Chapter 16 - Lab
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
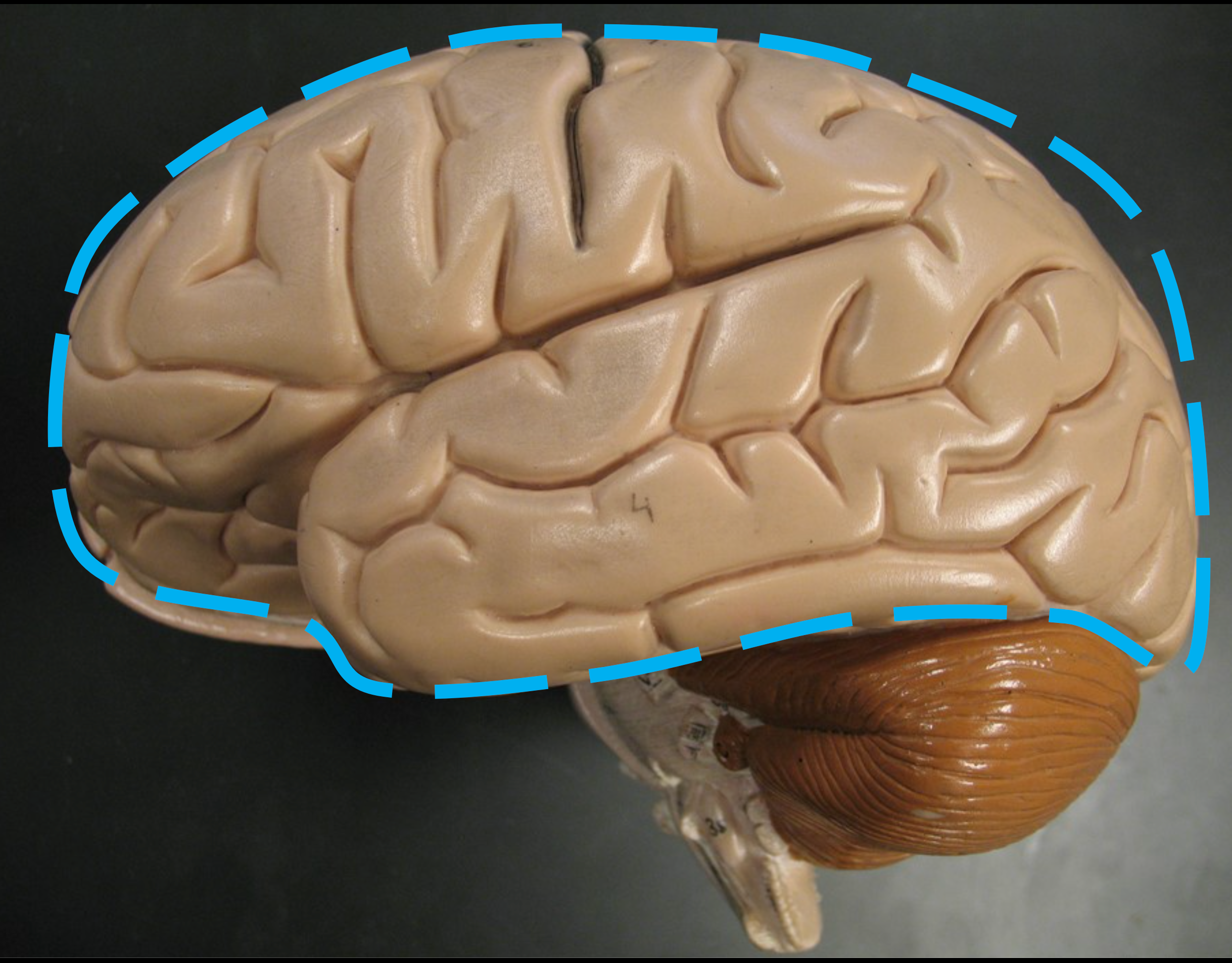
Cerebrum
Largest portion of the brain; responsible for conscious thought processes.
Diencephalon
Smallest portion of the brain; controls many homeostatic processes.
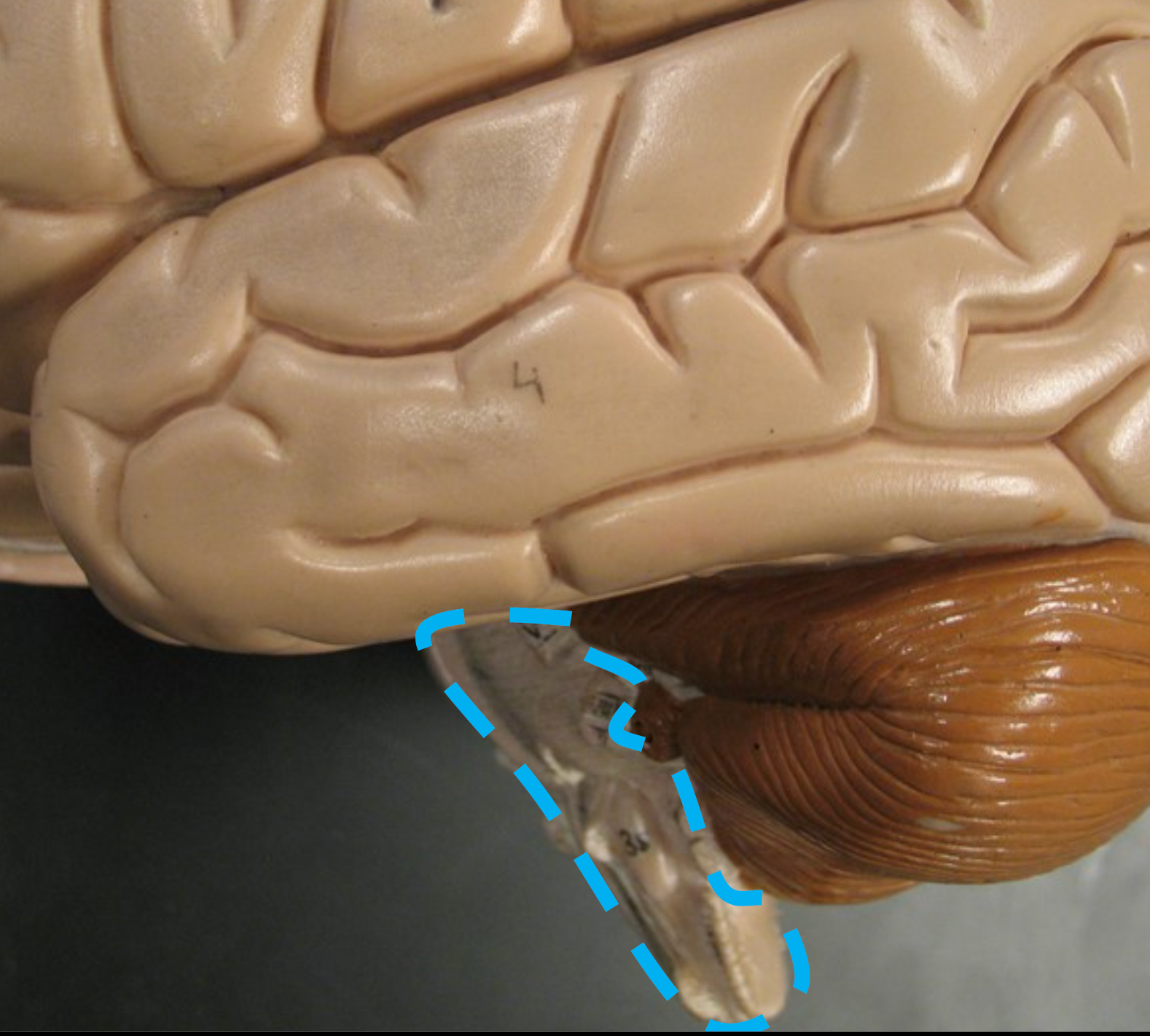
Brain Stem
Connects higher brain regions to the spinal cord and cerebellum.
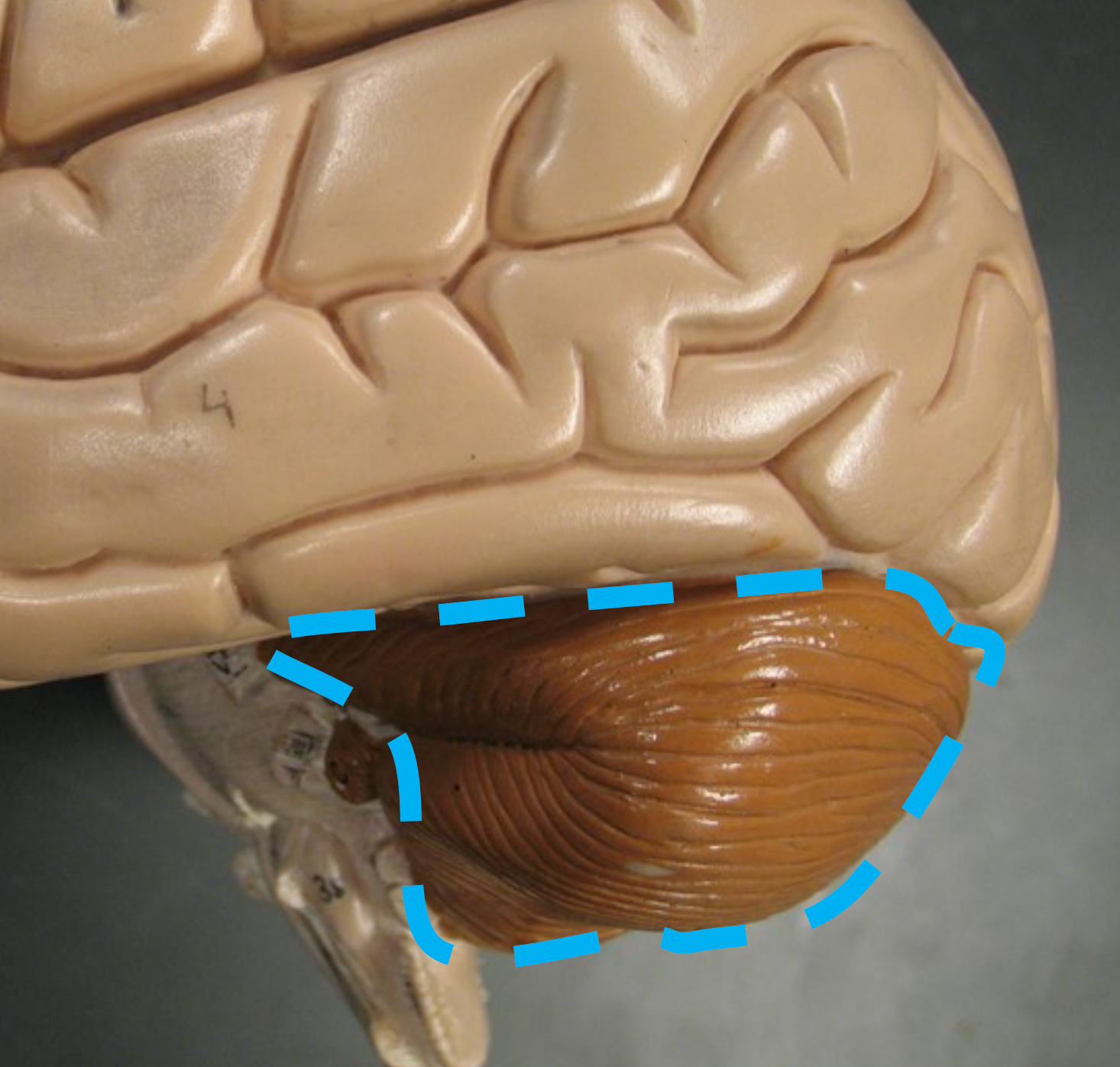
Cerebellum
Coordinates body movements.
Cranial Meninges
Three layers of connective tissue that protect the soft tissues of the brain and spinal cord.
Pia Mater
Very thin and nearly transparent layer of areolar connective tissue; directly covers the brain's surface.
Arachnoid Mater
Has a webbed-like appearance.
Subarachnoid Space
Space between pia mater and arachnoid mater; filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
Supports and protects the brain; delivers nutrients and removes waste.
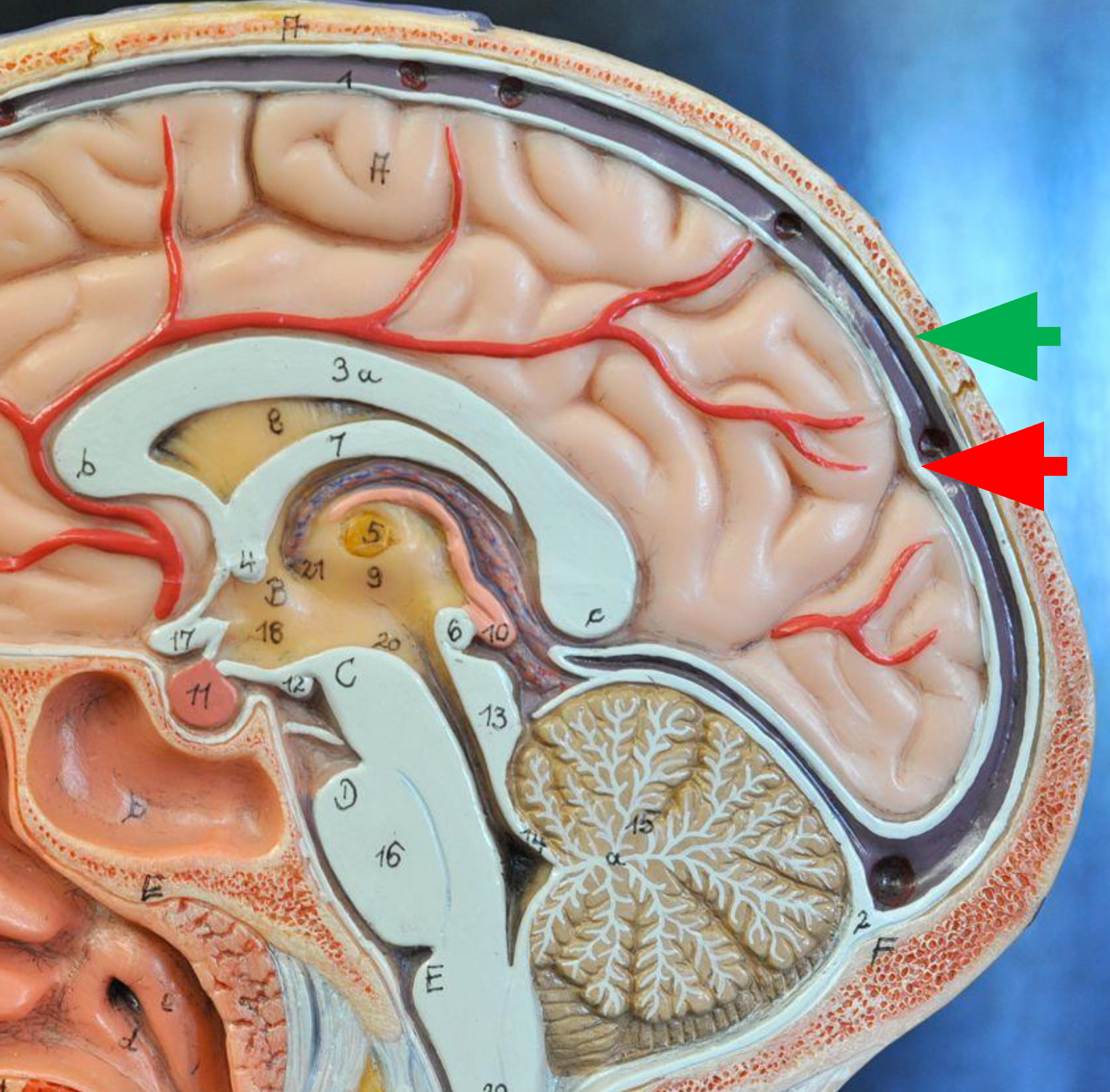
Dura Mater
Consists of two layers of dense irregular tissue, an inner meningeal layer and an outer periosteal layer.
Meningeal Layer
The inner layer of the dura mater; lies next to the arachnoid mater. (Red Arrow)
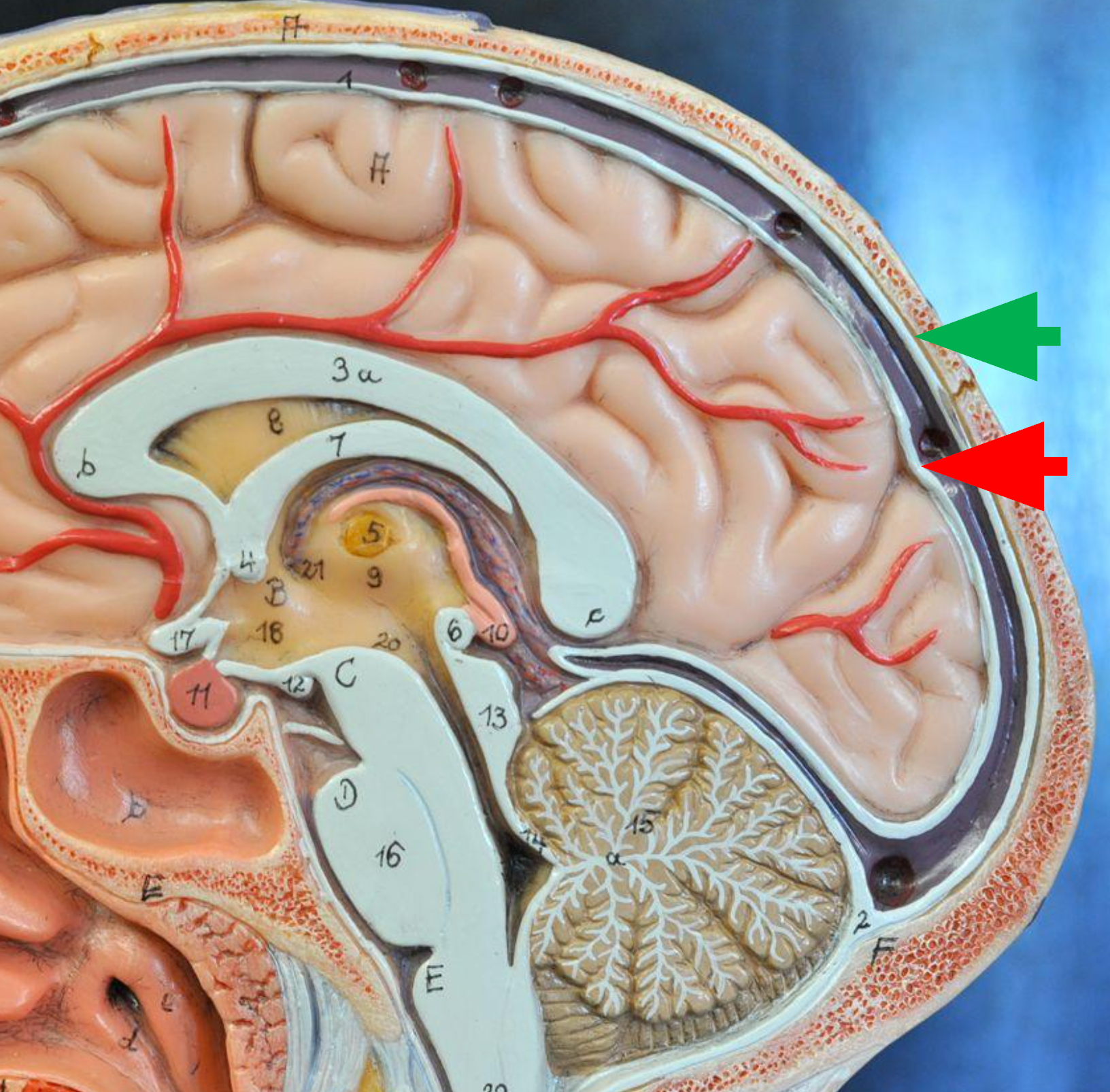
Periosteal Layer
The outer layer of the dura mater; lines the inside of the cranium. (Green Arrow)
Posterior/Dorsal
Describe the position of the cerebellum relative to the brain stem
loss of motor coordination and problems with balance.
What are some problems a person might have if a stroke damaged his cerebellum
Pia mater and Arachnoid Mater
Between which of the cranial meninges is cerebrospinal fluid found
Cerebral Cortex
Outer gray matter of the cerebrum containing billions of neuron bodies; responsible for conscious thought.
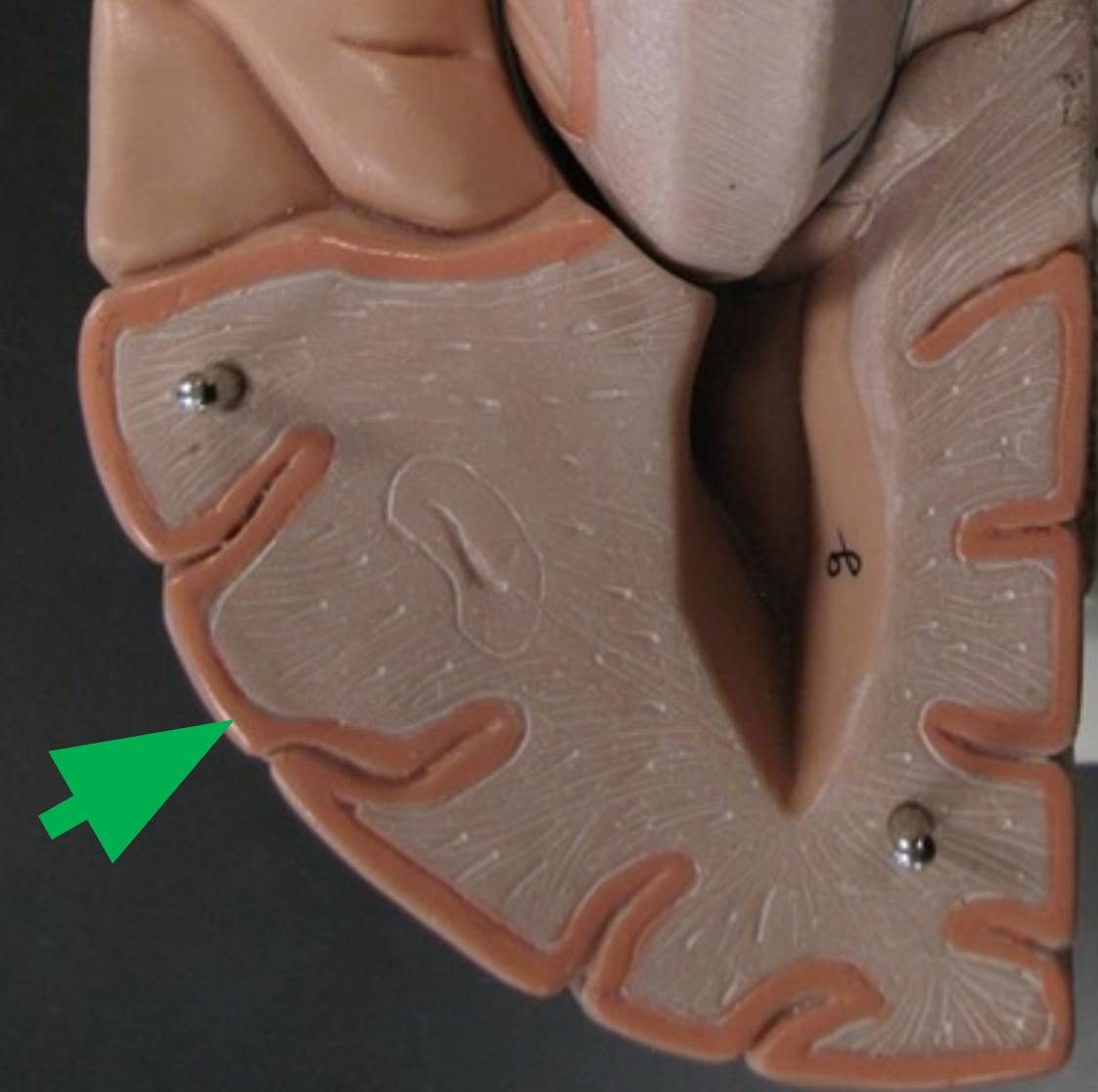
Gray Matter
Contains neuron somas, dendrites, and unmyelinated axons. General function is integration - the processing of information.
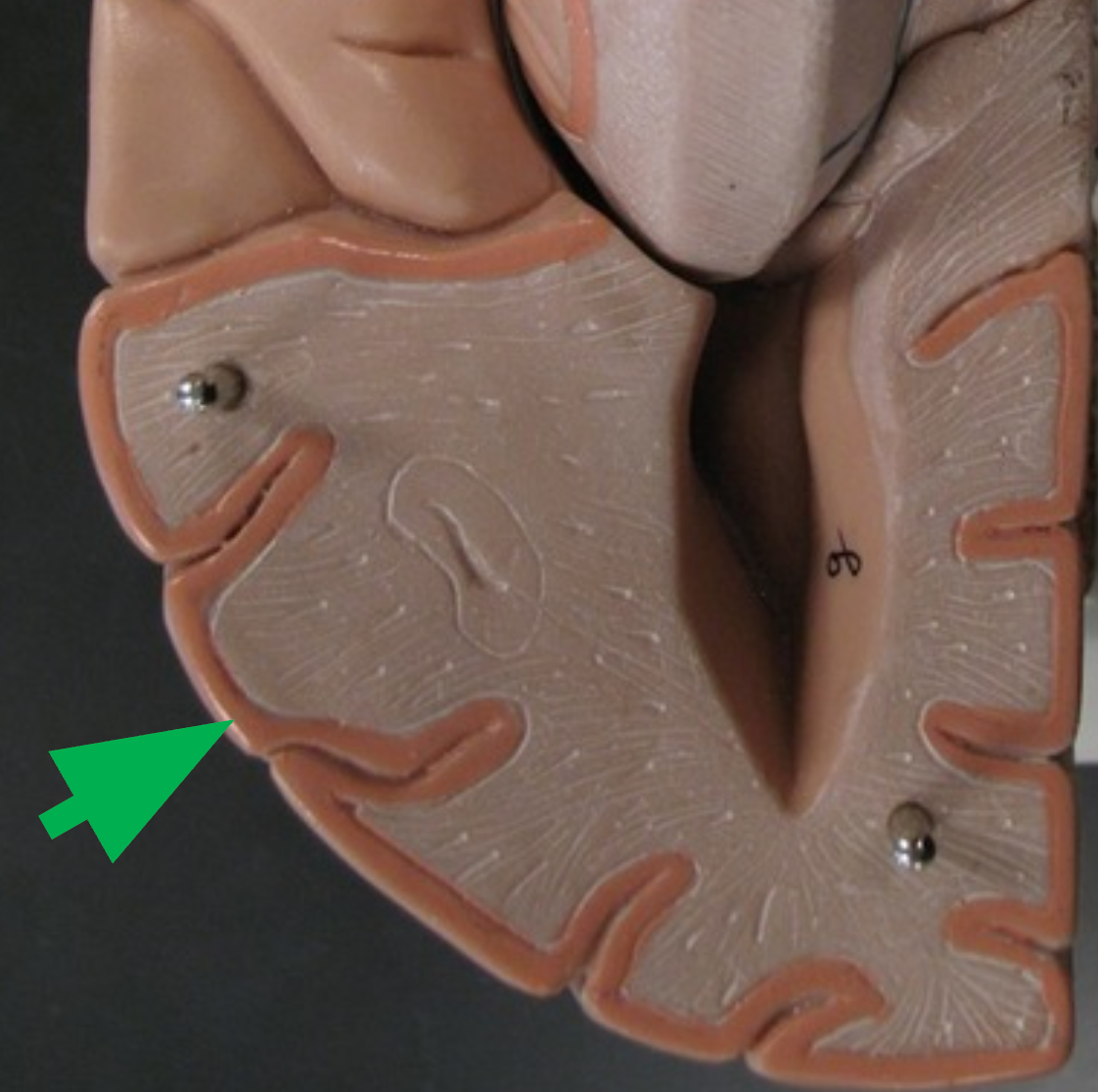
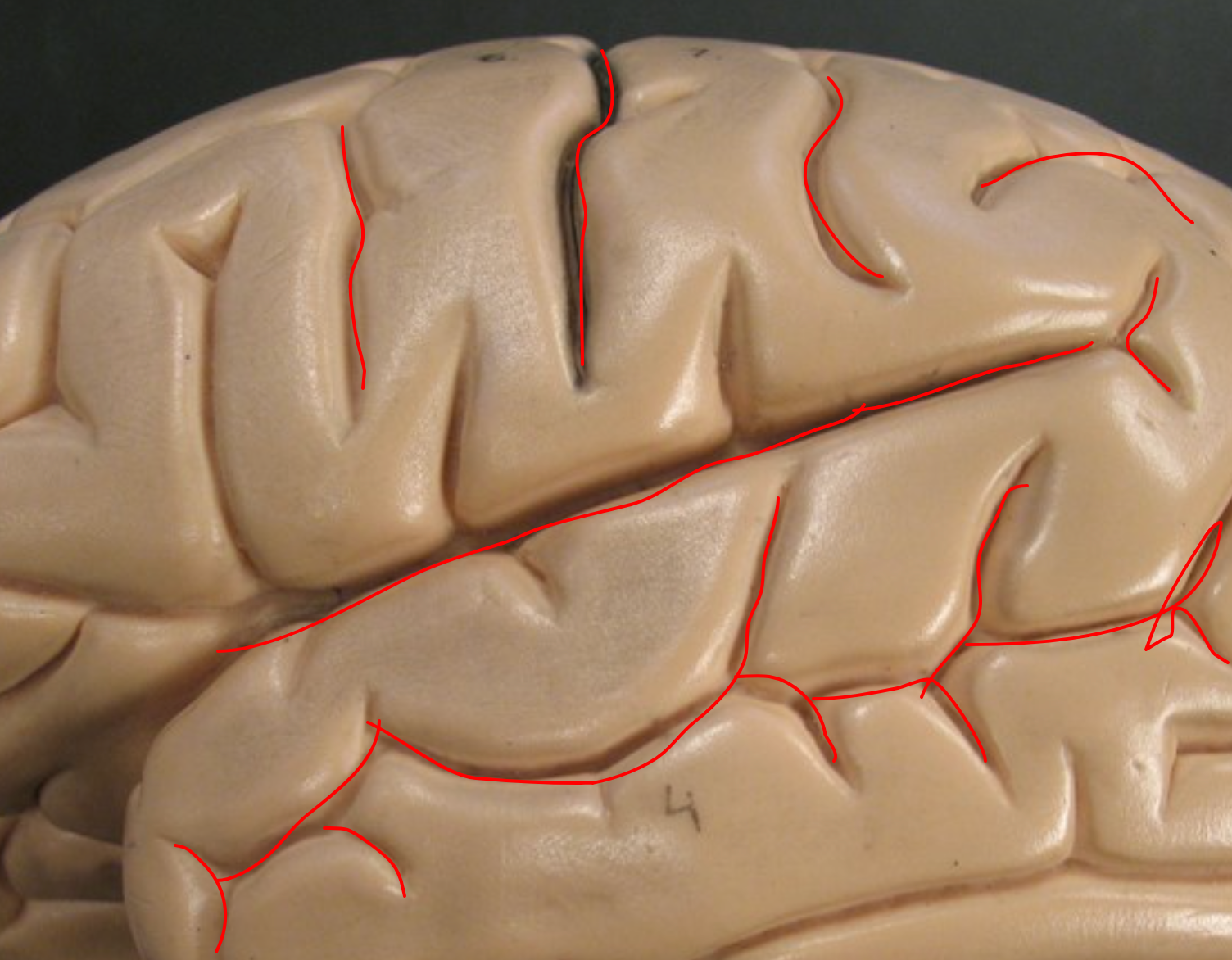
Gyri (Gyrus)
Folds of brain tissue that increase surface area of the cerebral cortex.
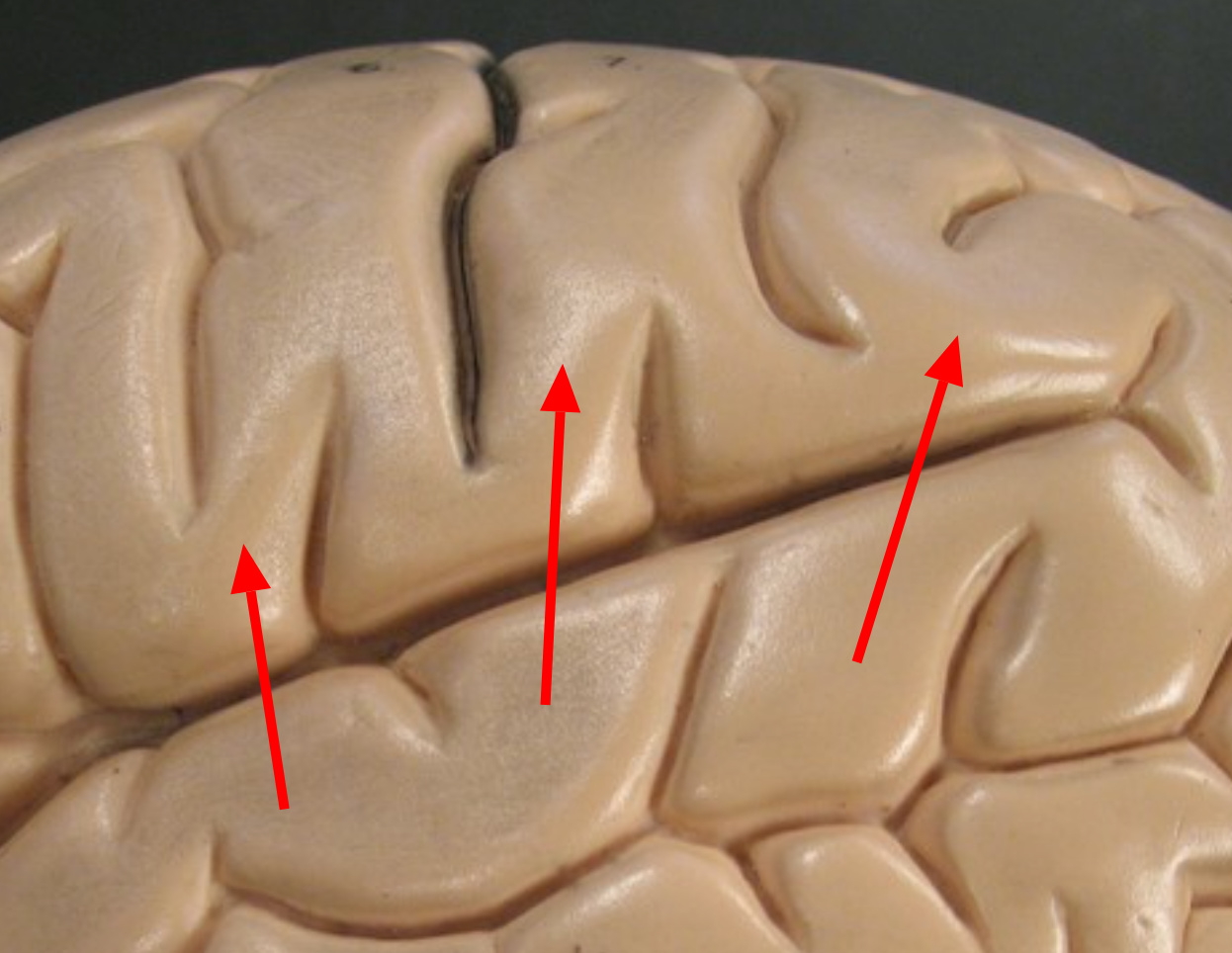
Sulci (Sulcus)
Narrow grooves between gyri on the cerebral cortex.
Cerebral Hemispheres
The left and right halves of the brain.
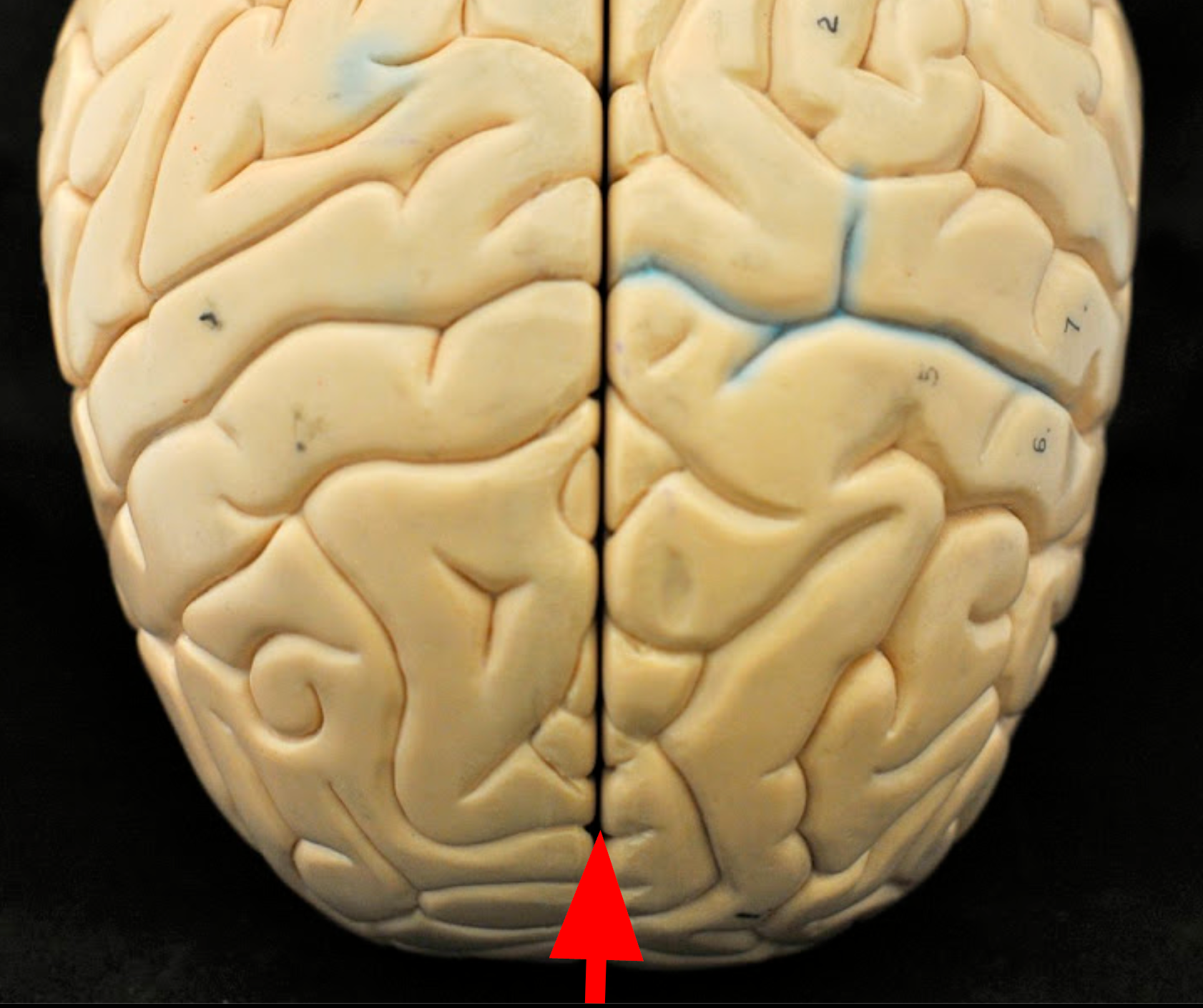
Longitudinal Fissure
Deep midsagittal groove dividing the cerebrum into left and right hemispheres.
Frontal Lobe
Anterior part of the cortex; involved in somatic motor control, speech, intellect, task management, and personality.
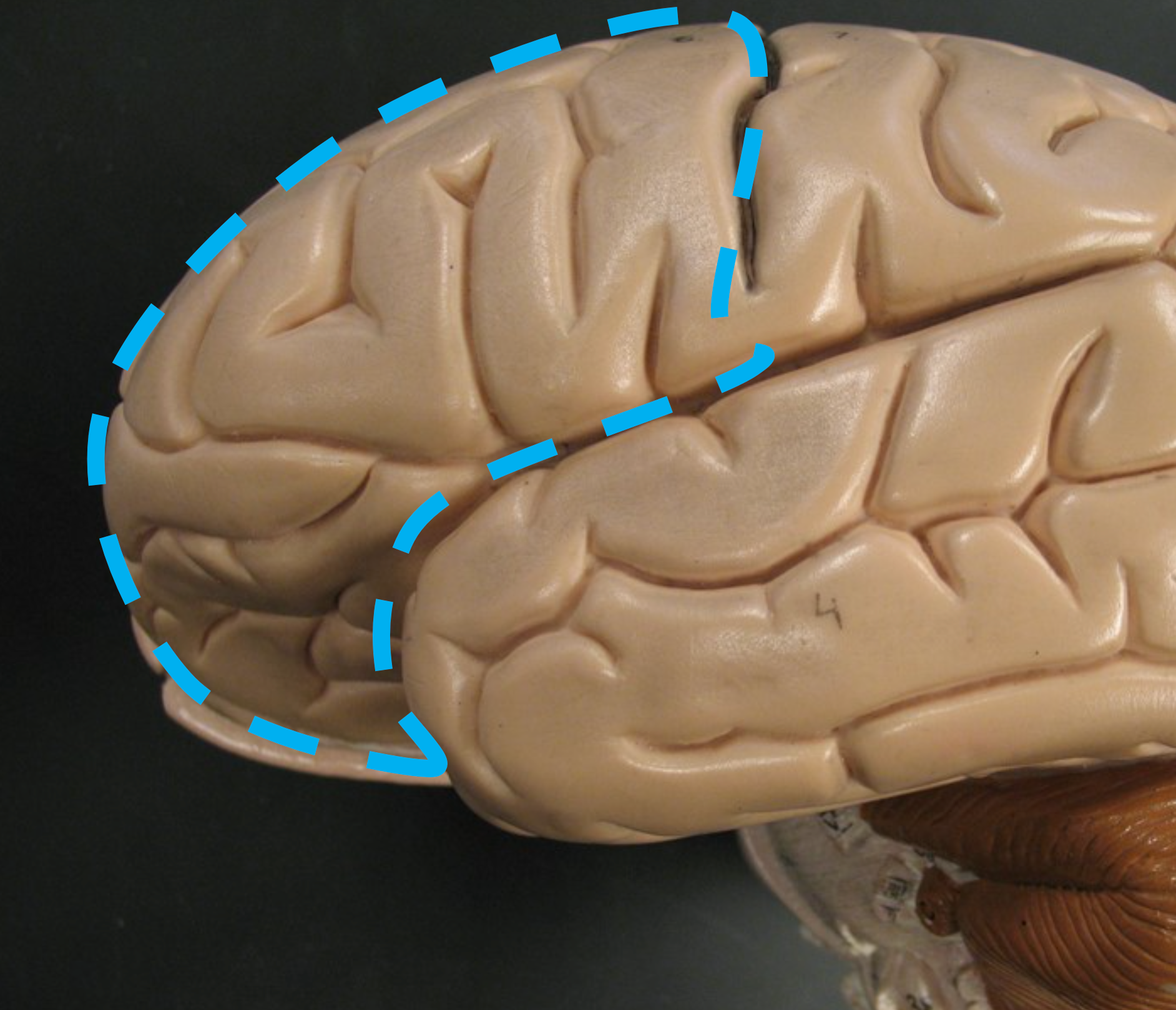
Precentral Gyrus
Part of the frontal lobe that directs somatic motor commands.
Parietal Lobe
Located at the top of each hemisphere; processes somatosensory info like touch and body position, and also language.
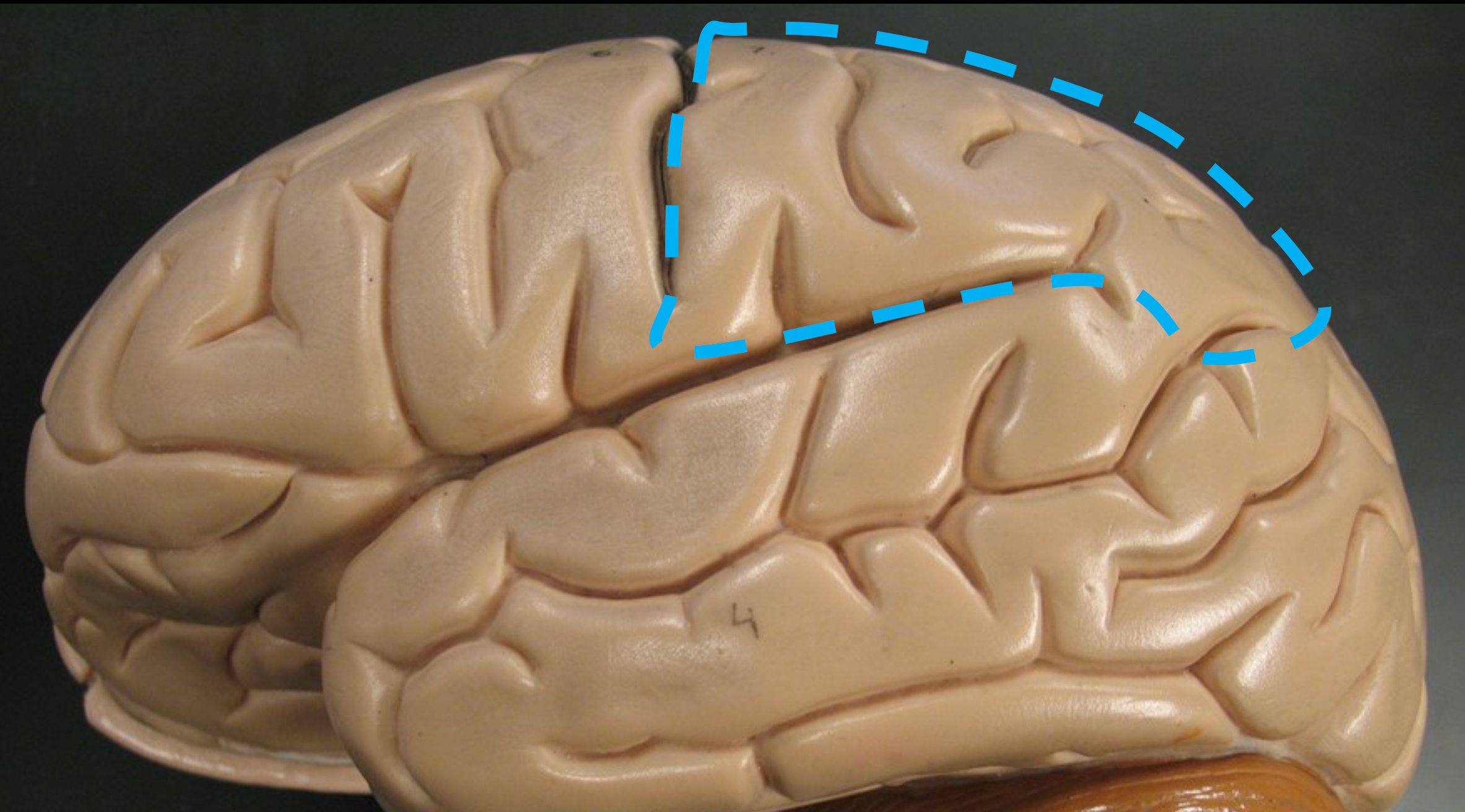
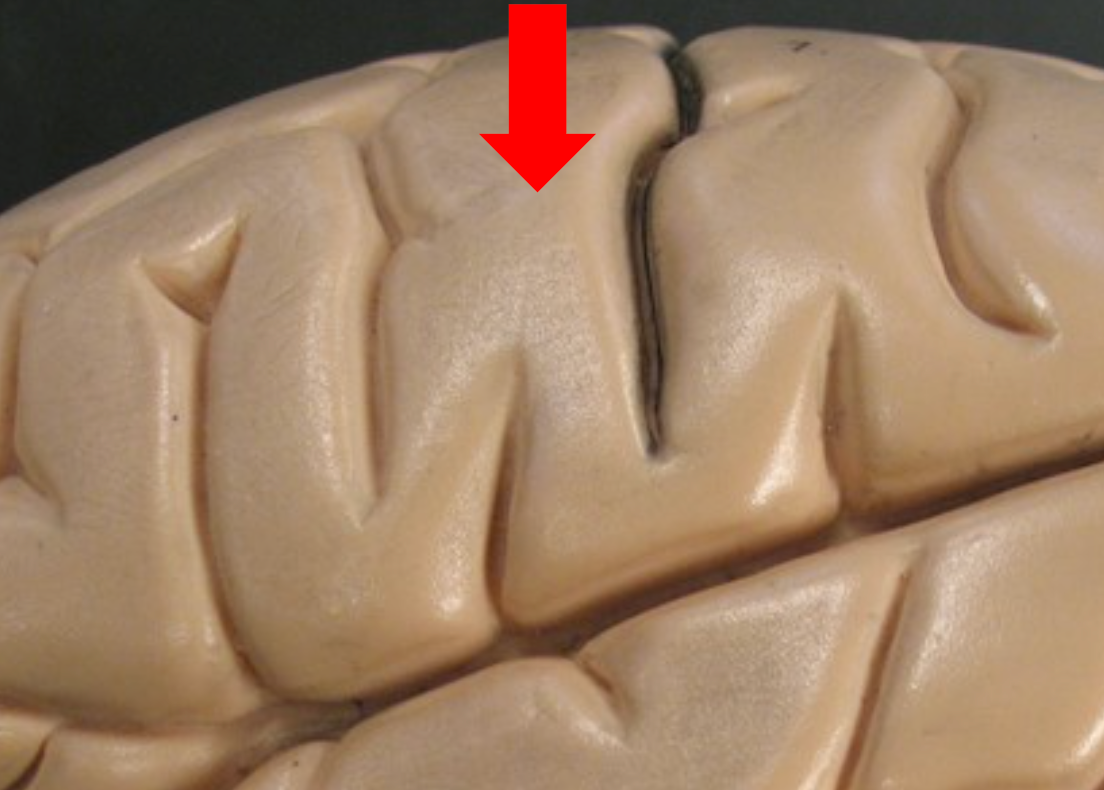
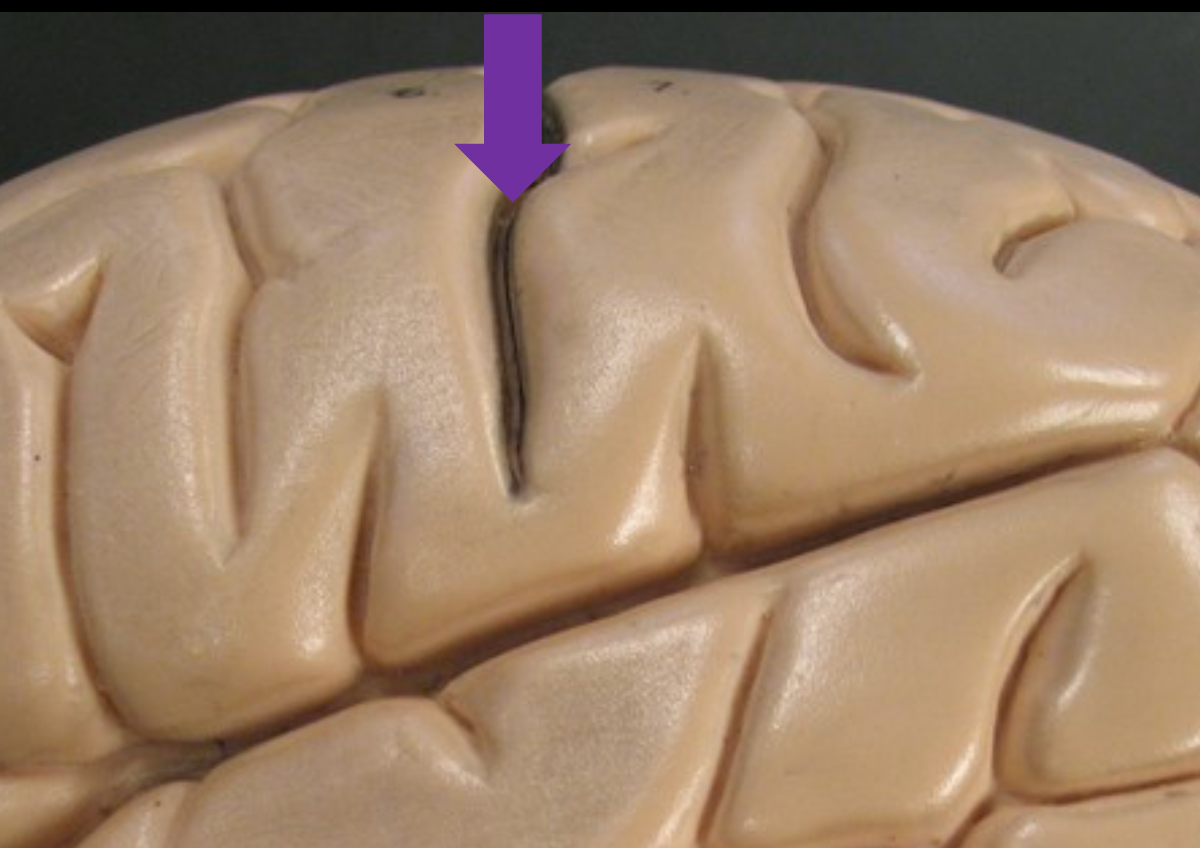
Central Sulcus
Separates the frontal and parietal lobes.
Postcentral Gyrus
Region of the parietal lobe responsible for processing somatosensory input.
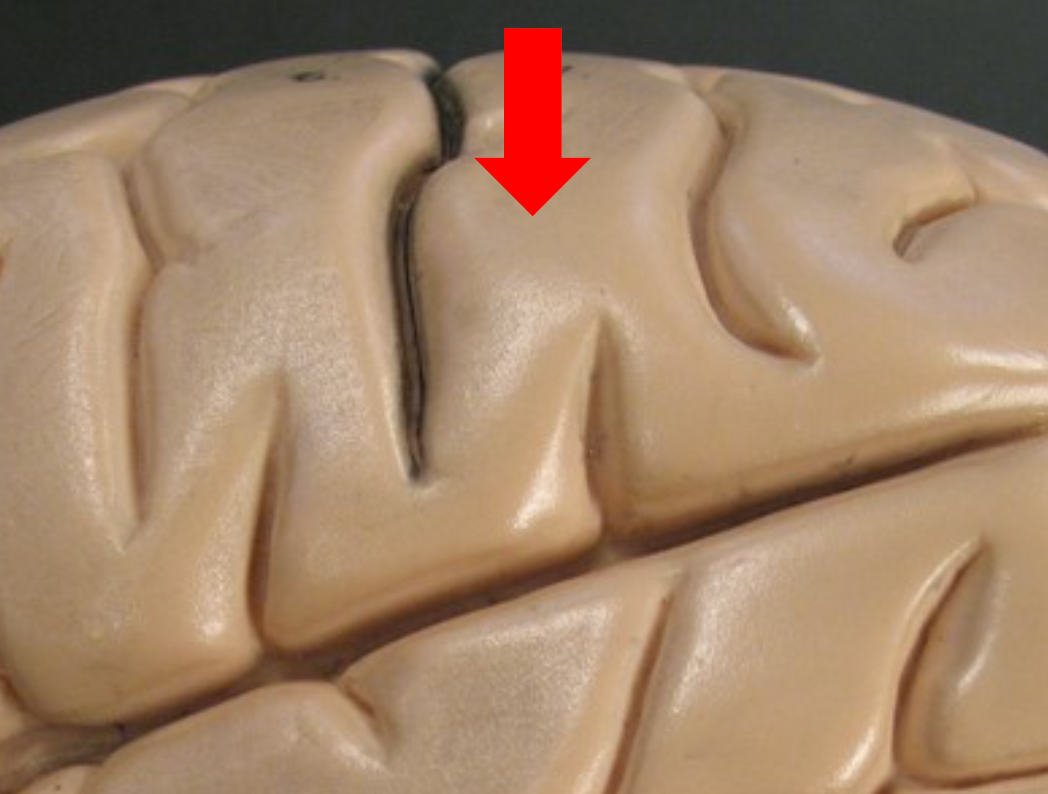
Temporal Lobe
Found inferior to the parietal lobe; processes auditory and olfactory sensations.
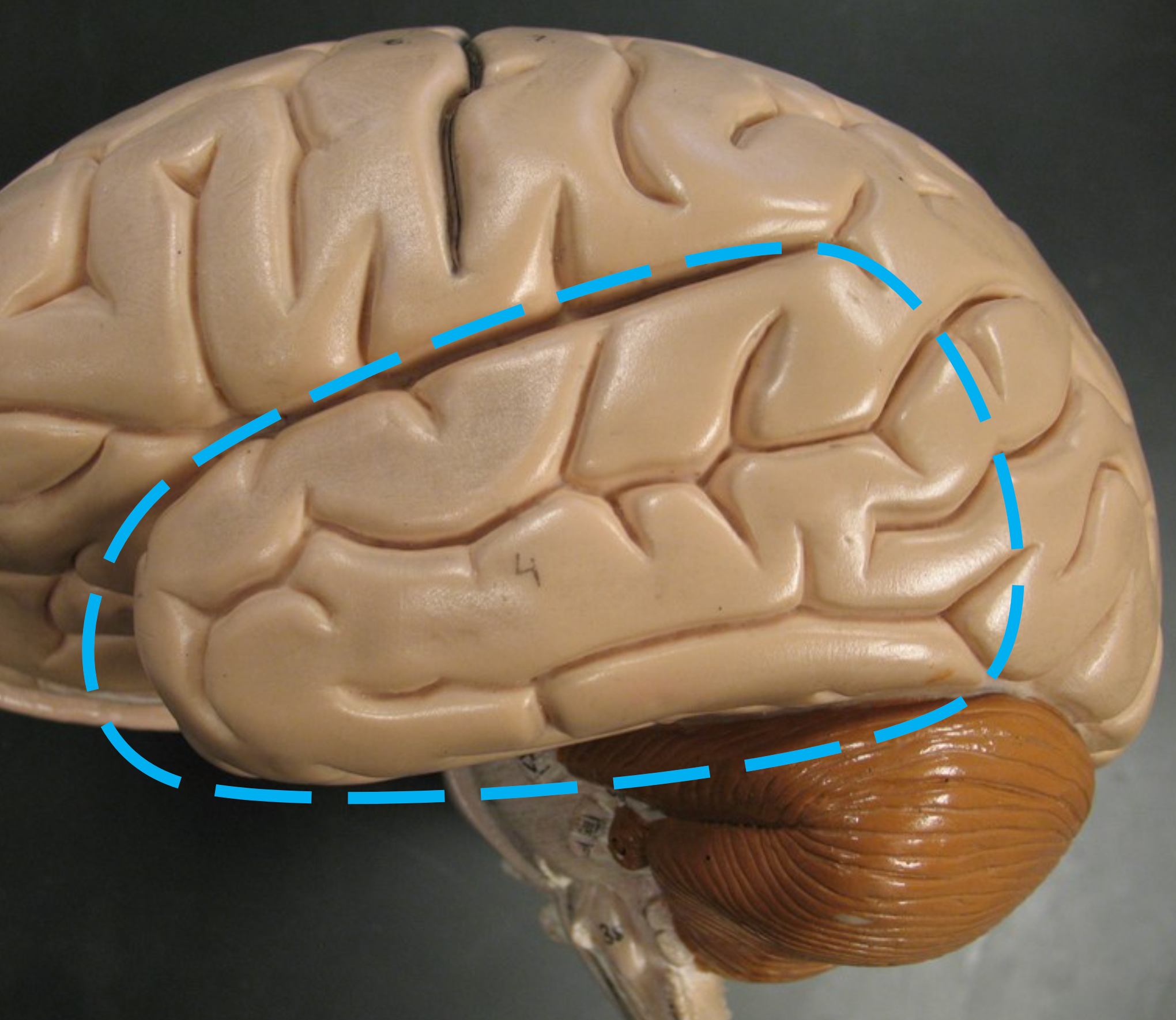
Lateral Sulcus
Separates the temporal lobe from the parietal lobe.
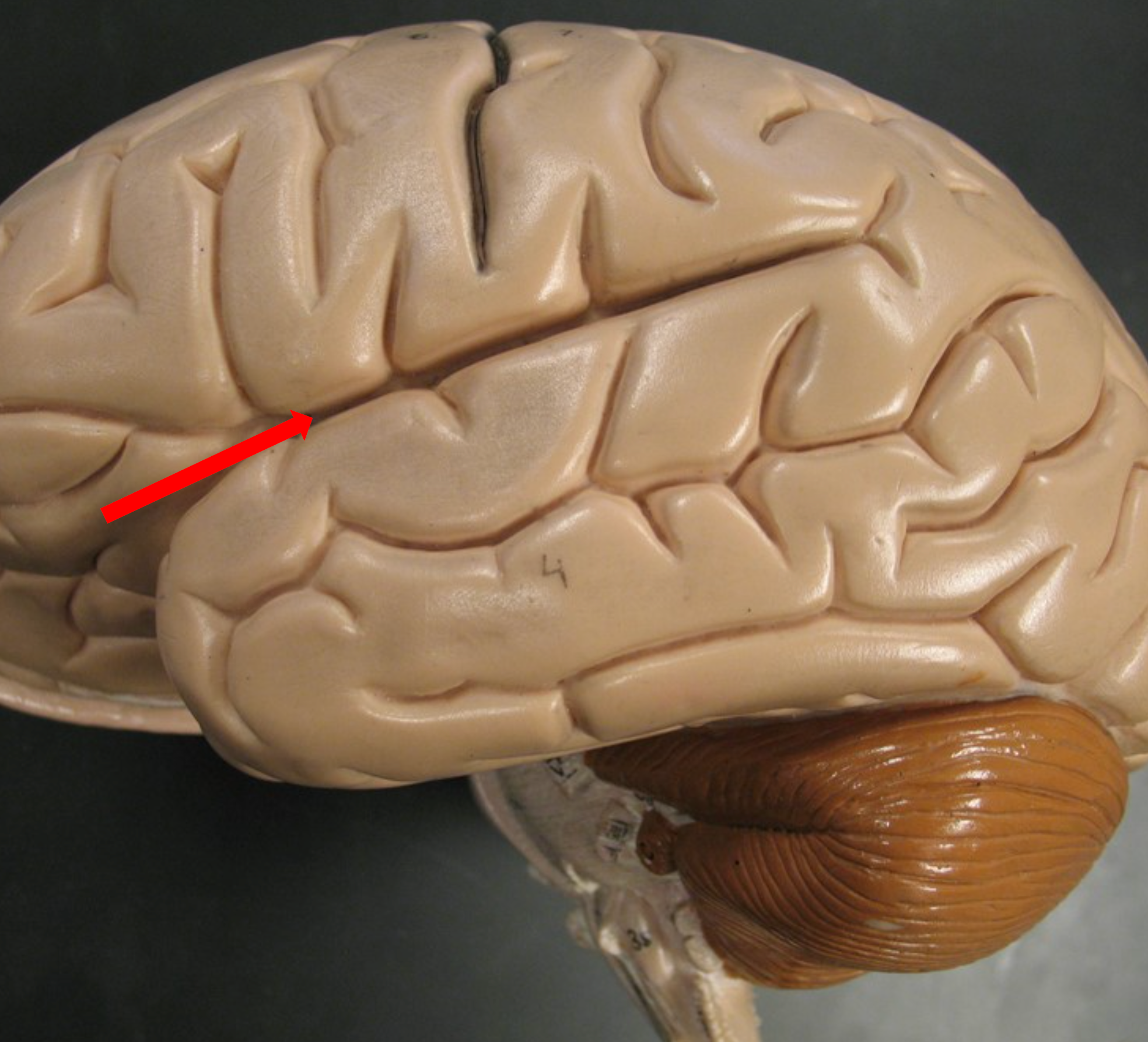
Occipital Lobe
Posterior lobe of the cortex; processes visual information.
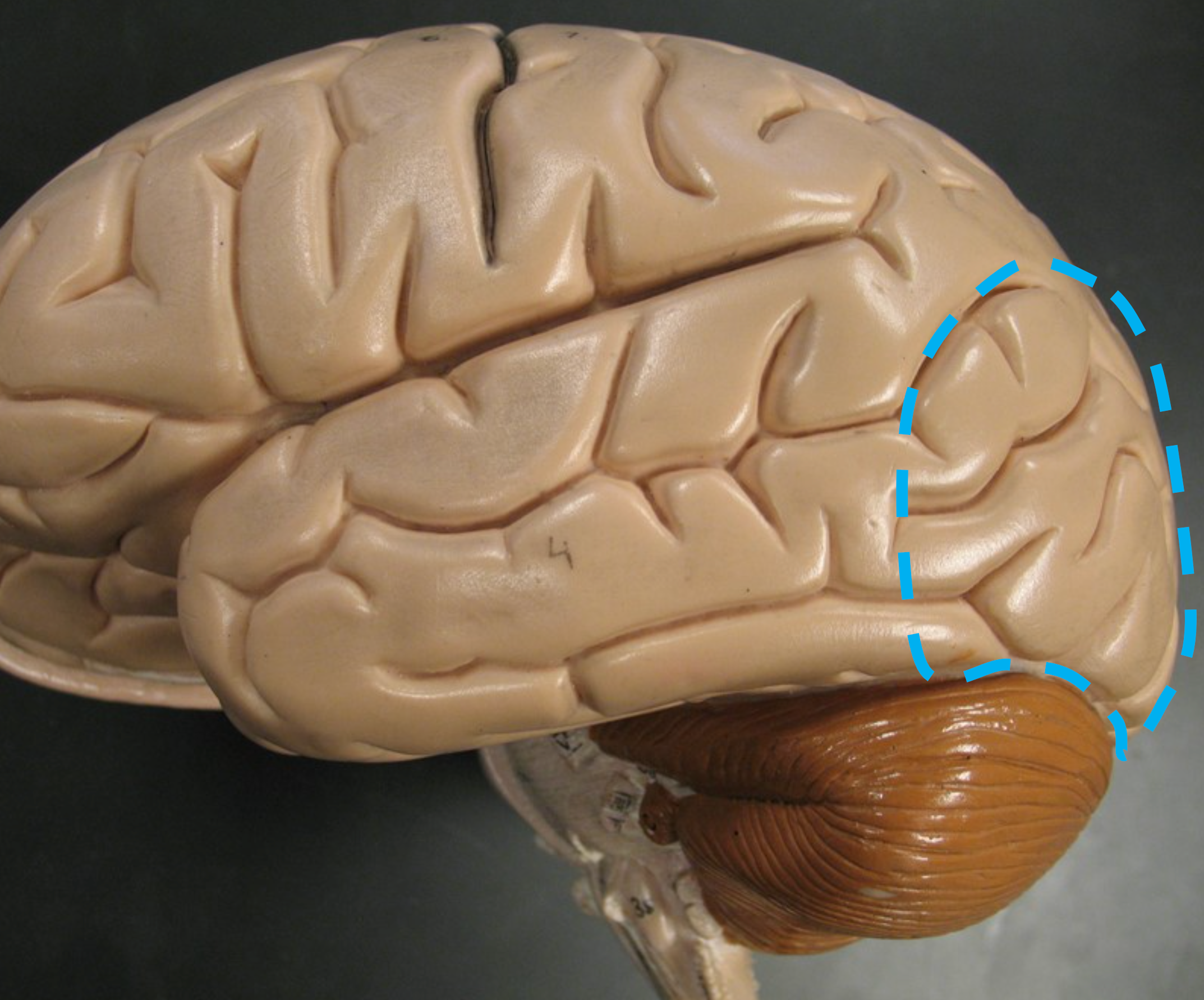
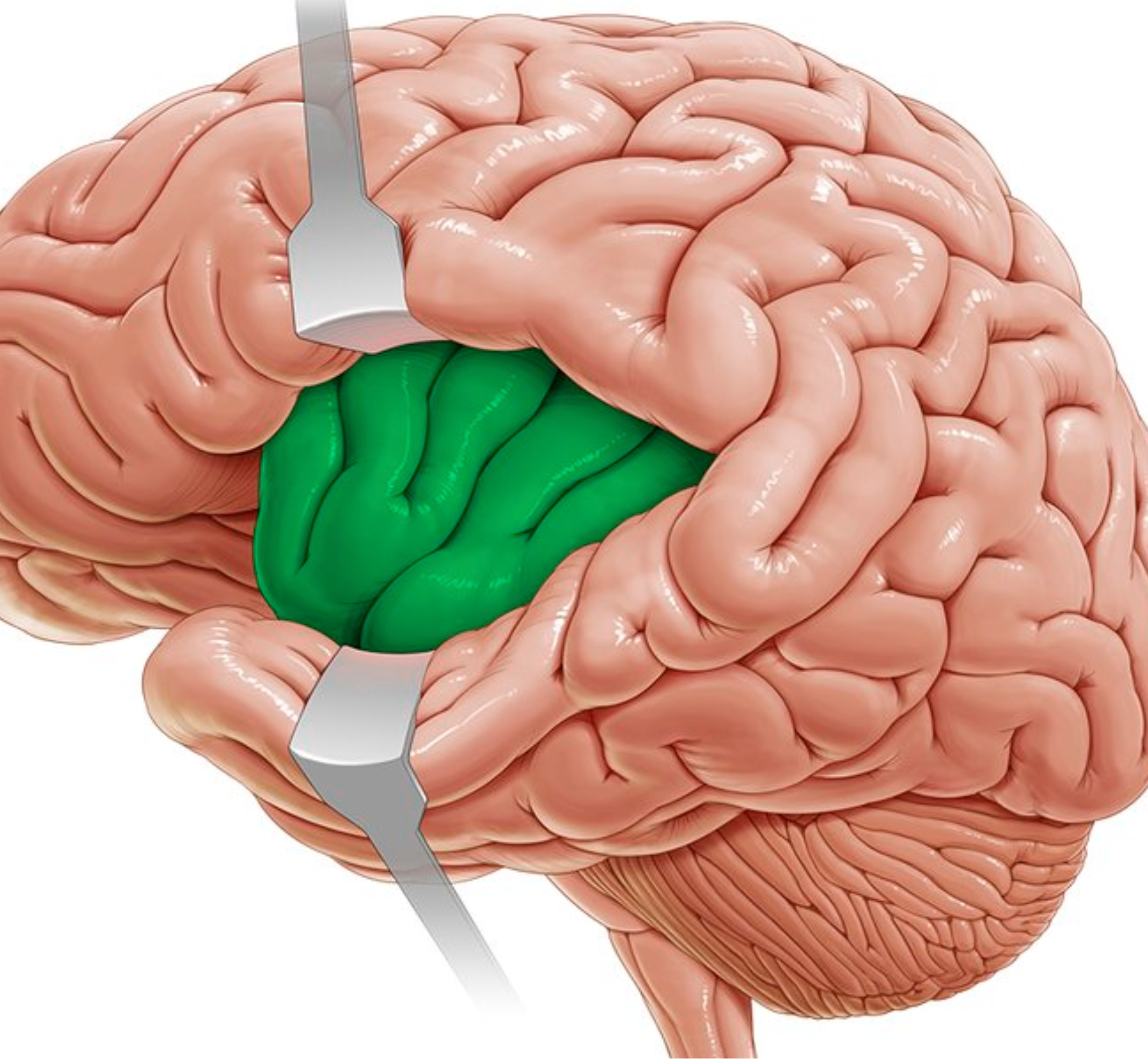
Insula
Deep lobe beneath the lateral sulcus; associated with taste perception.
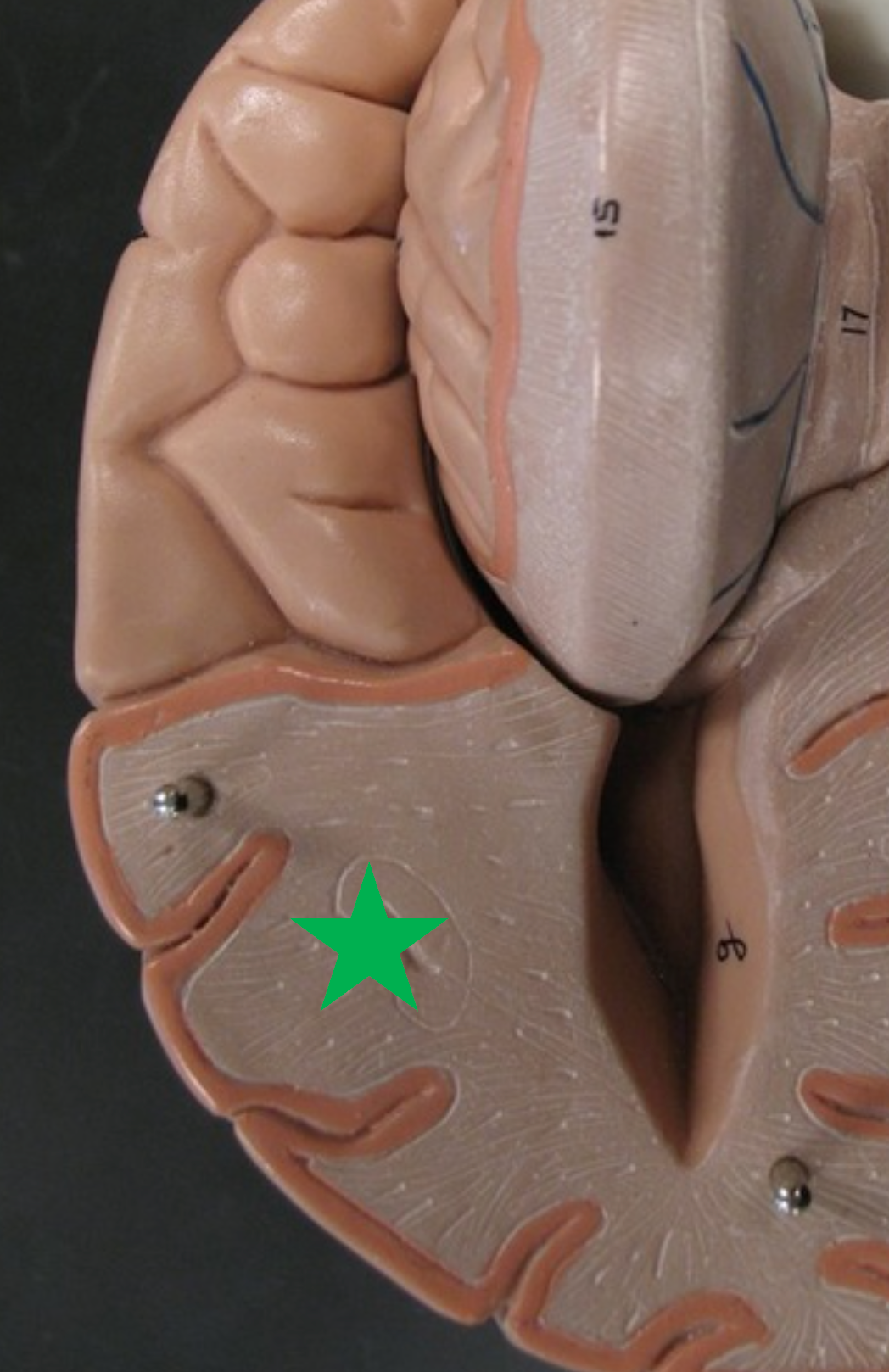
Cerebral White Matter
Tracts of myelinated axons beneath the cortex that connect cortical neurons to each other and to lower CNS areas.
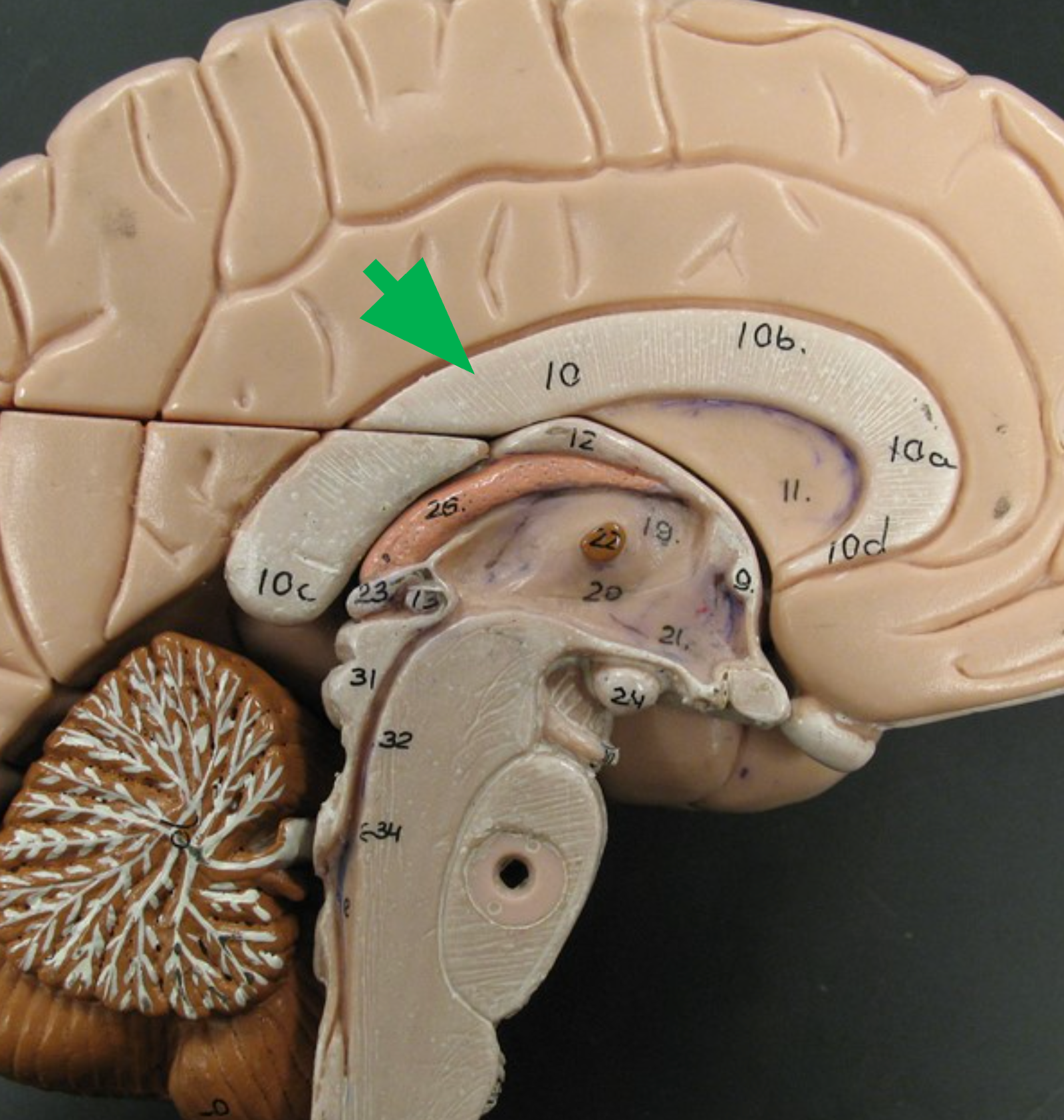
Corpus Callosum
C-shaped white matter structure connecting the left and right cerebral hemispheres.
Choroid Plexus
Network of capillaries that is the site of CSF production; each ventricle has one.
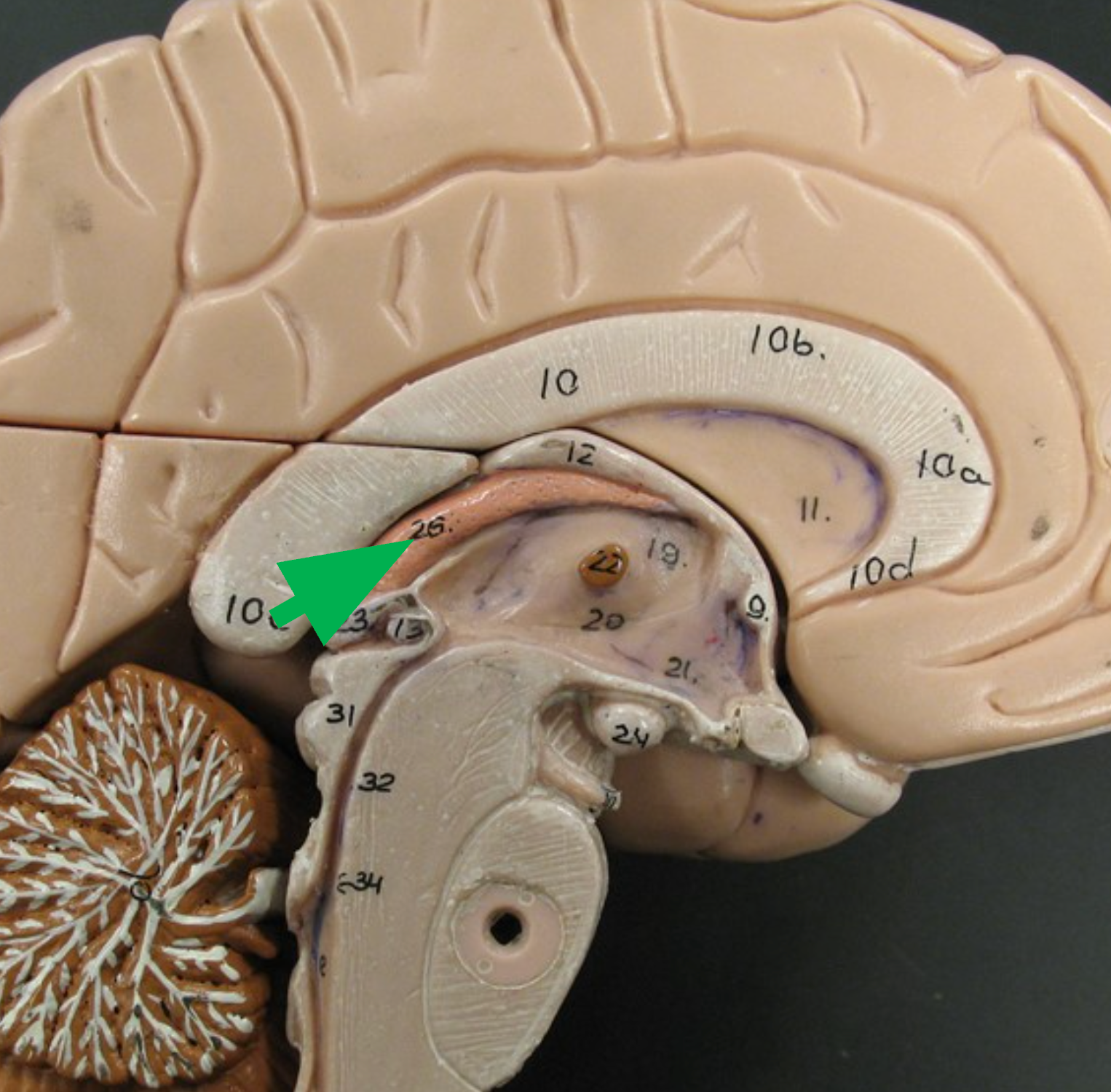
Fornix
White matter structure inferior to the corpus callosum that connects parts of the cerebrum with the diencephalon.
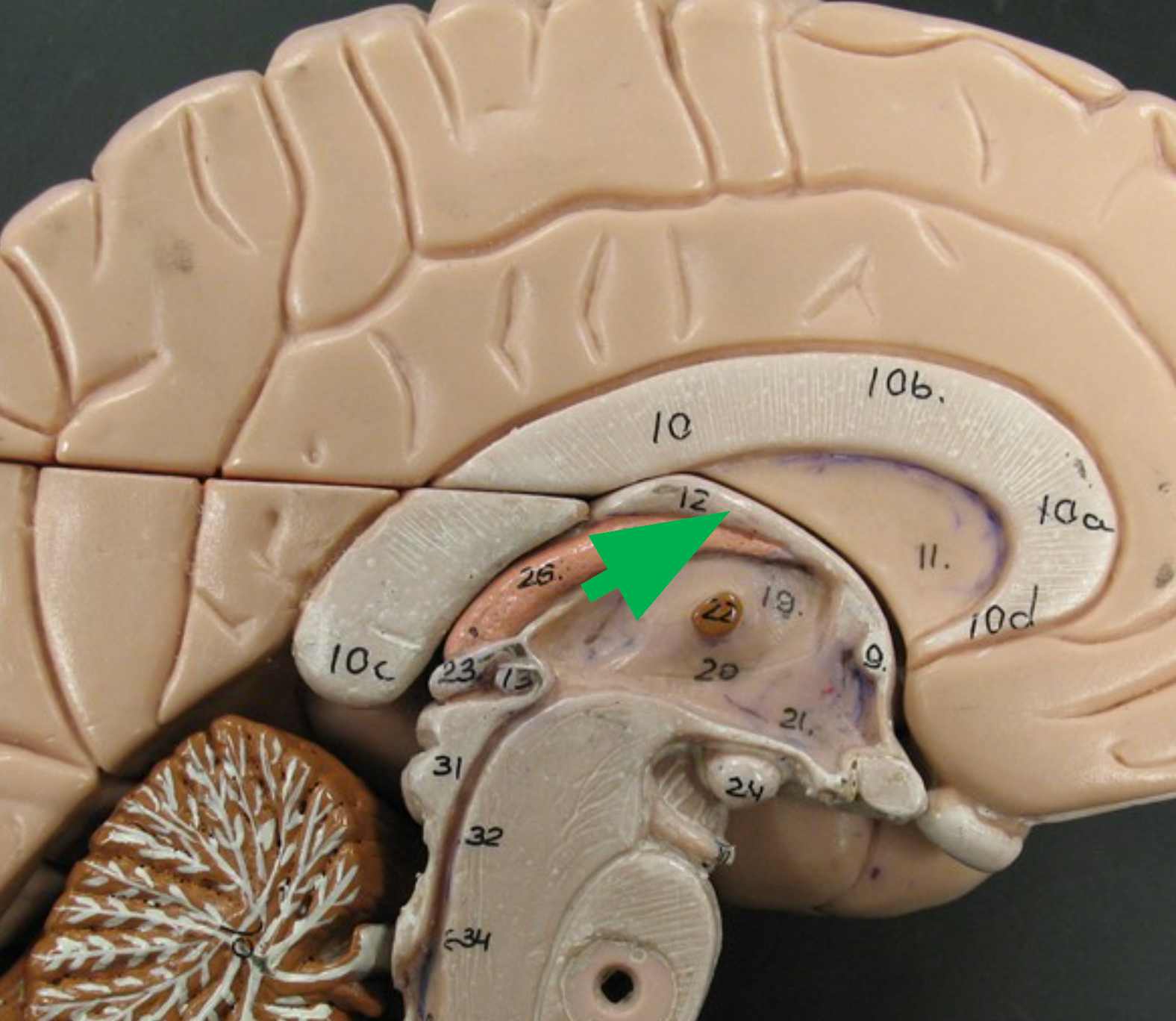
Septum Pellucidum
Thin membrane between the corpus callosum and fornix; separates the two lateral ventricles.
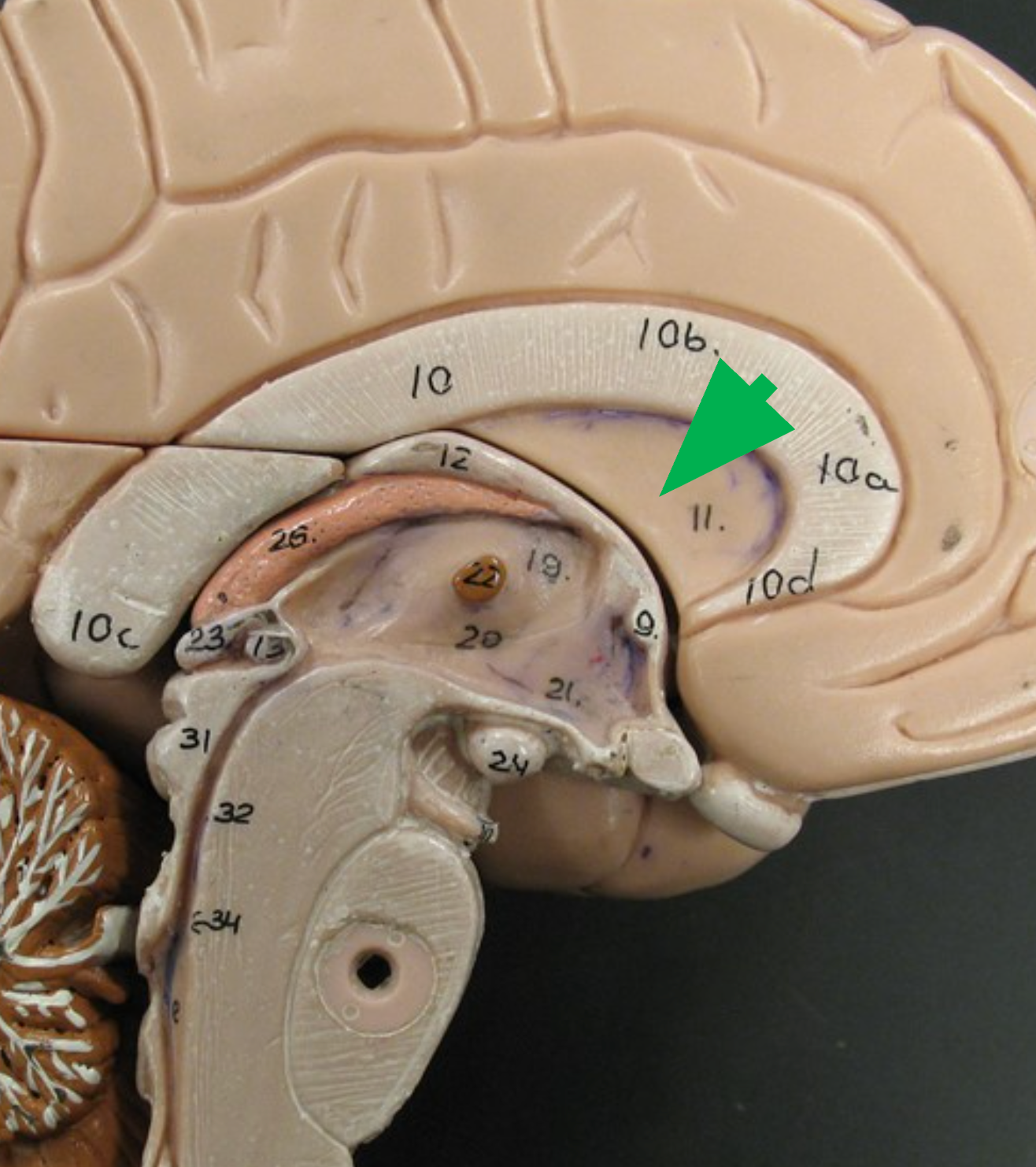
Ventricles
Cavities within the brain filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
Lateral Ventricles
The cavities within the cerebrum on the left and right hemisphere filled with cerebrospinal fluid.
FIssure
Which is more prominent a sulcus or fissure
The central sulcus
What visible structure separates the frontal lobe from the parietal lobe
Frontal lobe: movements for speech, Parietal lobe: process somatosensory information, Temporal bone - auditory sensations, Occipital bone: process visual information, Insula: Perception of taste.
List the five lobes of the cerebral cortex and state at least one function associated with each lobe
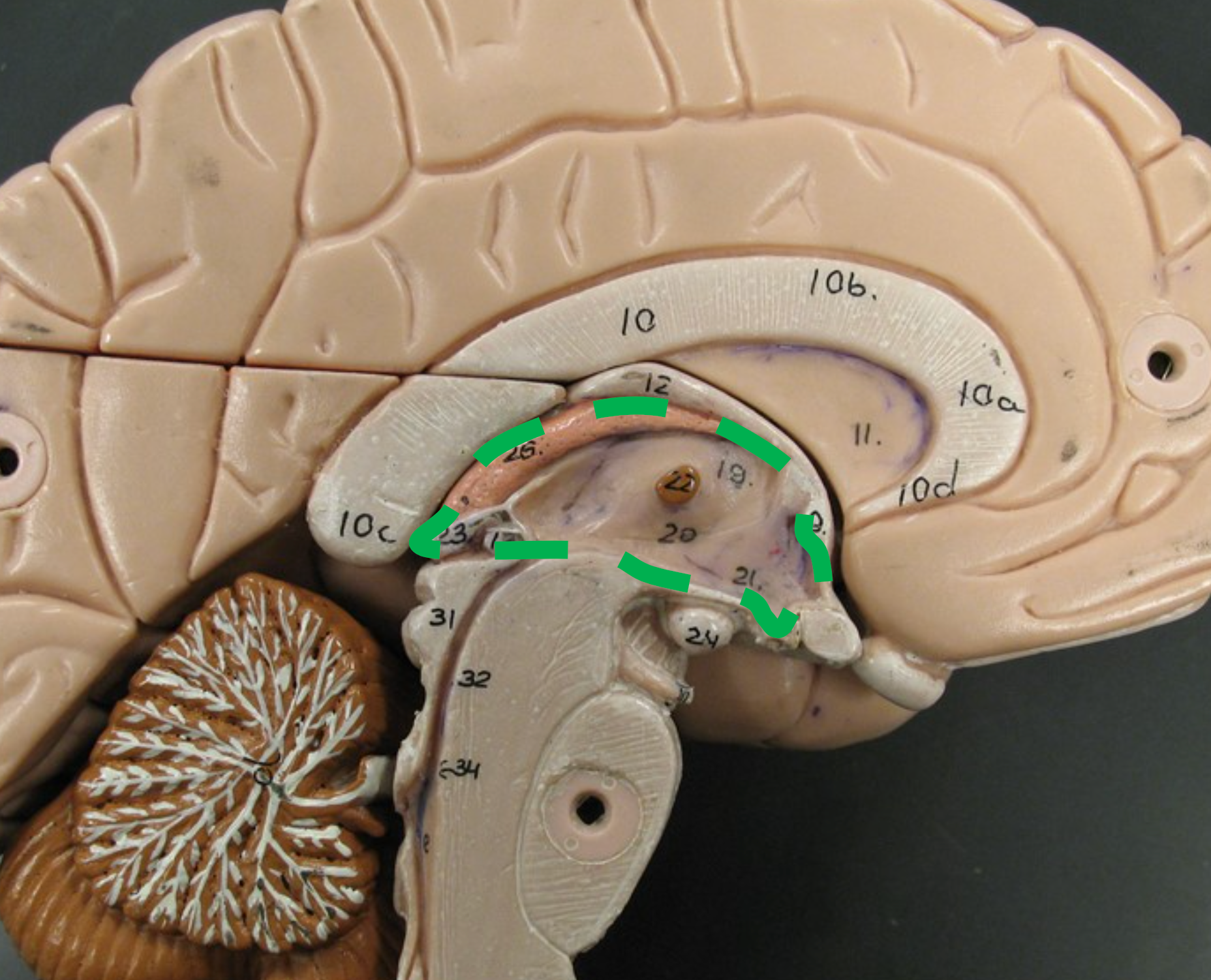
Diencephalon
Brain region located deep to the cerebrum and above the brainstem; includes the thalamus and hypothalamus.
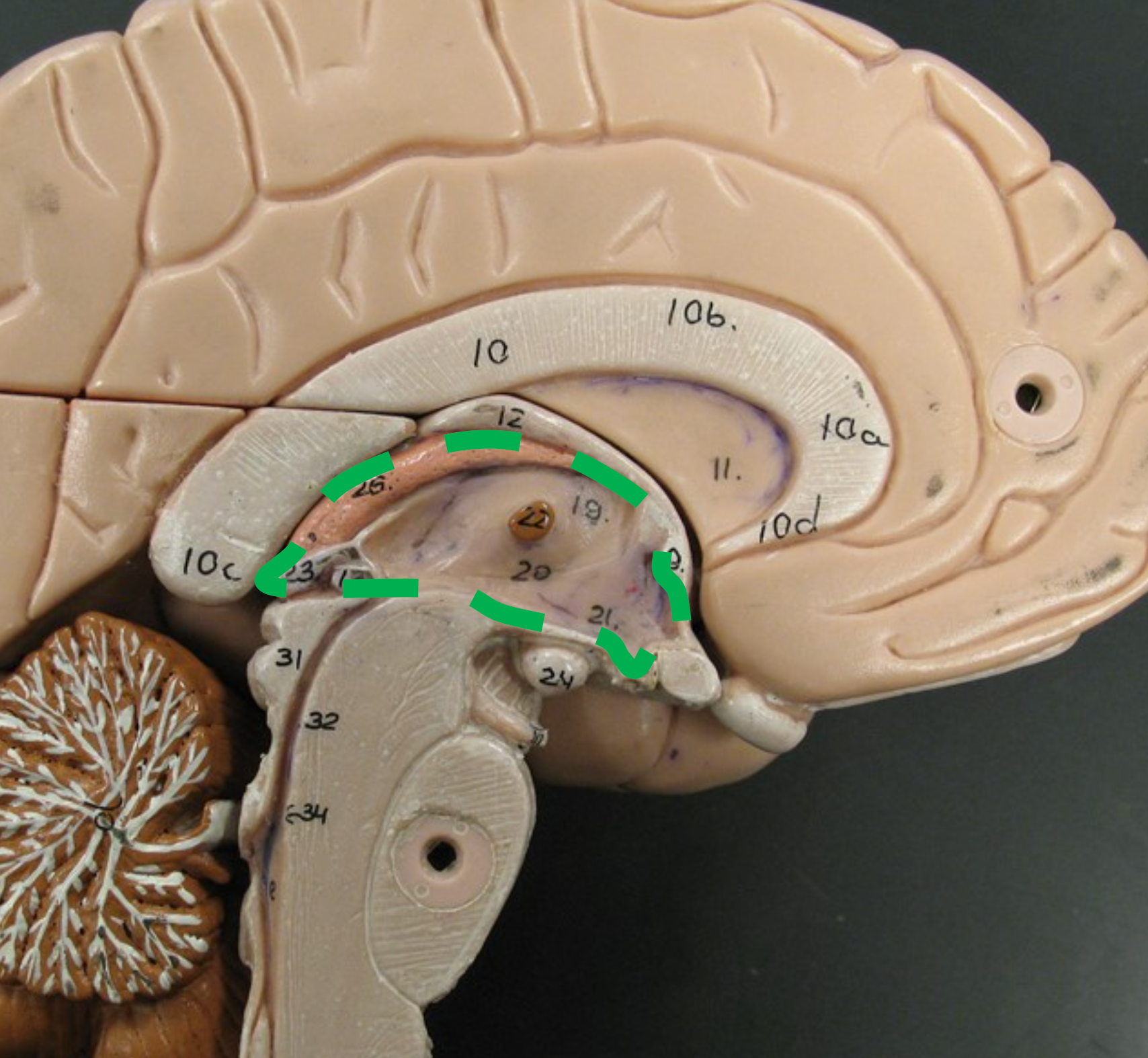
Thalamus
Paired, egg-shaped structures inferior to the fornix; filters and relays sensory input (except smell) to the cerebral cortex.
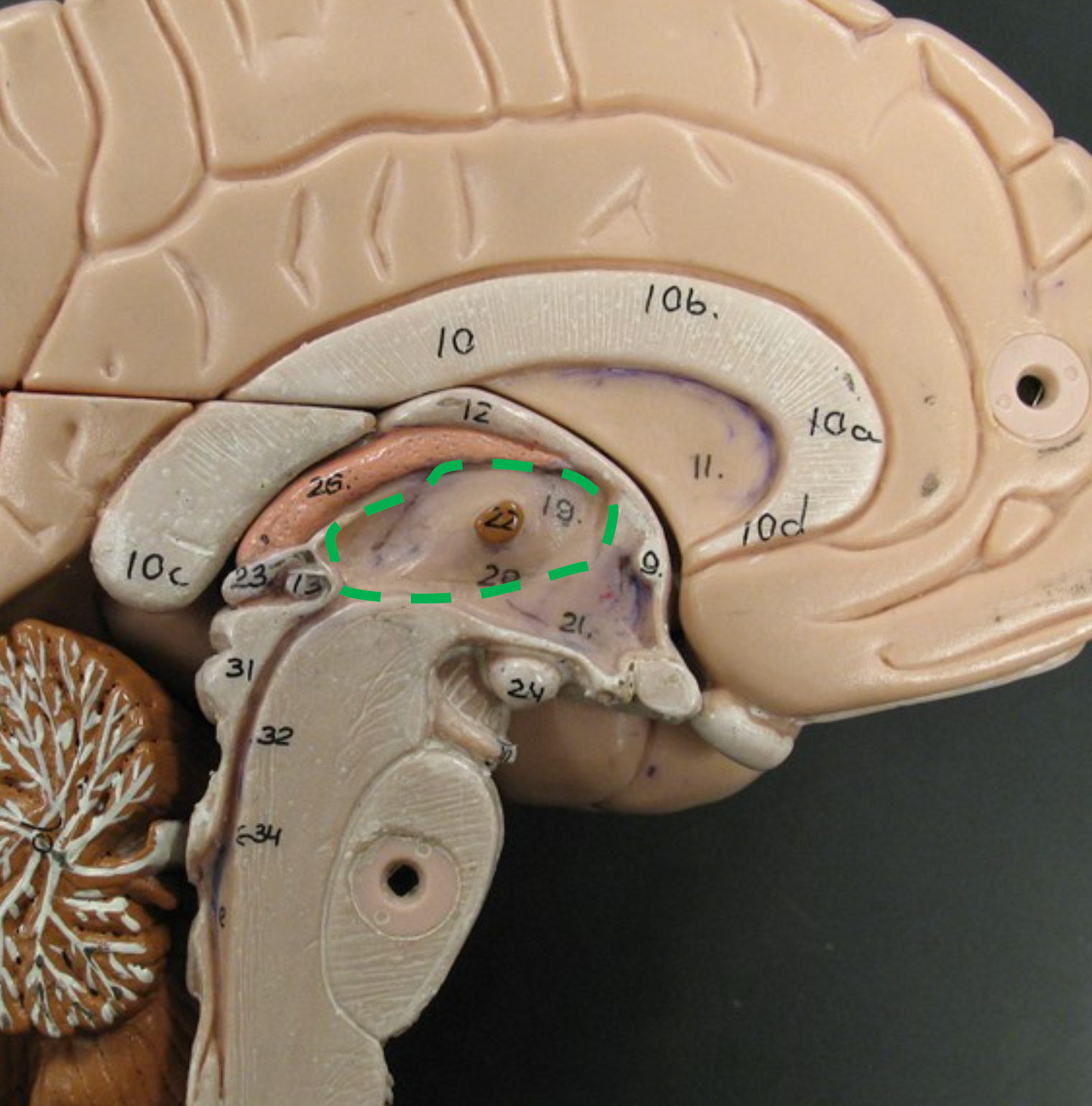
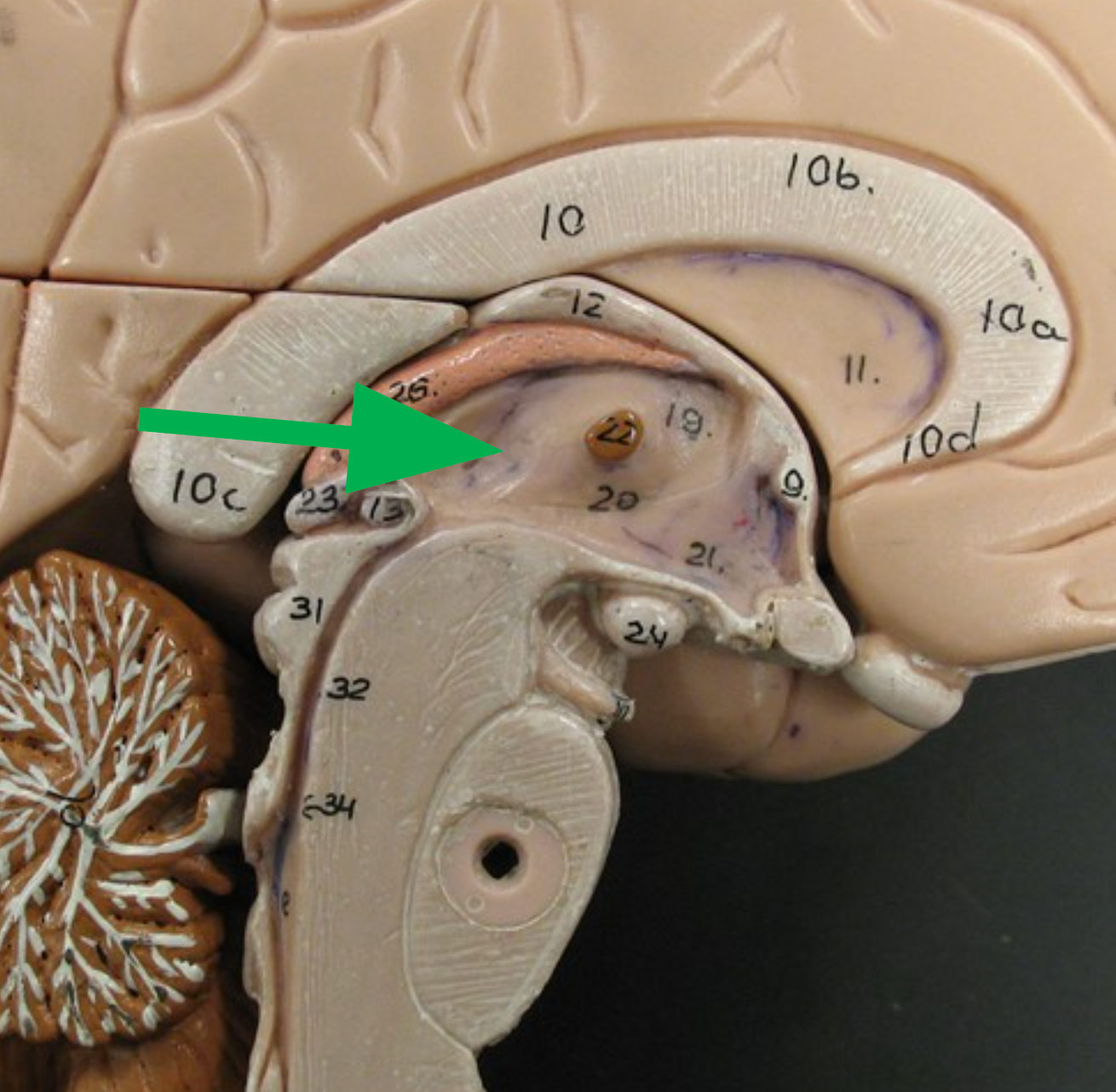
Interthalamic Adhesion
Connects the two halves of the thalamus.
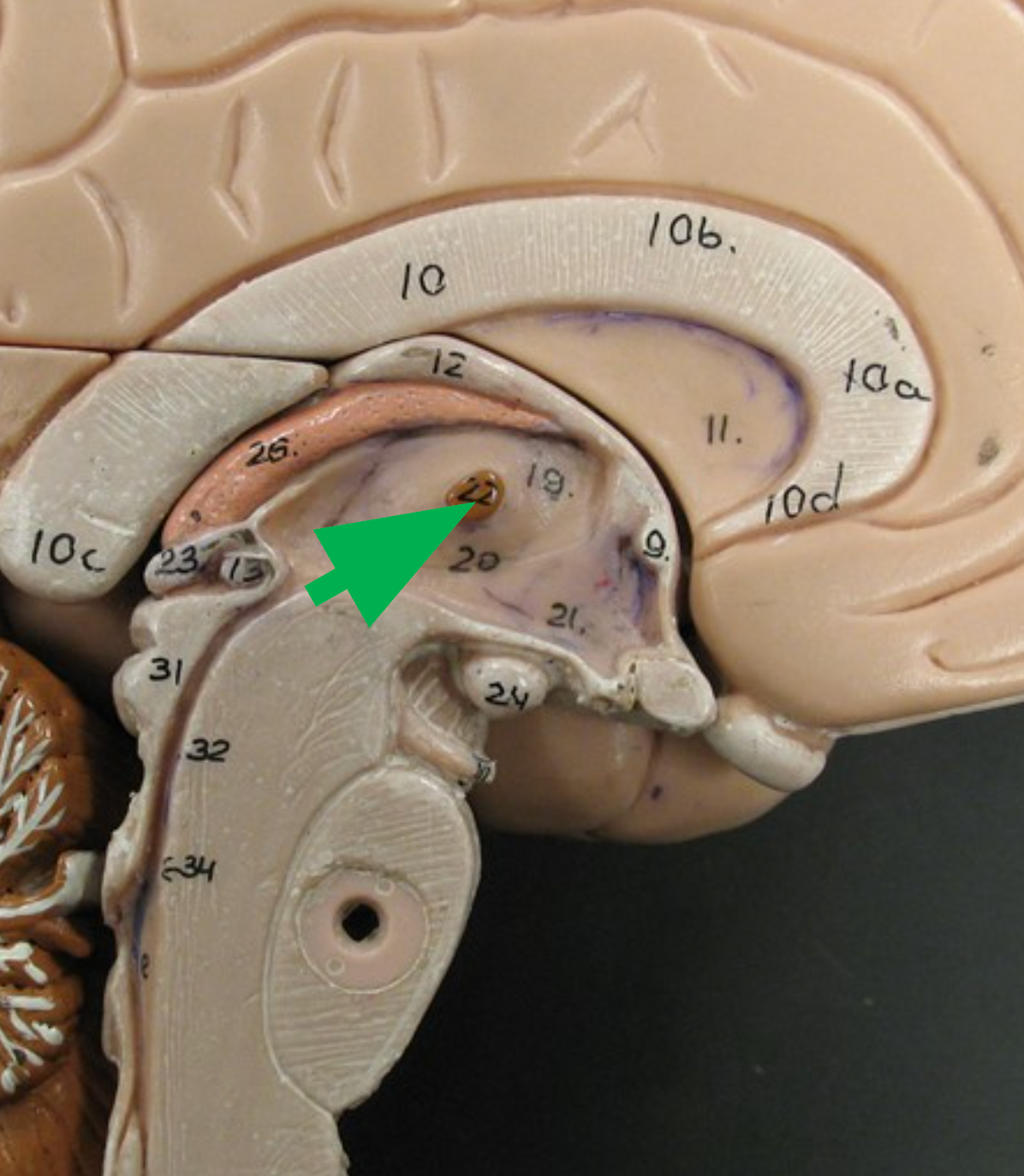
Hypothalamus
Brain structure located inferior to the thalamus; responsible for regulating homeostasis and filtering incoming olfactory information.
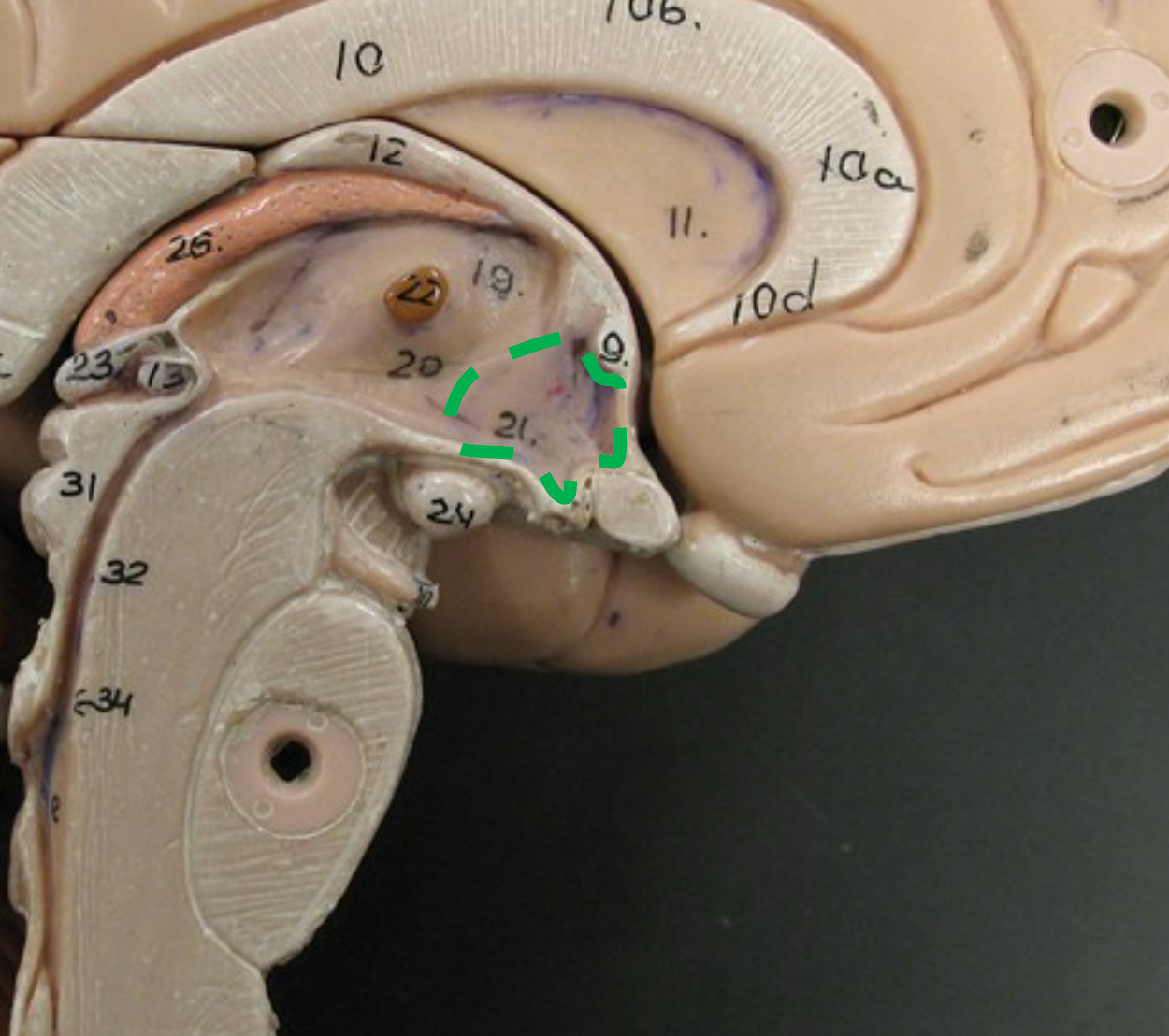
Optic Chiasm
Important point in the pathway for visual signals from the eye to the brain
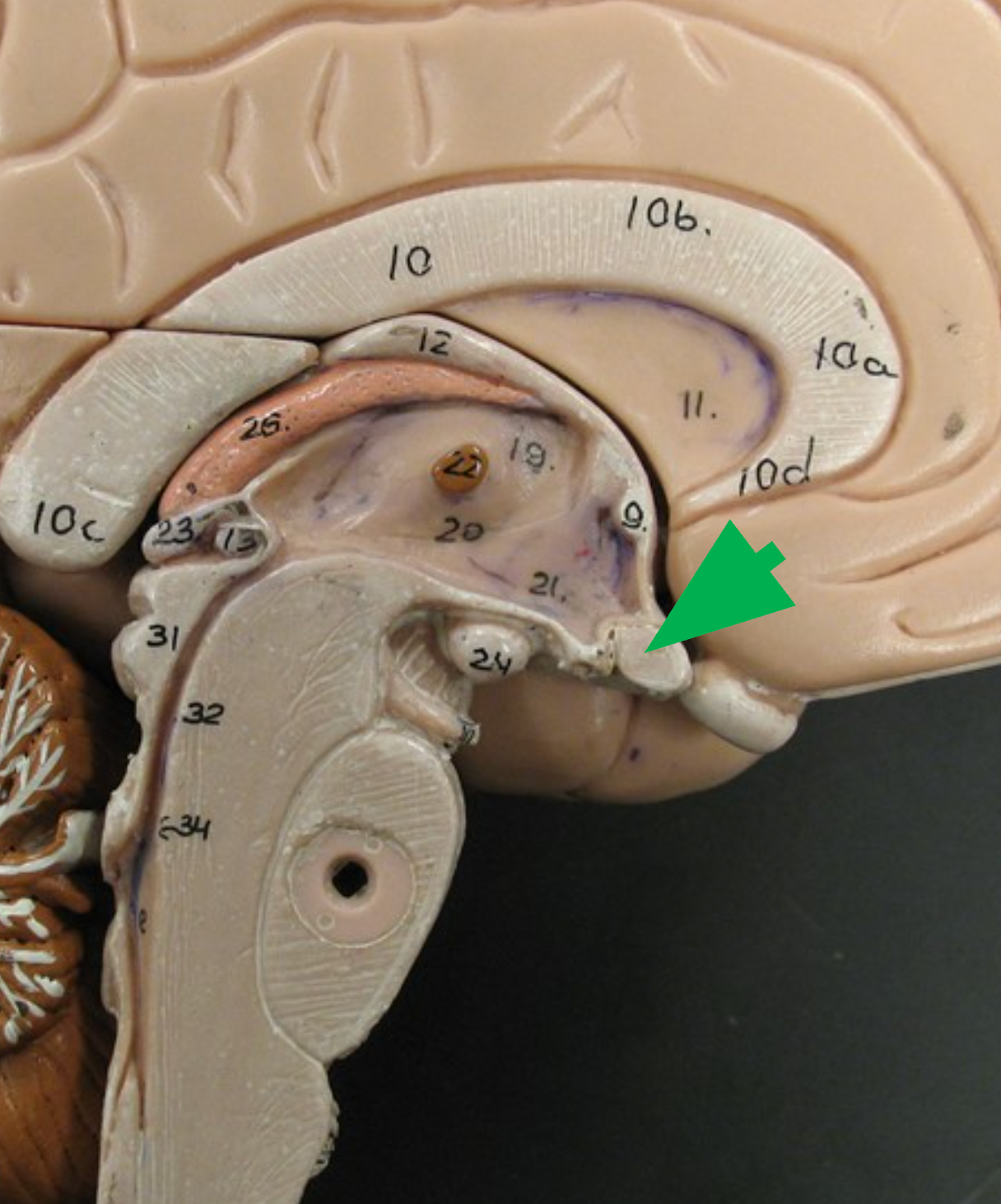
Optic nerve
Bundle of nerve fibers that transmits visual information from the retina to the Brian.
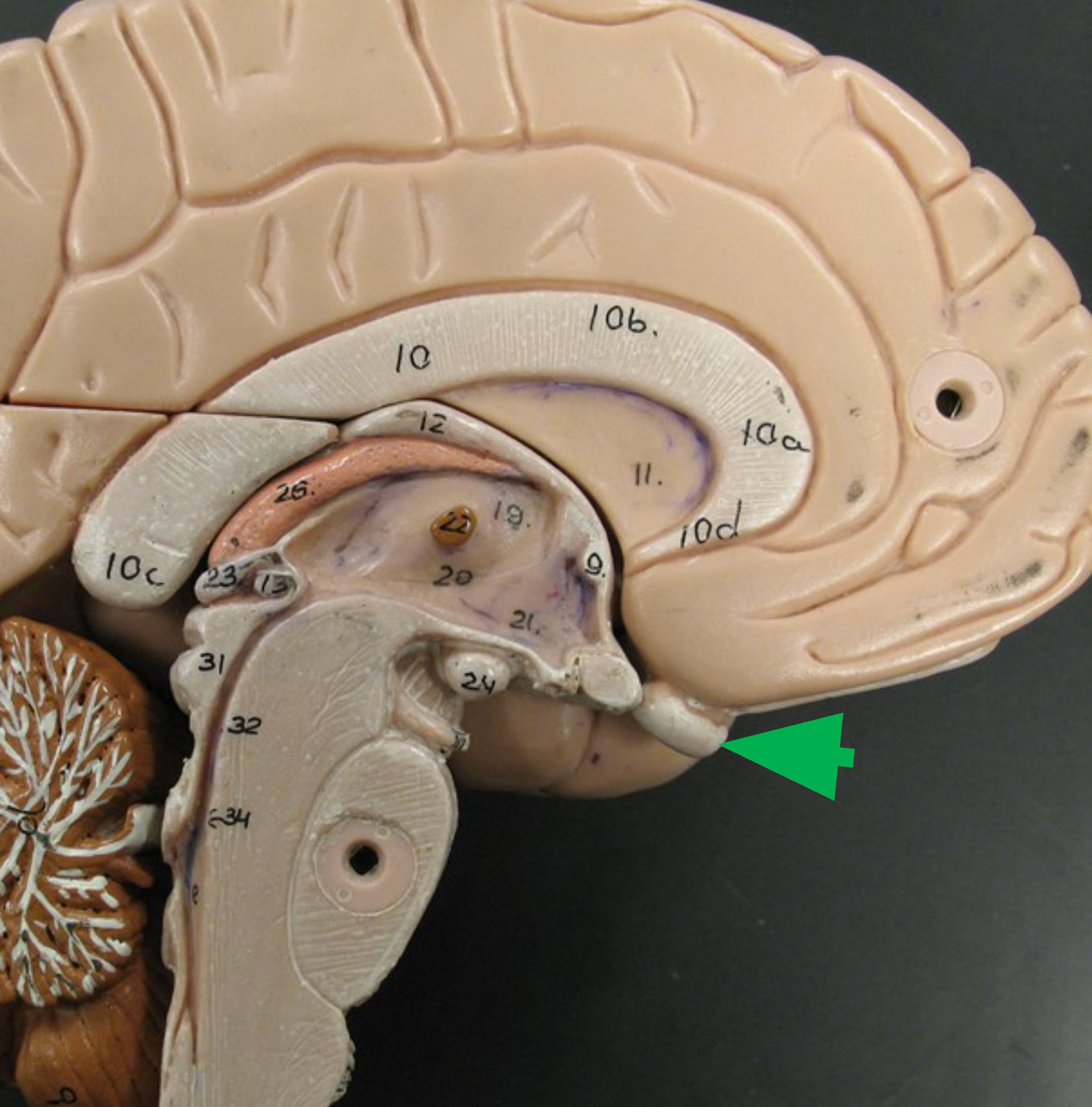
Mammillary Bodies
Small, round projections on the underside of the hypothalamus; potentially involved in memory and olfactory processing.
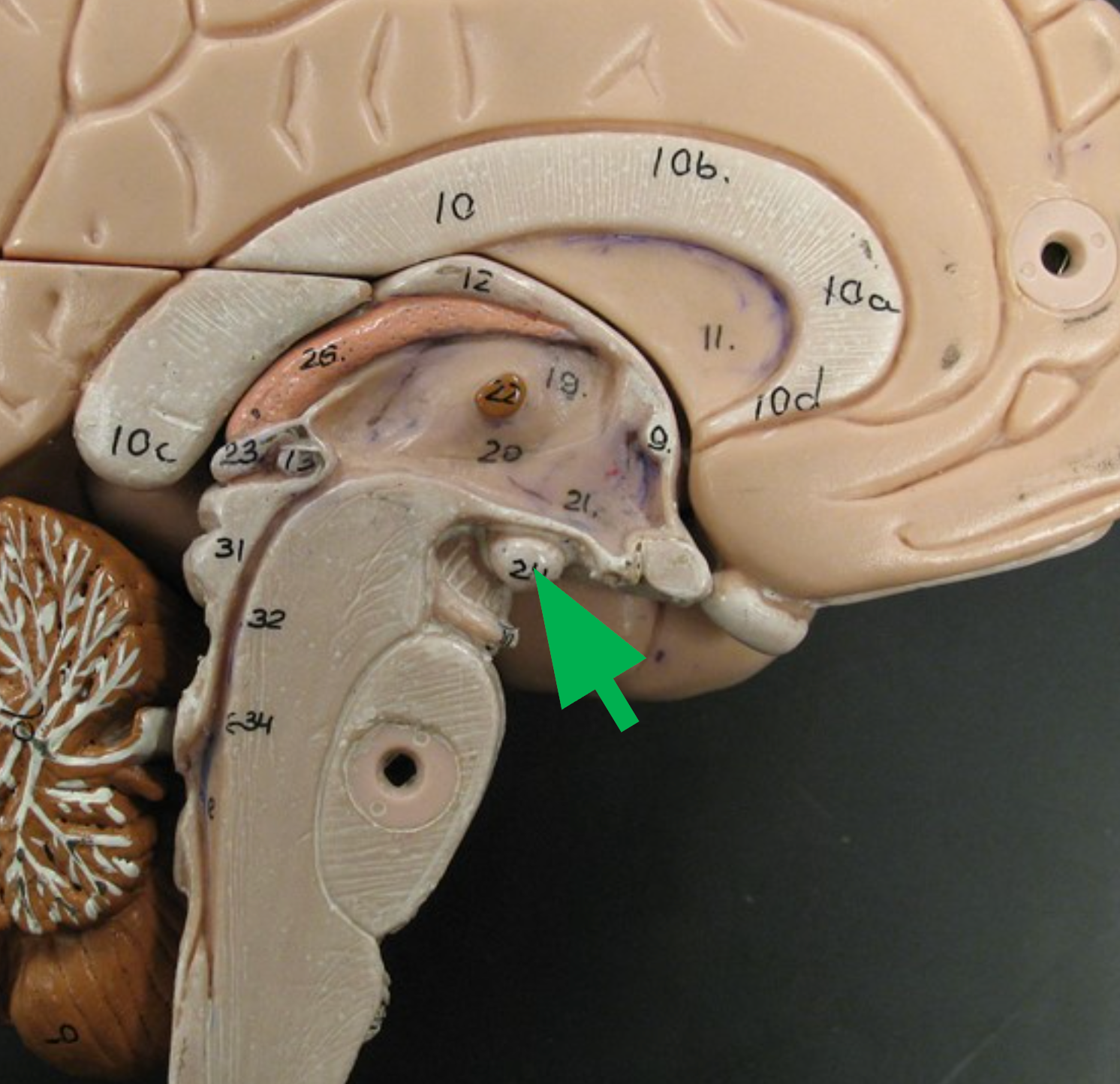
Pituitary Gland
Endocrine gland attached to the hypothalamus via the infundibulum; secretes hormones such as growth hormone, FSH, and TSH. (red arrow)
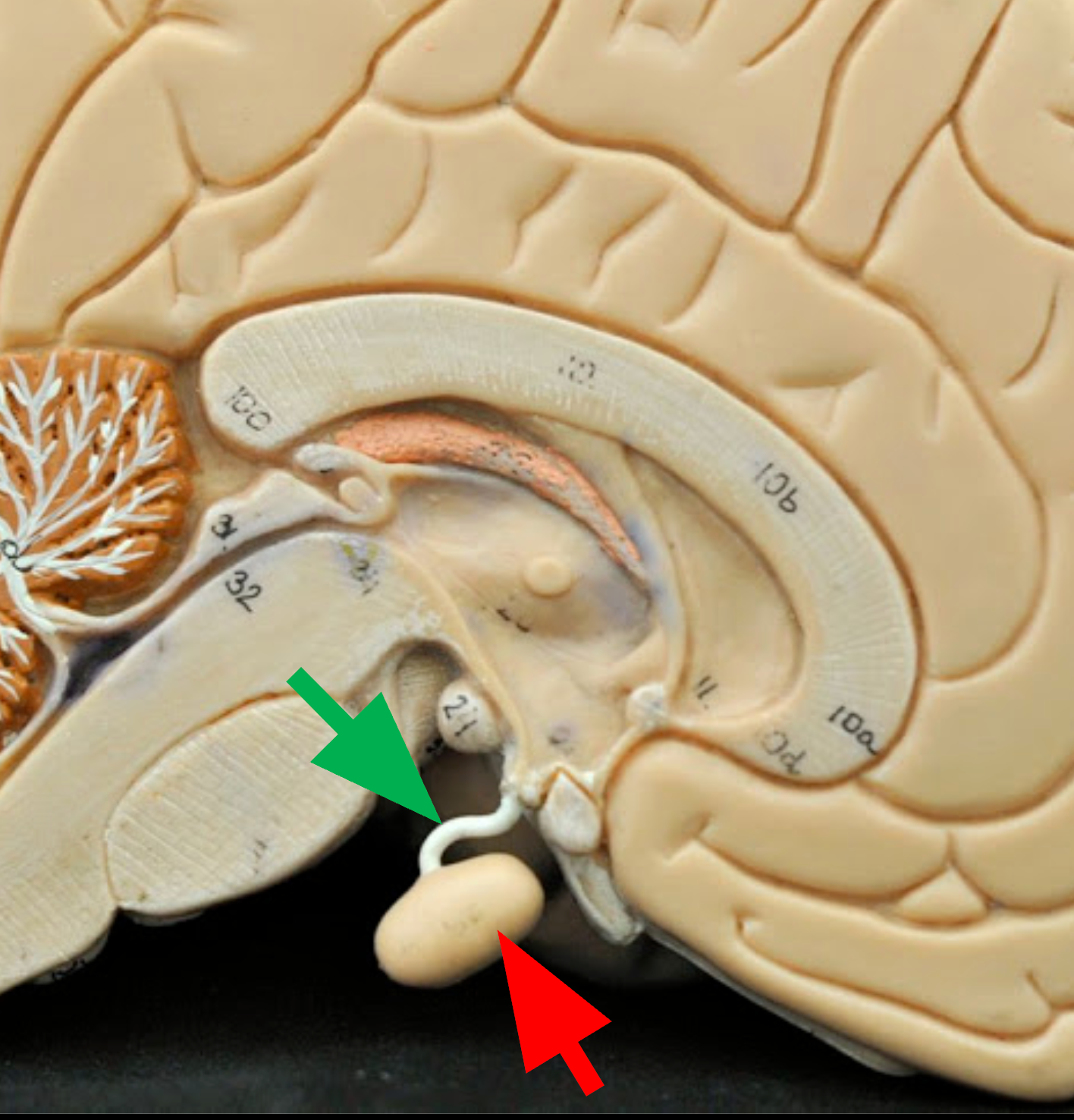
Infundibulum
Thin stalk that connects the pituitary gland to the hypothalamus. (green arrow)
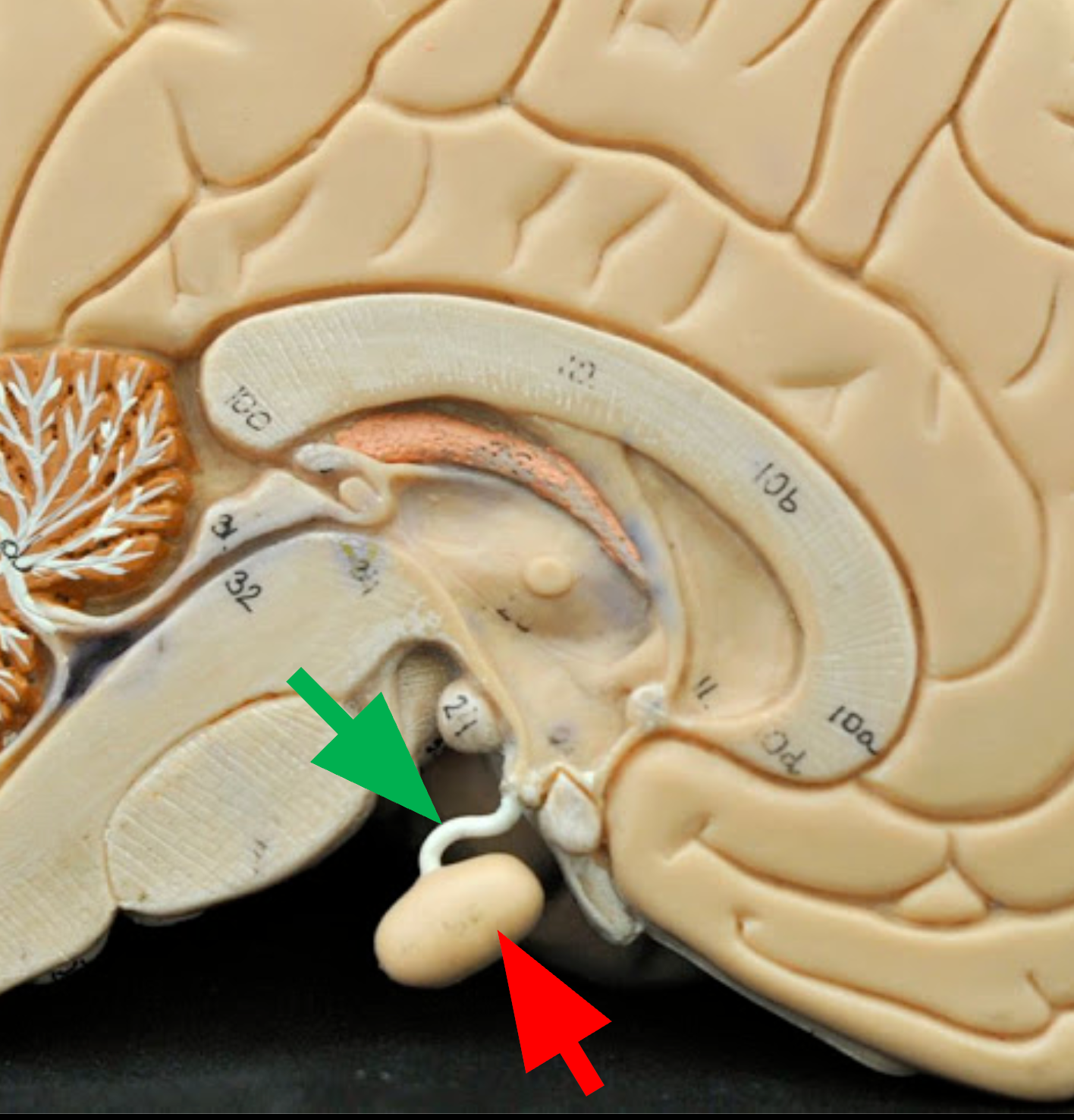
Third Ventricle
Narrow cavity located between the right and left sides of the diencephalon; filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
Hormone release, Blood pressure, heart rate, memory, body temperature regulation
List five functions of the Hypothalamus:
The two lateral ventricles in the cerebrum
What are the first and second ventricles, and where are they?