P15: Electromagnetism (2/2, generator effect)
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
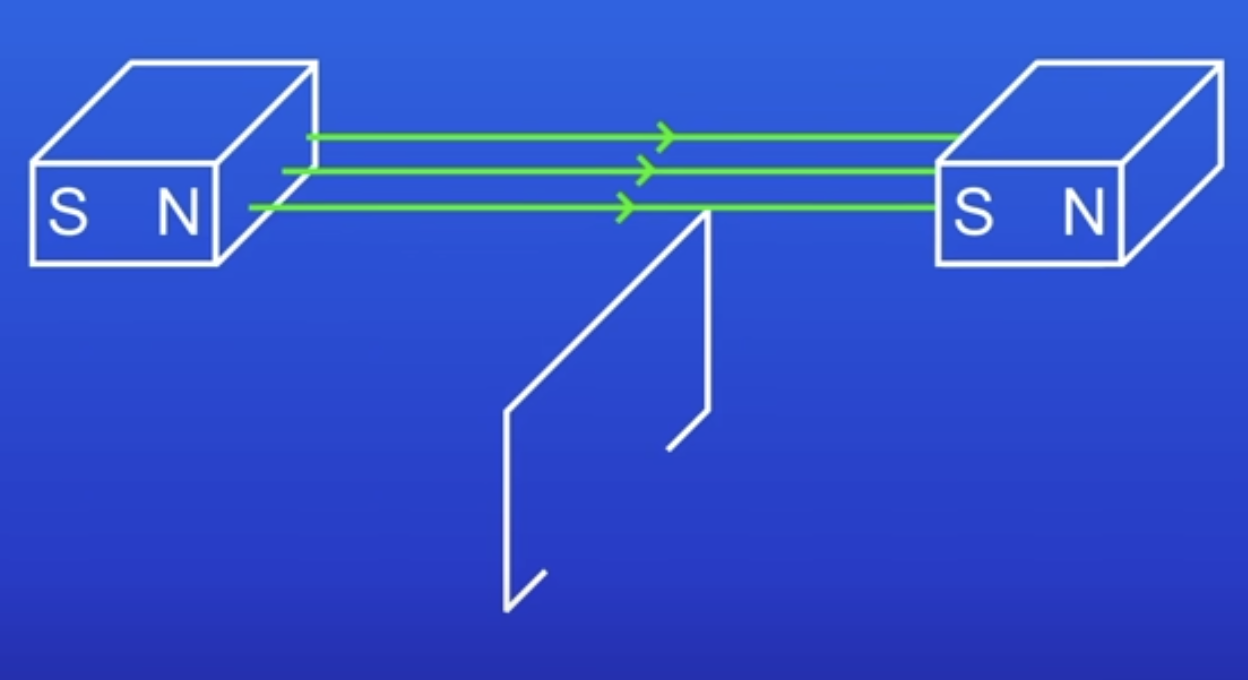
What does this image show?
A wire below a MF
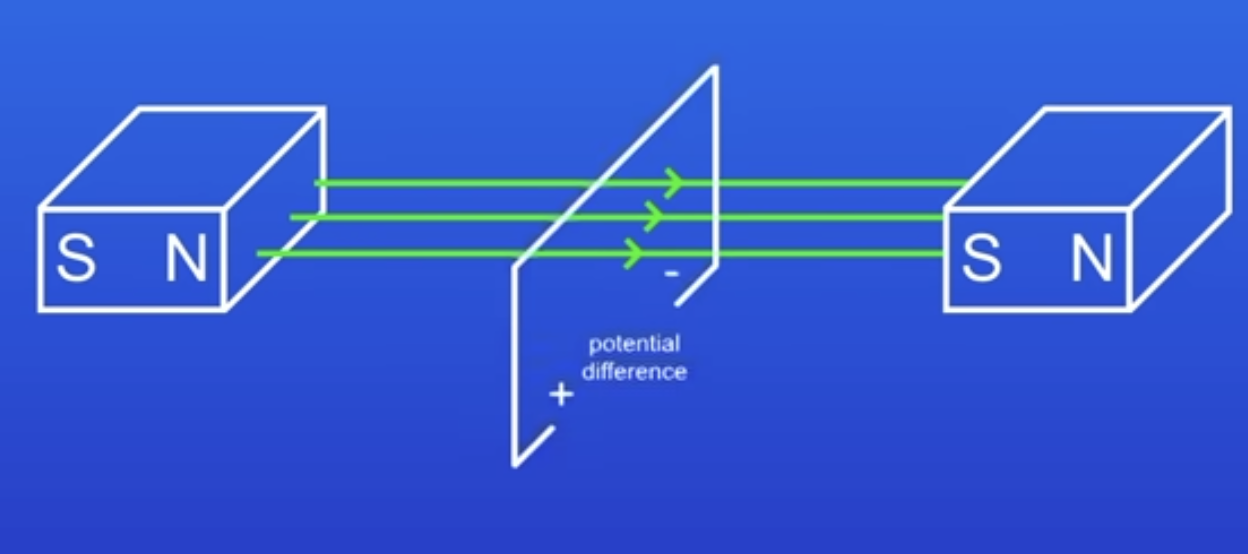
What happens if a wire is moved up through a MF?
A PD is induced across the ends of the wire
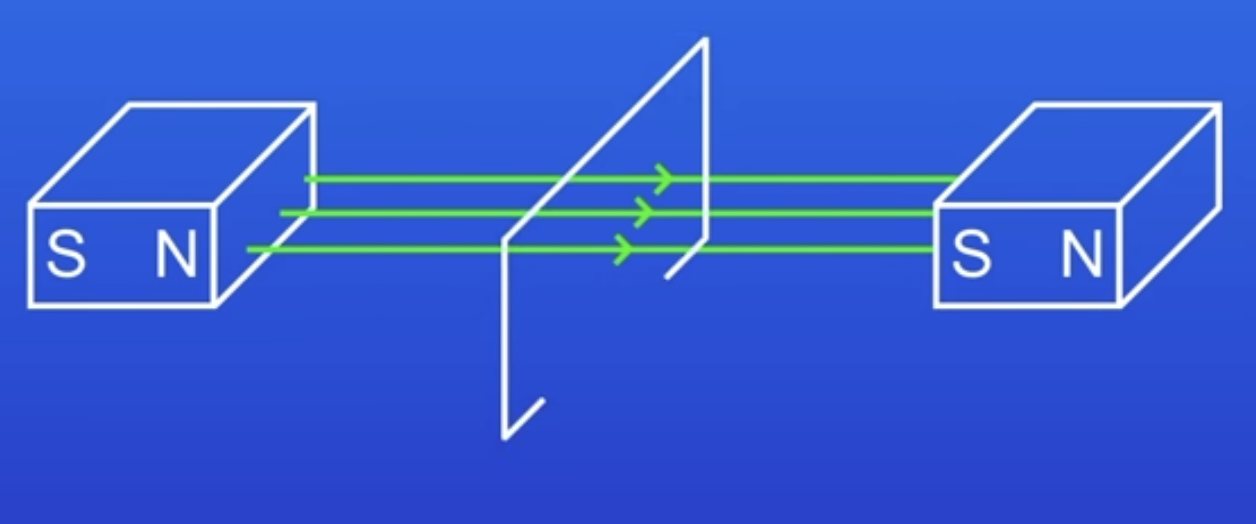

What happens when the wire stops moving?
The PD is lost
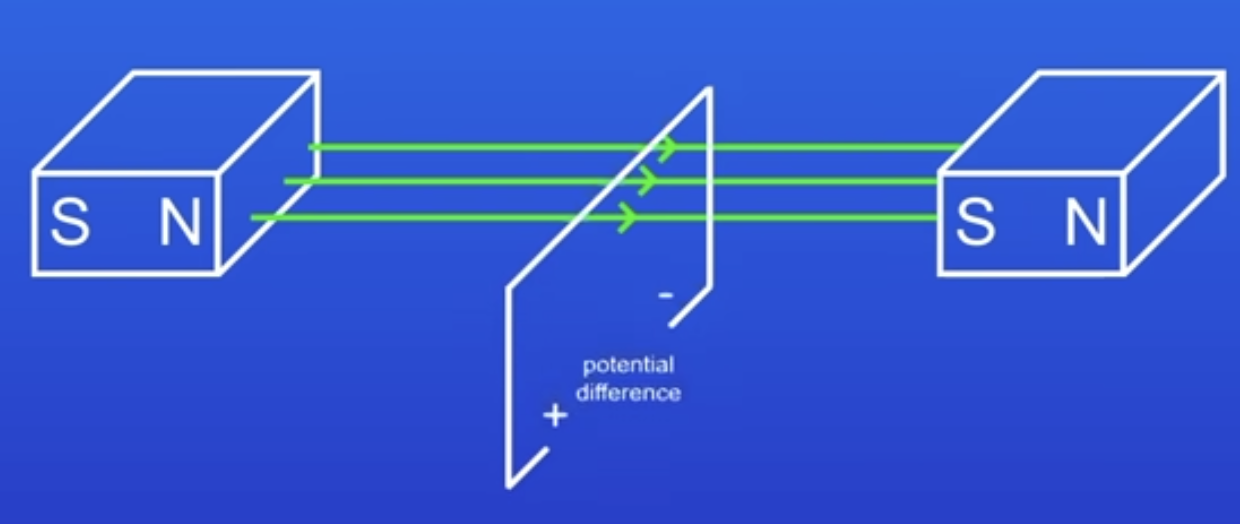
What happens if a wire is moved back down through the MF?
PD is induced again but in the reverse direction
Induced potential
Induced potential / electromagnetic induction
When a PD is created across a conductor (eg a wire) due to a change in the MF
What happens if the conductor is part of a complete, closed circuit?
A current is induced in the conductor
When is a PD induced across the ends of the conductor?
If an electrical conductor moves relative to a MF
Or if there is a change in the MF around a conductor (wire still, but move the MF)
Generator effect
When a PD is induced across the ends of the conductor (moving thru MF) part of a complete circuit
So a current is induced in the conductor
Direction of current switches when…
Direction of movement switches
Current stops when…
Movement stops
The generator effect is only seen if?
The wire passes thru the MF
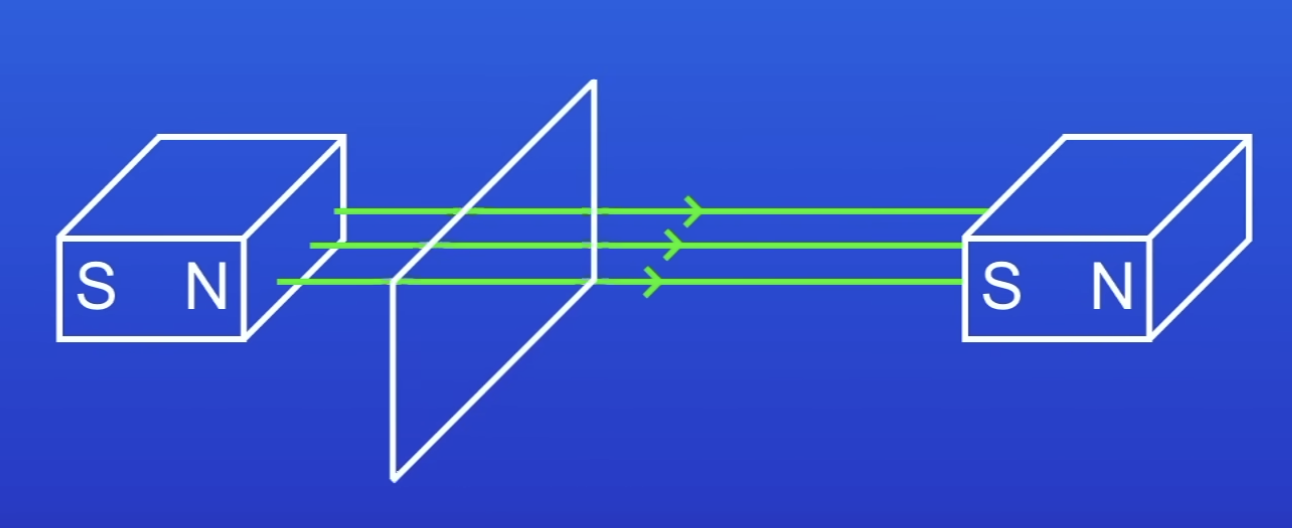
What happens if the wire moves along the MF?
No induced PD / current
How to increase size of induced PD / current
Use stronger MF
Move wire quicker
Shape wire into coil
Link betw no. of turns on the coil + size of induced PD and current
The greater the no. of turns on the coil… the greater the induced PD / current
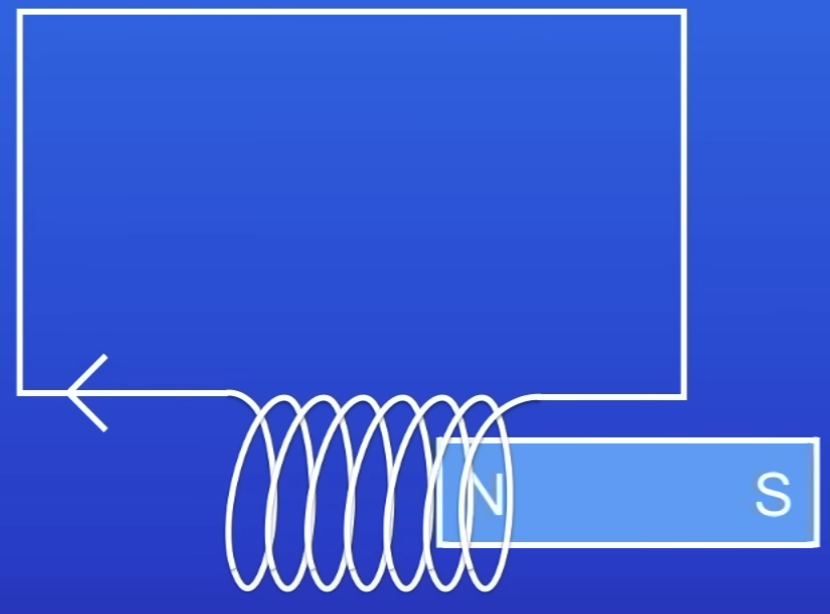
Does a magnet moving in + out of a coil of wire induce a PD / current?
Yes
Factors affecting the direction of the induced PD / induced current
Direction of movement (MF or conductor)
Direction of poles of magnet
Direction of current changes when…
Direction of movement changes (MF or conductor)
Switch poles of magnet
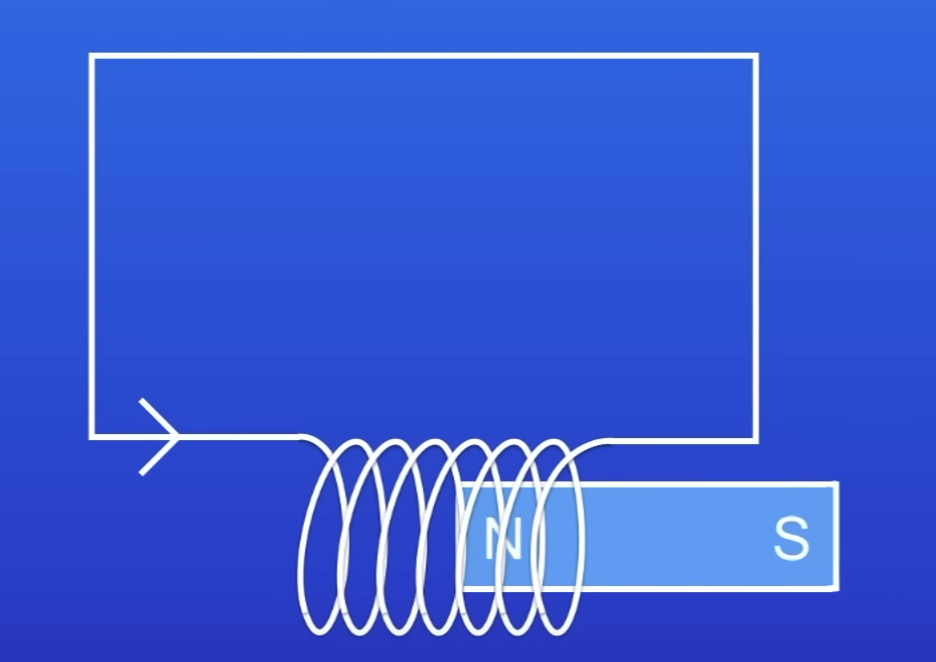
What happens when we move a magnet into a coil of wire?
Current is induced in the wire
Induced current creates its own…
MF
The MF induced current creates…
Opposes the og change
Movement of the conductor
Or the change in MF
eg movement of magnet
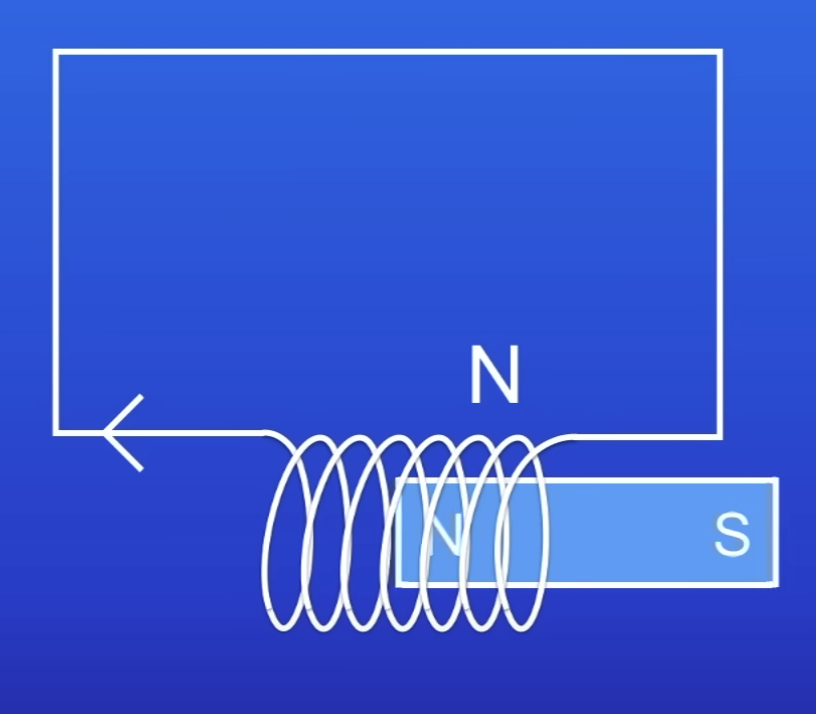
What happens when North pole of a magnet is inserted into a coil?
That end of the coil also becomes a N pole
This repels the magnet
So harder to push magnet in
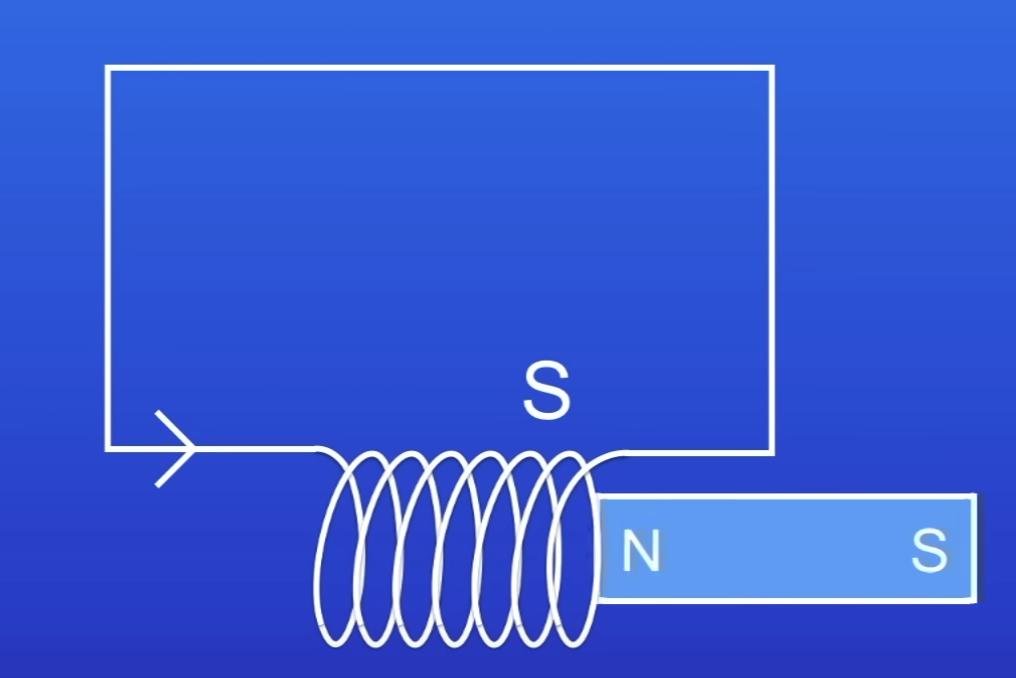
What happens when North pole of a magnet is pulled out of the coil coil?
That end of the coil becomes a S pole
This attracts the magnet
So harder to pull magnet out
Induced current makes it harder to?
Move the magnet
What does it mean if the induced current makes it harder to move the magnet thru the coil?
Work is done
ET from movement of magnet into movement of current
What is the generator effect used in?
Alternators
Dynamos
What does an alternator generate?
AC
What does a dynamo generate?
DC
Alternator
Coil of wire rotating in a MF
Generates AC
Set up of an alternator
Coil of wire rotating in a MF
Coil connected to 2 commutators (metal rings)
PD induced when wire passes thru MF

What does the commutator allow in an alternator?
Current to pass out of the coil
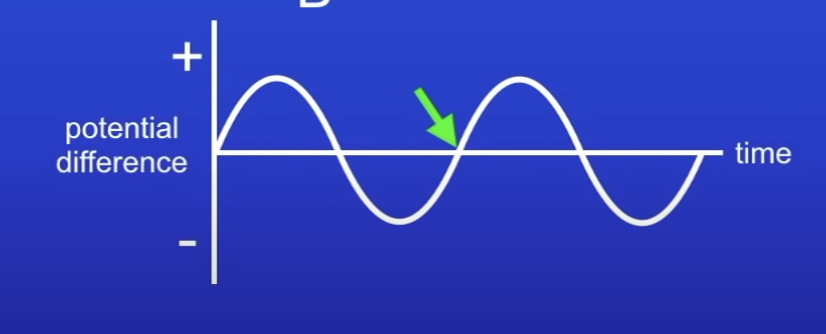
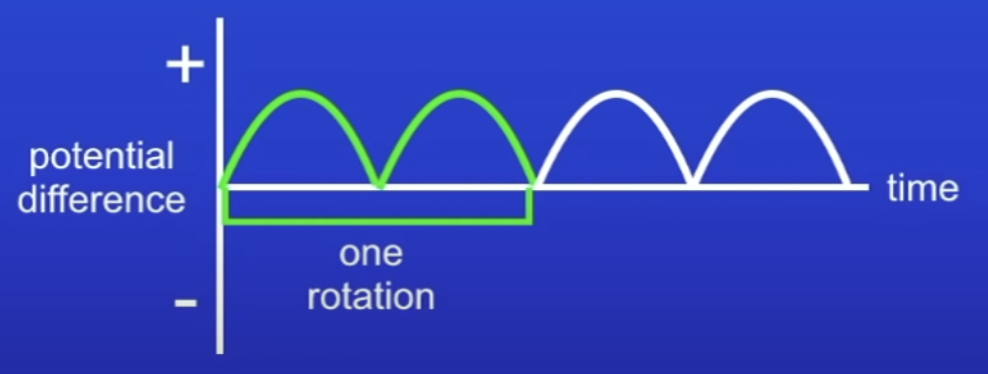
Explain this PD time graph for an alternator in terms of:
Max PD
0 PD
PD reversed
Max PD, when coil is horizontal
Wire sweeping directly thru MF lines at the fastest possible rate
Red moves down, orange moves up
0 PD, when coil is vertical
Coil moving parallel to MF → not cutting thru MF lines
PD reversed, as coil continues moving around
2 sides of coil moving in diff direction to before
Red moves up, orange moves down
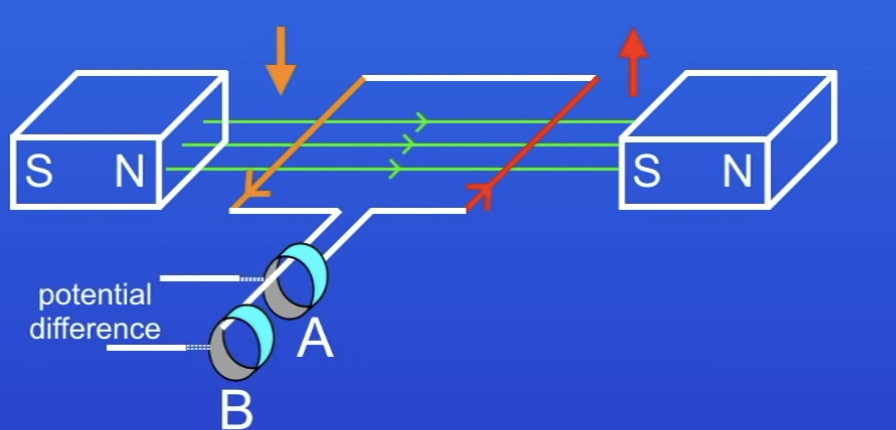
In an alternator:
The red side of wire is always connected to…
The orange side of wire is always connected to…
Ring A
Ring B
How to increase size of AC?
Increase
Strength of MF
No. of turns of coil/ area of coil
Rotation speed of coil

How to increase freq of AC?
Increase rotation speed of coil
Why does an alternator generate AC?
2 sides of coil are attached to 2 diff rings
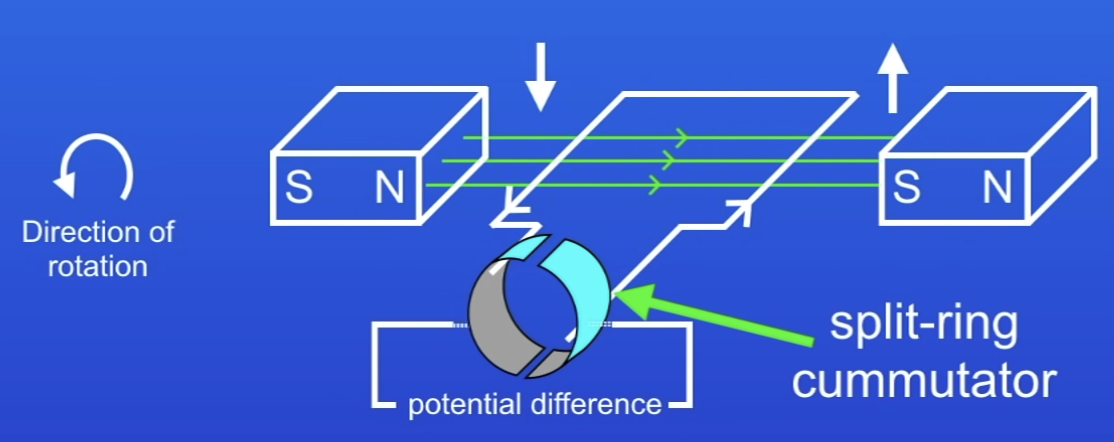
What does a dynamo contain?
Split ring commutator
SRC has 2 sides separated by a gap (A + B)
In a dynamo, the wire connected to 1 half of the SRC is always moving…
In the same direction
Red wire moving down → connected to part A of SRC
Orange wire moving down → connected to part A of SRC

Explain this PD time graph for a dynamo in terms of:
Max PD
0 PD
Max PD when coil is horizontal
Wire sweeping directly thru MF lines at fastest possible rate
Red moves down, orange moves up
PD 0 when coil is vertical
Moving parallel to MF
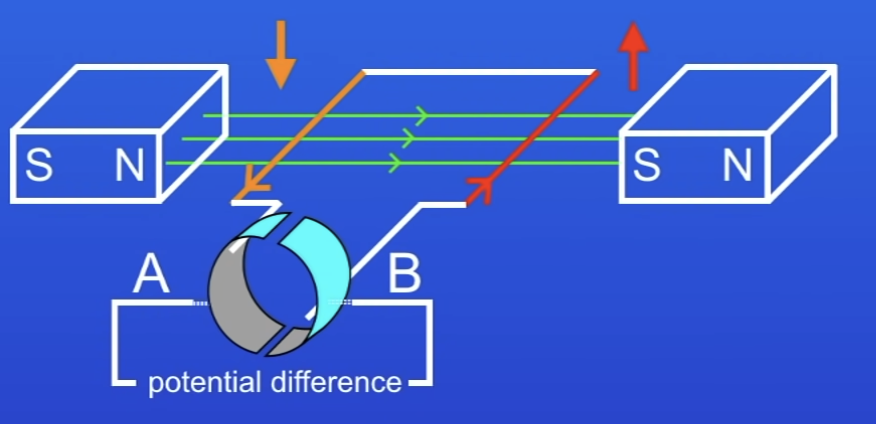
Why is PD not reversed in a dynamo?
Side of coil moving down still connected to the same part of SRC
How many peaks is in 1 full rotation of the coil + why?
2 peaks
Each side of the coil passes thru MF 2x during each cycle of rotation
Once up, once down
What effect do microphones use? (moving coil microphone)
Generator effect
What do microphones use the generator effect to do?
Convert the pressure variations in sound waves into variations in current in electrical circuits.
What current do microphones produce?
AC
PD reverses
What are transformers used to do?
Change the PD of an electrical supply
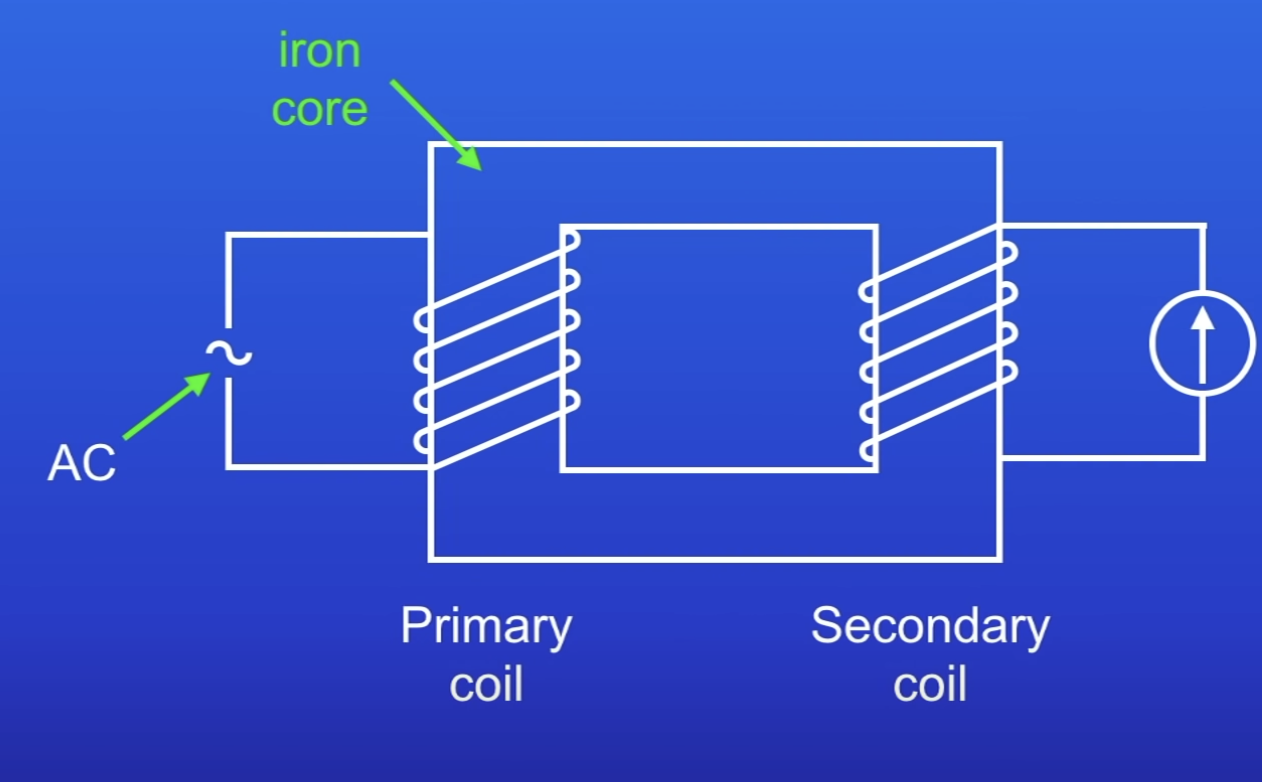
What does a basic transformer consist of?
A primary coil + a secondary coil wound on an iron core
The primary + secondary coil are…
Separate
Electrical current can’t pass directly from 1 coil to another
Why is an iron core used?
Iron is easily magnetized
What is the primary coil connected to?
AC
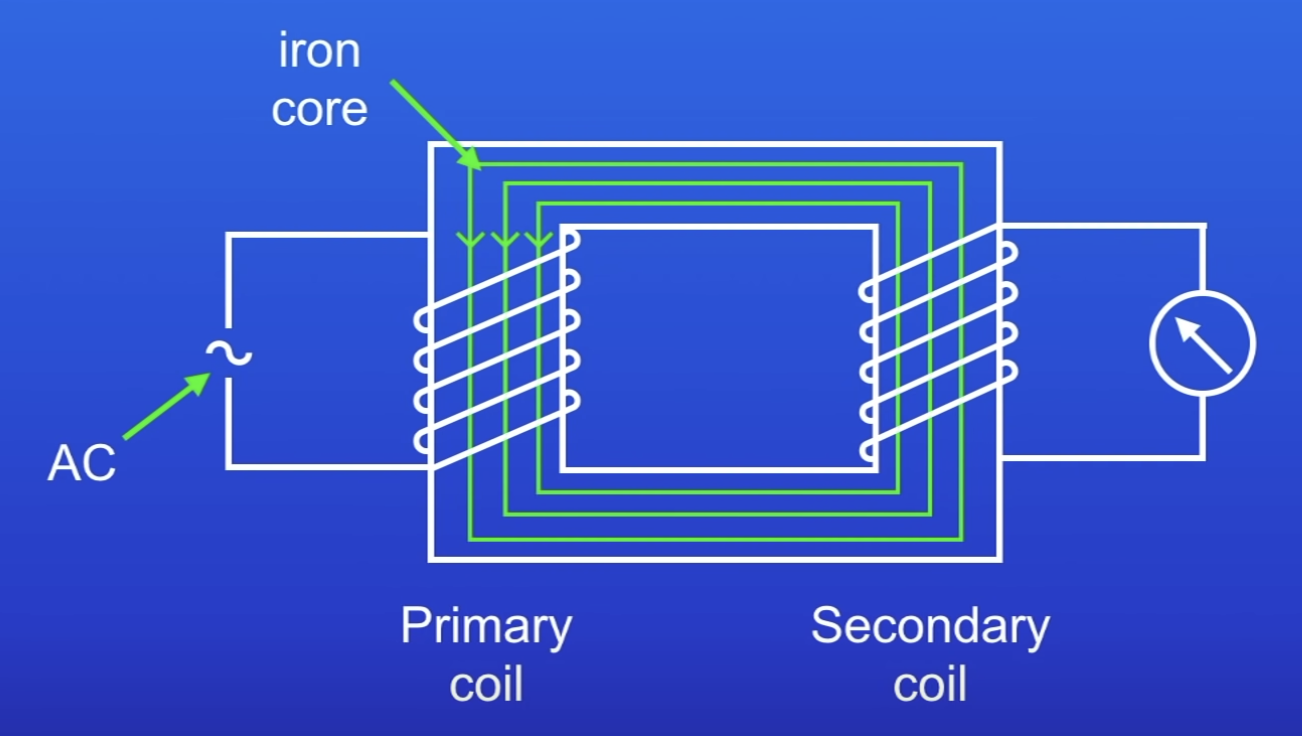
What happens as current flows thru the primary coil?
Generates a changing MF
The MF is transmitted along the iron core
+ Passes thru the secondary coil + induces a PD
When doing the changing MF induce a PD?
When it passes thru the secondary coil
What does the iron core do?
Increase strength of MF
What type of current do transformers only work with and why?
AC
Bc changing MF needed to induce a PD
Why does DC not work in transformers?
Produces constant MF
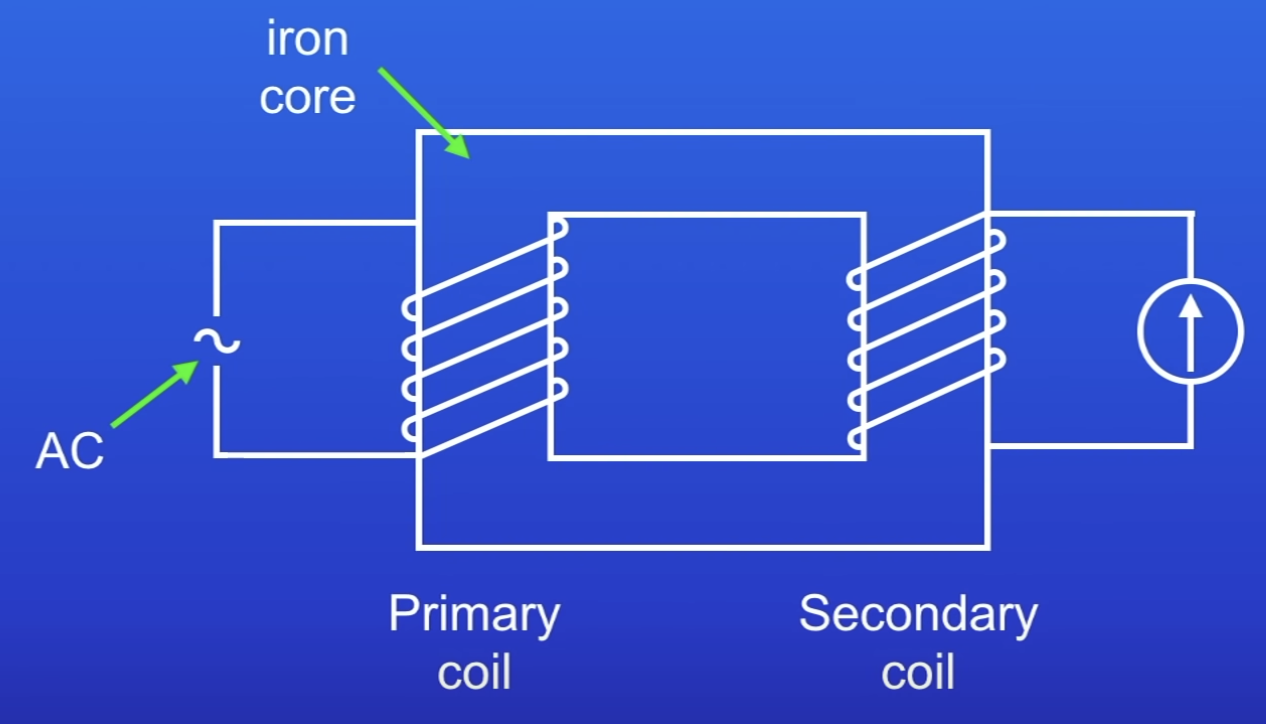
In this transformer what do the primary + secondary coil have in common? What does this mean?
Same no of turns
PD induced in secondary coil same as PD in primary coil
ONLY IF TRANSFORMER IS 100% EFFICIENT (no energy wasted)
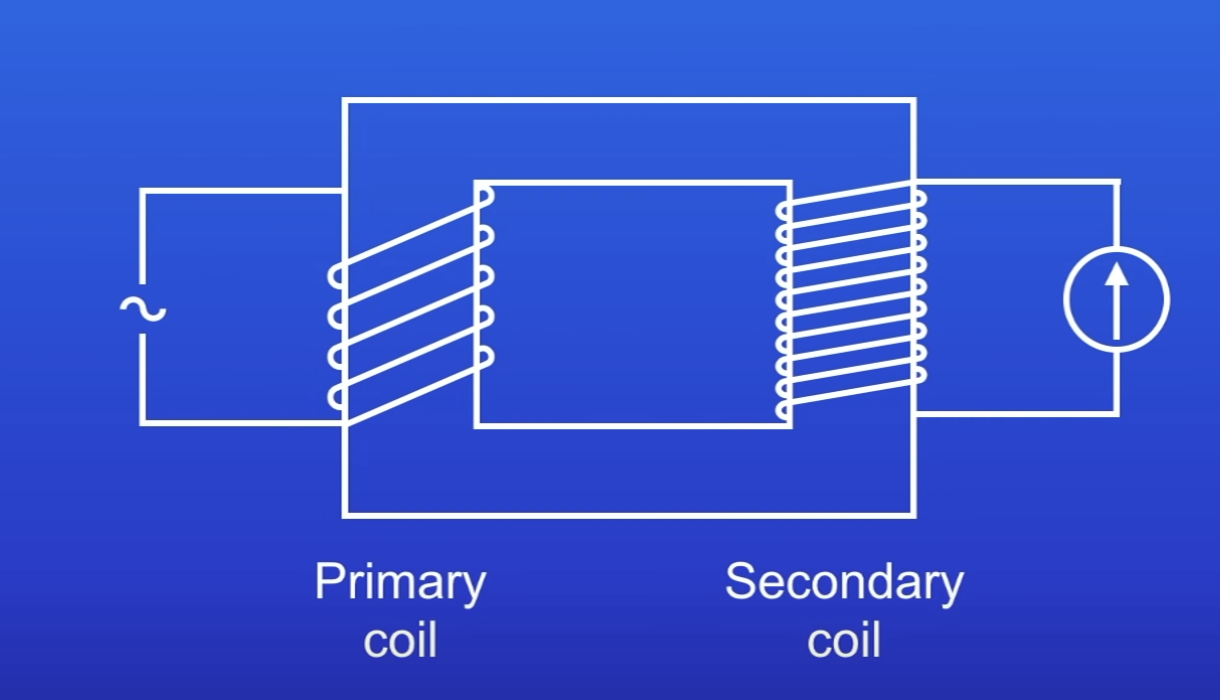
What happens if there are more turns in the secondary coil than in the primary coil?
PD induced in the secondary coil greater than PD in primary coil
Step up transformer
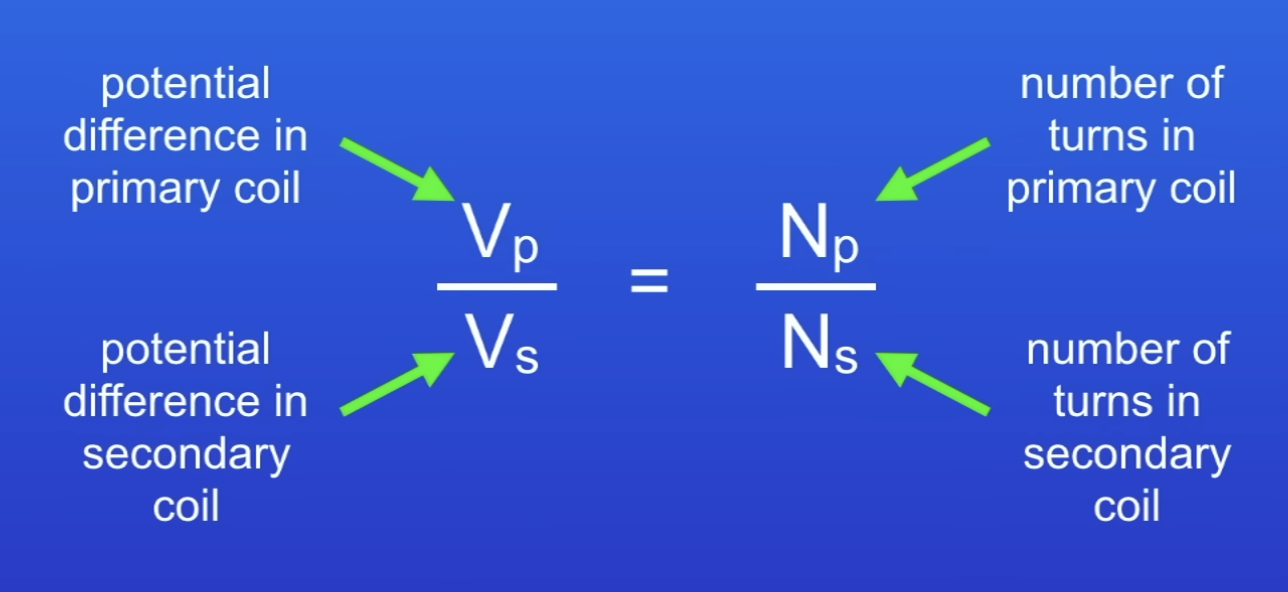
The ratio of the PDs across the primary + secondary coils of a transformer Vp and Vs depends on?
The ratio of the no. of turns on each coil, np and ns
Step up transformer
PD induced in the secondary coil greater than PD in primary coil
So increase PD of electricity supply

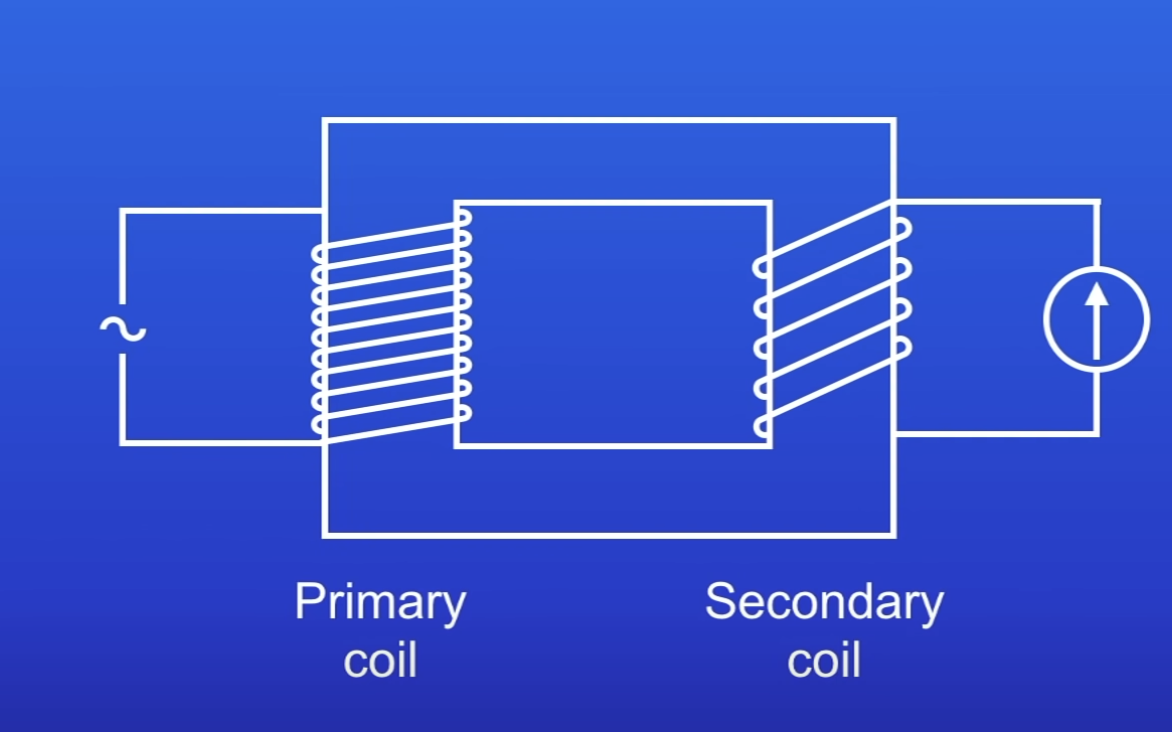
Step down transformer
PD induced in the secondary coil smaller than PD in primary coil
Decrease PD of electricity supply

Why does a step down transformer decrease PD?
Fewer turns in secondary coil than primary coil
Equation to calculate PD in secondary coil
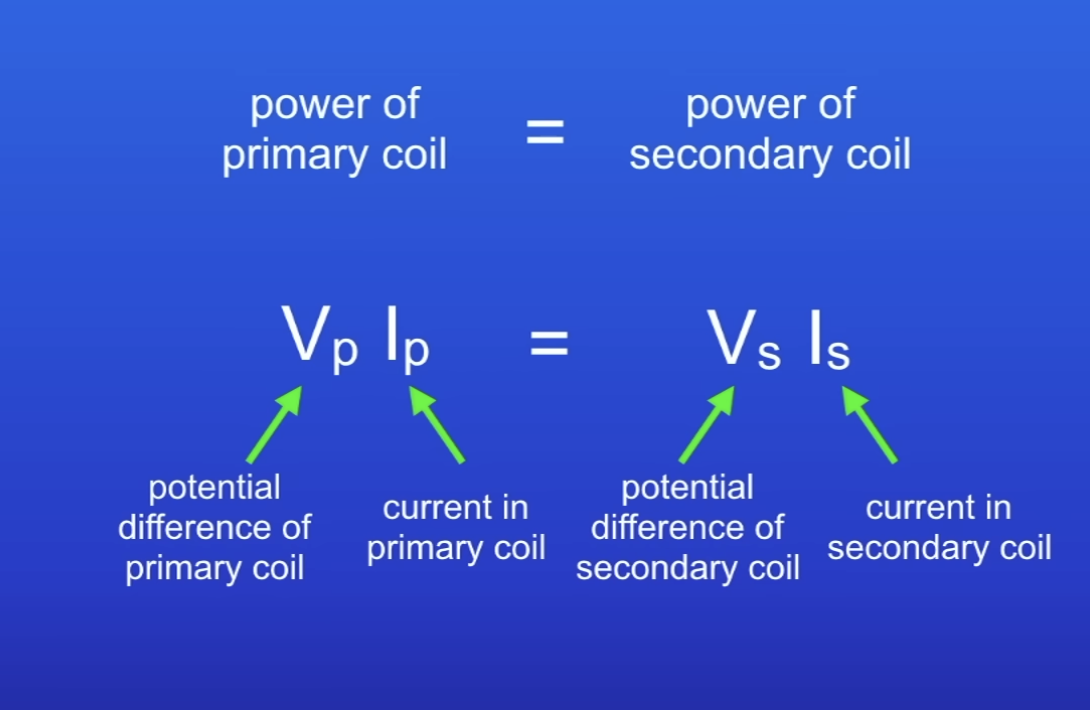
What if transformers were 100% efficient?
Electrical power output equals the electrical power input
In transformers…
Power is always conserved
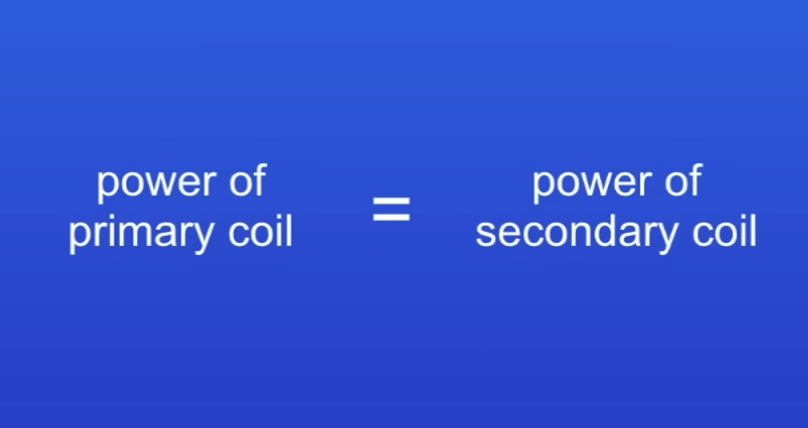
Power equation in a transformer
Assumes transformer is 100% efficient (no energy wasted)
How is electrical power transmitted from power stations to homes?
Thru high voltage cables
Power equation
Power = current x voltage
P = IV
What is used to transmit a large amount of power?
Large current or large voltage
Problems of the national grid?
Power wasted in transmission cables as heat
What does the amount of power wasted as heat depend on?
Current²
If a large current is used in transmission cables…
A huge amount of power would be wasted as heat
So a large PD is used
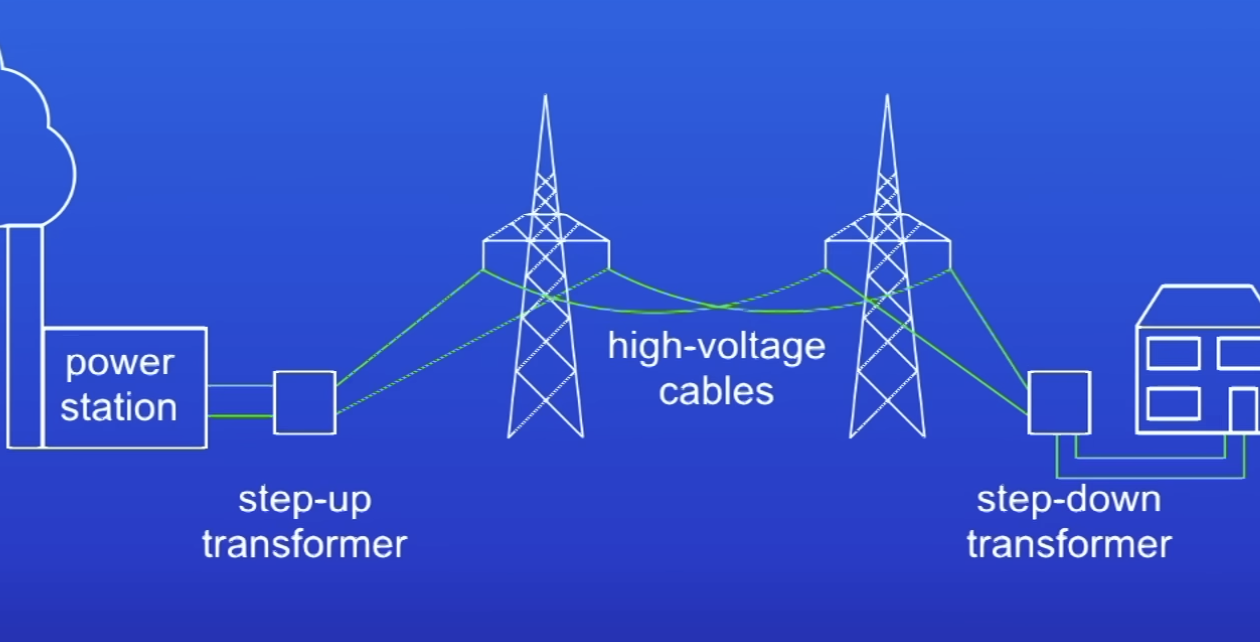
How is electricity transported in the national grid?
Electricity from PS passes thru SU transformer
Electrical power transmitted down high voltage cables
Electrical power passed thru SD transformer (reduces PD, 230 V)
What does the SU transformer increase PD to?
400 000 V
Using transformers helps…
Reduce power wastage by the national grid