Models of memory
1/20
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Cognition
Mental processes that take place in our mind
Primacy effect
First several words on the list are remembered better than the words from the middle of the list.
Recency effect
Last several words on list are remembered better than the words from middle of the list.
Word length effect
Refers to the fact that shorter words are generally easier to remember than longer words.
Theory Atkinson and Shiffrin - Multi store memory
The key aspects are:
Information flows sequentially from sensory to short-term to long-term
Short-term is limited capacity, long-term is unlimited
Rehearsal is required to transfer from short to long-term memory
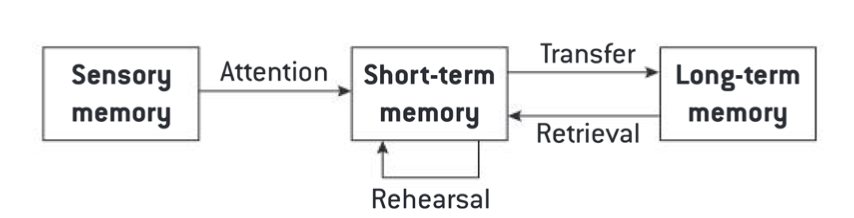
Sensory Memory
This is the first brief moment when you perceive information through your senses. 1 sec. visual, 2-5 sec. auditory. Everything in perceptual field. Required ATTENTION
Short Term Memory (Working Memory)
Where you temporarily hold and manipulate small amounts of information for no longer than 30 seconds. Chunking method (breaks down large amounts of information into smaller) REHEARSAL
Long Term Memory
Refers to the virtually unlimited, permanent storage of information in the brain.
Multi-Store Model - Strengths
One of the most influential memory models
Introduced the idea of separate memory stores
Rote rehearsal enables transfer of info from STM to LTM
Multi-Store Model - Limitations
Oversimplification
Does not pay enough attention to information flow between components
Some observed memory phenomena do not fit into unitary store idea
Further subdivisions may be needed
Emphasizes structure over process
Serial Position Effect - Primacy & Recency Effects - Glanzer & Cunitz (1966)
Aim: Investigate serial position effect with and without filler task
Method of Glanzer and Cunitz
Experiment with repeated measures design
46 army enlisted men participants
15-word lists read aloud
Free recall under 3 conditions:
Immediate recall
10 sec filler task (backward counting)
30 sec filler task
DV: # words correctly recalled
Results of Glanzer and Cunitz
Condition 1: Primacy & recency effects observed
Conditions 2 & 3: Primacy remained, recency diminished (more so in 3 than 2)
Conclusions of Glanzer and Cunitz
Supports separate short-term and long-term memory stores
STM has ~30 sec duration without rehearsal
Rehearsal helps transfer early words to LTM
Middle words hardest to rehearse/retain
Working Memory Model (Baddeley & Hitch)
Short-term memory has 4 parts:
Visuospatial Sketchpad
Phonological Loop
Episodic Buffer
Central Executive -Controls attention
The separate parts work together to temporarily hold and process different types of info (visual, audio, memories).
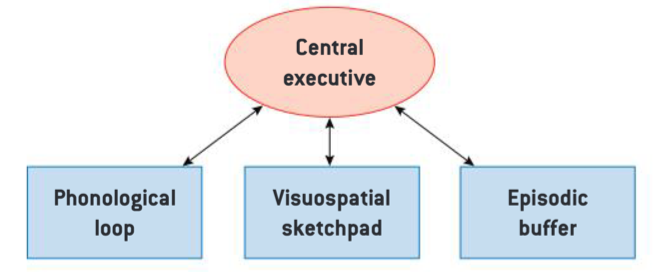
Visuospatial Sketchpad
Stores pictures/patterns you see
Phonological Loop
Stores sounds you hear
Has inner voice to repeat sounds
Episodic Buffer
Links visuals, sounds, and long-term memories
Central Executive -Controls attention
Decides what to focus on
Working Memory Model - Strengths
Explains wide range of memory phenomena
Not just short-term memory (STM)
Multi-store model accounts for aspects
Other memory models cannot explain
High explanatory power
Working Memory Model - Limitations
Complexity makes it difficult to test empirically
Only focuses on STM processes
Does not account for:
Sensory memory
Long-term memory processes