AP Psych Unit 8 Terms
1/44
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Stress
The process of perceiving and responding to events or situations that are appraised as challenging or threatening, causing a physiological and psychological reaction within an individual
Stressors
Any event, situation, or stimulus that places demands on a person and has the potential to cause stress
Stress response
The physiological and psychological reactions an individual experiences when faced with a perceived threat or challenging situation
Psychological stressors
Pressure
Frustration
Conflicts
ACEs
Environmental stressors
Catastrophes
Life changes
Hassles/uplifts
ACEs
Approach-approach conflict
2 desirable options
Avoidance-avoidance conflict
2 undesirable options
Approach-avoidance conflict
1 option with positive and negative aspects
Multiple approach-avoidance conflict
2 options with positive and negative aspects
Phase 1: Alarm reaction
When we encounter the stressor
Phase 2: Resistance
The body actively tries to fight off the stressor
Phase 3: Exhaustion
The body has depleted its resources and can no longer fight the stressor
Coping
The conscious thoughts and behaviors an individual uses to manage stressful situations, aiming to reduce the negative impact of stressors on their well-being
Problem-focused coping
A strategy for managing stress by directly addressing the underlying cause of the problem
Emotion-focused coping
A strategy for managing stress by focusing on and regulating one's emotions that come from the stressor
Subjective well-being
An individual's overall assessment of their happiness, life satisfaction, and emotional state
Objective well-being
The measurable and external aspects of a person's overall health and life satisfaction, independent of emotions and feelings
Emotion
A response of the whole organism involving physiological arousal, expressive behaviors, and conscious experience
Arousal
A physiological and psychological state of being alert and active in response to stimuli
Fight-or-flight response
The body's response to perceived threat or danger, involving physiological changes such as increased heart rate and adrenaline
James-Lange Theory of Emotion
Theorizes that physical changes occur before we experience an emotion → emotions are a result of arousal
Cannon-Bard Theory of Emotion
Theorizes that physical reactions and emotions occur simultaneously, not one after the other
Schachter-Singer (2 factor) Cognitive Arousal Theory
Theorizes that both physical changes and cognitive appraisal are necessary to experience an emotion fully
Lazarus’ Cognitive Theory of Emotion
Theorizes that our thoughts and understanding of a situation occur before our emotions about it
Zajonc and Ledoux Theory
Some of our emotions can be felt before we consciously process them → these reactions stem from a means of survival against threats
Paul Ekman Theory
Certain emotional expressions are universal across different cultures
Facial feedback effect
Smiling or frowning incites physical reactions within our body that influence what emotions we are experiencing
Behavior feedback effect
How we behave can directly influence what we think and how we feel, and the way we behave is greatly influenced by what we are taught in our culture
Display rules
Social norms that govern how people express their emotions
Hunger
A psychological state characterized by a desire to eat
Ghrelin
A hormone primarily produced in the stomach that signals hunger to the brain, often called the "hunger hormone"
Orexin
A neuropeptide located in the lateral hypothalamus that promotes food intake by delaying the onset of satiety
Leptin
A hormone produced by fat cells that is released into the bloodstream to interact with receptors in the hypothalamus, signaling that the body is full
PYY
A gut hormone that is released in response to eating, reducing appetite and food intake
Glucose
A type of sugar that circulates in the bloodstream and serves as the primary source of energy for the body's tissues → low levels of glucose can trigger feelings of hunger
Basal metobolic rate
The body’s resting rate of energy output
Set-point theory
Suggests our body has a pre-determined weight range to which it naturally tries to return to
Homeostasis
The process by which organisms maintain a relatively stable internal environment despite changes in external conditions
Metabolism
All chemical reactions involved in maintaining the living state of cells and organisms → the body's method of converting food into energy needed for bodily functions
Motivation
The psychological process that initiates, guides, and sustains behavior
Instinct theory of motivation
Human behavior is primarily driven by innate, biologically programmed instincts that are present from birth
People are motivated to act based on these ingrained patterns to ensure survival, without requiring prior learning or experience
Incentive theory of motivation
People are primarily motivated by external rewards and punishments
People are more likely to engage in behaviors that lead to positive outcomes (like a bonus) and avoid actions that could result in negative consequences (like reprimands)
Drive-reduction theory of motivation
People are motivated to behave in ways that reduce internal physiological imbalances or "drives" that arise from biological needs
People aim to maintain a state of homeostasis by satisfying these needs through actions that alleviate the discomfort caused by the drive
This theory can also include psychological needs → achievement, affiliation, and power
Arousal theory of motivation
People are driven to engage in activities that maintain an optimal level of physiological arousal
People seek out situations that keep them alert and engaged, but not overly stimulated
Yerkes-Dodson Law: Performance is best when arousal is at a moderate level, with performance declining when arousal is too low or too high
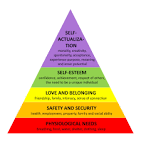
Hierarchy of needs theory
Outlines human needs in a pyramid structure, with the most basic physiological needs at the bottom and more complex needs like self-actualization at the top
Individuals must fulfill lower-level needs before progressing to higher ones