Biology Questions A LEVELS IAL
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
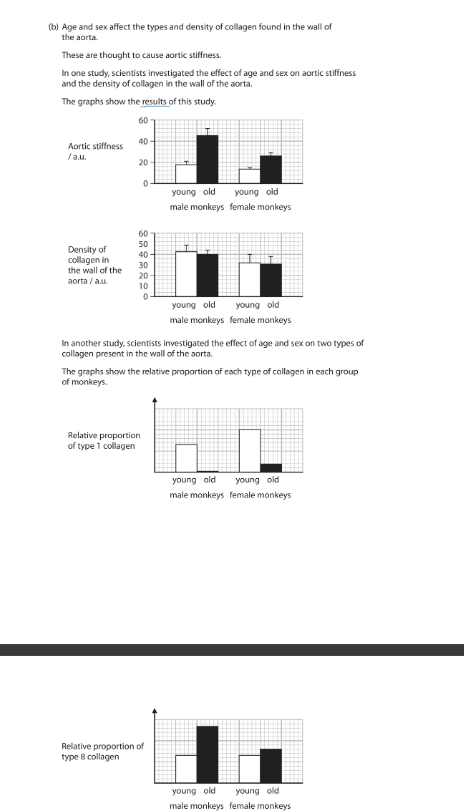
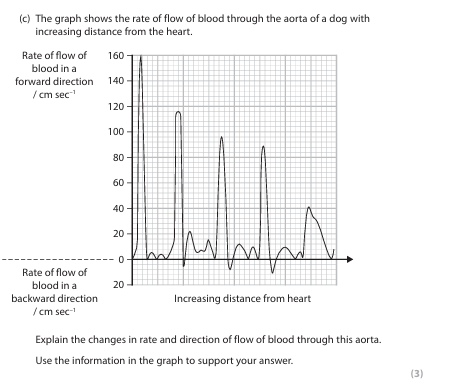
Comment on the effect of age and sex on the types of collagen found in the walls of the aorta and aortic stiffness. (6)
Use the information in the graphs to support your answer.

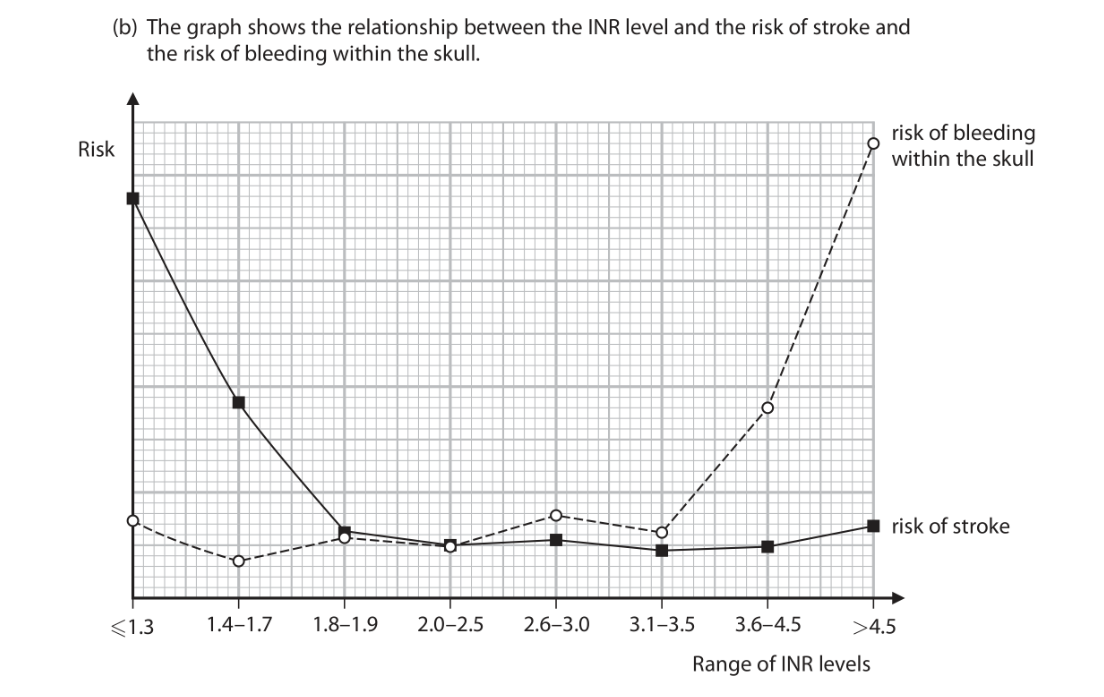
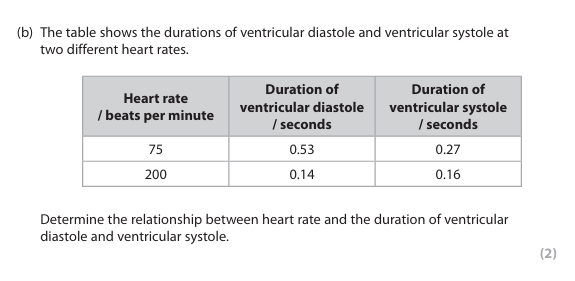
Deduce a safe INR level. (3)
1.8-3.5
below 1.8 there’s a high risk of stroke
above 3.5 there’s a high risk of bleeding within the skull
Too high of a warfarin dose can cause?
passing blood in your urine
passing blood in faeces or having black faeces
severe bruising
prolonged nosebleeds
vomiting or coughing up blood
heavy or increased bleeding during periods, or any other bleeding from the vagina
jaundice
In what ways can the primary structure of a protein differ?
(total) number of amino acids (in a peptide) / length of {(poly)peptide / chain}
{sequence / order / position} of amino acids
{proportion / number} of each type of amino acids (1)
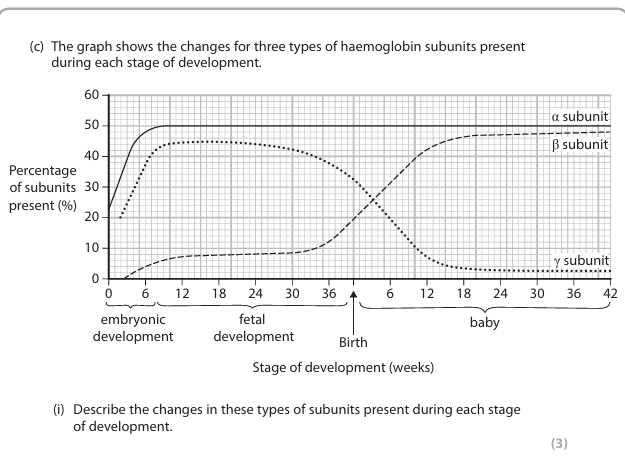

The oxygen affinity of fetal haemoglobin is different from adult haemoglobin.
Explain why this difference ensures the fetus obtains enough oxygen during development
fetal haemoglobin has higher affinity (than adult) (1)
{ACCEPT stronger {binding / association} (with oxygen)}
so that oxygen will leave the adult haemoglobin and bind to fetal haemoglobin (1)
at the same partial pressure of oxygen (1
Another form of CMT can be inherited as a sex‑linked trait on the X chromosome. Explain why a male with CMT cannot pass the disease on to his sons.

Explain why the wall of the aorta is thicker than the wall of a capillary. (3)
Warfarin is used as an anticoagulant to treat some patients.
Patients respond differently to this drug. This makes it difficult for doctors to select a safe but effective dose of warfarin to give to each patient.
Factors that affect the response of a patient to warfarin include age, body mass, liver function and genetic makeup.
(a) Explain why a safe but effective dose of warfarin needs to be given to a patient.
(b )Describe the role of mRNA in the production of enzymes.
*(ii) Pharmacogenomics analyses the genetic profile of individuals.
This analysis is used to determine the appropriate doses of a drug for individual patients.
Discuss the possible use of pharmacogenomics in selecting appropriate doses of warfarin for individual patients.
Use the information in the question and your own knowledge of the blood clotting process and genetic screening to support your answer. (6)
a)
(safe / not too high a dose) to avoid {uncontrollable bleeding / named examples of uncontrollable bleeding / internal bleeding} (1)
• (effective / not too low a dose) to reduce (the risk of) blood clotting (1)
b)
• to carry a copy of the gene {out of the nucleus / into the cytoplasm / to the ribosomes} (1)
• (used for) {(correct) ordering of the amino acids / producing amino acid sequence / formation of (poly)peptide chain} (1)

Eating soybeans may reduce cholesterol and low‑density lipoproteins (LDLs) in the blood.
Explain why eating soybeans may reduce the risk of heart disease.
• (less cholesterol) so reduces {build up of cholesterol / formation of atheroma / formation of a plaque} (1)
• in the (walls of the) coronary artery (1)
• so flow of blood to heart {muscle / cells / tissue} would not be prevented (1)
• so oxygen available for respiration for heart {muscle / cells / tissue / contraction} (1)
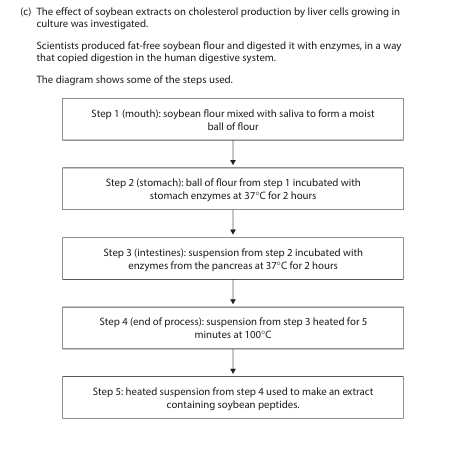
(i) Explain why the scientists used digested soybeans to make the extract for this investigation. (2)
(ii) Suggest why the soybean flour was incubated with different enzymes in steps 2 and 3. (1)
(iii) Explain why the soybean flour and enzymes were incubated at 37 °C for 2 hours in steps 2 and 3. (2)
(i) • because this (digestion) happens when a person eats soybeans / scientists wanted to mimic what was happening in the body (1)
• to {extract / separate / release} the {proteins / glycinin and β-conglycinin / active ingredients} (1)
• as enzymes needed to break (peptide) bonds (to produce the peptides) (1)
__________________________________________________________
ii) because they (different enzymes) are {found in different parts of the digestive system / needed to break down different proteins} (1)
ACCEPT more than one type of enzyme in the body two or more named parts of digestive system different substrates
________________________________________________________
iii) • 37°C because this is the {optimum temperature (for human enzymes) / (human) body temperature} (1)
• 2 hours because {this is enough time for complete digestion to occur / this is how long the digesting food stays in each part of the digestive system / this allows all the substrate to be broken down} (1)
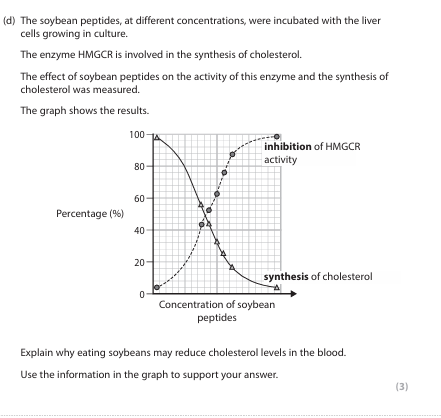
• as the concentration of soybean peptides increase, the inhibition of HMGCR increases and the synthesis of cholesterol decreases (1)
• because soybean peptides inhibit HMGCR
• because the peptides {bind to the HMGCR / compete with the substrate} (1) (ACCEPT bind to active site)
• as the cholesterol precursor cannot be converted into cholesterol (by HMGCR) (1)
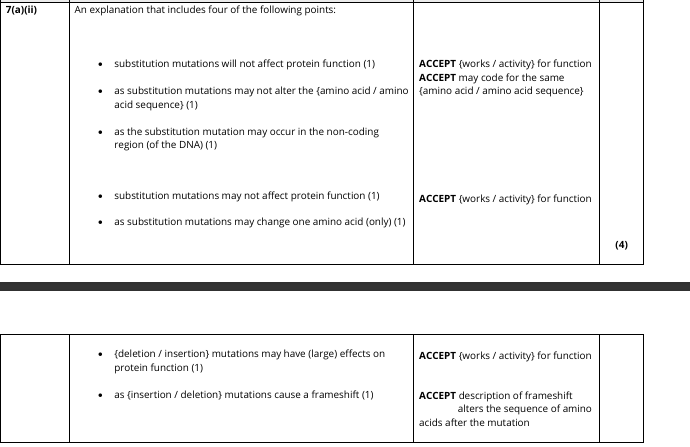
Describe how these types of mutation (Substitution and insertion and deletion) affect the DNA base sequence of a gene.
substitution mutations {swap / change / replaces} a {base / nucleotide} (1)
insertion and deletion mutations (results in a) change in the number of {bases / nucleotide} (1)
ACCEPT increases and decreases number of bases / length of DNA gets longer or shorter
Explain why these animals can survive with a greater number of substitution mutations than insertion and deletion mutations. (4)
Avocados are high in unsaturated fatty acids and low in saturated fatty acids.
Compare and contrast the structure of an unsaturated fatty acid and the structure of a saturated fatty acids.
Similarities:
• both contain carbon and hydrogen (and oxygen) (1)
• both contain covalent bonds (only) (1)
Differences:
• unsaturated fatty acids contain carbon-carbon double bonds but saturated fatty acids have only single carbon-carbon double bonds (1)
• unsaturated fatty acids have {fewer hydrogens (for same number of carbons) / lower hydrogen to carbon ratio / higher carbon to hydrogen ratio} (1)
• unsaturated fatty acids are {kinked / bent} and saturated fatty acids are {straight / linear} (1)
Suggest two reasons for the differences in the number of mutations per cell of these species of animal. (2)
• cells divide at different {rates / frequencies} (1)
• different {repair mechanisms / DNA polymerases} (1)
• exposed to different {factors (that cause mutations) / environment} 1)
• different {quantities of DNA / base sequences / genes} (
The effect of eating avocados each week on the risk of coronary heart disease (CHD) was investigated.
A group of men and women who had no signs of cardiovascular disease (CVD) or stroke were selected.
They were all between the ages of 30 and 75.
The group ate avocados each week to replace animal products in their diet whenever possible.
The group all completed a questionnaire about the food they ate at the start of the investigation and every four years after that for over 30 years.
There were 41 701 men and 68 786 women in the group
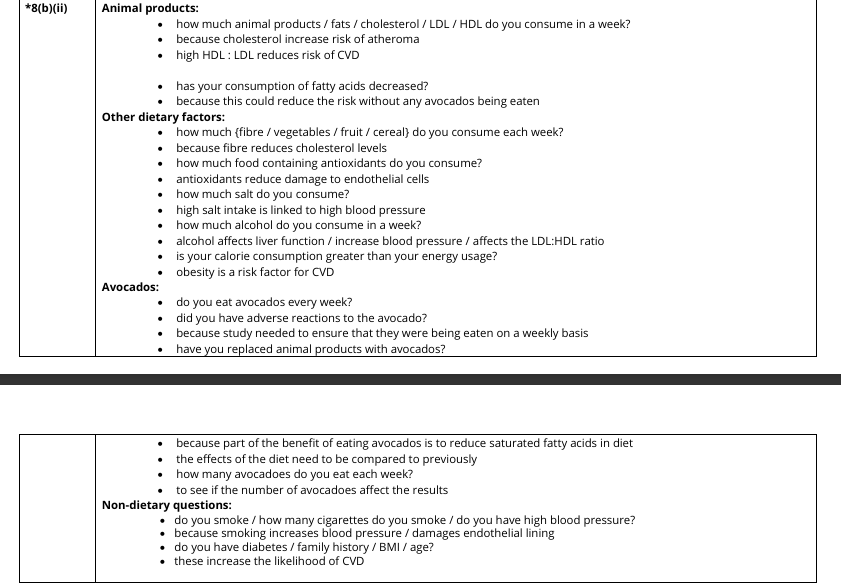
*(ii) Describe the questions that need to be in the questionnaire so that appropriate information can be gathered for this investigation. Give reasons for choosing these questions. (6)

Fick’s law of diffusion

(OCT 2022)


Discuss how the structure and behaviour of these salamanders are adapted for gas exchange. (6)
Structure
• salamanders have both lungs and their skin for more gas exchange
• lungs allow oxygen from air and skin oxygen from water
• the skin is folded to increase surface area
• flattened body to increase surface area
• so that gas exchange will be faster
• skin has a good blood supply so that there will be high concentration gradient
• skin is very permeable to gases so that they can diffuse in faster
Behaviour
• salamanders live in fast-flowing water which will have high levels of oxygen
• shallow water will also have higher levels of oxygen
• shallow water will make breathing with lungs easier
• the rocking / swaying movements stir up the water
• which helps to aerate the water
• so that water with higher oxygen content is in contact with their skin
• so that there is a higher concentration gradient
• so that {gas exchange / diffusion of gases} will be faster
• the rocking / swaying maintains the levels of oxygen in the blood
Graph
• at low levels of oxygen in the water the frequency of rocking is high
• accompanied by an increase in blood pO2
• as oxygen levels in the water increase the frequency of rocking decreases
• but the blood pO2 continues to increase
• sufficient oxygen in water to diffuse into lungs and skin
• to maintain levels of oxygen
• rocking stops to conserve energy
Describe the structure of collagen?
Collagen is a fibrous protein with aa triple helix structure. Hled toegtehr by hydrogen bonds between the chains.
How does protease break down elastin?
Active site of protease binds to the elastin substrate. The activation energy is lowered. And the peptide bond is broken in a hydrolysis reaction.
Why do fatty acids with more double Carbon-Carbon bonds have less risk of causing CVD?
Fatty acids with more double bonds (polyunsaturated fats) are generally more fluid and less prone to contributing to artery-clogging plaques.
They also help reduce LDL (“bad”) cholesterol and have anti-inflammatory properties, unlike saturated fats which raise LDL and promote inflammation.
Name start and stop condons
Start:
AUG
Stop:
UAA
AUG
UGA
Note: These are mRNA codons
Explain the use of stop and start codons?
Start Codon (AUG): This is the initiation signal for translation. It tells the ribosome where to start assembling the polypeptide chain and always codes for the first amino acid, methionine.
Stop Codons (UAA, UAG, UGA): These are the termination signals. They do not code for an amino acid. Instead, when a ribosome reaches one, it causes the release of the finished polypeptide chain and the ribosome subunits to disassemble.
(b) Explain why some amino acids, such as alanine, have more than one genetic code.
Because it is a degenerate code, which means that there are more codes than needed, so, more than the number of amino acids. There are 64 possible combinations of amino acids and 20 amino acids to code for, so this minimizes the effect the mutations.
Explain the roles of the other three genetic codes?
They are stop codons, so that no more amino acids can be added to the polypeptide chain/protein.
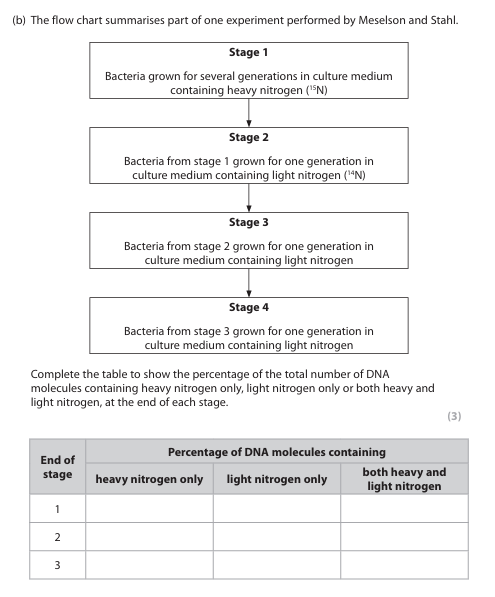
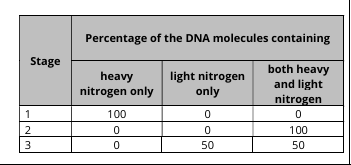
What is meant by the term semi-conservative replication?
It means an increase in the number of DNA molecules, and each new molecule consist of one parent strand and one new strand.
Explain the importance of semi-conservative replication in the production of new cells.
Because it results in genetically identical daughter cells, with the same genetic information so they’ll have the same structure.

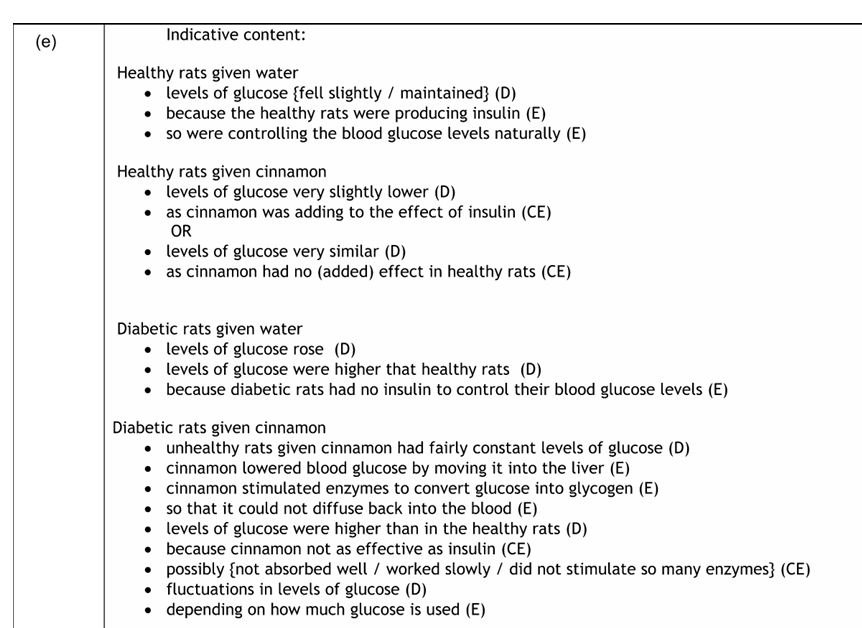
Indicative content:
sugar solution with a lower water potential than the cytoplasm of the cell (D)
sugar solution should be hypertonic (D)
so that water will pass out of the cytoplasm by osmosis (E)
concentration of sugar solution should be the same as the cytoplasm (D)
so that sugars will not diffuse out (E)
each individual sugar concentration should be the same as the cytoplasm (D)
mean concentration of sugars stated (fructose = 1.52, glucose = 1.08, sucrose = 8.55) (D)
range of sugar concentrations stated (from table) (D)
so that concentration of each sugar remains the same (E)
another solute needs to be used (D)
so that the sugar concentration remains the same but the water passes out (E)
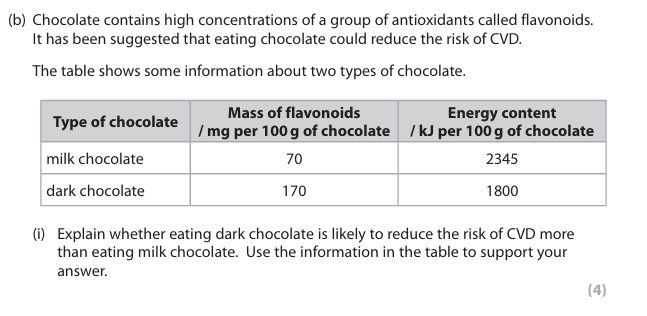

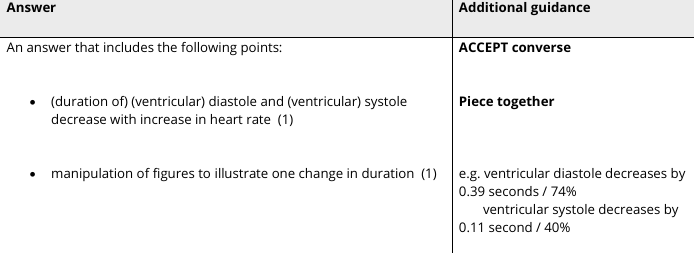
Explain why the arteries near the heart of the giraffe are highly elastic?
The blood is under high pressure, so the arteries need to widen, and the elastic recoil is necessary to maintain high blood pressure.
Explain why the very narrow capillaries prevent excessive bleeding.
They reduce the amount of blood near the surface, so the blood clot will form more easily.
Silkworms are caterpillars that produce silk. Silk is a fibrous protein that can be used in clothing and in medicine. Silkworms have been selectively bred to produce a modified silk that could have even more medical uses. The modified silk is made by these silkworms by inserting a synthetic amino acid, AzPhe, into the protein. This replaces the naturally-occurring amino acid phenylalanine.
The diagram shows the structure of AzPhe.
) Transfer RNA (tRNA) is involved in translation. The amino acid AzPhe requires a special tRNA molecule during the synthesis of silk. Suggest why AzPhe is not inserted into proteins in silkworms that have not been selectively bred.
because AzPhe is not a naturally-occurring amino acid (1)
therefore there is no {DNA / mRNA} codon for AzPhe (1)
therefore there is no tRNA (that can bind to the AzPhe) (1)
therefore AzPhe not held in position for peptide bond to form (1)
The R group of phenylalanine is smaller than the R group of AzPhe.
Suggest how inserting an amino acid with a larger R group could affect the properties of silk fibres.
properties of a protein is dependent on the structure of a protein (1)
AzPhe could affect the {secondary structure / folding / 3D shape} (of the silk) (1)
because different bonds (between R groups) could form (1)
new bonds might make the {silk / fibres / molecule / protein} stronger (1)
larger R groups will make the protein insoluble (1)
Elastin and collagen are proteins found in connective tissue.
(a) Describe the structure of collagen
Collagen is fibrous protein that is made up of a triple helix. It’s held by hydrogen bonds between chains. There is a repeating sequence of amino acids.
Explain how protease breaks down elastin?
The active site of the protease binds to the elastin substrate. The activation energy is lowered, and the peptide bond is broken by hydrolysis.
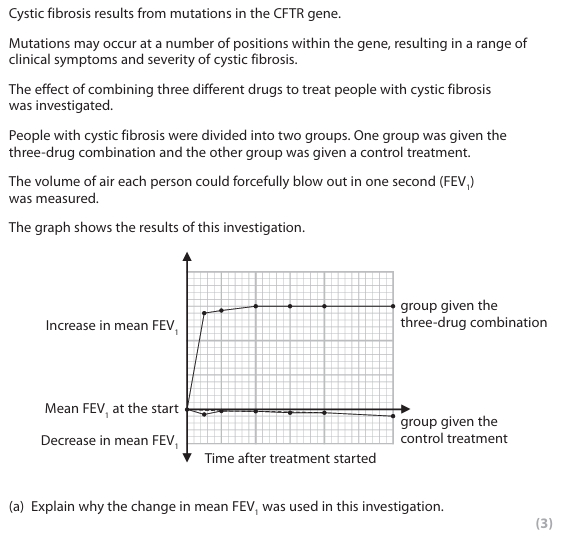
because people with cystic fibrosis produce {thick / sticky} mucus (1)
which reduces the air {into / out of} the lungs (1)
so FEV1 will improve if the treatment is working (1)
a mean is used to increase the validity of the {data / results} (1)
a mean as different people have different FEV1 (1)
Compare and contrast the davsen-danielli and the fluid mosaic model. (3)
Similarities:
both have proteins (1)
both have {phospholipid / phospholipid bilayer} (1) Differences:
FMM has proteins {embedded / intrinsic}, but DDM has proteins {outside / in a layer/ extrinsic} (1)
FMM has cholesterol but DDM does not (1)
FMM has {glycoproteins / glycolipids} but DDM does not (1)
Cells can repair damage to the cell membrane. This involves fusion of parts of the membrane around the edge of the damage. Explain why parts of the membrane are able to fuse together to repair the damage
Once the membrane has fused together, other processes are needed to complete the repair of the membrane. Suggest what else the cell needs to do to complete this repair.
because the phospholipids (and proteins) {can move / are fluid} (within the membrane) (1)
therefore {phospholipids / fatty acids} can interact and bond(1)
more membrane needs to be made (1)
membrane needs restructuring / proteins added to membrane (1)
increase rate of {respiration / ATP synthesis / release of energy} (1)
Substitution, insertion and deletion.
Substitution mutation:
substitution swaps one base for another
may not alter the amino acid coded for
as the genetic code is degenerate
triplet codon codes for the same amino acid
therefore, no effect on the protein
therefore, no effect on the phenotype
amino acid could be different
therefore, shape of protein may or may not be (significantly) different
depending on significance the phenotype may stay the same
depending on the significance the phenotype may become the same as one of the parents
a stop codon could be coded for
so the protein may be {shorter / not coded for}
so the phenotype may become the same as one of the parents
Insertion / deletion mutation:
deletion removes one base
insertion adds in a base
causing a frameshift
this will probably have a huge effect on protein
phenotype may become one of parents
may have little effect on protein if near the end of the gene sequence
and therefore, have very little effect on phenotype
Explain why a stent is used in the treatment of atherosclerosis in a coronary artery. (3)
• to widen (the lumen of) the (coronary) artery / (blood) vessel (1)
• so that more blood can flow to the heart {cells / muscle} (1)
• for respiration (in the heart muscle) / so that heart muscle can contract (1)
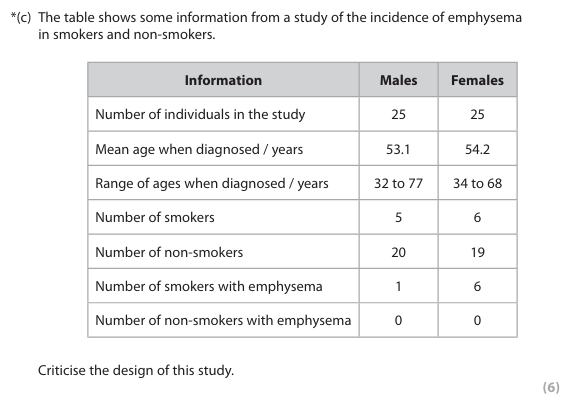
Critisize
Indicative content: Repeatability:
• sample size is small
• smokers are being studied and their sample size is very small*
• no statistical data available
• no indication of the location of the individuals (could be a validity comment as well)
Validity:
• mean age at diagnosis is similar but not identical
• there is a greater range of ages for males than females
• no indication of the actual ages of the people
• so there could be more people at the extremes in one group
• no information about other lifestyle factors
• e.g. working in polluted environment, living in the city
• no information about non-lifestyle factors • e.g. ethnicity
• no indication if individuals lived with other smokers (passive smokers)
• no indication of how long people been smoking for*
• no indication of how many cigarettes were smoked by the smokers each day*
• no indication if the non-smokers had ever smoked previously*
• no indication of severity of emphysema*
• no indication if emphysema is self-diagnosed or clinical diagnosis*
Explain the role of the primary structure in determining the properties of the protein . (4)
• because the sequence of amino acids determine the {tertiary / quaternary} structure of the protein (1)
• by determining the {position / type} of bonds that form between the R groups (1)
• {hydrophobic / non-polar} {(R) groups / amino acids on (the outside of) the part of the protein that is embedded in the fatty acid tails (1)
• {hydrophilic / polar} {(R) groups / amino acids} (on the outside of) the part of the protein that is {amongst the phosphate heads / facing the cytoplasm / facing the aqueous environment} (1)
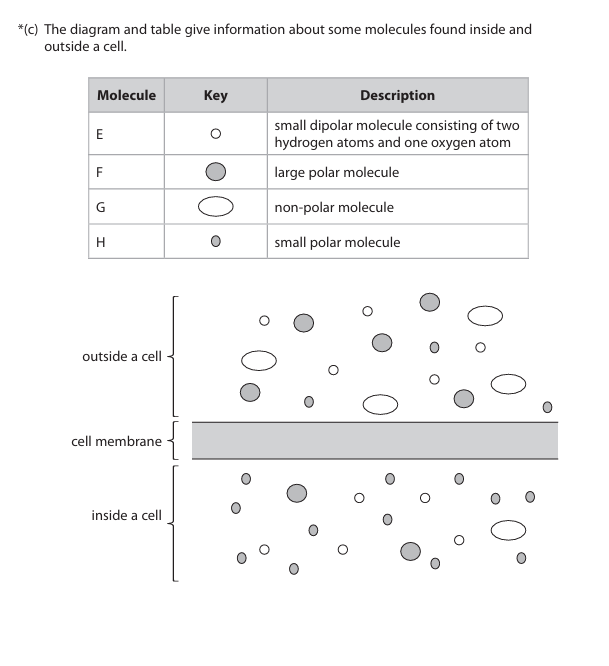
Explain why each of these molecules enters the cell by a different mechanism. Use the information in the table and the diagram to support your answer. (6)
