The Islamic Caliphates - Notebook Page 3
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
1
New cards
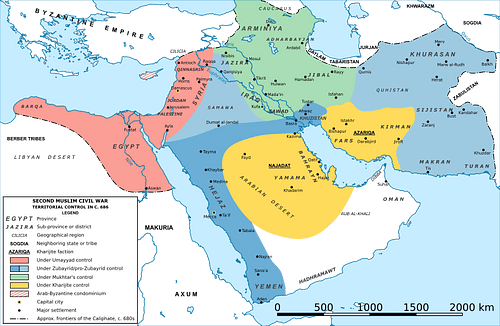
The Umayyad Caliphate
The Umayyad dynasty or Umayyads were the ruling family of the caliphate between 661-750 and later of al-Andalus between 756-1031. In the previous Islamic period, they were a prominent clan of the Meccan tribe of Quraysh, descended from Umayya ibn Abd Shams.
2
New cards
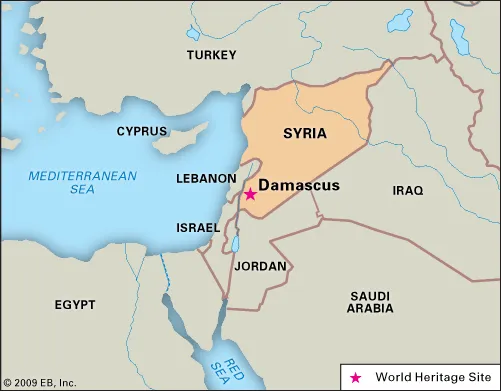
Damascus
Damascus is the capital of Syria, the oldest capital in the world, and according to some, the fourth holiest city in Islam. Damascus was also the capital of the Umayyad Caliphate for the majority of its existence.
3
New cards
Mamluks
Mamluks is a term most commonly referring to non-Arab, ethnically diverse slave-soldiers and freed slaves who were assigned military and administrative duties, serving the ruling Ottoman and Arab dynasties in the Muslim world.

4
New cards
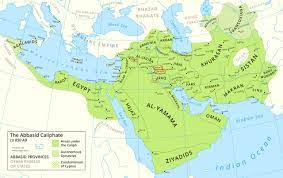
The Abbasid Caliphate
The Abbasid Caliphate was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet, Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad’s uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttalib, from whom the dynasty takes its name.
5
New cards
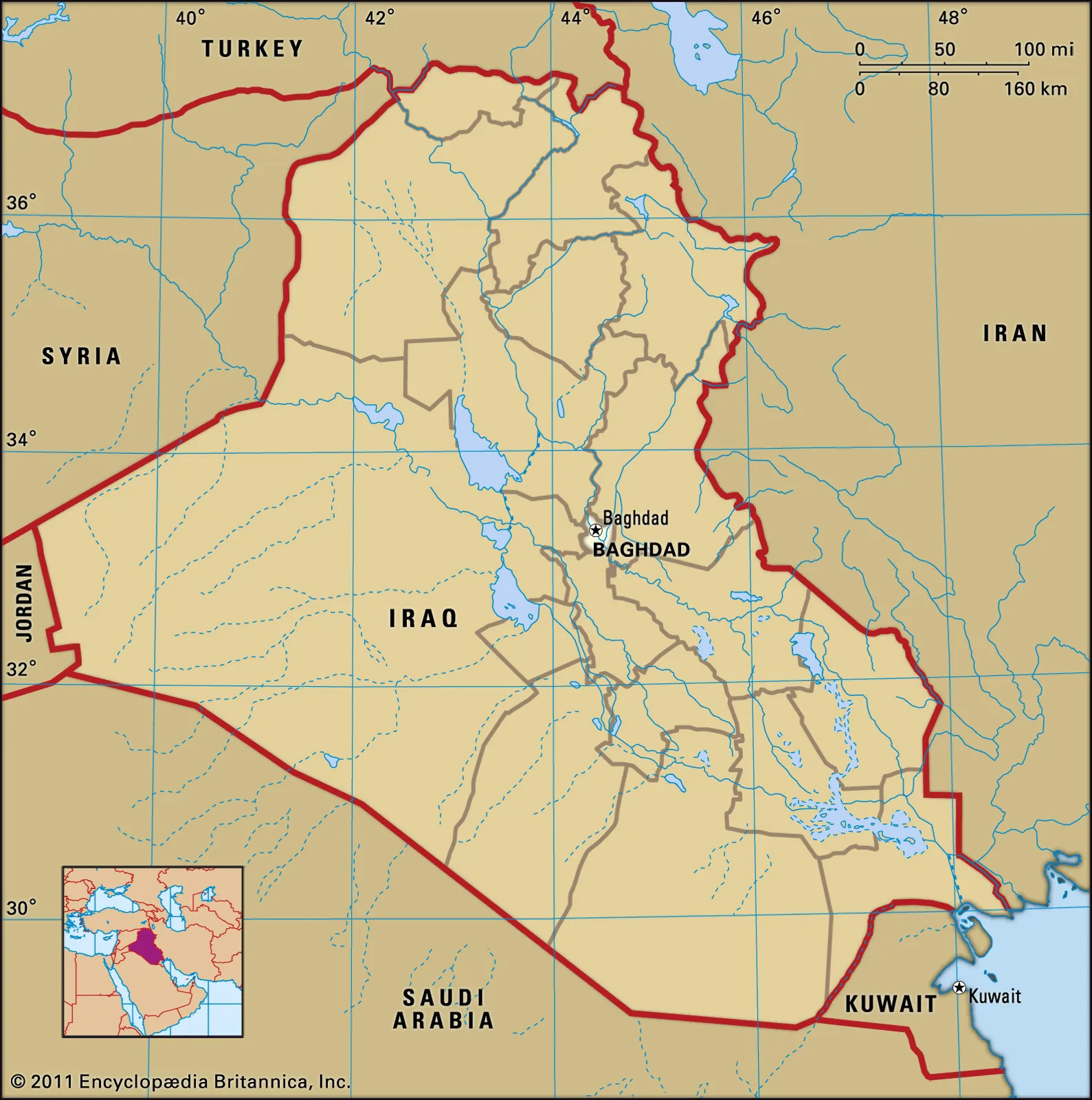
Baghdad
Baghdad is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient city of Babylon. In 762 CE, Baghdad was chosen as the capital of the Abbasid Caliphate, and became its most notable major development project.
6
New cards
The Golden Age of Islam
The Islamic Golden Age was a period of scientific, economic, and cultural flourishing in the history of Islam, traditionally dated from the 8th century to the 13th century.

7
New cards
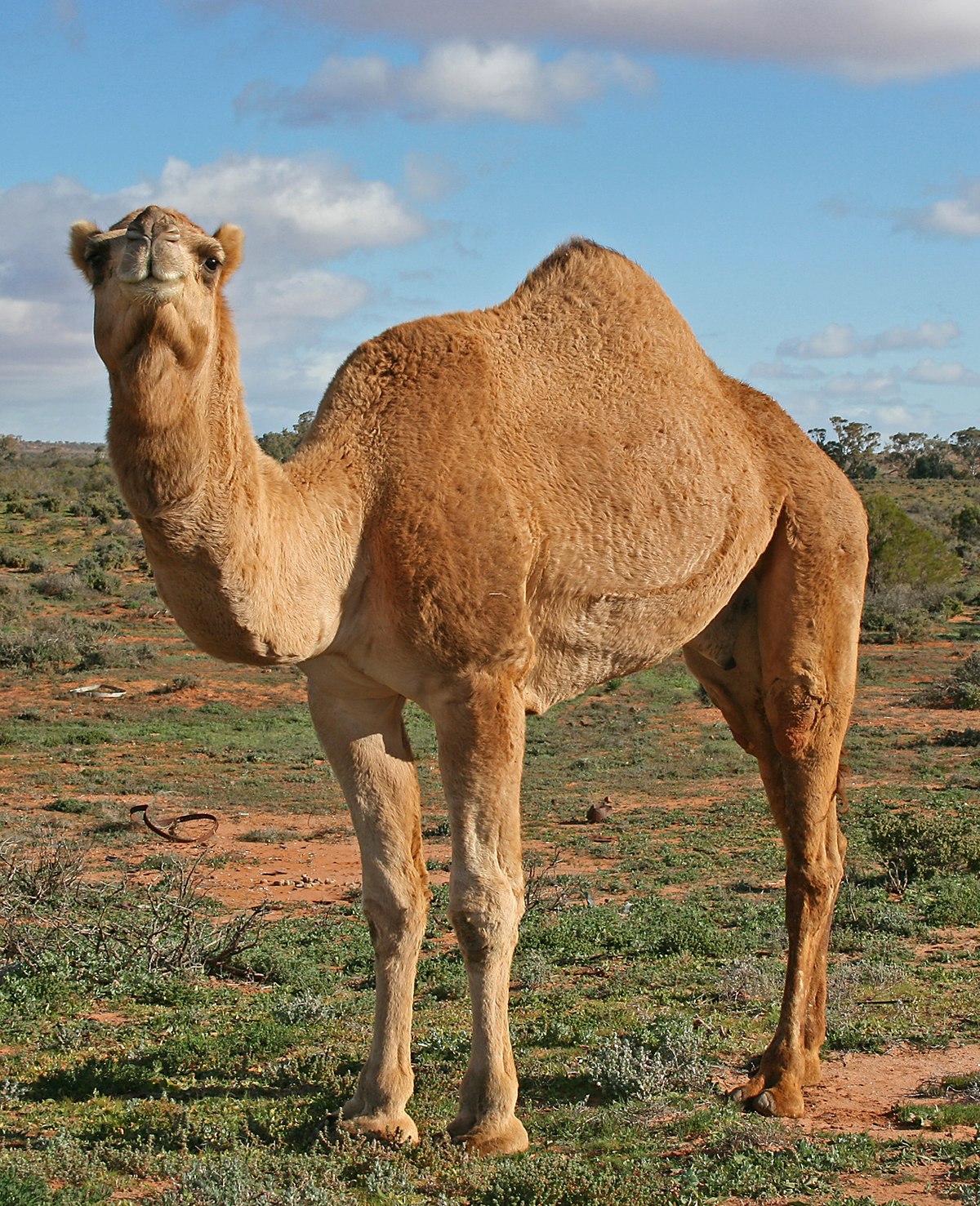
Camels
A camel is an even-toed ungulate in the genus Camelus that bears distinctive deposits known as “humps” on its back. Camels were important in the Trans-Saharan Trade because they could carry lots of weight, and they could go long periods without water.

8
New cards
Caravans
A caravan or cafila is a group of people traveling together, often on a trade expedition. Caravans were used mainly in desert areas and throughout the Silk Road, where traveling in groups aided in defense against bandits as well as helped improve the economics of scale in trade.

9
New cards
Sunni
Sunni is the larger of the two main branches of Islam, followed by 85%-90% of the world’s Muslims; its names comes from the world Sunnah, referring to the tradition of Muhammad. A Sunni is a Muslims who believes that the caliph, Abu Bakr, was the rightful successor to Muhammad after his death. A member of the branch of Islam accepts the first four caliphs as rightful successor to Muhammad.

10
New cards
Shi’a
Shi’a is the smaller of the two main branches of Islam, followed especially in Iran, and it rejects the first three Sunni caliphs and regards Ali, the fourth caliph, as Muhammad’s first true successor.

11
New cards
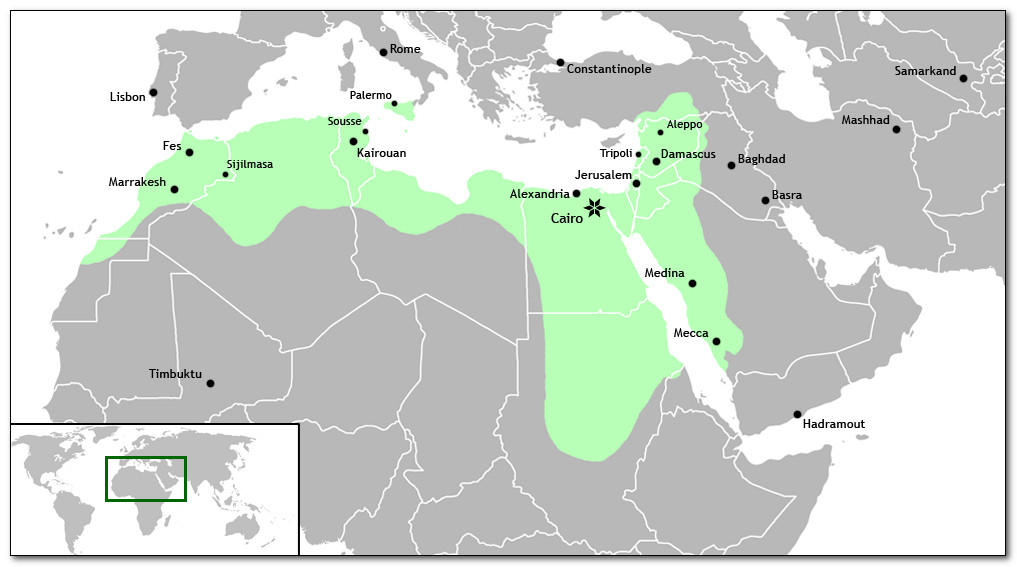
The Fatimid Caliphate
The Fatimid Caliphate was an Ismaili Shi’a caliphate extant from 909-1171 AD. Spanning a large area of North Africa, it ranged from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to the Red Sea in the east.
12
New cards
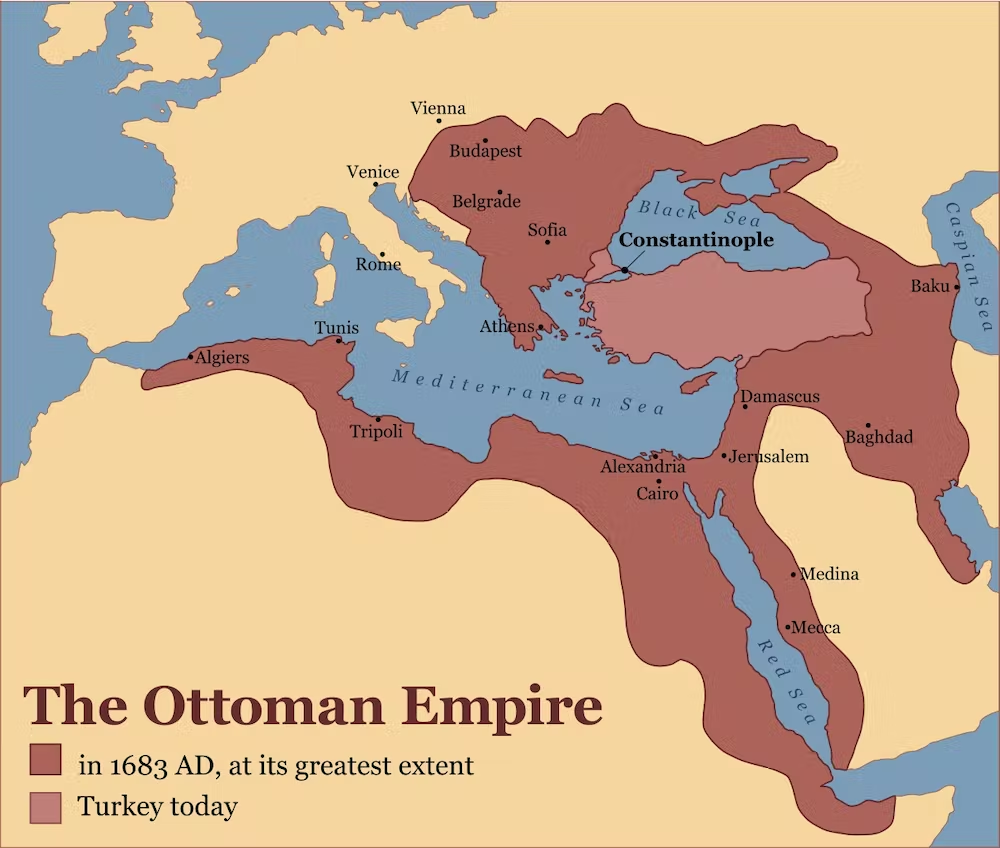
The Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, historically and colloquially the Turkish Empire, was an empire that controlled much of Southeast Europe, Western Asia, and Northern Africa between the 14th and early 20th centuries.
13
New cards
The Safavid Dynasty
The Safavid dynasty was one of Iran’s most significant ruling dynasties reigning from 1501-1736. Their rule is often considered the beginning of modern Iranian history, as well as one of the gunpowder empires.
