Exam 3-Abnormal Child Psych
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
Intellectual Disability
A disorder characterized by deficits in intellectual functioning and adaptive behavior, typically diagnosed before age 18.
Co-occuring Disorders of ID
ADHD, Self-injury, Aggression, & Autism
Diagnostic Overshadowing
where the presence of a diagnosed disorder leads to overlooking of other concurrent issues
DSM-5 (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders)
evaluates in terms of “mild,” “moderate,” “severe,” and “profound” have been used to describe the severity of ID
AAIDD (American Association on Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities)
characterized by significant limitation in both intellectual functioning and adaptive behavior as expressed in conceptual, social, and practical, originating before age 18.
IQ
A measure of a person's intellectual capabilities, where an IQ of 70 or below indicates a diagnosis of intellectual disability.
Adaptive Behavior
The collection of conceptual, social, and practical skills that people learn in order to function in their daily lives.
Flynn Effect
IQ scores in populations systematically improve over time
4 Categories of risk and etiology according to the AAIDD?:
Biomedical, Social, Behavioral, & Educational
What are levels of needed support?
The levels of needed support refer to the varying intensities and types of help individuals with intellectual disabilities require in different settings to function effectively. These levels can range from intermittent support to pervasive, depending on the individual's needs.
What are the levels of ID
Levels of Intellectual Disability (ID) typically include mild, moderate, severe, and profound, classified based on the conceptual, practical, and social domain
Measured intelligence
intelligence is measured by the presentation of tasks that assess both general and specific abilities
Mental age (MA)
the age corresponding to the chronological age (CA) of children whose performance they equaled
IQ (intelligence quotient)
the ratio of an individual’s mental age to chronological age x 100
Down Syndrome
A genetic disorder caused by trisomy 21, characterized by moderate to severe intellectual disabilities and distinct physical features.
An advantage of Down syndrome
It’s said to be easier to raise a child with DS versus other developmental disabilities; many parents report positive experiences with their disabled child despite the challengess
Fragile X syndrome
The most common inherited form of intellectual disability, caused by a mutation on the X chromosome, long faces, prominent jaws, & large ears—more common in boys and often associated with social anxiety and attention deficits.
Williams Syndrome
A rare genetic disorder caused by deletions on chromosome 7, associated with mild to moderate intellectual disability and distinct social behavior.
Prader-Willi Syndrome
70% of cases result from paternal deletion of genes on chromosome 15, hyperphagia and food hoarding/obesity, other compulsions, such as skin-picking
Epidemiology of Intellectual Disabilities
The study of the prevalence and incidence of intellectual disabilities, suggesting a rate of 1-3% in the general population.
Co-occurring disorders
The occurrence of two or more disorders in the same individual, such as ADHD and autism spectrum disorders alongside intellectual disabilities.
Conduct Disorder
A persistent pattern of behavior that violates the rights of others and societal norms, often diagnosed in childhood or adolescence.
Oppositional Defiant Disorder (ODD)
A behavioral disorder in children characterized by a pattern of angry, irritable mood, argumentative/defiant behavior, or vindictiveness lasting over six months (at least 4 symptoms per week)
Response to Intervention (RTI)
An educational strategy that identifies struggling students early and provides targeted teaching to improve their performance.
Autism Spectrum Disorder
A Neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by deficits in social skills, repetitive behaviors, and communication difficulties, typically diagnosed in early childhood.
Joint attention
A fundamental social skill where two people focus on the same object or event to share the experience, often seen in early developmental stages.
Theory of mind
The ability to understand that others have thoughts, beliefs, and perspectives different from one's own, and how it impacts how individual’s act.
Central Coherence
It refers to the cognitive ability to integrate or synthesize information into a coherent whole, often impaired in individuals with autism.
Executive Functions
Cognitive processes that enable goal-directed behavior, including planning, working memory, and inhibition control.
Primary Features of ASD
persistent impairments in social communication and interaction and restricted/repetitive behaviors
Secondary Features of ASD
Sensory/perceptual impairments including over/undersensitivity, and overselectivity
Co-occurring disorders of ASD
ID, anxiety, depression, ADHD, and ODD
School/education opportunities of ASD
TEACHH & IDEA is a teaching/educational approach designed to support individuals with ASD in learning and social interactions.
Behavioral Intervention
Therapeutic approaches focused on modifying specific behaviors using reinforcement strategies and direct observations.
Phonological Disorder
A communication disorder characterized by difficulty understanding and using speech sounds correctly.
Communication & Learning Disabilities
Disorders that affect a child's ability to understand or use language and academic skills effectively, impacting their overall learning process.
Definition Concerns for learning disabilities
There are no specific criteria for identifying learning disabilities & the definition excludes many children whose disabilities are due to multiple factors
Criteria issues for learning disabilities
The exclusionary criteria is questioned because it may be hard to differentiate learning problems due to emotional disturbance, lack of motivation, or cultural or economic disadvantage
IQ-achievement discrepancy model
It was assumed that if a specific learning disability exists, performance on measures of general ability (IQ tests) would significantly differ from achievement in specific academic tasks.
Achievement tests
This approach identifies disabilities by determining if a child is below the expected grade level or age in at least one academic area.
Response to Intervention (RTI)
An innovative approach to addressing learning disabilities is by exposing children to intervention prior to diagnosing them with a disability; children whose response to valid intervention are poorer than their peers are said to have a learning disability.
Normal Language Development
serves as a framework for understanding disabilities, effective receptive & expressive language— the basic components of language: phonology, morphology, syntax, semantics, & pragmatics.
Atypical Language Development
general deficits in phonology, morphology, etc; problems in speech, language, or both; and receptive/expressive language problems
Language Disorder
Difficulties in acquiring or using language due to impairments in comprehending or producing vocabulary, sentences, and discourse
Co-occurring disorders of Language Disorders (Communication Disorders)
learning disabilities, internalizing/externalizing behaviors, and anxiety
Cognitive deficits in children with Communication Disorders
limited information-processing capacity—delayed reaction time to information, deficits in auditory processing, deficits in verbal short-term and working memory, and executive functioning.
Specific Learning Disorder
a specific neurodevelopment problem in reading, writing, and arithmetic (math) related to classroom learning and everyday functioning.
SLD with Impairment in Reading
deficits in language abilities, cognitive skills, understanding of the conventions of written text (reading from left to right), and a store of knowledge about the world.
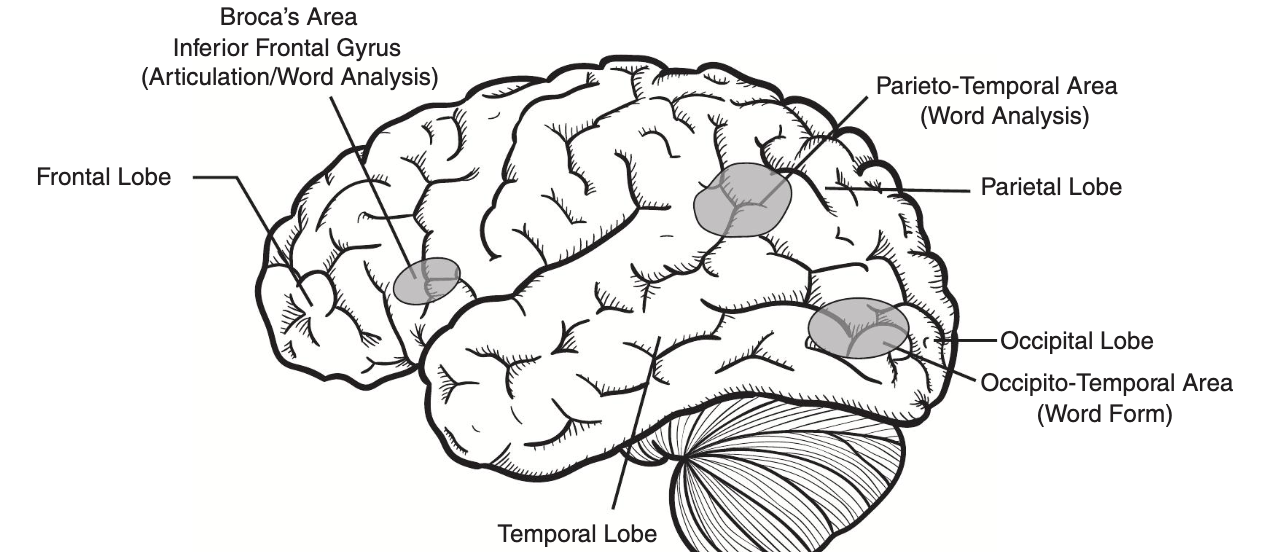
Word-level reading problems (Dyslexia)
Difficulties in recognizing words, decoding, and spelling due to differences in processing written language.
Text-level reading problems (Problems of Comprehension)
These children can decode and recognize single words, read a sentence outloud, but fail to understand it; this often co-occurs with Word-level reading problems
Matthew Effect
the widening of the gap between strong and weak readers over time, where struggling readers fall further behind.
Co-occurring disorders of Reading Impairments
ADHD, externalizing problems, ASD, anxiety, and depressive disorders
SLD with Impairment in Written Expression
These children’s writings may have errors, difficult to decipher, and contain disorganized content lacking in length and richness.
SLD with Impairment in Math
Problems in basic arithmetics skills or math reasoning that are well below average for age in number sense, addition, subtraction, etc.
Social problems associated with learning/communication disorders
include difficulties in peer relationships, social skills deficits, and challenges in understanding social cues, leading to increased risk of isolation and emotional issues.
Brain abnormalities associated with learning disabilities
cerebral palsy, epilepsy, nervous system infections, head injury, prenatal alcohol use, very preterm/low birth weight, and neurological delays and soft signs
The Education for All Handicapped Children Act of 1975
Educational services available to children/adolescents with disablities
Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
A neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by persistent patterns of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity that interfere with functioning or development.
Co-occurring disorders of ADHD
learning disabilities, anxiety, depression, ODD, and CD
Primary features of ADHD
Include inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity, significantly affecting daily functioning.
Secondary features of ADHD
Deficits in motor skills, intelligence/academic achievement, executive functions, emotional regulation, and social skills.
Gender differences in ADHD
Boys are more frequently diagnosed than girls (3:1 ratio), often exhibiting more externalizing symptoms, while girls may present with more internalizing behaviors.
Conduct Problems
the general group of disruptive/antisocial behavior problems often manifesting in aggression, deceitfulness, and violation of rules.
Externalizing
problems that tend to place young people in conflict with others.
Intermittent Explosive Disorder
characterized by recurring and frequent behavioral outbursts, like verbal temper tantrums or physical aggression towards others
Antisocial Personality Disorder (APD)
individuals who display a persistent pattern of aggressive and antisocial behavior after the age of 18; a pattern of disregard and violation of the rights of others.
Conduct Disorder
a more severe form of behavioral disorder in children and adolescents, marked by persistent violation of age-appropriate societal norms and the rights of others, often leading to issues such as aggression, deceitfulness, and bullying.
Co-occurring disorder of CD
ADHD & ODD
Childhood onset of CD
refers to the onset of conduct disorder symptoms before the age of 10, often leading to more severe behavior issues in the future.
Adolescent onset of CD
refers to the onset of conduct disorder symptoms after the age of 10, which may present with fewer aggressive symptoms but still involves rule-breaking and antisocial behavior.