Edexcel IGCSE Biology - Transport in Plants
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
why do unicellular organisms not need transport systems?
they have a large surface area to volume ratio so substances can diffuse directly into the cell
why do multicellular organisms need transport systems?
direct diffusion from outer surfaces would be too slow, therefore a transport system is needed to transport substances to each cell quickly
what are the two main transport systems in plants?
xylem and phloem
what is the xylem?
a long hollow tube made up of dead xylem cells
what does the xylem transport?
water and mineral ions
in what direction does the xylem transport things?
from the roots, up the shoot, to the leaves along the transpiration stream
what is the phloem?
a tube made up of living phloem cells which are hollow and have sieve plates at each end to allow substances to move through
what does the phloem transport?
sugars like sucrose and amino acid
what is the process by which the phloem transports sugars called?
translocation
what direction does the phloem transport substances in?
all directions - throughout the plant
what cells take in water from the soil into the roots?
root hair cells
what process do root hair cells take in water by?
osmosis
how are root hair cells adapted for absorption of water?
there are millions of root hair cells in the roots
they have lots of microscopic hairs which give the plant a large surface area for absorbing water from the soil
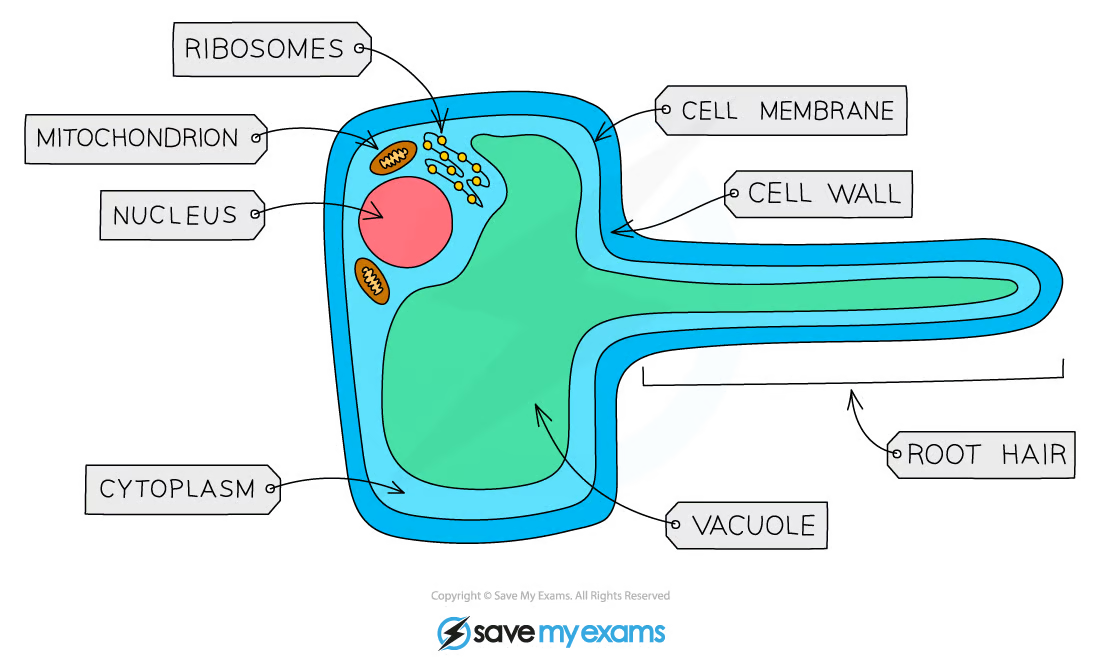
by what process do root hair cells take up mineral ions into the plant?
active transport
what is the combined name for the xylem and phloem?
vascular bundle
in the stem and roots, how do you identify the xylem and phloem?
xylem always is the part closest to the centre (including the x)
how do you identify the xylem and phloem in a leaf?
the xylem is always on top
what is transpiration?
the evaporation of water from the surface of a plant
where does most transpiration take place?
on the leaves
what does transpiration create in the xylem?
creates a shortage of water in the leaf - negative pressure, and so more water is drawn up from the rest of the plant through the xylem
this means more water is drawn up from the roots, so there is a constant transpiration stream through the plant
which 4 factors affect the rate of transpiration?
light intensity
temperature
wind speed
humidity
how does an increase in light intensity affect transpiration rate?
increases the transpiration rate
this increases rate of photosynthesis so more stomata open meaning more water can evaporate
how does an increase in humidity affect rate of transpiration?
increase in humidity decreases transpiration rate
this is because there is a reduced concentration gradient between the inside and outside of the leaf, resulting in a slower rate of diffusion so the transpiration rate decreases
how does an increase in wind speed affect rate of transpiration?
increase in wind speed increases rate as it removes water vapour from leaf surfaces so there is a greater concentration gradient between the leaf and the air so the rate of diffusion increases
how does an increase in temperature affect transpiration rate?
an increase in temperature increases transpiration rate
this is because water molecules have more kinetic energy so move faster so the water evaporates faster and the rate of transpiration increases
what piece of apparatus is used to measure transpiration rate?
potometer
how do you set up a potometer?
cut a shoot underwater to prevent air from entering the xylem - cut it at a slant to increase surface area
assemble it underwater and insert the shoot underwater so no air can enter
remove the apparatus from the water but keep the end of the capillary tube submerged in a beaker
check the apparatus is water- and air- tight
dry the leaves and allow time for the shoot to acclimatise
shut the tap
remove the end of the capillary tube from the beaker of water until one air bubble has formed then put the tube back in
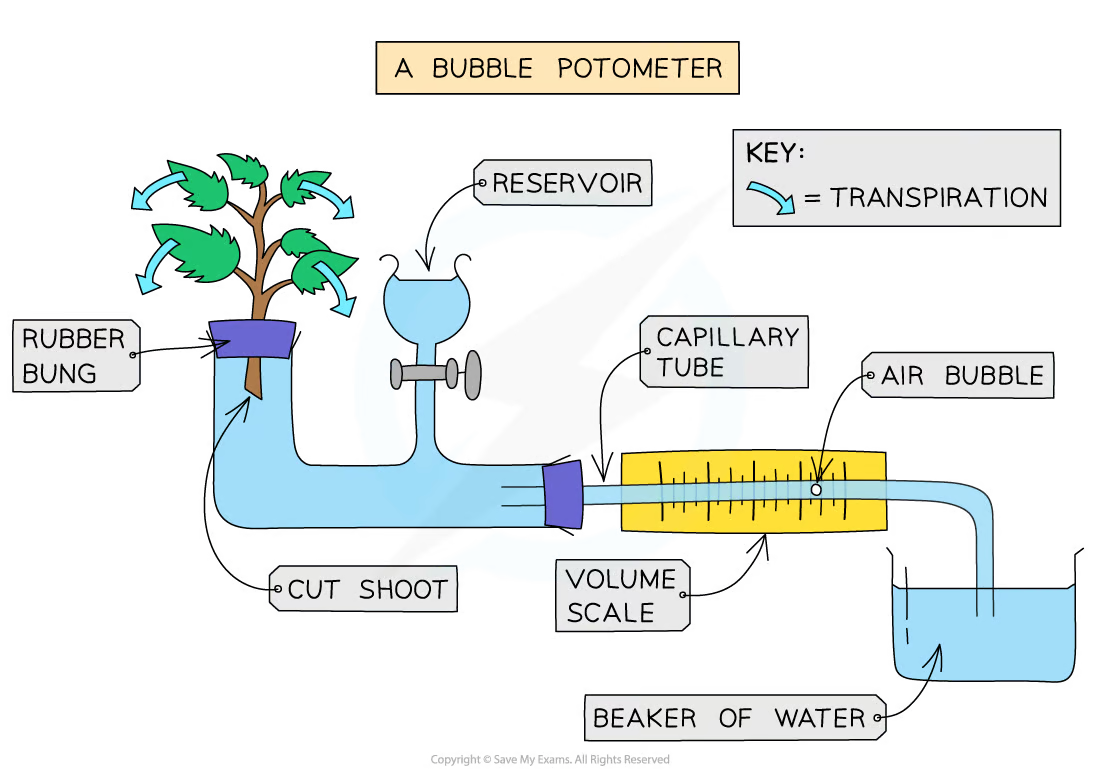
how do you carry out the experiment to investigate transpiration rate using a potometer?
set up the potometer
record the starting position of the air bubble
start a stopwatch and record the distance moved by the bubble in a set time period - 10 minutes
keep conditions constant throughout - change one each time (see below)
how would you modify the potometer to measure the effect of light intensity on transpiration rate?
use a lamp to modify the light intensity at different distances from the apparatus or put it in a cupboard
how would you modify the potometer to measure the effect of temperature on transpiration rate?
put the apparatus in warmer or colder rooms
how would you modify the potometer to measure the effect of humidity on transpiration rate?
to increase the humidity, you could place a wetted plastic bag around the apparatus and seal it
how would you modify the potometer to measure the effect of wind speed on transpiration rate?
you could use a fan to alter the wind speed around the plant