria
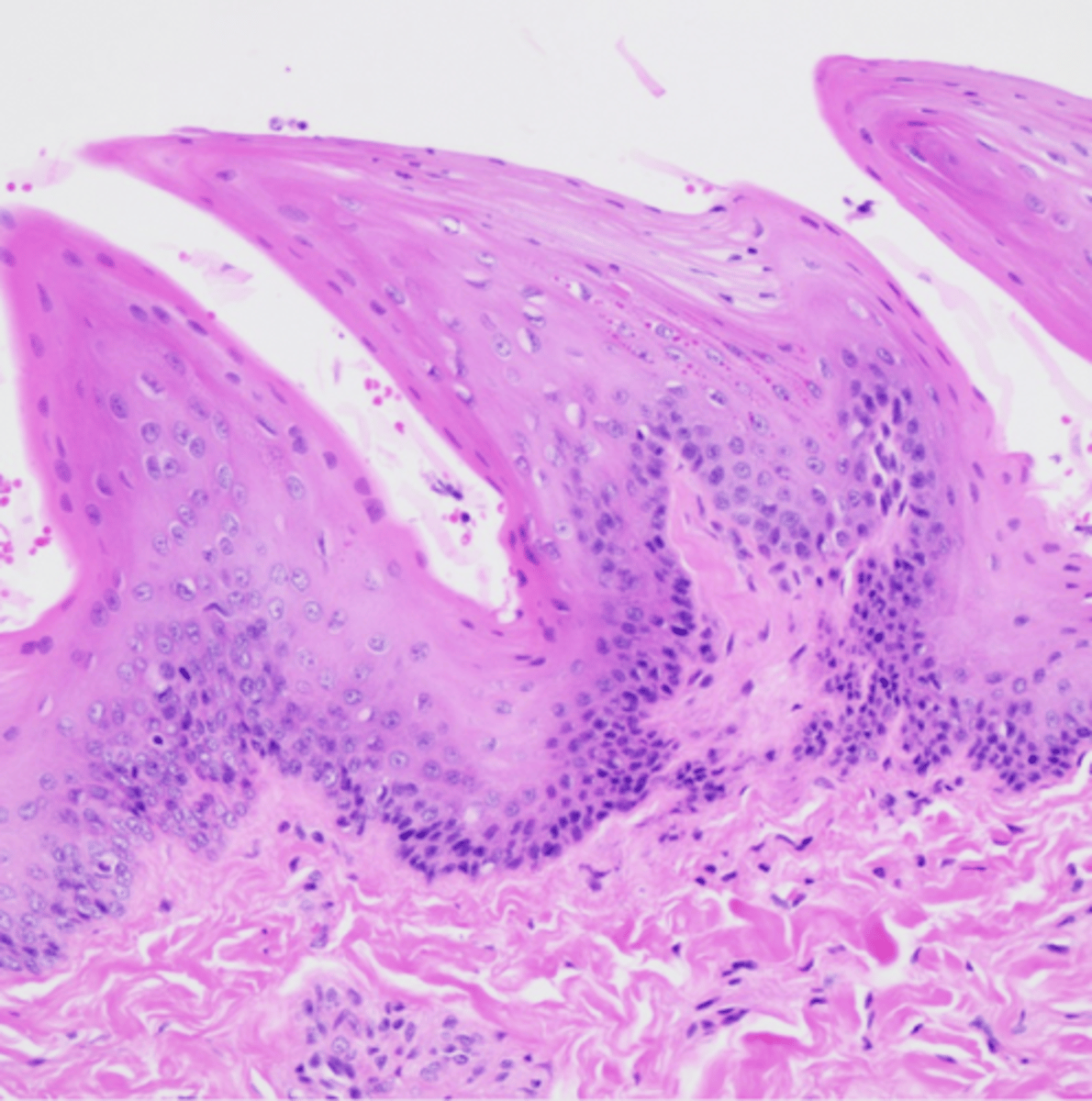
What structure is this epithelium found in?
the tongue
What are the projections coming off this epithelium?
tongue papillae
What structure is this epithelium found in?
the tongue
What species does this epithelium belong to?
the cat (spiky papillae used for grooming)
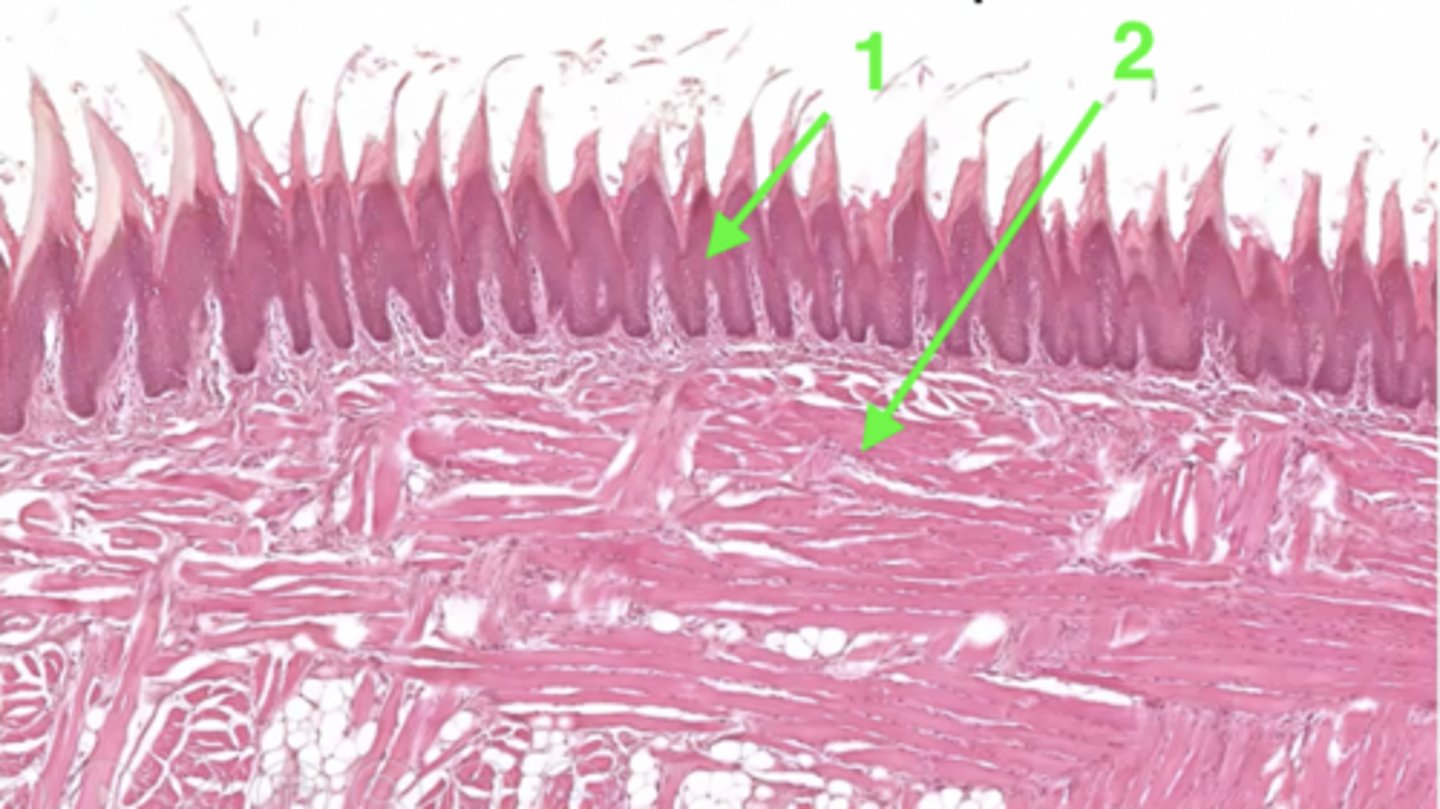
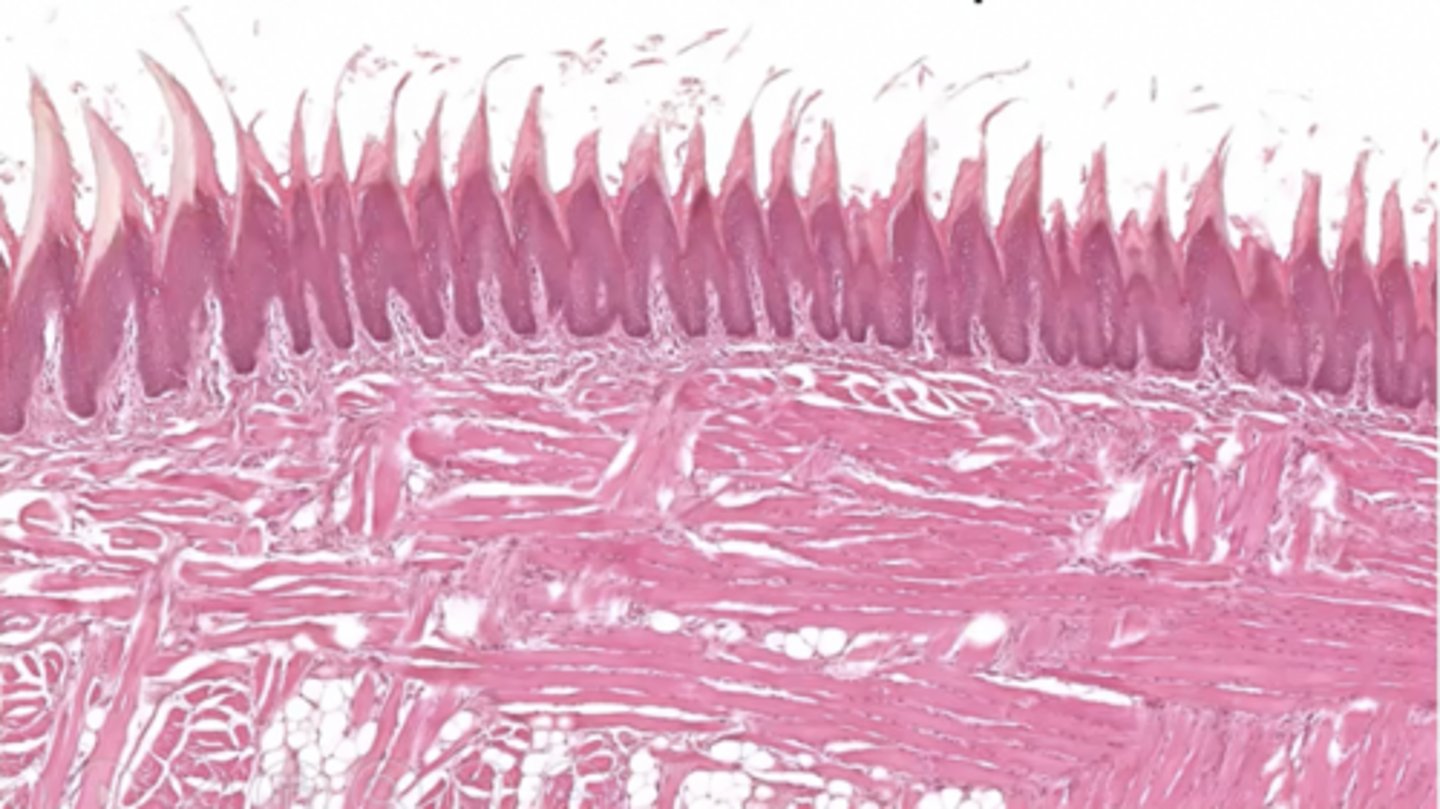
1 (type of tissue)
keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
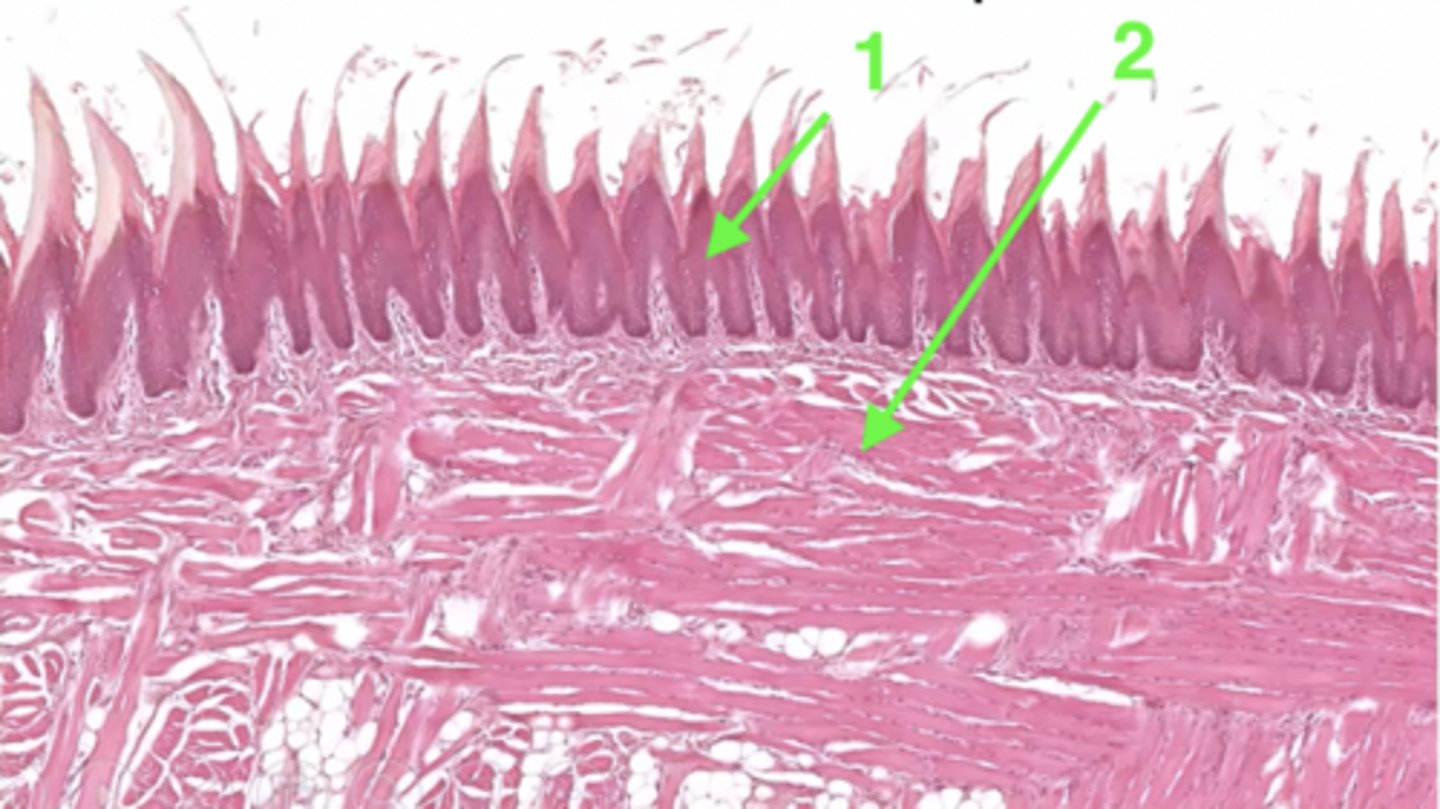
2 (type of tissue)
skeletal muscle
What structure is this epithelium found in?
the tongue
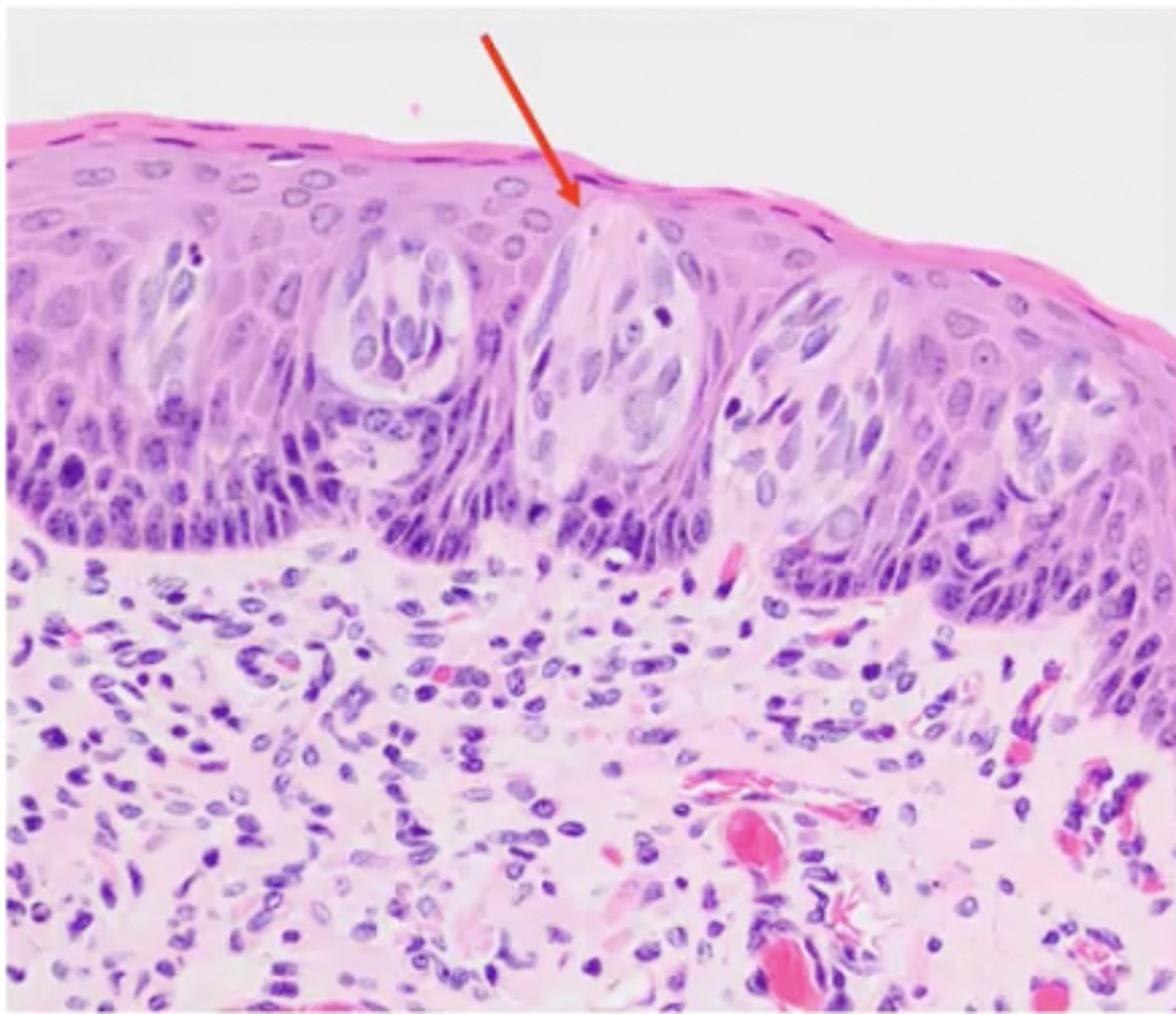
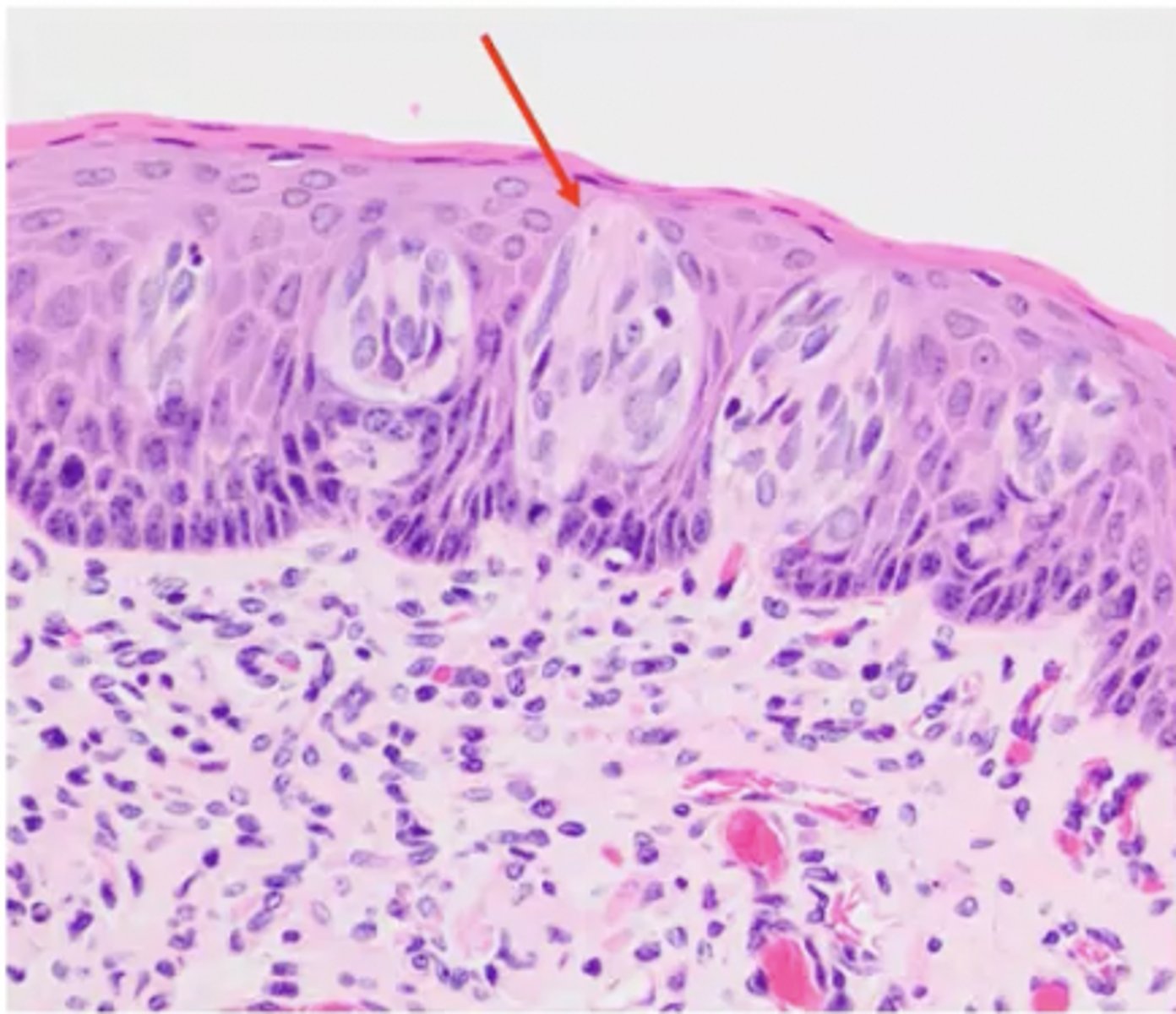
What is the arrow pointing to?
chemoreceptor cells (taste buds)
What upper GI tract structures are lined by simple cuboidal epithelium?
salivary glands
Function of simple cuboidal epithelium of the salivary gland in the upper GI tract
secretion
The simple cuboidal epithelium of salivary glands is arranged in two ways:
1.) acini
2.) ducts
Acini of salivary glands
make and secrete saliva into ducts
Two types of epithelium cells found in acini:
1.) mucous
2.) serous
Mucous epithelium cells of acini appearance
pale, basophilic (blue) to clear cytoplasm
serous epithelium cells of acini appearance
pale, eosinophilic (pink) granular cytoplasm
What is the function of mucous epithelial cells of acini?
Make mucus for lubrication
What is the function of serous epithelial cells of acini?
Make proteins that contain digestive enzymes
Ducts of salivary glands
convey saliva to the mouth
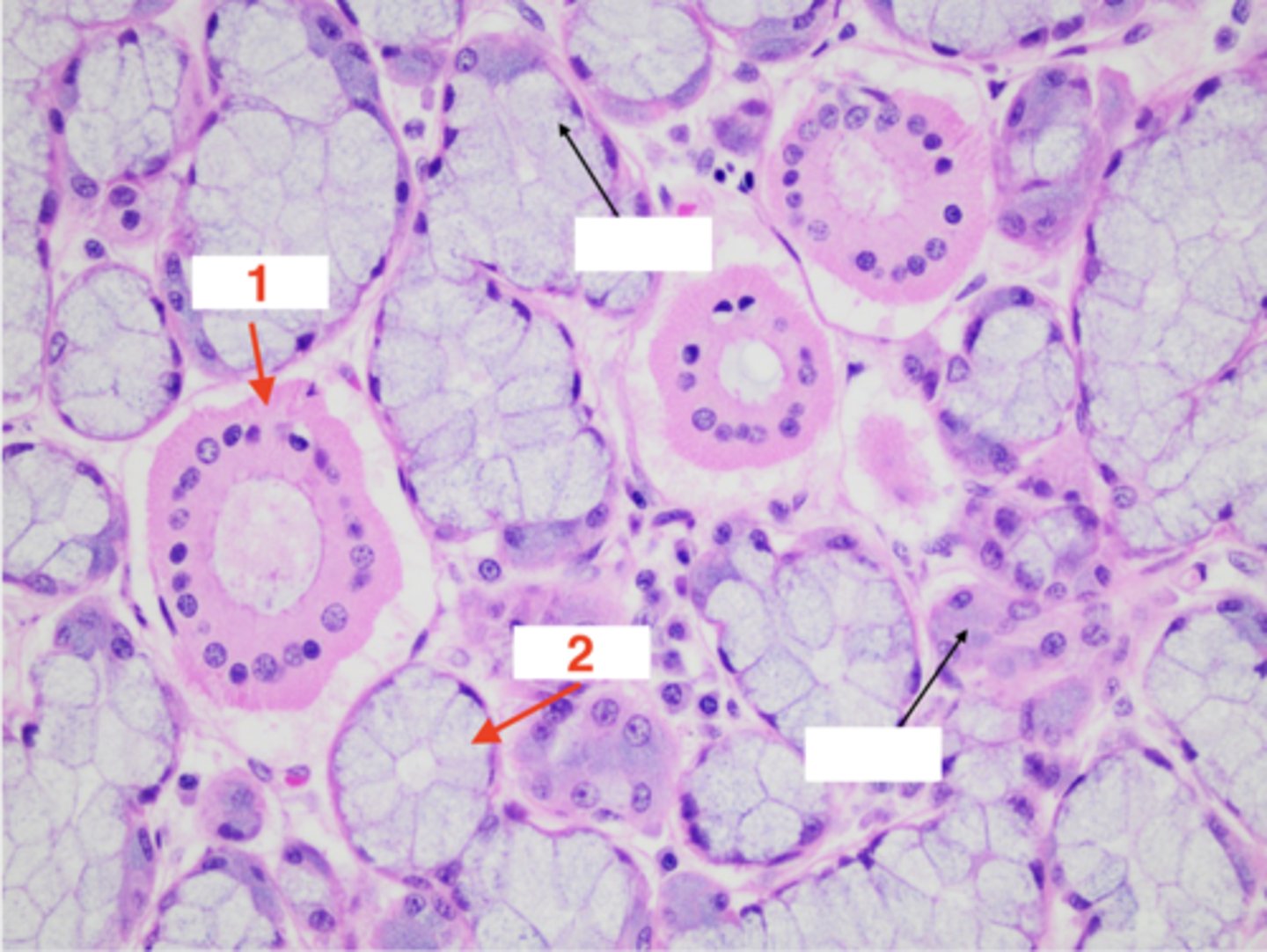
What structure is this tissue part of?
salivary gland
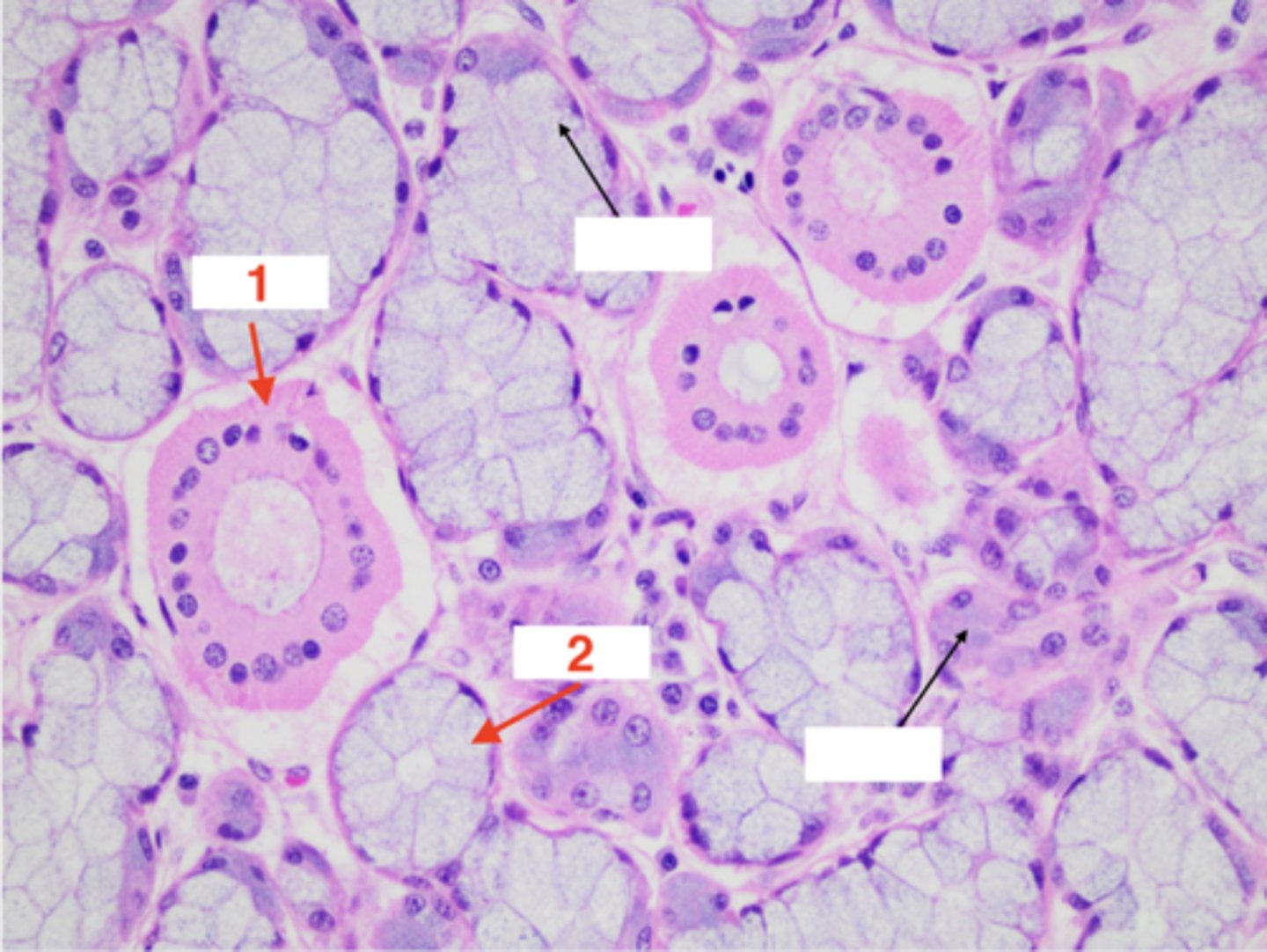
1
salivary duct
2
salivary acini
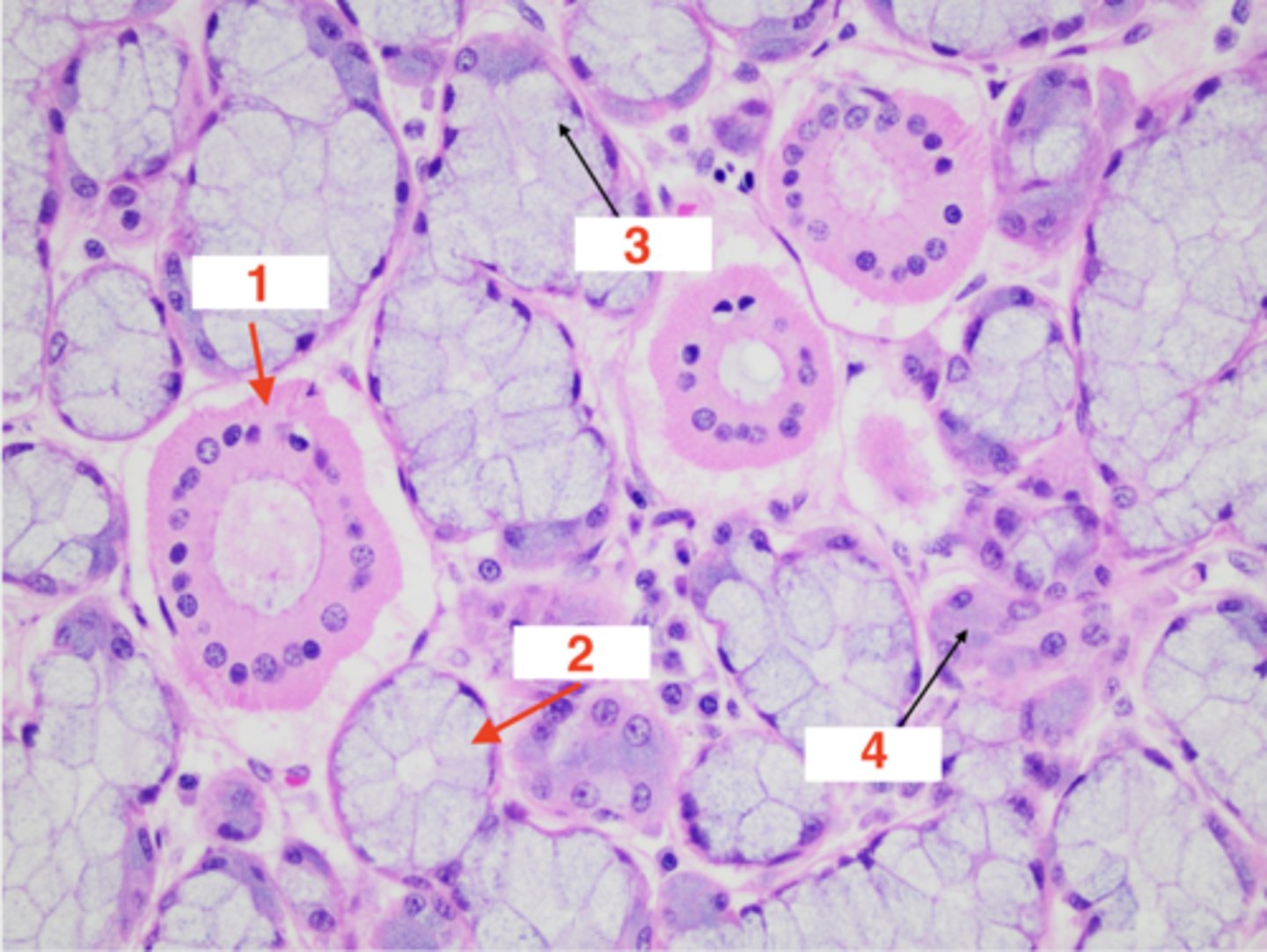
3 (type of epithelial cell in acini)
mucous
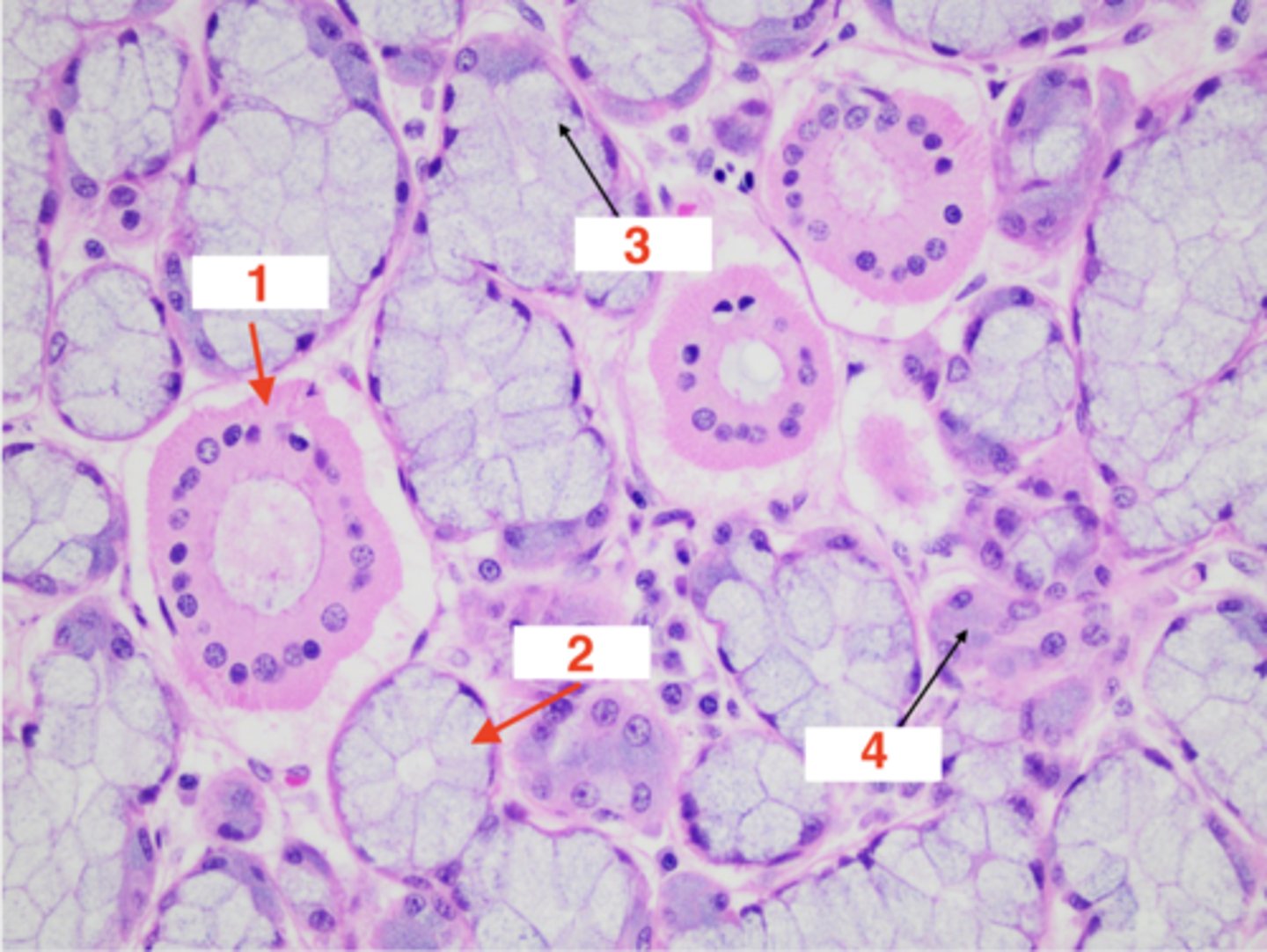
4 (type of epithelial cell in acini)
serous
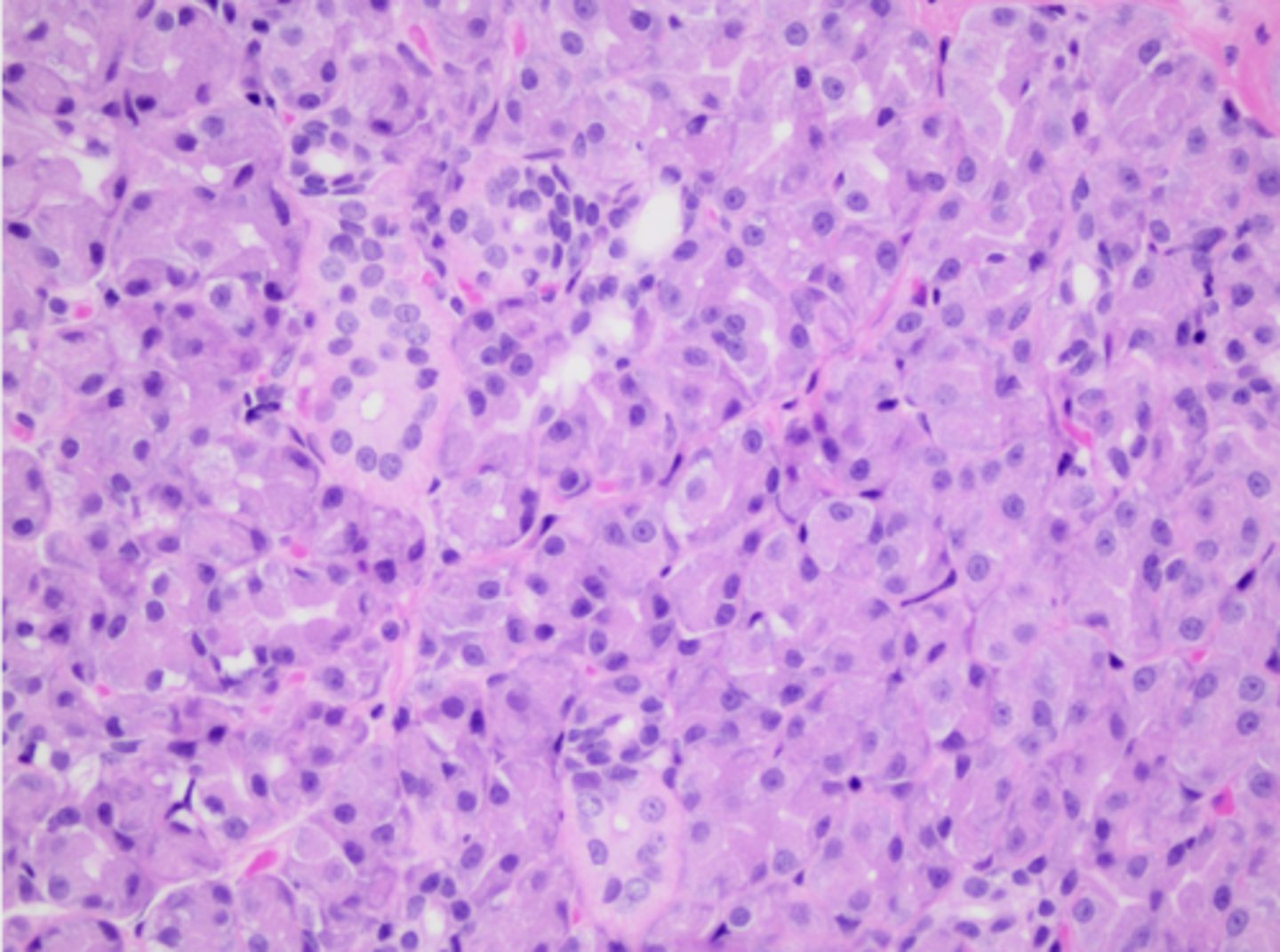
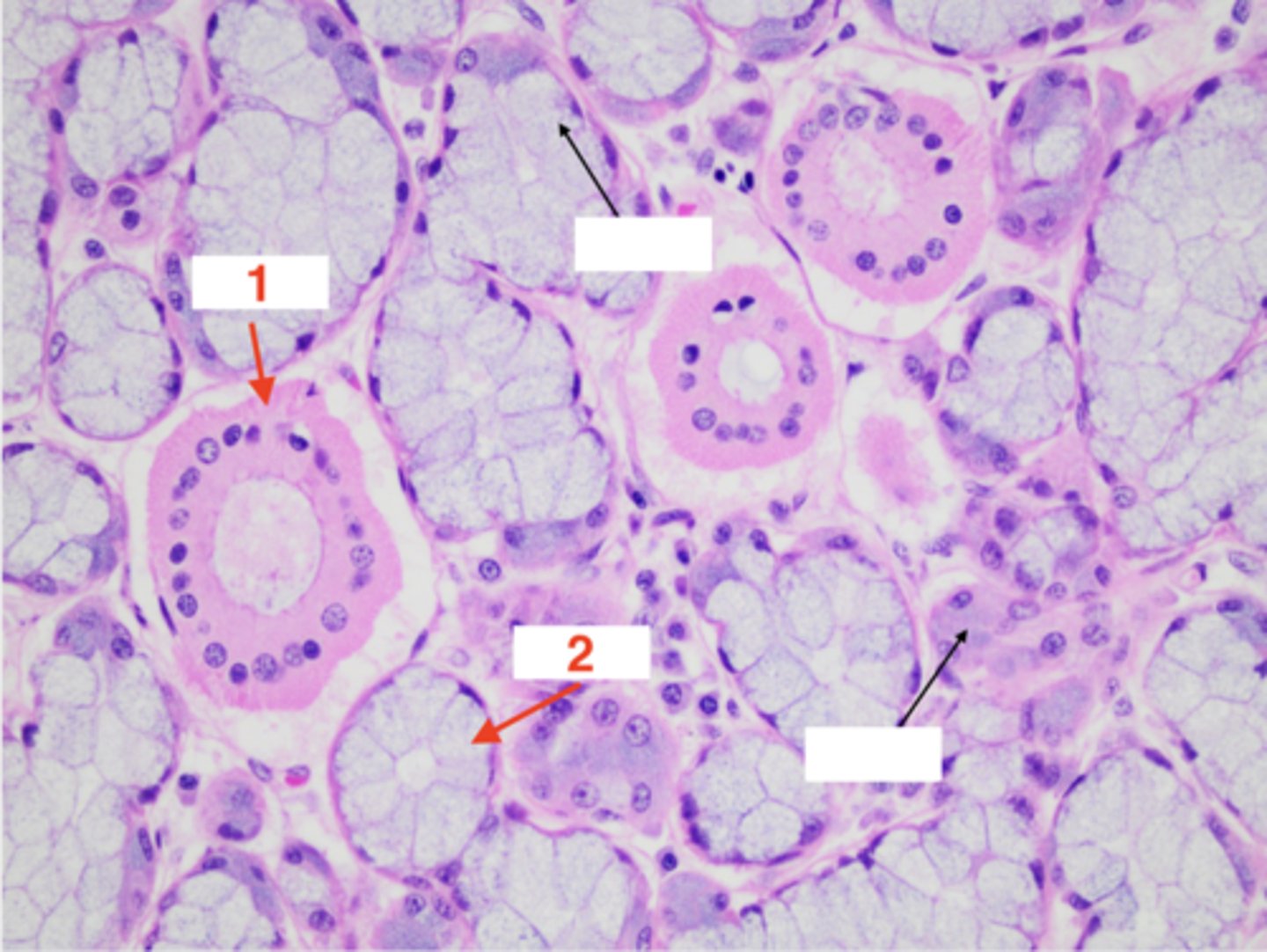
What structure is this tissue part of?
salivary gland
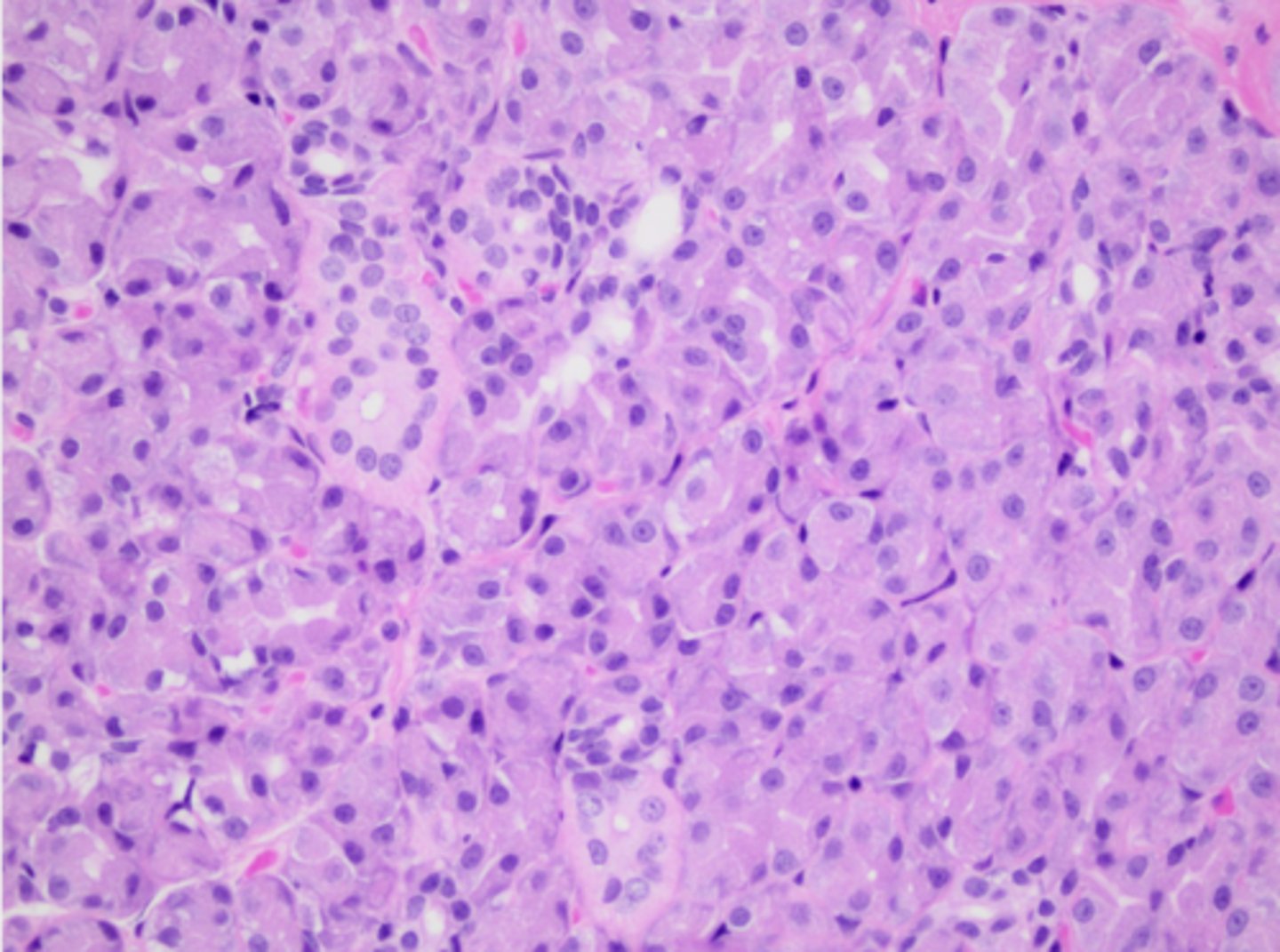
This salivary gland tissue is mostly composed of mucous or serous acini epithelium?
serous (pink color, granular)
Four layers of the tubular GI tract, from deep to superficial:
1.) mucosa
2.) submucosa
3.) muscularis
4.) serosa
Muscosa
innermost lining of the GI tract where epithelium is located
Three layers of the mucosa, from deep to superficial:
1.) epithelium
2.) lamina propria
3.) muscularis mucosae
Submucosa
A mostly connective tissue layer of the tubular GI that contains glands and lymphoid tissue
muscularis
Comprised of smooth muscle in both a circular and longitudinal arrangement
Function of muscularis layer of tubular GI
Together, the two layers of muscle contract in 2 dimensions, helping to propel food along the GI tract
serosa
outermost layer of the GI tract lined by mesothelium
mesothelium
epithelium that lines body cavities
Muscularis mucosa
A very thin muscle layer between the mucosa layer and submucosa layer of the tubular GI
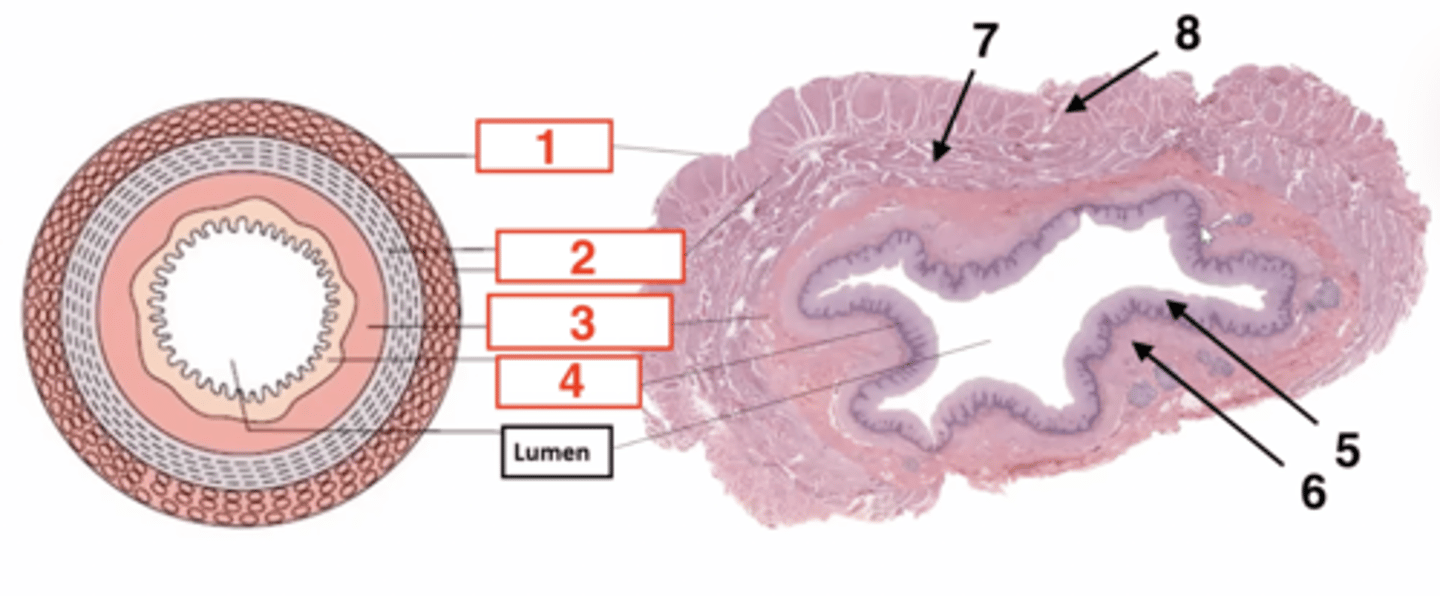
1
serosa
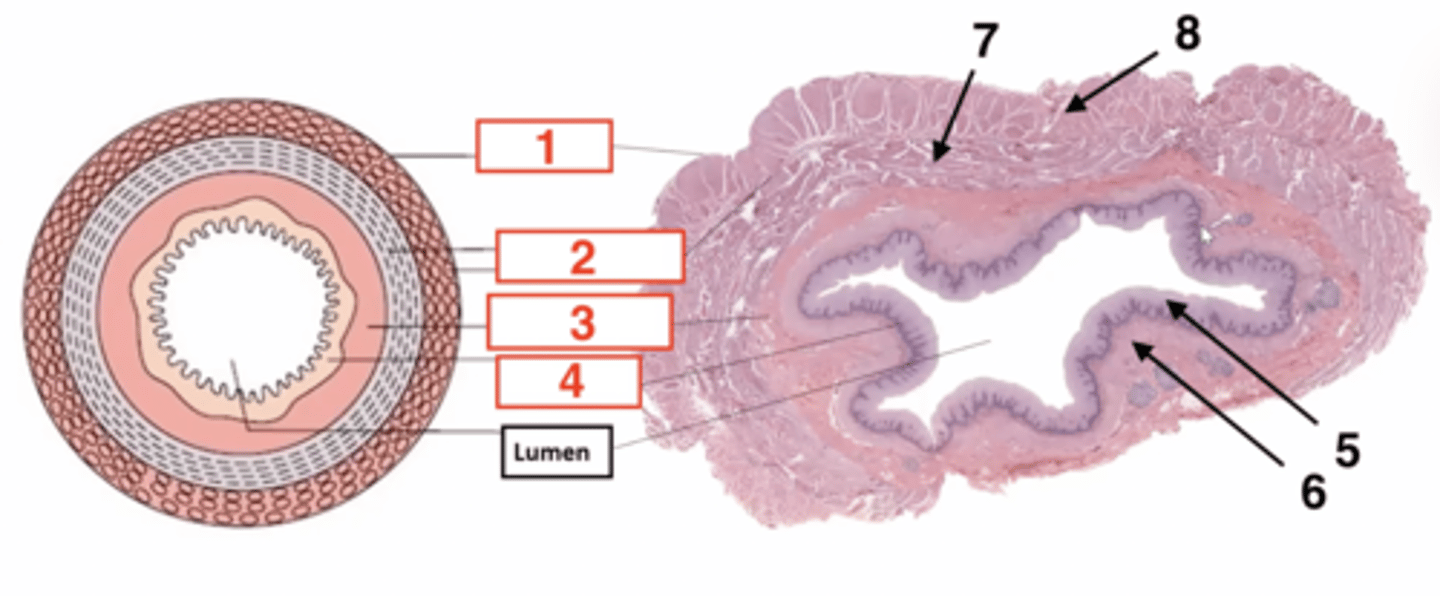
2
muscularis
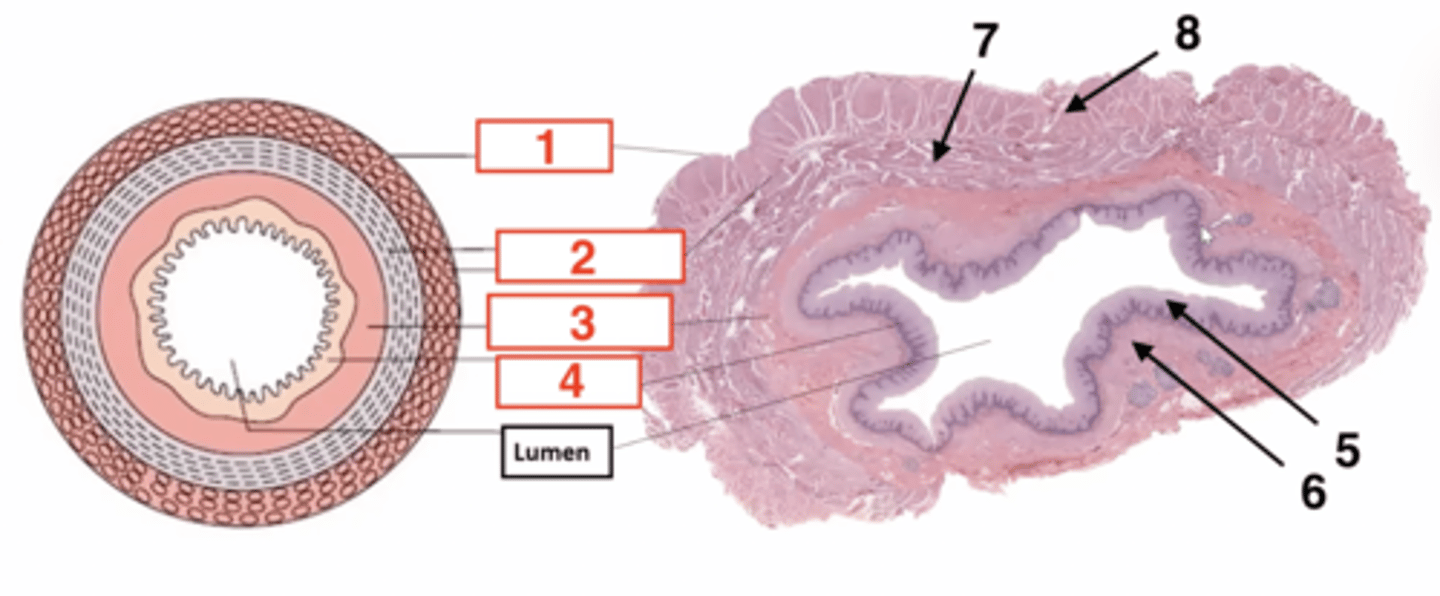
3
submucosa
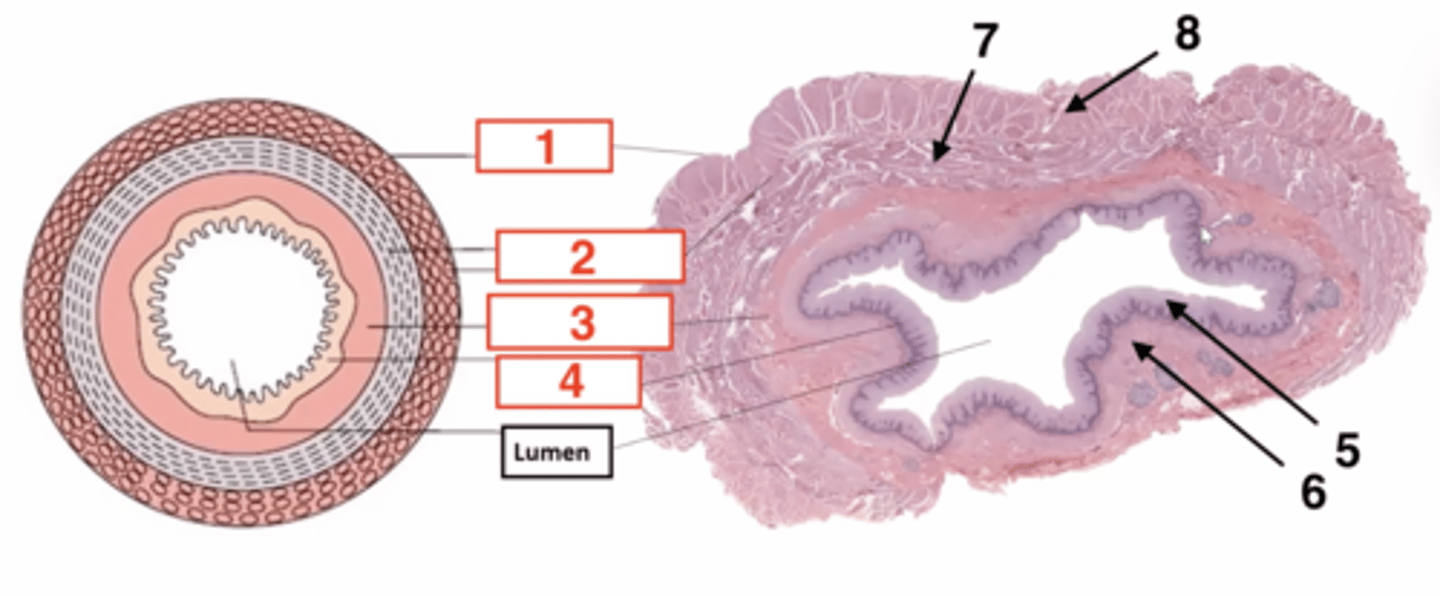
4
muscosa
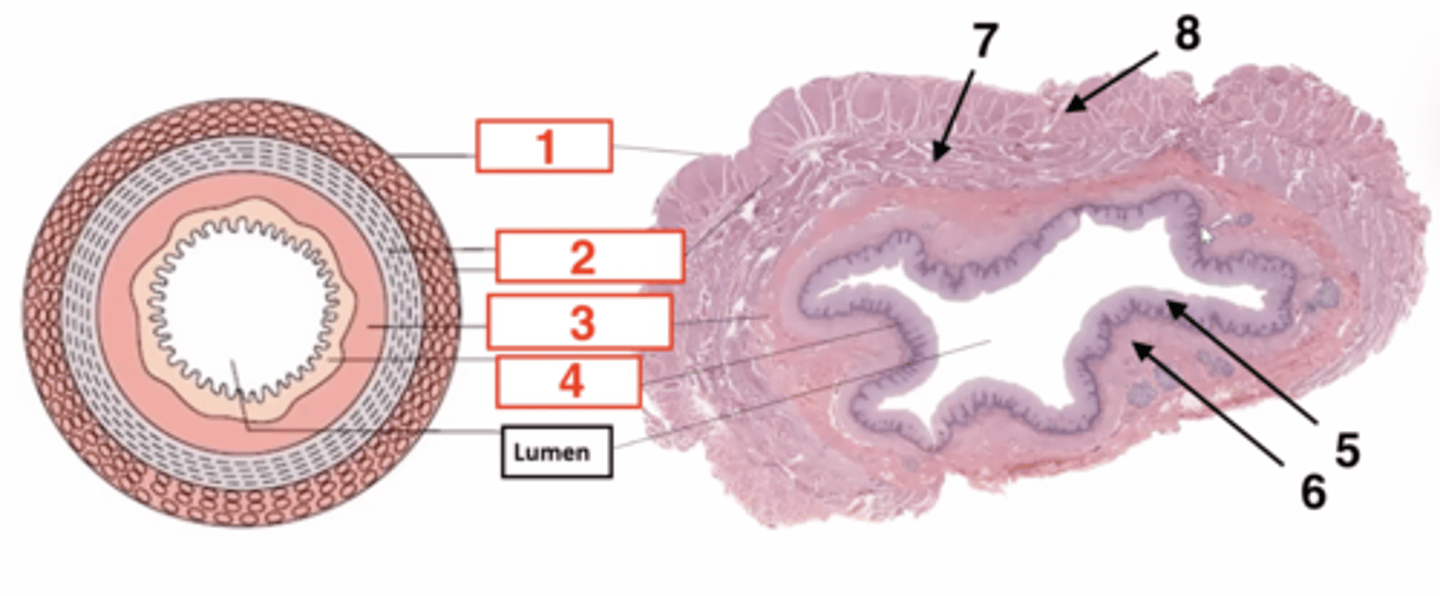
5 (part of mucosa)
epithelium
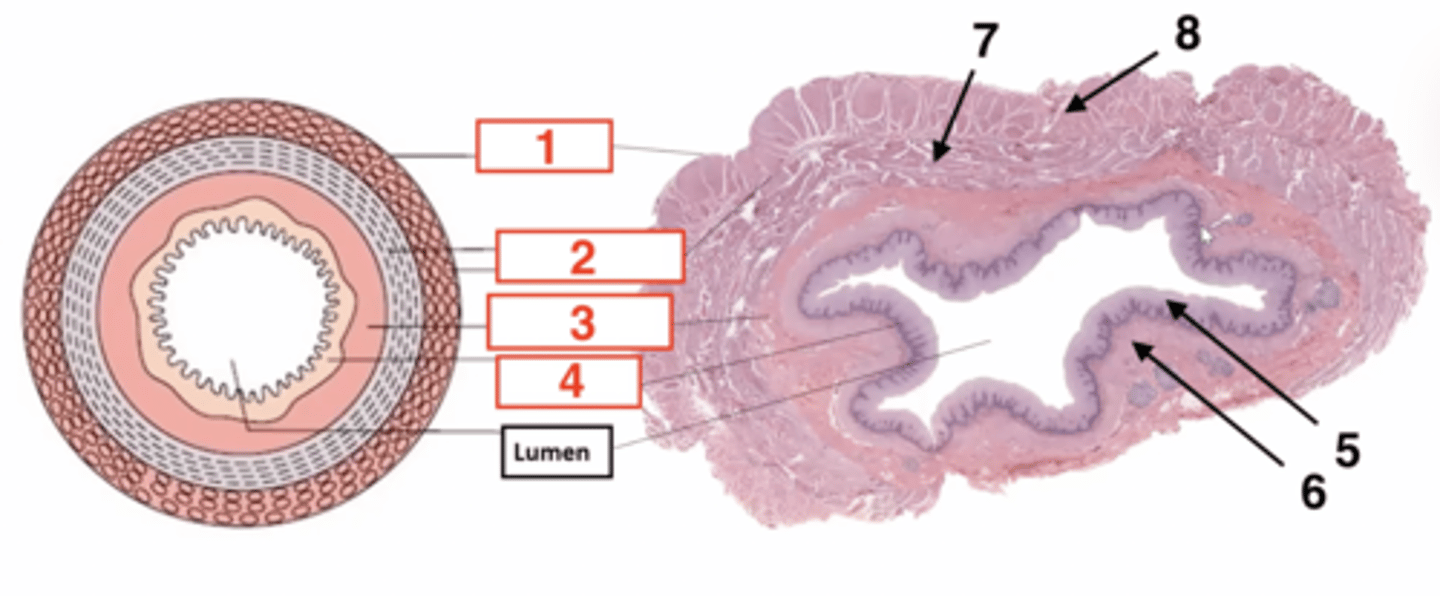
6 (part of mucosa)
muscularis mucosae
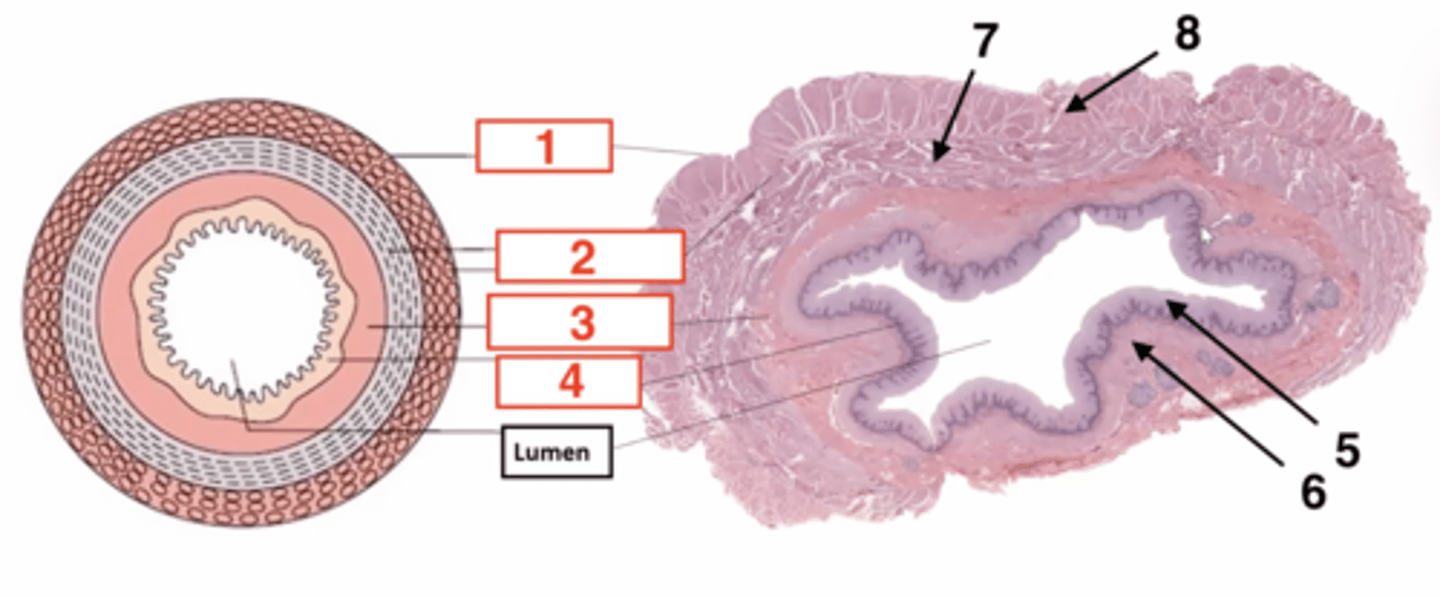
7 (part of muscularis)
circular smooth muscle
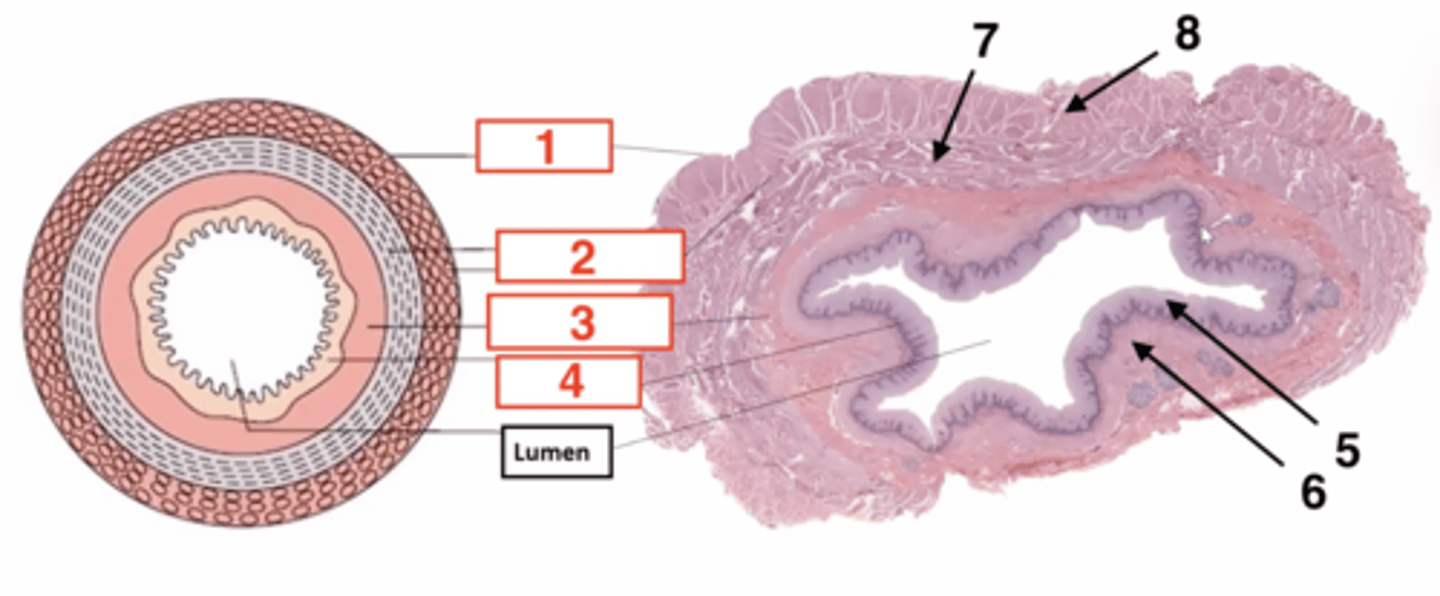
8 (part of muscularis)
longitudinal smooth muscle
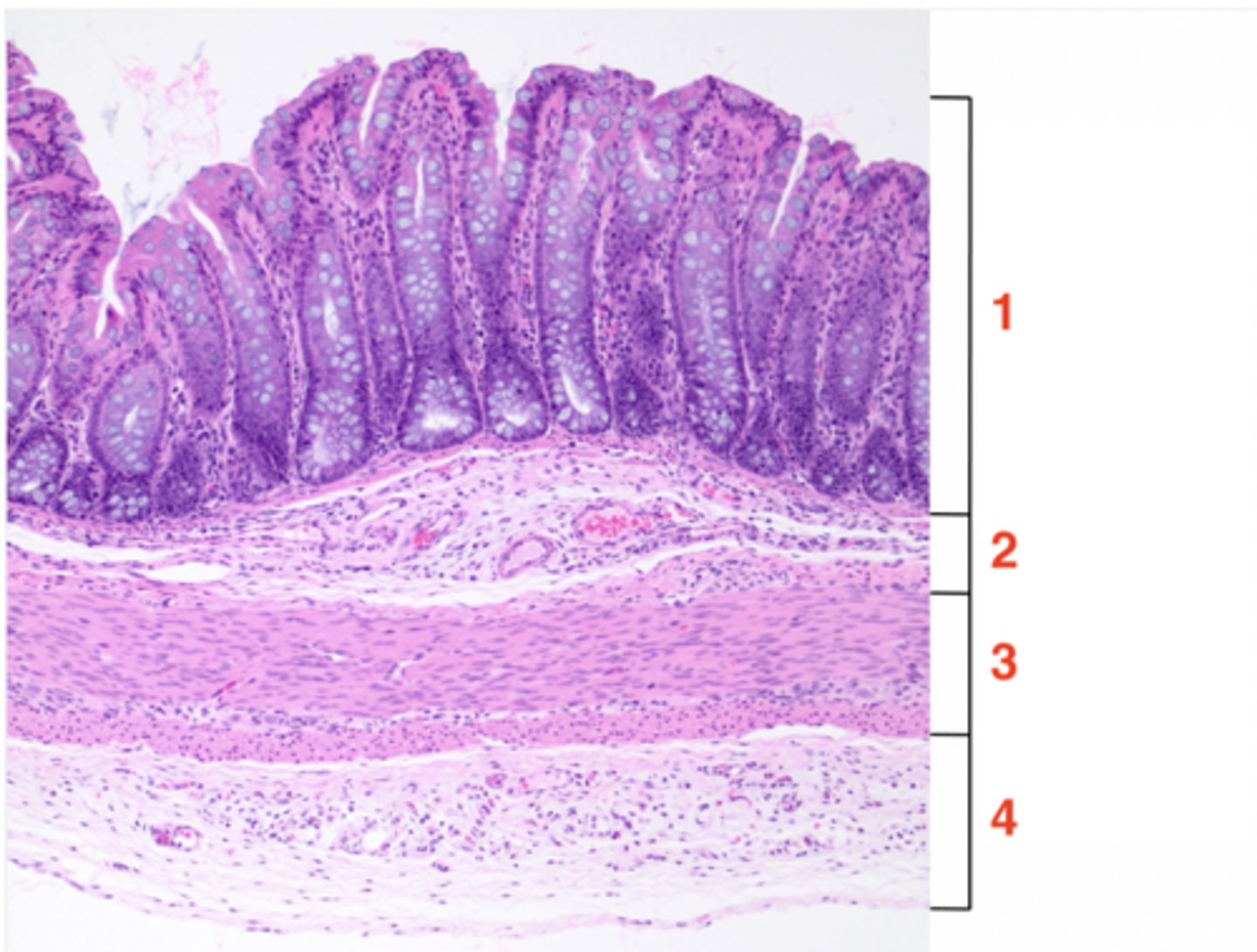
1
muscosa
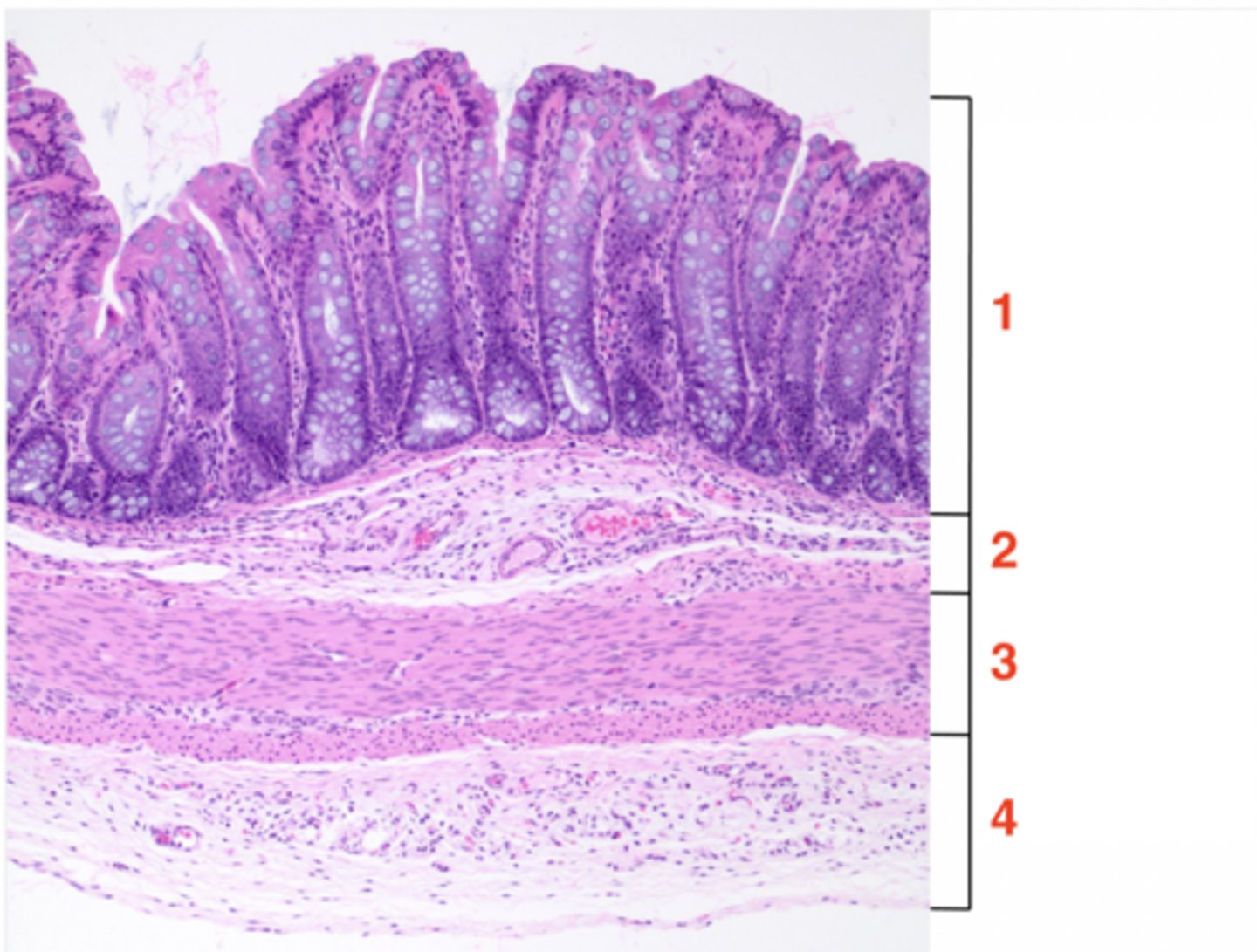
2
submucosa
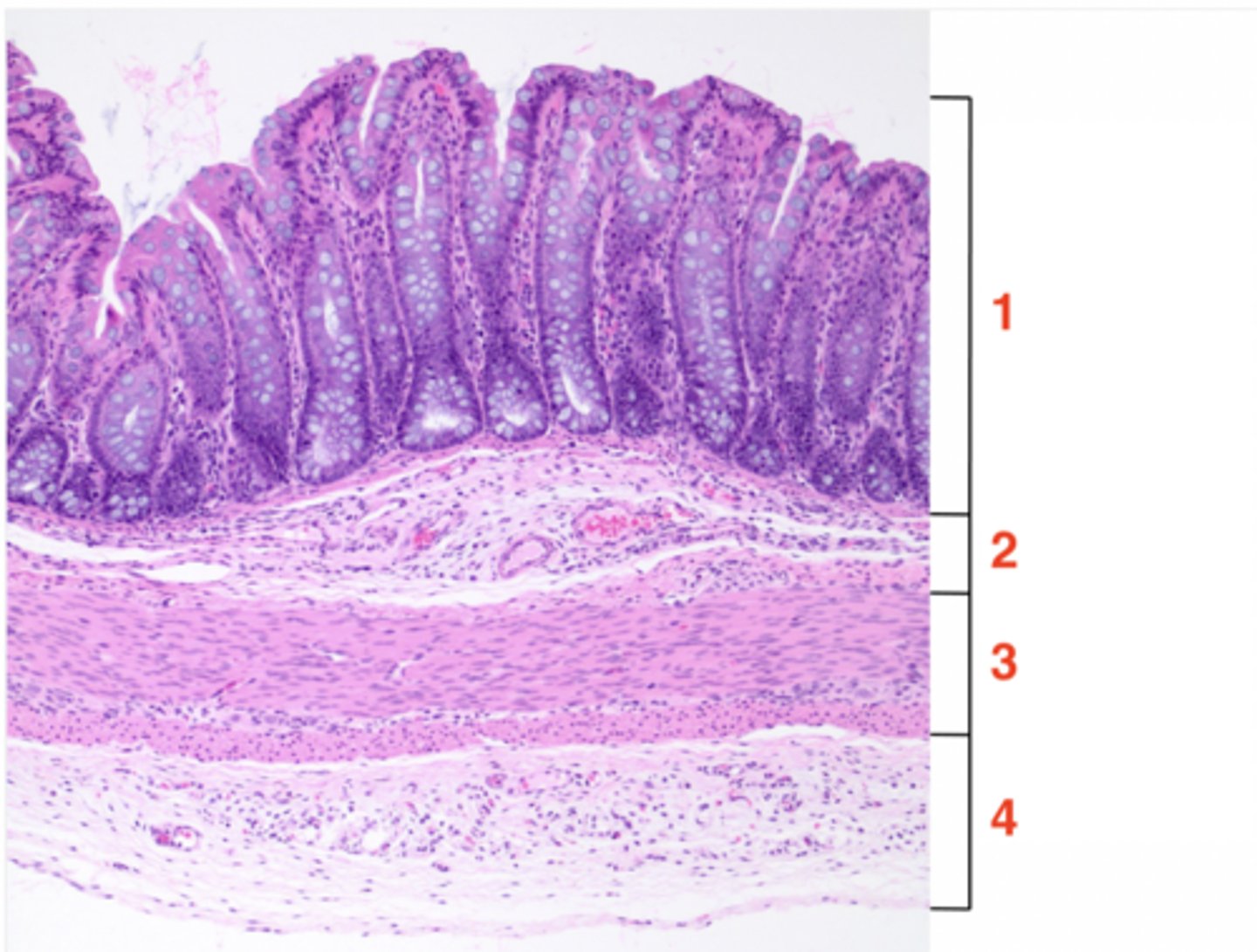
3
muscularis
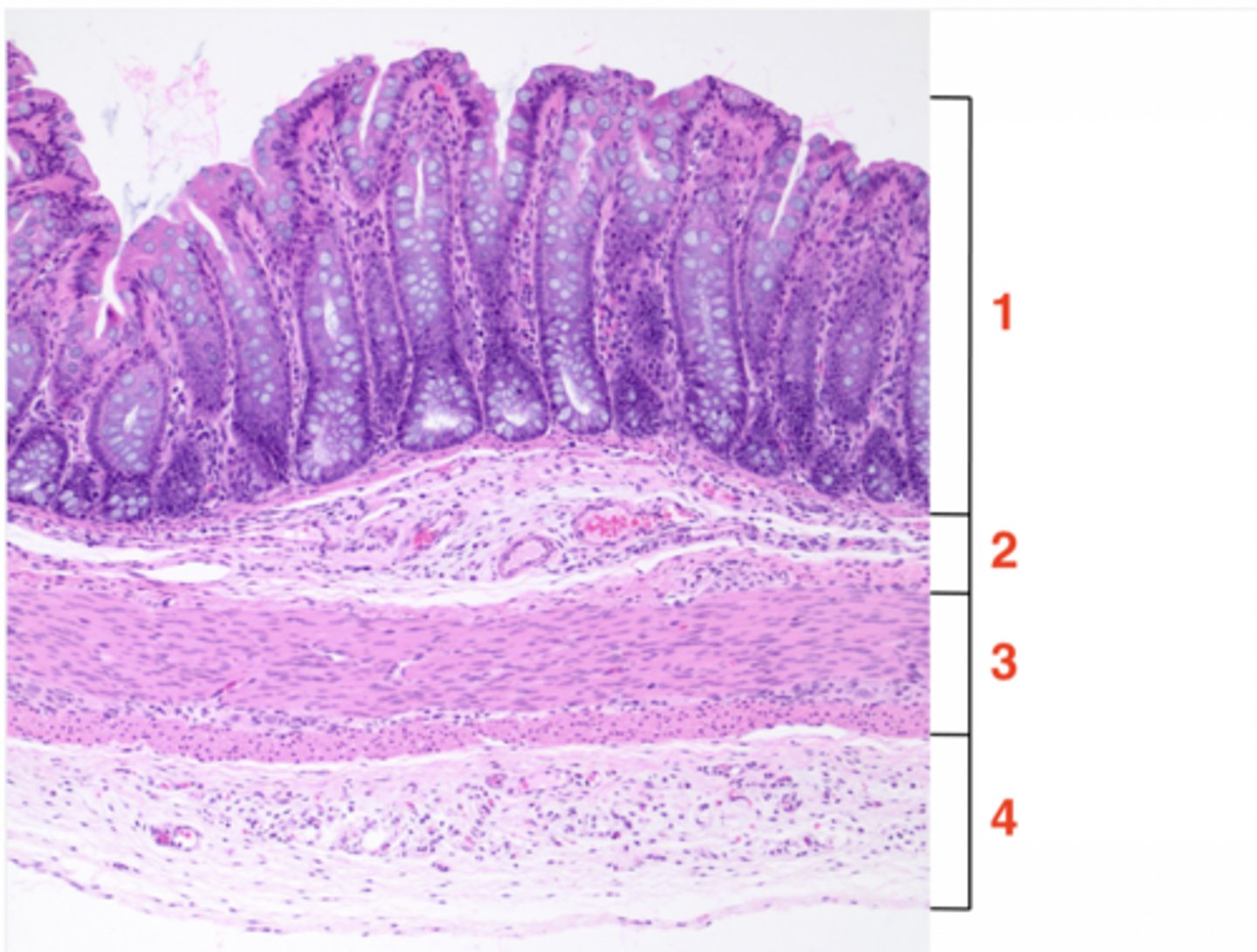
4
serosa
Mucosa of esophagus structure
stratified squamous epithelium +/- keratinization
In which species will the epithelium of the mucosa of esophagus be keratinized?
herbivores
Submucosa of esophagus structure
glands lined by simple cuboidal/columnar epithelium
Muscularis of esophagus structure
divided into sections based on type of muscle, which varies by species
Layers of muscularis of esophagus in pigs and humans
upper third: skeletal muscle
middle third: skeletal + smooth muscle
lower third: smooth muscle
Upper third layer of muscularis of esophagus in pigs and humans
skeletal muscle
Middle third layer of muscularis of esophagus in pigs and humans
skeletal + smooth muscle
Lower third layer of muscularis of esophagus in pigs and humans
smooth muscle
Layers of muscularis of esophagus in cats and horses
proximal 2/3: skeletal muscle
distal 1/3: smooth muscle
Proximal 2/3 layer of muscularis of esophagus in cats and horses
skeletal muscle
Distal 1/3 layer of muscularis of esophagus in cats and horses
smooth muscle
Layers of muscularis of esophagus in dogs and ruminants
100% skeletal
The outer layer of the esophagus can be called two named based on location:
1.) serosa
2.) adventitia
Where is the outer layer of the esophagus called adventitia?
Thoracic cavity
Where is the outer layer of the esophagus called serosa?
Abdominal cavity
What structure of the GI tract has the most variation histologically across species?
stomach
Two types of mucosa in the stomach:
1.) squamous
2.) glandular
Squamous mucosa of stomach: histology
non glandular; covered by stratified squamous epithelium
Squamous mucosa of stomach: function
mechanical protection; in ruminants, microbial fermentation and absorption of microbial products
Glandular mucosa of stomach: histology
simple columnar epithelium
Glandular mucosa of stomach: function
secretes mucous, hydrochloric acid, pepsin, and gastrin