IB Physics Option C Key Concepts
0.0(0)Studied by 7 people
Card Sorting
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:29 PM on 5/1/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
1
New cards
What happens when wavefronts pass through a regularly curved interface between two transparent media?
refraction changes their shape and can make them converge towards a or diverge away from a point.
2
New cards
How can we make the reflection and refraction of wavefronts is easier to understand?
when we use straight rays in diagrams to represent the direction in which the wavefronts are travelling.
3
New cards
What are converging lenses?
A lens which is thicker in the middle than at its edges will converge the rays that are passing through it (unless they come from an object which is too close to the lens).
4
New cards
How do diverging lenses compare to converging lenses?
thinner in the middle than at the edges and they cause rays to diverge.
5
New cards
What is the principal axis?
the imaginary straight line passing through the centre of the lens, which is perpendicular to its surfaces.
6
New cards
What is the focal point of a lens?
The focal point of a lens is the point through which all rays parallel to the principal axis converge after passing through the lens (or the point from which they appear to diverge)
7
New cards
How can we define the (optical) power of a lens?

8
New cards
How are real images formed?
where real rays actually converge to a focus
9
New cards
How can virtual images be seen?
They can only be seen by looking through lenses, or mirrors, to the points from which the rays appear to diverge.
10
New cards
How can ray diagrams be used to predict the properties of images formed by objects placed in different positions?
Ray diagrams drawn to scale can be used to predict the properties of the images formed by objects placed in different positions. If an object is a long way from a converging lens, a smaller, real, inverted image is formed on a screen placed close to the focal point. As the object and lens get closer together, the image moves further away from the lens and gets larger (and dimmer), but it remains real and inverted. If the object is closer to the lens than the focal point, no real image can be formed, but a magnified, upright, virtual image can be seen by looking through the lens.
11
New cards
What do ray diagrams show for diverging lenses?
Ray diagrams for diverging lenses confirm that the images are always upright, virtual and diminished.
12
New cards
How can ray diagrams be used to locate the image formed by a system of tw lenses?
Ray diagrams can also be used to locate the image formed by a system of two lenses. The image formed by the first lens is treated as the object for the second lens.
13
New cards
What is the thin lens equation?
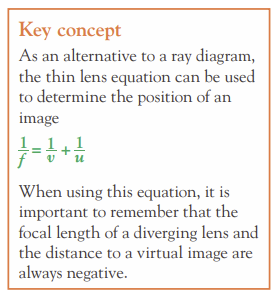
14
New cards
For a ray diagram, what symbol is given to the distance from the eye to the near point?
The distance from the eye to the near point is given the symbol D and it is assumed to be 25 cm for a normal eye.
15
New cards
What is the formula for linear magnification and angular magnification?
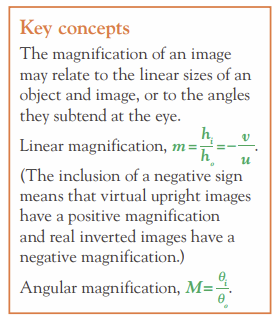
16
New cards
What will the lens act as when the object is placed closer to a converging lens? How can we get the angular magnification?

17
New cards
What is an spherical aberration?
the inability of a lens or mirror which has spherically shaped surfaces to bring all (monochromatic) rays from the same point on an object to the same point focus.
18
New cards
what is a chromatic aberration?
the inability of a lens to bring rays of different colours (from a point object) to the same focus.
19
New cards
What does a simple optical compound microscope consists of?
It consists of two converging lenses. The lens close to the object (the objective lens) forms a real magnified image, and the second lens (the eyepiece) acts as a magnifying glass to further magnify the size of the final image, which is virtual and inverted
20
New cards
How can we calculate the angular magnification of a compound microscope?
The angular magnification of a compound microscope equals the linear magnification of the objective lens multiplied by the angular magnification of the eyepiece lens
21
New cards
When does an optical system is described as producing a good resolution?
An optical system may be described as producing good resolution if two close points on an object can be seen as separate on the image.
22
New cards
How can we measure the actual resolution achieved?
The actual resolution achieved can be measured as the angle subtended at the optical system by two points which can just be resolved. (A smaller angle means better resolution.)
23
New cards
What is the equation for the expected angular resolution?

24
New cards
What can have an effect on the resolution of images produced by optical telescopes?
The atmosphere also scatters radiation and this can have a significant effect on the resolution of images from astronomical telescopes. Irregular refraction in the atmosphere can also cause problems for optical telescopes.
25
New cards
What are the main advantages of satellite-borne telescopes?
The main advantages of satellite-borne telescopes are (1) better resolution, (2) more sensitive, (3) unaffected by weather and pollution.
26
New cards
The objective lens of a telescope forms a diminished, real and inverted image of a distant object at its focal point. The eyepiece then acts as a magnifying glass to produce a final image at infinity because the first image is also at the focal point of the eyepiece lens. The final image is inverted and virtual