Aural Rehabilitation
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards about aural rehabilitation including self-advocacy, hearing assistive technology (HAT), telephone access, electronic media, pediatric and adult needs assessment, age-specific recommendations, technology, device considerations, emergency signals, and considerations for personal safety.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
self-advocacy in aural rehabilitation
Disclosure of reason for misunderstanding.
Is extremely hard
What should be evaluated for adults during traditional needs assessment for Hearing Assistive Technology (HAT) and Aural Rehabilitation (AR)?
Face to face communication, Telephone access, Reception of electronic media, Reception of alerting signals.
What signal types can be used to overcome background noise?
FM (Radio waves), Magnetic waves, Electrical signals, Infrared light.
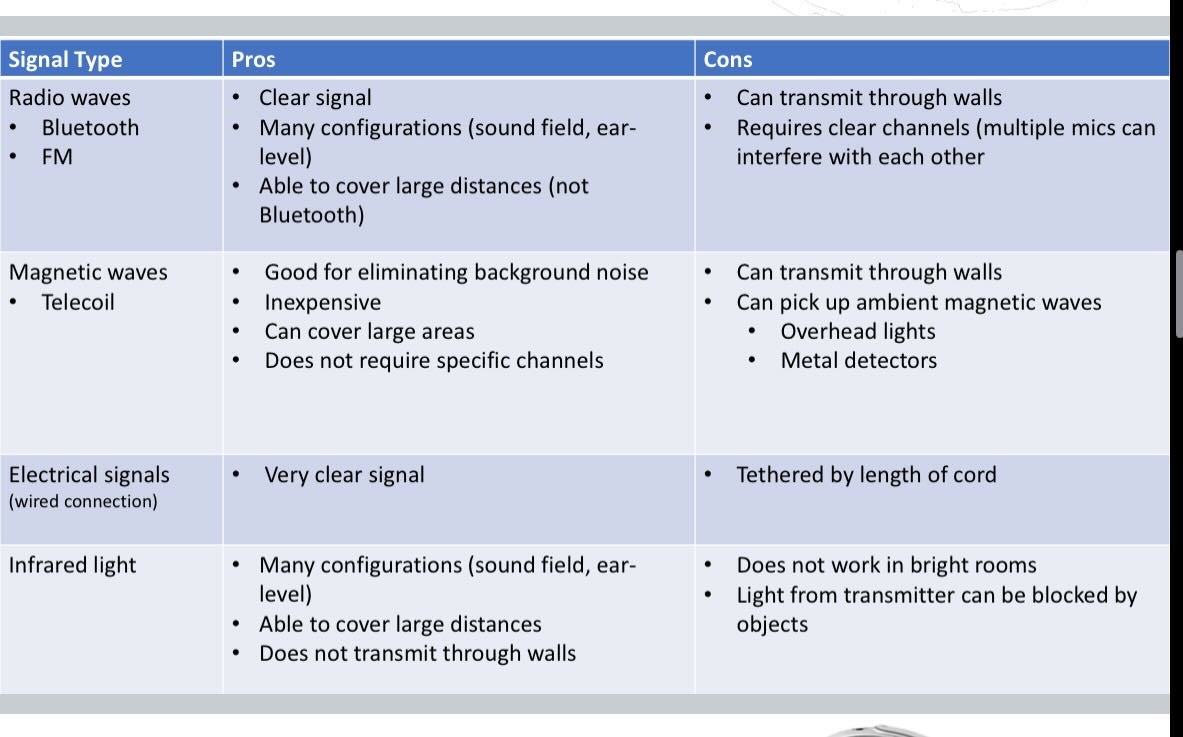
How can telephone access be improved for individuals with hearing loss?
Telecoil setting, FM transmitter with or without Bluetooth, Manufacturer transmitters, Visual supports, Telephone captioning relay systems, Video relay operations, Text message relay.
What does VCO stand for in telephone captioning?
Voice Carry Over
What does a Telecoil do?
Detects magnetic waves produced by phone speakers and translates them to an electrical signal, then to an acoustic signal.
Eliminates background noise if the microphone is off or set to quieter setting
What are the best ways to access sound from electronic media?
FM or other direct system, Loop systems, or Infrared systems.
What three areas needs are included in the Action Plan for Adult Rehabilitative HAT's?
Technological interventions, Environmental controls, Behavioral modifications.
What two questions are key to the Pediatric Habilitative Needs Assessment, and what is the answer?
Why a habilitative approach and Why do we believe in intervening early? To curb the effects of sensory deficits on growth and development.
When assessing HAT needs in adults, what should be used to determine communication needs?
The job description.
When assessing HAT needs in children, what should be used to determine communication needs?
Typical development (Job description).
What are the 4 categories contained in Age-Specific Recommendations?
BEST (Behavioral, Environmental, Safety, Technology)
What are the behavioral modifications for children age 0-12 months?
Decreased distance from speaker, Eye contact, Full sensory input (e.g., touch, vision, etc.), Behavioral alerts-e.g. touching bed before baby, Repetition/Rephrasing-response to commands
What is the order of behavioral modification from ages 1-2 years to 3-5 years?
Introduce Ownership of Devices (2-3 years) and Ownership of Devices (4-5 years)
What are some examples of communication strategies introduced for children aged 3-5 years?
Clarification/Confirmation, Key words, Spelling, Code words, Writing, Signing/Fingerspelling
What self-advocacy skills do children between 6-11 years old demonstrate?
Ownership of medical appointments, involved with hearing aid check appointment, understanding of hearing loss and its impact (emerging), IEP involvement and planning, able to advocate for 'positive listening space', demonstrates communication strategies through role-play
What are the age-specific skills for children 12+?
Transition planning for Jr. High School, Complete ownership of appointments (Parents as back-up), Independently sets goals for communication, Art of Compromise, Transition planning for High School (12-13 years), ADA/Legal protection (14+ years), Transition planning for College/Vocation (14+ years)
What technology is used for children aged 0-12 months?
Hearing aids
What is the technological progression from children 1-2 years to 3-5 years?
FM system, connectivity
What expanded technological interventions should be reassessed for children aged 6-11 years?
Amplification, Expanded technology repertoire, CART Services, Video Relay Interpreting, CapTel, VCO, Computer Assisted Note Taking (CAN), Personal Cell phone compatability, Work-specific technologies
What general device considerations should be assessed?
Effectiveness, Affordability, Operability, Quality/dependability, Portability, Versatility, Mobility, Cosmetics, Previous experience
From the emergency stimuli signals study, what was found?
Present low intensity then increase until waking response; Auditory signals calibrated at ear level
What knowledge should be assessed regarding personal safety?
Last name, home address, self-advocacy regarding hearing loss, how to contact emergency services, where can they go or who they can talk to when bad things happen
Video Relay Systems (VRS) Interpreting
Call placed by person with hearing loss who uses sign
Call intercepted by ASL interpreter
Interpreter calls desired party
Interpreter signs response from other party