Software Engineering
1/91
Earn XP
Description and Tags
CS4320
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
Which of the following best defines a failure?
A deviation from specified behavior during execution, indicating that the software does not perform as intended.
Verification ensures that
The software adheres to specifications
A _______ simulates a called module, while a ____ simulates a caller module.
stub; driver
Cyclomatic complexity is calculated using the formula
v = e - n + 2, where e = edges and n = nodes. High complexity (v > 10) harder to test code.
Which incremental testing approach uses stubs for lower-level modules?
Top-down testing
The triple constraint includes:
scope (what is the project trying to accomplish), time, and cost.
The ______ document formally authorizes a project and defines its objectives.
project charter
Which PMBOK knowledge area focuses on managing project risks?
Project Risk Management
A business case analysis typically includes:
a) ROI, NPV, and Payback Period
b) Stubs, Drivers, and Test Scripts
c) Baseline, Codeline, and Timestamp
d) DMAIC, DMADV, and Six Sigma
ROI ( return on investment) , NPV (Net Present Value), and Payback Period, which evaluate the financial viability and potential return on investment for a project.
What does PMBOK stand for?
Project Management Body of Knowledge. It is a set of guidelines and best practices for effective project management.
The Measureable Organizational Value (MOV) must be _______, _______, and ________
Measurable, agreed upon, verifiable
McCall’s product transition quality factor includes:
Portability, Reusability, and Interoperability
A ______ is a stable version of a system, while a ______ is a sequence of component versions.
Baseline, Codeline
What is verification
Check whether the software correctly implements the specified functionality.
What is Validation
Check whether the software is according to the client requirements
What is an error?
An incorrect state of the system.
What is a fault?
Something that leads to a failure and stems from errors. AKA defect / bug
What is a test plan?
Defines test objectives and expected results. Higher-level document.
What does a test plan contain?
Test items, deliverables, and responsibilities
What is a test script?
a series of instructions or a short program for checking some software application/product functionality.
What is program behavior?
Plain natural language, a state diagram, formal mathematical specification
Describe incremental testing.
Integrate step-by-step through build cycles (Look this up more because I do not think this is enough )
Top-down approach
Start with top-level modules; use stubs for lower levels
Top-Down Advantages
The SIT engineers continually observe system-level functions as the integration process continue
Isolation of interface errors becomes easier because of the incremental nature of the ______ integration
Test cases designed to test the integration of a module M are reused during the regression tests performed after integrating other modules
Top-Down Disadvantages
It may not be possible to observe meaningful system functions because of an absence of lower level modules and the presence of stubs.
Test case selection and stub design become increasingly difficult when stubs lie far away from the top-level module
What is a stub?
Routines that don't actually do anything other than declaring themselves and the parameters they accept and returning something that is usually the values expected in one of the "happy scenarios" for the caller.
What is a driver?
which are the "calling" programs. _____ are dummy code, which is used when the sub modules are ready, but the main module is still not ready. Used in bottom-up testing approach
What is Bottom-up testing
A test driver mimics behavior to integrate lowest-level modules, then replace the test driver with the actual module and a new test driver is used.
Bottom-up advantages?
One designs the behavior of a test driver by simplifying the behavior of the actual module
If the low-level modules and their combined functions are often invoked by other modules, then it is more useful to test them first so that meaningful effective integration of other modules can be done
Bottom-Up Disadvantages
Discovery of major faults are detected towards the end of the integration process, because major design decision are embodied in the top-level modules
Test engineers can not observe system-level functions from a partly integrated system. In fact, they can not observe system-level functions until the top-level test driver is in place
What is the big-bang approach?
First, all modules individually tested, then all modules are put together to construct the entire system which is tested as a whole.
What is the Sandwich approach
Uses all three approaches. Bottom-up approach to integrate modules in the bottom layer. Top-down for top and big bang once top and bottom integrated.
What is the value-driven approach when it comes to improving likelihood of success when making a project?
Plain & Simple: IT Projects must provide value to the organization
The decision to fund or invest in an IT project should be based on the value that the completed project will provide the organization.
Otherwise, what is the point of spending all that time, effort, and money?
What is the socio-technical approach when it comes to improving likelihood of success when making a project?
The business, organizational, and technical aspects of IT projects should be addressed.
Involving end users and stakeholders early and often in the development process ensures they become invested partners in the project's success; however, technical aspects take precedence.
What is the Project Management approach when it comes to improving likelihood of success when making a project?
Pre-defined processes and infrastructure (Methodology), i.e., results are more a function of the Methodology then the selection individual team members.
Estimate and control resources costs
Communication and status reports giving the ability to manage expectations of stakeholders
What is the Knowledge Management approach when it comes to improving likelihood of success when making a project?
Lessons learned, best practices, and shared knowledge
What are the PMBOK (Project Management Body of Knowledge) Knowledge Areas
1. Project Scope Management |
2. Project Time Management |
3. Project Cost Management |
4. Project Quality Management |
5. Project Human Resources Management |
6. Project Communications Management |
7. Project Risk Management |
8. Project Procurement Management |
9. Project Integration Management |
10. Project Stakeholder Management |
What is a IT Project methodology?
A strategic-level plan for managing and controlling IT projects.
What does the IT project methodology recommend?
Phases and deliverables
Processes
Tools
Knowledge Areas
What is a project charter?
Clarifies the projects goal and defines the project’s objectives in terms of:
Scope, schedule, budget, and quality objectives
What is a project plan?
Provides detail description of who will carry out the work and when and developed by the stakeholders
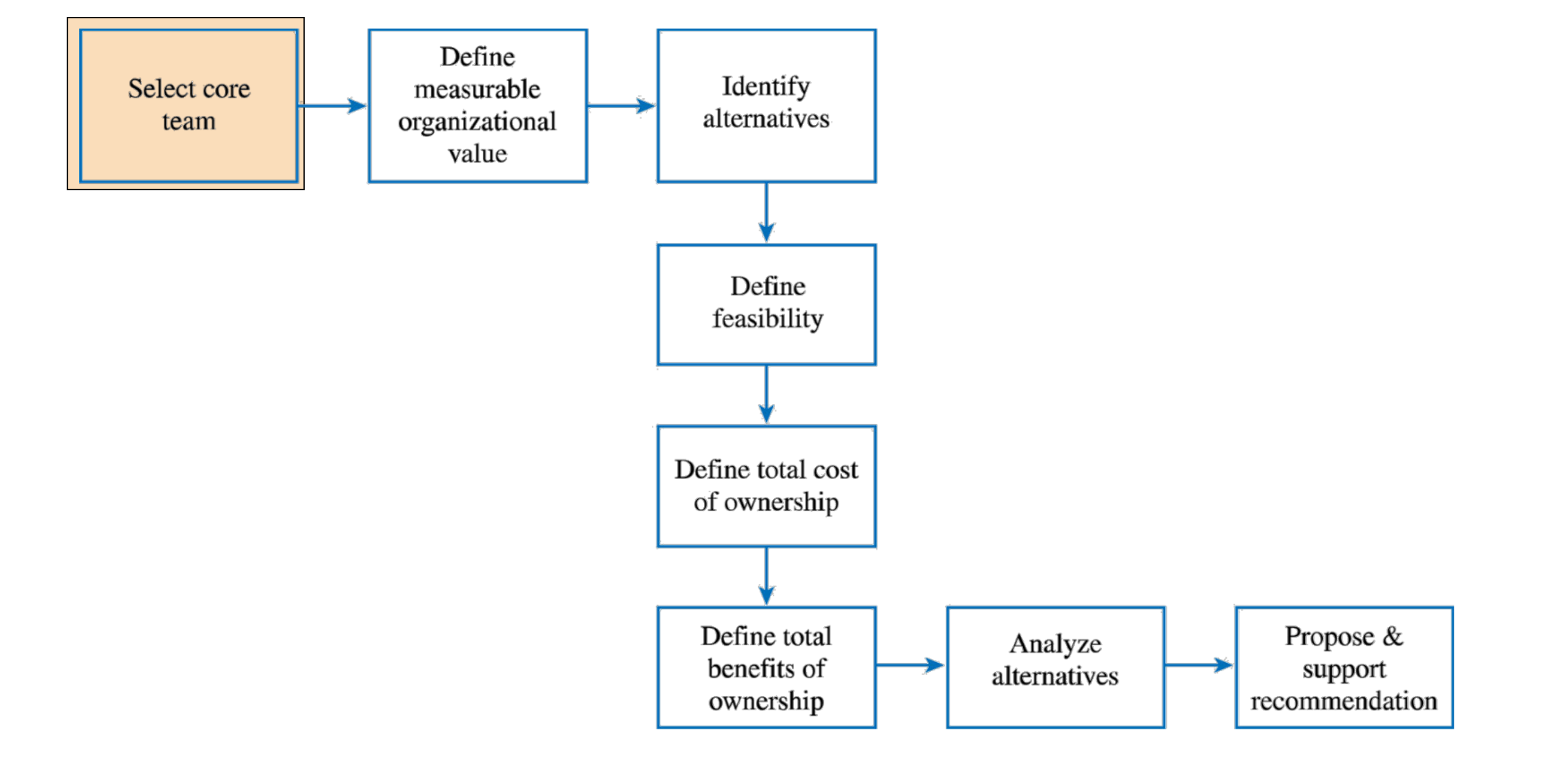
What does this picture show
The developing of the Business Case where MOV (measurable organizational value). Essentially, how does this project measure how valuable it is to the organization.
How do we determine MOV (Measurable Organizational Value)?
Identify desired area of impact (e.g. Strategic, Customer, financial, Operational, Social)
Identify desired value of IT project
Develop an appropriate metric
Set a time frame for achieving MOV
Verify and get agreement from project stakeholders
Summarize in a clear and concise statement.
What are the McCall’s software quality product OPERATION factors
Correctness, reliability, Efficiency, Integrity, Usability
McCall’s Software quality product REVISION factors
Maintainability, flexibility, and testability
What is a baseline?
A definition of a specific system. Specifics the component versions that are included in the system plus a specification of the libraries used, configuration files
What is a codeline?
A sequence of versions of source code with later versions in the sequence derived from earlier versions. Normally apply to components of systems so that there are different versions of each component
What is a timestamp?
Compares modification times of source/object files
What is a checksum?
Uses a hash value to detect code changes
What are the stages of process improvement?
Measurement: baseline current process
Analysis: Identify bottlenecks in the system
Change: Implement improvements
Principal Dependability Properties
Availability, Reliability, Safety (operate without catestrophic failure), Security (System protects itself), Resilience (system able to resist and recover from damaging events)
What are the System Design 8 issues
Identify design goals
Subsystem Decomposition
Identify concurrency
Hardware/software mapping
Persistent Data Management
Global Resource Handling
Software Control
Boundary Conditions
What is Coupling?
Number of dependencies between two subsystems. You would like this to be low
What is Coherence?
Number of dependencies within a subsystem. You would like this to be high
If a subsystem contains many objects that are related to each other and perform similar tasks, its ____ is high
What is the design goal to reduce system complexity while allowing change?
High coherence (dependencies within subsystems and Low coupling (dependencies between subsystems)
What are examples of architectural styles?
Layered, MVC, pipe-and filter, repository , hybrids
What is the difference between physical and logical concurrency?
Physical is implemented in the hardware and logical is implemented in the software
What is authorization?
Helps determine and restrict the access of verified user to certain actions, programs, and resources after gaining entry to the system.
What is authentication?
Verifying the identify of a user before providing access to the secured system.
What are the four access control policies?
Discretionary Access Control (DAC), Mandatory Access Control (MAC), Role-based Access Control (RBAC), and Attribute-based access Control (ABAC)
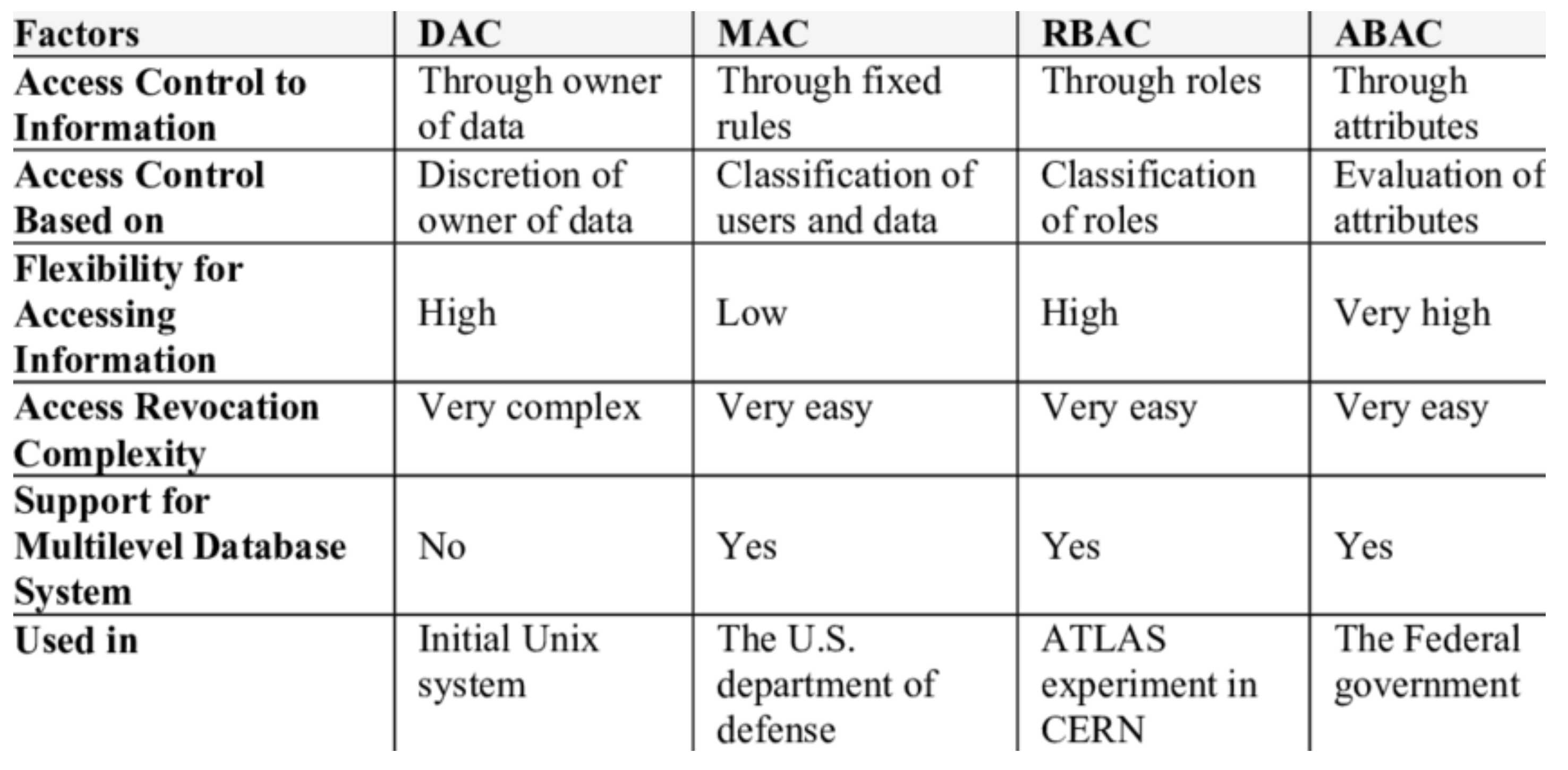
What is Discretionary Access Control (DAC)? ( YOU WILL NEED TO EXPLAIN 1 OF THE 4 )
Type of access control as a means of restricting access to objects based on identity of subjects and/or groups to which they belong.
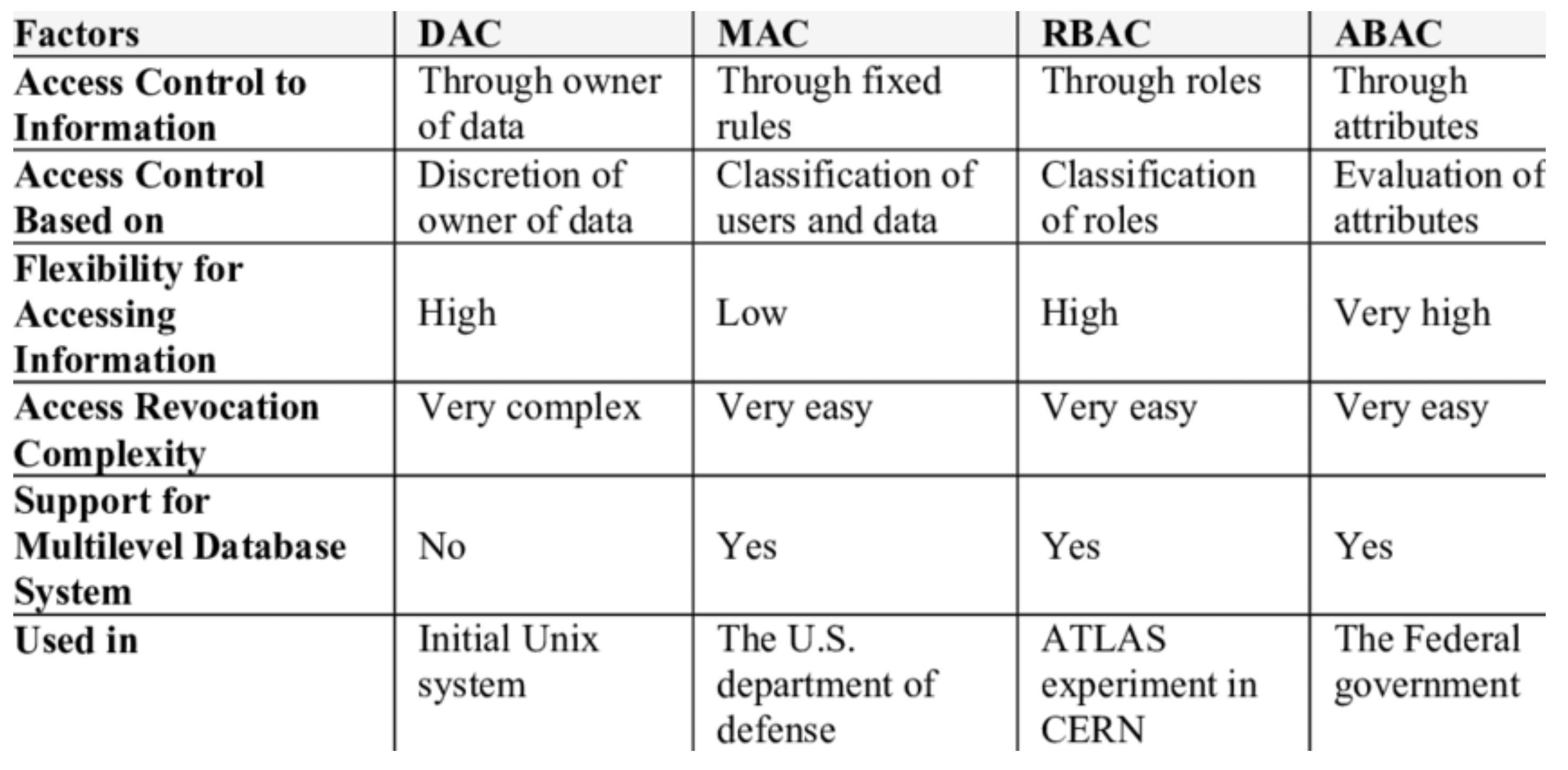
What is Mandatory Access Control (MAC)? ( YOU WILL NEED TO EXPLAIN 1 OF THE 4 )
Limiting access to resources based on the sensitivity of the information that the resource contains and authorization of the user to access information with that level of sensitivity.
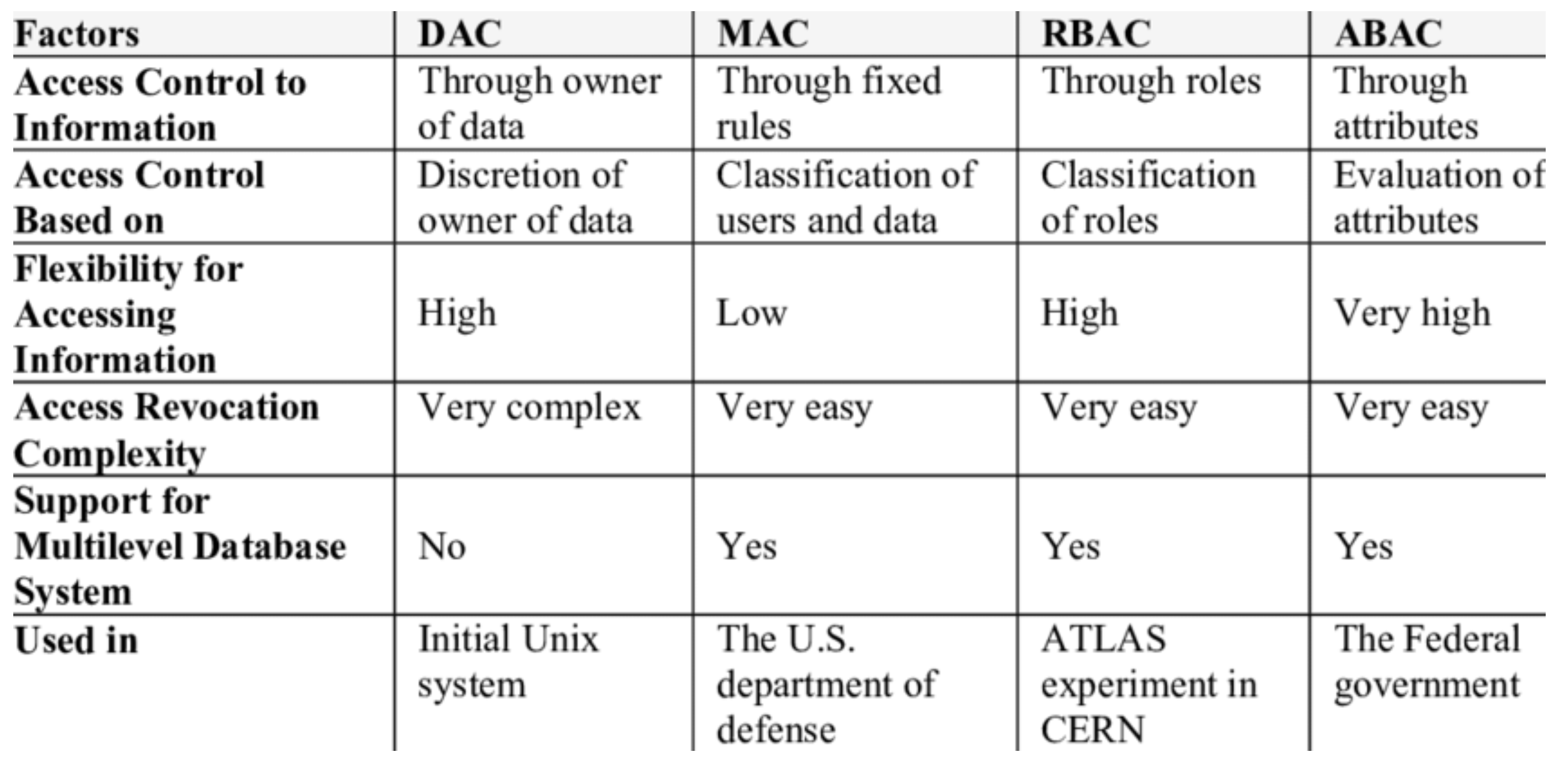
What is Role-based Access Control (RBAC)? ( YOU WILL NEED TO EXPLAIN 1 OF THE 4 )
A policy-neutral access-control mechanism defined around roles and privileges. Used to implement MAC or DAC
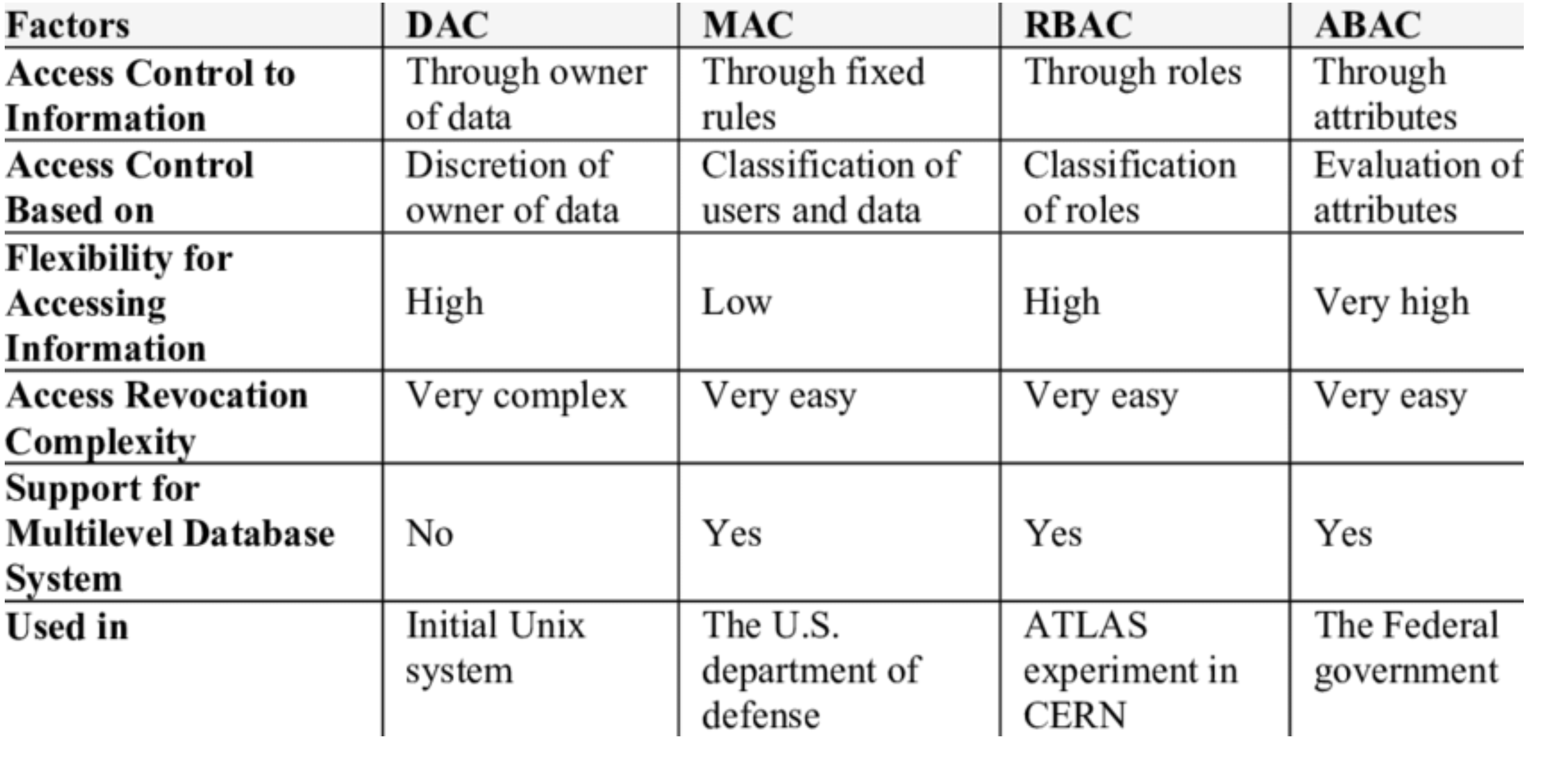
What is Attribute-based access control (ABAC) ( YOU WILL NEED TO EXPLAIN 1 OF THE 4 )
Defines an access control paradigm where a subject’a authorization to perform a set of operations is determined by evaluating attributes associated with the subject, object, requested operations, and sometime environmental attributes.
What are the different software control design choices?
Implicit control (non-procedural, declarative languages), explicit control (procedural languages)
What is a centralized design when it comes to software control?
One control object or subsystem controls everything
Pro: Change in the control structure is easy
Con: Single control object is a possible performance bottleneck
What is a decentralized design when it comes to software control?
Not a single object in control, more than one control object.
Pro: Fits nicely in object oriented development
Con: The responsibility is spread out
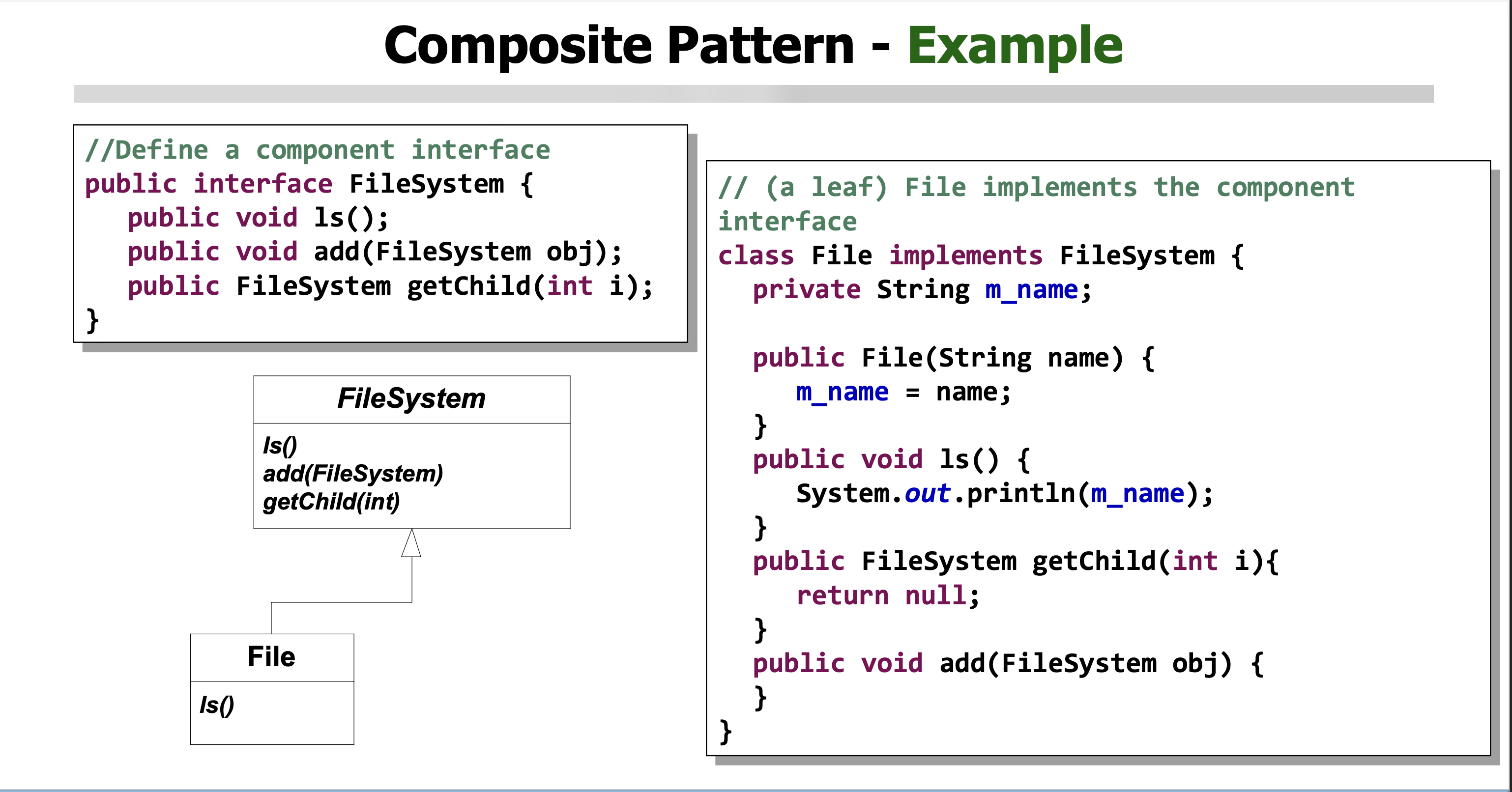
What is a composite pattern software design?
Treat individual objects and groups of objects uniformly by putting them into tree-like structures. Clients interact with single objects and compositions identically.
Pros: Easy to add new component types
What is the decorator pattern software design?
Dynamically add responsibilities to objects without subclassing. Wrap objects in _______ to extend functionality.
Pro: Flexibility to combine features at run time
What is the chain of responsibility
Pass requests through a chain of handlers until one handles it. Decouples sender and receiver.
Pro: reduces coupling, allows dynamic addition/removal of handlers
What is a state pattern?
Change an object’s behavior when its internal state changes. Encapsulate state-specific logic into separate classes.
Pro: Eliminates large conditional statements, makes state transitions explicit and centralized.
How do you determine actors from a text excerpt?
External entities interacting with the system (e.g. FieldOfficer initiates “ReportEmergency”)
Software Development Life Cycle:
Requirement Elicitation
Analysis
System design
Object design
Implementation
Testing
Delivery
Maintenance
When would you use «include»?
Reuse common behavior across use case. (Must go to the node pointed to in order to complete use case)
When would you use «extend»?
Adding an optional/exceptional behavior to a base use case. (Does not need to access this node for the original use case to end)
What is overriding?
When a subclass redefines a method from the superclass and is evaluated at runtime
What is overloading?
Multiple methods with the same name but different parameters.
What is the software engineering definition?
Problem solving, modeling, knowledge acquisition, rationale management, and quality control.
When would the waterfall model be useful?
Clear requirements, when looking at big-picture projects, familiar technology
When would you use the v-model?
Systems requiring high reliability, strong testing needs, regulatory compliance.
When would you use incremental/iterative (phased) methodology?
Early feature delivery needs, evolving requirements, complex projects, good on all time schedules
When would you use system prototype methodology? (I don’t think this will ever be the strongest one)
Unclear user interface requirements, new domains, user feedback is crucial
When would you use throw-away prototyping?
When there are unclear requirements or technology, when a reliable system is needed (poor short term)
When would you use spiral methodology?
When there is high risk involved, large complex projects. Poor in the short term.
When would you use XP methodology?
Unclear user requirements/changing user requirements. Short time frame, small teams
When would you use SCRUM methodology?
Complex adaptive problems, cross-functional teams, and customer involvement. Can be flexible in time (sprints)
What is six sigma?
A set of techniques and tools for process improvement. Seeks to improve quality output of a process by identifying and removing the causes of defects and minimizing variability in manufacturing and business processes.
What are the two project methodologies six sigma projects fall into?
DMAIC (Define, measure, analyze, improve, control)
DMADV (Define, measure, analyze, design, verify)
When is DMAIC used?
Used for projects aimed at improving an existing business process.
What does DMAIC stand for?
Define, measure, analyze, improve, control
When would you use DMADV?
Used for projects aimed at creating new product or process designs.
What does DMADV stand for?
Define, measure, analyze, design, verify