Biotechnology Chapter 3-4
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/144
Last updated 4:16 PM on 12/23/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
145 Terms
1
New cards
when measuring volumes that are smaller than 10 mL
When do you use a pipette in terms of measuring?
2
New cards
* draw fluid into a pipette use the pipet bulb/pump
* these pumps/builds evacuate the air in the pipette which creates a vacuum that causes liquids to rise to a specific level
* these pumps/builds evacuate the air in the pipette which creates a vacuum that causes liquids to rise to a specific level
Describe how to use a regular pipette.
3
New cards
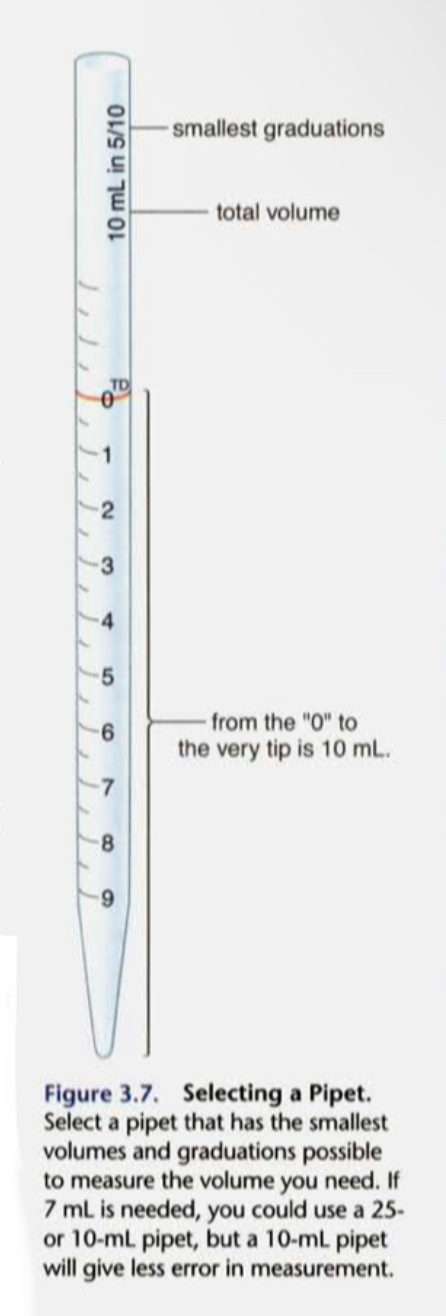
How do you select a specific pipette?
4
New cards
Measure volumes
When should one use a micropipette?
5
New cards
microliter(one millionth(6) of a liter/ thousandth(3) of a milliliter)
What are the metric measurements for a micropipette?
6
New cards
What is the process of using a micropipette?
1) use correct size and type of tip for samples that you will be transferring
2) set volume and turn volume adjustment know till desired volume appears in digital display window(volume is read top to bottom)
2) set volume and turn volume adjustment know till desired volume appears in digital display window(volume is read top to bottom)
7
New cards
What are the volume ranges of P-100 micropipettes?
10-100 nanoliters
8
New cards
What are the volume ranges of P-200 micropipettes?
20-200 nanoliters
9
New cards
Why should you measure 200 nanoliters of a substance with a certain micropipettes?
* measure 200 pL on both a P-1000 and a P-200, but the P-200 allows you to estimate down to a hundredth of a microliter while the P-1000 does not allow such precision
10
New cards
Name the different parts of a micropipette.
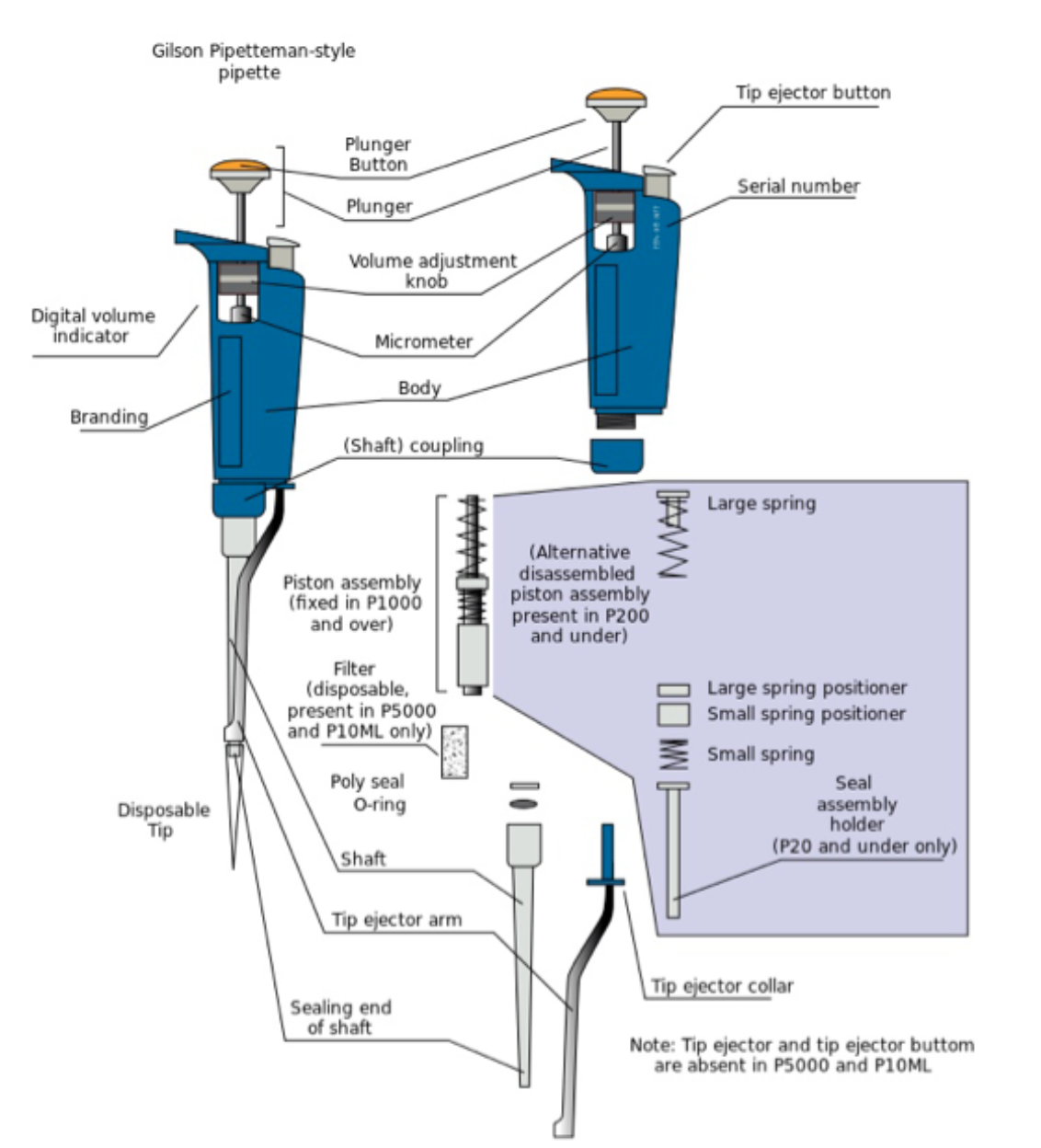
11
New cards
Describe different parts of a micropipette.
1. Plunger Button: used to fill and sell samples
2. Tip Ejector Button: used to remove used tips
3. Volume adjustments: used to adjust the volume of liquid that needs to be transferred
4. Digital display window: displays volume being selected
5. Shaft/Ejector Arm: ejects used tips disposable pipette tips
12
New cards
What are the volume ranges of P-1000 micropipettes?
100-1000 microliters
13
New cards
What are the volume ranges of P-10 micropipettes?
0\.5-10 microliters
14
New cards
What types of solutions are made in labs daily?
* Many reactions involve nucleic acids in an aqueous solution
* Include: Salt(solute)+Water(solvent)=Salt water (solution) \*\*\*\*Solutes can be liquids(chemicals) or solids
* Include: Salt(solute)+Water(solvent)=Salt water (solution) \*\*\*\*Solutes can be liquids(chemicals) or solids
15
New cards
What substance is normally used as a solvent?
* water(distilled or deionized)
* from this water mineral impurities removed as they interfere with reactions and so tap water is only used for glass washing
* from this water mineral impurities removed as they interfere with reactions and so tap water is only used for glass washing
16
New cards
why is water not always the solvent?
* However some molecules(mainly organic such as lipids) don't readily dissolve in water
* These molecules are put into other solutions where they are dissolved by other solvents such as ethanol
* These molecules are put into other solutions where they are dissolved by other solvents such as ethanol
17
New cards
How are solid solutes measured?
They are measured on balances(scales)
18
New cards
What are the two types of balances?
Electronic/tabletop/portable AND Analytical
19
New cards
What is the standard unit?
* The standard unit for measuring mass with these balances is grams however they can differ based on where they a measured
* Example: R&D may use mL to measure while manufacturing facilities may use kg
* Example: R&D may use mL to measure while manufacturing facilities may use kg
20
New cards
\
What is the importance of solution prep?
What is the importance of solution prep?
* avoid contamination of solutions with chemicals that can interfere with chemical reaction
21
New cards
What are the steps for solution prep?
1. Wash glassware vessel with lab soap and water
2. Rinse with tap water until no evidence of the soap is visible
3. Rinse 5 more times and a final rinse with deionized water
22
New cards
What is concentration?
* Proportion of solute to solvent
* Measured in several ways such as mass/volume, volume/volume,morality, normality(acids and bases only),etc
* Measured in several ways such as mass/volume, volume/volume,morality, normality(acids and bases only),etc
23
New cards
What is the difference between concentrated orange juice and a regular drinkable orange juice?
* Concentrated frozen orange juice has a higher ratio of solute molecules to a solvent than is present in diluted,drinkable organs juice
* To use these highly concentrated substances one must add water to dilute it down to a drinkable concentration with a LOWER ratio of solute to solvent molecules
* To use these highly concentrated substances one must add water to dilute it down to a drinkable concentration with a LOWER ratio of solute to solvent molecules
24
New cards
How is concentration of a solution expressed?
* amount of mass per unit of volume(mass/volume)
* For example: a concentration of 1 mg/mL= every mL of the solution contains 1 mg of protein
* For example: a concentration of 1 mg/mL= every mL of the solution contains 1 mg of protein
25
New cards
What is the mass/volume concentration equation and what is its importance?
* This equation ensures that every mL of the solution has the same amount of solute in it

26
New cards
What types of solutions often have their concentrations reported as percentages?
* *Salt Solutions*
27
New cards
What is the mass/volume concentration equation with percentages?
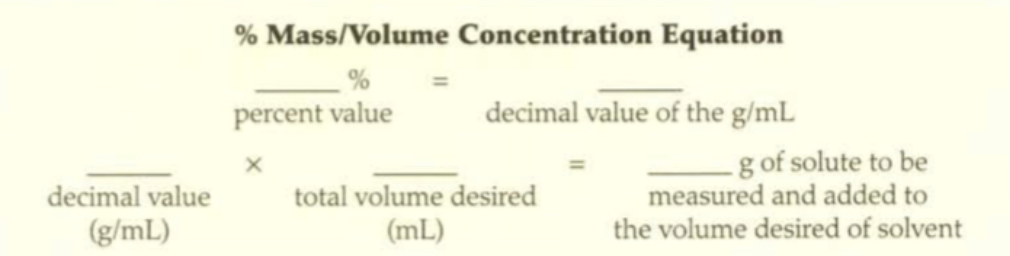
28
New cards
What is another way a concentration of a solution can be measured?
* number of moles of a solute in a liter of solution
29
New cards
What is morality and what are its measurements?
* Concentration measurement and the unit of measurement is moles/liter(mol/L)
30
New cards
What is the unit mole equal to?
* the mass, in grams,of 6 × 10^23 atoms or molecules of a given substance
* one mole is equivalent to the molecular weight of a given substance, reported as grams
* one mole is equivalent to the molecular weight of a given substance, reported as grams
31
New cards
How do you measure a mole of a substance?
* *measure out the molecular weight in grams of the chemical and you will have a mole of that compound( also have 6 x 10^23 of that compound)*
32
New cards
Explain how to find the mole of NaCL.
* Molecular weight of NaCl is 58.5 amu because one Na atom weighs 23.0 amu and one Cl atom weights 35.5 amu
33
New cards
* How to find formula weight of a compound using Periodic Table?
1. Determine elements of the compound
2. look up atomic mass of each element and add together( many chemical bottle labels also list the molecular weight of certain compounds)
34
New cards
What is the purpose of molecular weight?
Used to determine how to make up molar solutions
35
New cards
* Describe how is a liter of 1 Mole of NaCL prepared.
1. Weight out 1 mol of NaCl and place it into a container
2. When stirring to dissolve salt add deionized water up to a total volume of 1 L
36
New cards
What is the molarity concentration equation?

37
New cards
In what conditions are solutions usually made and what are they converted to?
* Many solutions are often prepared too concentrated and so a dilution of the concentrated solution is prepared to bring the concentration down to a usable level(workable concentration)
38
New cards
What are the reasons for preparing and using concentrated stock solutions?
1. Easier to prepare higher-concentration solutions that lower-concentration ones
* Difficult to be accurate with small amounts of solutes and weighing out a larger mass is more efficient Less expensive/easier to ship or store small volumes of concentrated samples than large volumes of diluted samples The smaller,more concentrated solutions can be diluted as needed
1. Large volume of a working solution can be made in a single dilution
* This allows for the same solution to be used a numerous amount of times and increases consistency of trials
39
New cards
Explain the process of concentrating or diluting a sample.
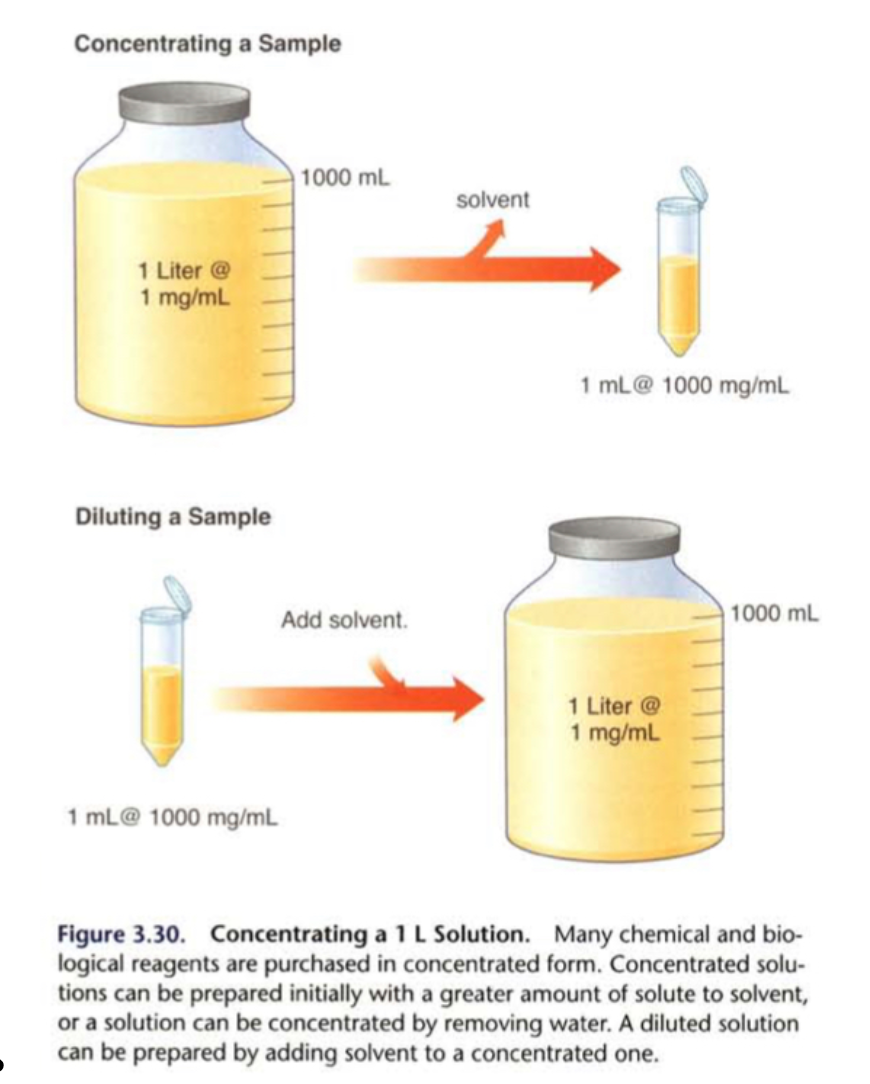
40
New cards
What is a concentration ratio?

41
New cards
* Where are proteins and nucleic acids stored?
* Buffered Solutions (Different salts at a variety of concentrations are used depending on the kind of buffer needed)
42
New cards
What is a TAE buffer made of?
* TRIS,acetic acid, and EDTA
* Difficult to make a fresh batch of 1X TAE when needed and it is much more efficient to store concentrated TAE and dilute when needed
* Difficult to make a fresh batch of 1X TAE when needed and it is much more efficient to store concentrated TAE and dilute when needed
43
New cards
What is at the center of most biotechnology research and development?
The manipulation of genetic information(DNA and RNA)
44
New cards
What does arrangement of nitrogen bases on a DNA strand determine?
the RNA sequence and the RNA code which then determines the amino acids that are placed in the polypeptide chain of a protein
45
New cards
*What is the “Central Dogma of Biology”?*
* A theory that explains how genetic information is converted into structures and functions.
* To be more specific, this theory describes how genes are transricbed int mRNA(messenger RNA) molecules which are in turn translated at ribosmes into proteins of the cell.
* To be more specific, this theory describes how genes are transricbed int mRNA(messenger RNA) molecules which are in turn translated at ribosmes into proteins of the cell.
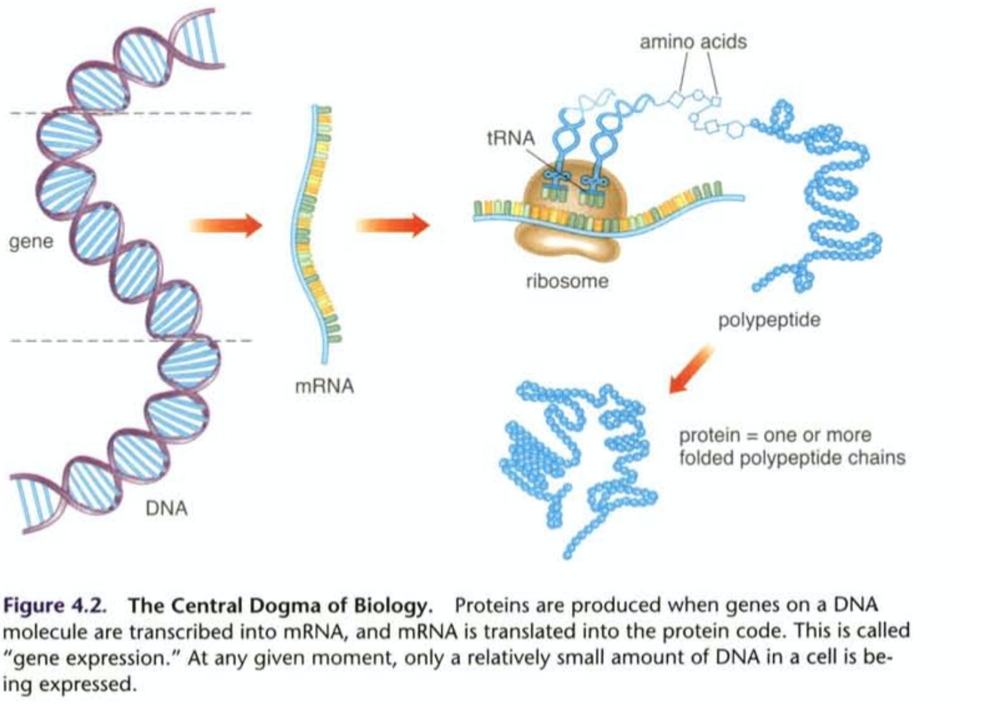
46
New cards
What cell has doesn’t have the same genome/ genetic makeup?
sex cells
47
New cards
What are the similarities of DNA molecules among organisms?
1. ^^Composed of four nucleotide monomers that have four bases( A,C,G,T)^^
2. ^^Double helix structure of repeating nucleotides^^
* Nucleotides connect to other nucleotides in individual strands through strong phophodiester bonds between sugars and phosphatase of adjacent nucleotides
* Hydrogen bonds are formed between the two strands that make up DNA
* A-T(U) and C-G
3. ^^**amount of A= amount of T** and **amount of G=amount of C** in each double-strand of DNA^^
* Both are prymides
* Width of A-T base pair= Width of G-C base pair
4. ^^strands are anit-parallel and this arrangement gives the directionality to a DNA strand^^
5. ^^Uniform shape= enzymes ad regulatory molecules can recognixe the DNA molecule and allow for coiling and packaging of DNA^^
* The nitrogenous base are stacked 0.34 nanometers apart with 10 nitrogen bases per complete turn of the helix
* Stacking of bases ensures that the shape of DNA molecule is consistent
* 6) Semiconcervative replication: two daughter strands from a singular parent strand
*Process:*
* Strand unzips
* each original strand acts as a template/model for building a new side and by the replication is complete two identical DNA strands have been produced
* process continues as one of each copy ges into forming a daughter cell during cell division
48
New cards
Name the four variations in a DNA molecule?
1. Number of DNA strands in the cells of an organism such as number of chromosomes
2. Length of base pairs in DNA strands
3. Number and type of genes(nucleotide sequences that code for protein production) and noncoding regions
4. The shape of the DNA strands(cirular or linear chromosomes)
49
New cards
How do scientists find sources of DNA?
* can find cells in nature or they can grow cultures of cells in a lab
\*Scientists have learned how to grow many different cells on/in a medium(source of nutrients) prepared in lab
\*Scientists have learned how to grow many different cells on/in a medium(source of nutrients) prepared in lab
50
New cards
What does the process lysis entail?
Cells in cell cultures that are broken up once collected
51
New cards
What do Lysed cells do?
* Release their DNA in a mixture of other cellular molecules
* through the separation technique the DNA molecules are isolated from other cell molecules
* through the separation technique the DNA molecules are isolated from other cell molecules
52
New cards
Where is DNA located in a prokaryotic cell?
Floating in the cytoplasm and is attached at one spot to the cell membrane
53
New cards
What kind of DNA molecules does bacteria have?
\-One long,circular DNA molecule
\-Supercoiled(folding over on itself like a twisted rubber band)
\-Small and only contains a couple genes
\-Supercoiled(folding over on itself like a twisted rubber band)
\-Small and only contains a couple genes
54
New cards
What is a plasmid?
* extra small rings of DNA floating in the cytoplasm
* contains very few genes(5-10)
* these geneys usually code for proteins that offer some extra characteristics needed in extreme conditions
* contains very few genes(5-10)
* these geneys usually code for proteins that offer some extra characteristics needed in extreme conditions
55
New cards
What is the most familiar plasmid?
* R plasmid
* contain antibiotic *resistance genes*(bacteria with these resistance genes can survive exposure to antibiotics that would normally kill them)
* contain antibiotic *resistance genes*(bacteria with these resistance genes can survive exposure to antibiotics that would normally kill them)
56
New cards
What can bacteria transfer between each other?
Plasmids which means they can transfer genetic info between themselves
57
New cards
Name one negative consequence of bacteria transferring.
* nGenes(antibiotic resistant) can be transferred between bacteria and lead to a deadly antibiotic-resistant form of disease-causing bacteria
* In other words this transferring of plasmids between bacteria may give the bacteria a way of “evolving” by gaining certain characteristics for survival
* In other words this transferring of plasmids between bacteria may give the bacteria a way of “evolving” by gaining certain characteristics for survival
58
New cards
How is gene transferring information useful to scientists?
Scientists have learned how to use plasmids to transfer “genes of interest” into cells
59
New cards
When is a cell called transformed?
The cell takes up foreign DNA and starts expressing the genes
60
New cards
Name one use of plasmids.
Due to their small size and how easy they are to extract from cells, they are often used as rDNA vectors to transform cells
61
New cards
What is the process of using a plasmid as a vector?
1)Foreign DNA fragments(genes) can be cut/pasted into a plasmid vector
2) The recombinant plasmide may then be introduced to a cell
3)Cell will read the DNA code on the plasmid and start making proteins coded for on the foreign gene
2) The recombinant plasmide may then be introduced to a cell
3)Cell will read the DNA code on the plasmid and start making proteins coded for on the foreign gene
62
New cards
Example of plasmid being used as vector.
* First manipulated E.coli to make human insulin
* In other words, scientists tricked the E.coli cells into reading the human genes that had been inserted into them on recombinant plasmids
* In other words, scientists tricked the E.coli cells into reading the human genes that had been inserted into them on recombinant plasmids
63
New cards
What is one prominent difference between prokaryotic DNA and DNA fron eukaryotic cells?
Gene expression(gene turned off or on) in prokaryotes is simple with very little controls
64
New cards
What does a real bacterial chromosome have that is lined up one after the other?
Operons(two or more genes and their controlling elements)
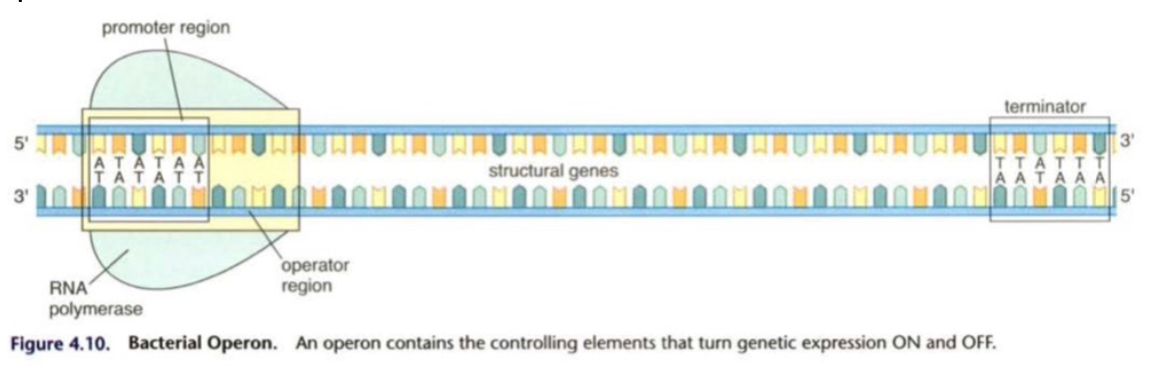
65
New cards
What is a structural gene?
* section that codes for one or more mRNA molecules which will later be translated into proteins
* for this section to be expressed as a functional protein other areas are required
* for this section to be expressed as a functional protein other areas are required
66
New cards
What must happen so gene expression can occur in prokaryotes?
1. Enzyme must synthesize a mRNA molecule
2. RNA polymerase must attach to a segment of DNA at a promoter region of the operon
3. The RNA polymerase works its way down the DNA strand to a structural gene
4. Here it builds a mRNA molecule from free-floating nucleotides using the DNA strand as a template
5. Synthesized mRNA is decoded into a peptide at a ribosome
6. A region called the operator is located just prior to the structural gene can turn off the “operon” which turns on the gene expression and If a regulatory molecule attaches at the operator, the operon is turned off (along with the gene expression) because the RNA polymerase is blocked from continuing down the strand of the genes
67
New cards
How do bacterial cells only make certain proteins at specific times?
* They block or unblock the operator
* For example: It would make no sense if a cell made beta-glactosidase(breaks down lactose into monosaccharides) if there was no lactose around
* For example: It would make no sense if a cell made beta-glactosidase(breaks down lactose into monosaccharides) if there was no lactose around
68
New cards
How do genetic engineers take advantage of this information?
* They utilize the promote and operator regions to turn on and off the production of specific genes
* When the insulin gene from humans was genetically engineered into E. coli cells, a bacterial promoter region had to be attached to the human insulin gene because without it the E. coli cells would not have recognized the new gene, and it would not have been transcribed and translated into protein.(no gene expression)
* When the insulin gene from humans was genetically engineered into E. coli cells, a bacterial promoter region had to be attached to the human insulin gene because without it the E. coli cells would not have recognized the new gene, and it would not have been transcribed and translated into protein.(no gene expression)
69
New cards
Describe a Lac Operon.
\
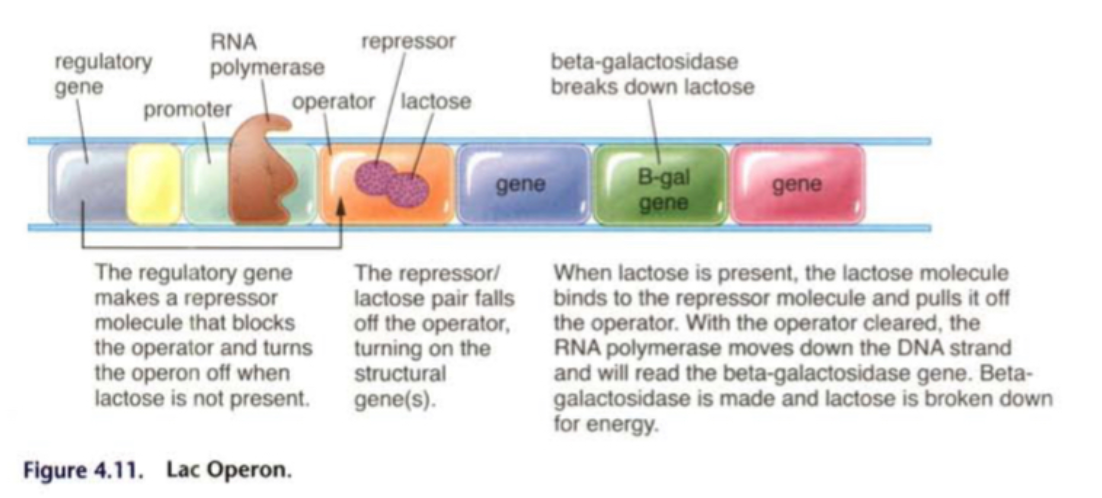
70
New cards
What is needed to study and manipulate bacteria DNA?
* Bacteria cells
71
New cards
How is one to grow bacteria cells in a laboratory?
* Provide enviorment/medium that cells “like”
* Ex: liquid medium(broth) or solid medium(agar)
* Ex: liquid medium(broth) or solid medium(agar)
72
New cards
What is agar and describe the process of making it?
* Mixture of water and protein molecules
* **How is Agar prepared?**
1. Researchers mix the powdered agar in water until the agar is completely suspended
2. The agar is sterilized at a high temperature(121 degrees Celsius of higher at a high pressure of 15 pounds per square inch at higher for a minimum of 12 minutes
3. Agar cools to about 65 degrees Celsius and is poured under sterile conditions into sterile Petri dishes
4. Agar cools and solidifies in 15-20 minutes and the poured plates may be used after 24 hours
* **How is Agar prepared?**
1. Researchers mix the powdered agar in water until the agar is completely suspended
2. The agar is sterilized at a high temperature(121 degrees Celsius of higher at a high pressure of 15 pounds per square inch at higher for a minimum of 12 minutes
3. Agar cools to about 65 degrees Celsius and is poured under sterile conditions into sterile Petri dishes
4. Agar cools and solidifies in 15-20 minutes and the poured plates may be used after 24 hours
73
New cards
How are liquid/broth cultures formed?
Grow as suspensions of millions of floating cells
74
New cards
How do these cultures start off?
* 1)Researcher introduces a colony of cells under sterile conditions into the broth
* 2)Cells then grow and divide and spread themselves throughout the liquid
* *Side note: Broth culture cells reproduce faster in general*
* 2)Cells then grow and divide and spread themselves throughout the liquid
* *Side note: Broth culture cells reproduce faster in general*
75
New cards
What does a technician need to learn to be able to grow cell cultures?
Learn media prep/sterile techniques
76
New cards
What is arguably the most important part of all in media prep?
Sterilizing the medium(medium in any container must be free of any unwanted bacteria/fungi before used)
77
New cards
What is used to destroy cells/spores in the medium?
An autoclave
78
New cards
How is the medium to be transferred to other flasks?
Transferred under sterile conditions to the new sterile vessel
79
New cards
What is sterile technique?
* Process of doing something without contamination by unwanted mircroorganims/spores
* Must be practiced during cell culture
* Must be practiced during cell culture
80
New cards
* Why is practicing sterile technique so important in biotechnology?
* They want to only grow specific cells so if a single unwanted cell were to contaminate the experiment it would ruin the entire experiment
81
New cards
What are the similarities between prokaryotic and eukaryotic DNA?
1. Use the same nucleotide codes A,C,G,T
2. Many share the same double helix structure which hydrogen bonds and repeating nucleotides
3. both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells have promoter regions
82
New cards
What are the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic DNA?
* DNA from “higher” organisms is organized in chromosomes
* Many chromosomes per cell
* Lack of operators in eukaryotes
* Many chromosomes per cell
* Lack of operators in eukaryotes
83
New cards
What is the structure of a chromosome?
* Single,linear,long molecule of DNA coiled around proteins
* Several million nucelotides
* Several million nucelotides
84
New cards
Why do humans have more chromosomes than ferns despite humans being more complex organisms?
* Eukaryotic DNA(humans) is non-coding(does not transcribe into protein)
* Much of the DNA in higher organisms is spacer DNA within genes
* Much of the DNA in higher organisms is spacer DNA within genes
85
New cards
What is the evolutionary advantage of widely spaced genes?
* 1)Genes that are far apart are often involved in recombination which shuffles around different genes from one chromosome to another
* 2)This leads to new combinations of genes being sent to sex cells
* 3)The end result of variant set cells is increased diversity in the next generation
* \
* 2)This leads to new combinations of genes being sent to sex cells
* 3)The end result of variant set cells is increased diversity in the next generation
* \
86
New cards
How is gene expression in eukaryotic cells?
Genes are on and expressed on a “low level”
87
New cards
When is expression increased or decreased?
* Molecules interact with enhancer or silencer regions(on gene or somewhere else on chromosome) on eukaryotic DNA strands
* Molecules that bind enhancer/silencer regions are called transcription factors(growing area to understand their function in gene regulation and how to manipulate them is a prominent field of research)
* Molecules that bind enhancer/silencer regions are called transcription factors(growing area to understand their function in gene regulation and how to manipulate them is a prominent field of research)
88
New cards
How does gene expression work in an prokaryotic cell?
1) mRNA transcript is translated into a polypeptide at a ribosome
89
New cards
What are structural genes in eukaryotic DNA composed of?
Intron and Exon
90
New cards
What are exons?
* DNA sections that contain protein code
* These proteins are “expressed” hence the name
* Many found in code of functional mRNA molecule
* These proteins are “expressed” hence the name
* Many found in code of functional mRNA molecule
91
New cards
What are introns?
92
New cards
Describe the process of gene expression.
1. Polymerase molecule attaches at the promoter and moved down an entire structural gene including the intron sections which produce a long mRNA molecule
2. the sections on the mRNA that correspond to introns are removed so only exon regions remain in mRNA molecule
3. when reassembled the mRNA molecule is decoded into a protein at a ribosome
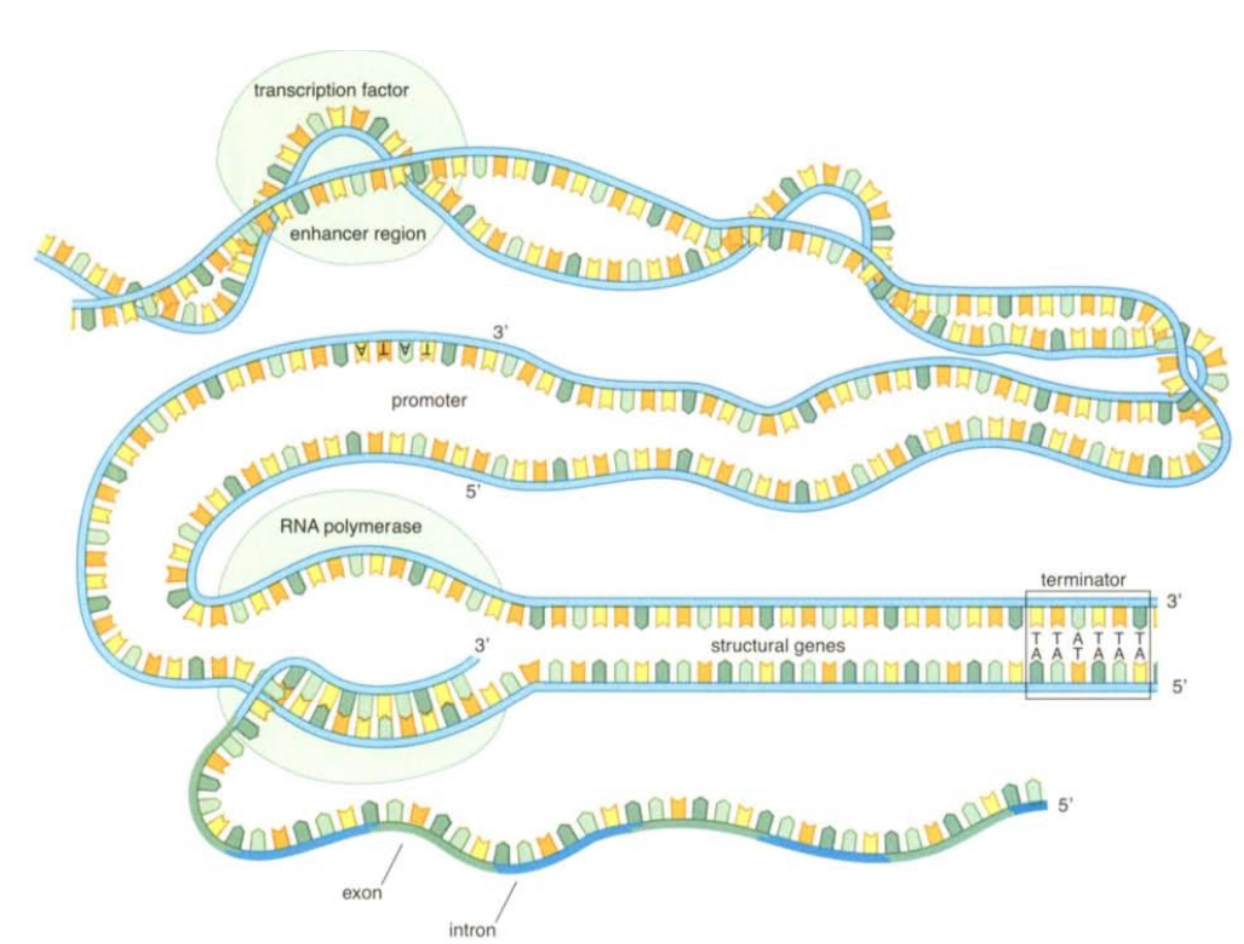
93
New cards
How are eukaryotic genes also regulated?
Way their chromosomes are coiled
94
New cards
What are histones?
chromsomes in higher organims that are highly coiled around structural proteins
95
New cards
What does the histone do?
* DNA complex wraps around itself again and again which conceals genes
* When genes are buried RNA polymerase can’t transcribe them in mRNA
* Gene has been turned “off”
* DNA has to uncoil all the way to expose the DNA heli to be transcribed/translated
* When genes are buried RNA polymerase can’t transcribe them in mRNA
* Gene has been turned “off”
* DNA has to uncoil all the way to expose the DNA heli to be transcribed/translated
96
New cards
* Why is it harder to grow mammalian cells than bacteria cells?
Mammalian cells needed to be provided with an environment that is a good substitute for their complex regular environment
97
New cards
How are mammalian cells grown on a small scale ?
* Mammalian cells needed to be provided with an environment that is a good substitute for their complex regular environment
98
New cards
How are mammalian cells grown on a small scale ?
* Grown in broth culture in special tubes or bottles with a bottom surface
99
New cards
How are mammalian cells grown on a large scale?
* Grown in suspension broth cultures in fermenters
* Media is specifically designed to have all special nutrients that each cell type may want
* Certain __*indicators*__ may be added to monitor culture
* Ex:Phenol red(changes from red to gold when the solution becomes acidic from cell overcrowding
* Media is specifically designed to have all special nutrients that each cell type may want
* Certain __*indicators*__ may be added to monitor culture
* Ex:Phenol red(changes from red to gold when the solution becomes acidic from cell overcrowding
100
New cards
How are viruses used in biotechnology research?
* Nonpathogenic viruses/virus particles are used in biotech research as vectors to carry DNA between cells