Cardiothoracic Surgery
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/62
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
1
New cards
procedure recommended for 50 year old with aortic stenosis
open heart surgery (NOT TAVR)- too young for TAVR
2
New cards
Indications for CABG
-Greater than 50% blockage in left main artery
-Other vessels > 70% or 50-70% proximal or mid lesion with a positive fractional flow reserve (less than 0.8)
-Two vessel disease involving LAD and RCA or Vx in patients with DM or a large area of myocardium supplied by diseased vessels
-Multivessel disease
-Other vessels > 70% or 50-70% proximal or mid lesion with a positive fractional flow reserve (less than 0.8)
-Two vessel disease involving LAD and RCA or Vx in patients with DM or a large area of myocardium supplied by diseased vessels
-Multivessel disease
3
New cards
Indications for surgery for aortic stenosis
Severe symptomatic
Symptomatic critical aortic stenosis
Aysmptomatic AS with decreased EF
Symptomatic critical aortic stenosis
Aysmptomatic AS with decreased EF
4
New cards
Aortic stenosis diagnosed with....
echocardiogram
5
New cards
MC cause of mitral stenosis
rheumatic fever
6
New cards
Indications for mitral stenosis surgery
Severe symptomatic MS despite optimal medical therapy
Asymptomatic with severe pulmonary HTN
Asymptomatic with decreased LVEF
New onset of Afib (progressive dilation of LA)
Asymptomatic with severe pulmonary HTN
Asymptomatic with decreased LVEF
New onset of Afib (progressive dilation of LA)
7
New cards
Acute mitral regurgitation can occur _____ and can cause
after MI with rupture of papillary muscle or chordae teninae
Causes cardiogenic shock and acute pulmonary edema due to increased LA pressure (body didn't have time to compensste- chronic regurg has normal pressures)
Causes cardiogenic shock and acute pulmonary edema due to increased LA pressure (body didn't have time to compensste- chronic regurg has normal pressures)
8
New cards
Main cause of tricuspid regurgitation
Endocarditis (S. aureus)
9
New cards
Gold standard test for endocarditis
echocardiogram
10
New cards
Indications for surgery- endocarditis
s/s of heart failure
Persistent bacteremia with appropriate antibiotic therapy for 5-7 days
Fungal infection
Recurrent emboli
Large mobile vegetation > 10 mm
Valvular disease
Heart block
Persistent bacteremia with appropriate antibiotic therapy for 5-7 days
Fungal infection
Recurrent emboli
Large mobile vegetation > 10 mm
Valvular disease
Heart block
11
New cards
Meds to treat symptomatic ventricular septa defect
Lasix and digoxin
12
New cards
S/S of VSD
Can be asymptomatic
Bluish color lips, nails, skin
Failure to thrive, trouble feeding
SOB
Fatigue
LE edema
Bluish color lips, nails, skin
Failure to thrive, trouble feeding
SOB
Fatigue
LE edema
13
New cards
Type A aortic dissection tx
Open heart surgery
14
New cards
De Bakey Type 1
originates in the ascending aorta ,elongates to the arch and possibly the descending
15
New cards
De Bakey type II
Originates in and is confined to the ascending aorta
16
New cards
De Bakey type III
Originates in the descending aorta and extends distally down the aorta or, rarely, retrograde into the aortic arch and ascending aorta
17
New cards
Stanford type A aortic dissection
All dissections involving ascending aorta, regardless of the site of origin
18
New cards
Stanford Type B aortic dissection
All dissections NOT involving ascending aorta
19
New cards
Type B uncomplicated aortic dissection tx
Medical therapy
20
New cards
Sternal precautions required for ____ post op
6-8
21
New cards
Indications for carotid endarterectomy (CEA)
•Symptomatic patients with TIA or minor CVA with 70-99% stenosis and no ipsilateral endarterectomy
•Symptomatic patients with 50-69% stenosis
•Asymptomatic patients with 60% or greater stenosis
•Symptomatic patients with 50-69% stenosis
•Asymptomatic patients with 60% or greater stenosis
22
New cards
Contraindications for carotid endarterectomy (CEA)
•Asymptomatic complete carotid occlusion- absolute contraindication
•Acute major CVA
•PMH that increases perioperative risk (CAS in these patients)
•Major CVA with minimal recovery
•Significantly altered level of consciousness
•Acute major CVA
•PMH that increases perioperative risk (CAS in these patients)
•Major CVA with minimal recovery
•Significantly altered level of consciousness
23
New cards
Gold standard in diagnosing carotid artery stenosis
Angiogram
24
New cards
S/S of peripheral artery disease
•Initially asymptomatic
•Claudication- LE pain with activity and relieved with rest
•LE pain at rest
•Ulcers
•Skin changes
•The 5 P's (Pulselessness, Paralysis, Paraesthesia, Pain & Pallor)
•Claudication- LE pain with activity and relieved with rest
•LE pain at rest
•Ulcers
•Skin changes
•The 5 P's (Pulselessness, Paralysis, Paraesthesia, Pain & Pallor)
25
New cards
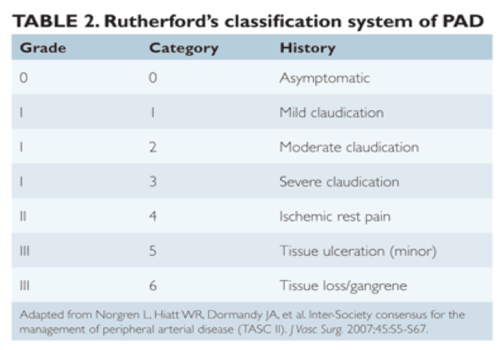
Rutherford's classification of PAD
26
New cards
Treatment of
Conservative management
27
New cards
Treatment of > 5.5 cm and asymptomatic AAA
Elective repair
28
New cards
Symptomatic AAA treatment
Elective repair
29
New cards
second most common cancer
lung cancer
30
New cards
Typical lung cancer is ____ grade
Atypical is ____
Atypical is ____
low grade
intermediate grade
intermediate grade
31
New cards
T/F: lung cancer metastasis is rare and has an excellent prognosis
True
32
New cards
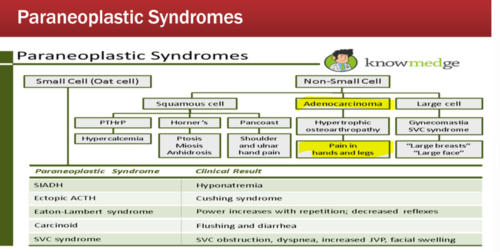
SPHERE pneumonic - complications of lung cancer
Superior vena cava syndrome
Pancoast tumor
Horner syndrome
Effusion
Recurrent laryngeal symptoms
Endocrine
Pancoast tumor
Horner syndrome
Effusion
Recurrent laryngeal symptoms
Endocrine
33
New cards
TNM staging
classifies cancer according to tumor size, node involvement, metastasis
34
New cards
Pneumonectomy
•A surgical procedure in which an entire lung is removed. A pneumonectomy is most often done for cancer of the lung that cannot be treated by removal of a smaller portion of the lung. A pneumonectomy is an open chest technique (thoracotomy).
35
New cards
Lobectomy
Also called a pulmonary lobectomy, it is a common surgical procedure that removes one lobe of the lung that contains cancerous cells. Removal of two lobes is called bilobectomy.
36
New cards
Sleeve lobectomy
•A surgical procedure that removes a cancerous lobe of the lung along with part of the bronchus (air passage) that attaches to it. The remaining lobe(s) is then reconnected to the remaining segment of the bronchus. This procedure preserves part of a lung, and is an alternative to removing the lung as a whole (pneumonectomy).
37
New cards
Wedge resection
A wedge resection is a surgical procedure during which the surgeon removes a small, wedge-shaped portion of the lung containing the cancerous cells along with healthy tissue that surrounds the area. The surgery is performed to remove a small tumor or to diagnose lung cancer. A wedge resection is performed instead of a lobectomy (removing a complete lung lobe) when there is a danger of decreased lung function if too much of the lung is removed. A wedge resection can be performed by minimally-invasive video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS) or a thoracotomy (open chest surgery).
38
New cards
Segment resection
•A segment resection removes a larger portion of the lung lobe than a wedge resection, but does not remove the whole lobe.
39
New cards
Porcelain aorta
Porcelain aorta: extensive calcification of the ascending aorta or aortic arch, can cause issues with aortic cross-clamping or aortotomy
40
New cards
Dental clearance may be needed for CT surgery to avoid...
infective endocarditis
41
New cards
DOC for malignant hyperthermia that may be caused by use of halogenated anesthetics
IV Dantrolene
42
New cards
Malignant hyperthermia
A hereditary condition of uncontrolled heat production that occurs when susceptible people receive certain anesthetic drugs. Release of Calcium
High fever, muscle rigidity
High fever, muscle rigidity
43
New cards
ECMO

44
New cards
What arrhythmia is MC after CT surgery
a fib
45
New cards
Common vessels used for CABG
internal mammary artery
saphenous v
radial a
saphenous v
radial a
46
New cards
Severe aortic stenosis grading: Valve area and aortic velocity
Area:
47
New cards
Lung mass vs nodule
Nodule:
48
New cards
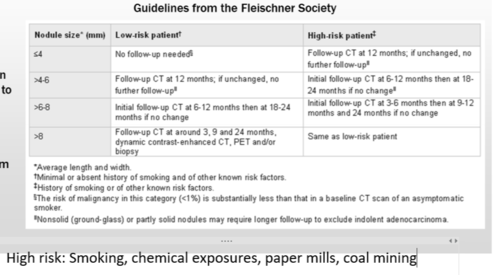
Fleishner Society grading of lung nodules
49
New cards
MC type of lung cancer
Adenocarcinoma (non-small cell)
50
New cards
Stage 1 lung cancer
Tumors only in lung - NOT in lymph nodes yet
51
New cards
Stage 2 lung cancer
In lungs and near the lymph nodes
52
New cards
Stage 3 lung cancer
In lungs and spread to lymph nodes
53
New cards
Stage 4 lung cancer
Spread to lungs, around the lungs and other organs (distant metastasis)
54
New cards
pain in hands and legs is indicative of what type of lung CA?
Adenocarcinoma (NSC)
55
New cards
Horner's syndrome symptoms
ptosis, myosis, anhydrosis
56
New cards
Paraneoplastic syndrome treatment
Supportive/ symptomatic care
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy
57
New cards
paraneoplastic syndrome
medical condition caused by tumor secretions (hormones, cytokines, TNF, Interleukin-1), may cause hypercalcermia, hypoglycemia, SIADH
58
New cards
SVC syndrome s/s
JVD
UE edema
Facial edema
Dyspnea
HA
Dizzy
UE edema
Facial edema
Dyspnea
HA
Dizzy
59
New cards
Pancoast tumor
Occurs in apex of lung and causes horner syndrome
Shoulder and ulnar hand pain
Shoulder and ulnar hand pain
60
New cards
Absolute contraindication to carotid endarterectomy (CEA)
Asymptomatic complete carotid occlusion
61
New cards
ABI - normal, mild to moderate and severe disease
0.91-1.30 --> normal
0.41-0.90 --> mild to moderate PAD
0.00-0.30 --> severe PAD
0.41-0.90 --> mild to moderate PAD
0.00-0.30 --> severe PAD
62
New cards
how to calculate ABI
Right side: Higher right ankle pressure / higher arm pressure
63
New cards
Paraneoplastic syndromes
symptom complexes arising in patients with cancer that cannot be explained by local or distant spread of their tumors