Unit 6 Nervous System Test Review Packet
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What are the two major parts the nervous system can be divided into and what makes up each part?
Central Nervous System - brain and spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System - nerves connecting CNS to rest of body
How do the CNS and PNS work together? draw diagram and label
1
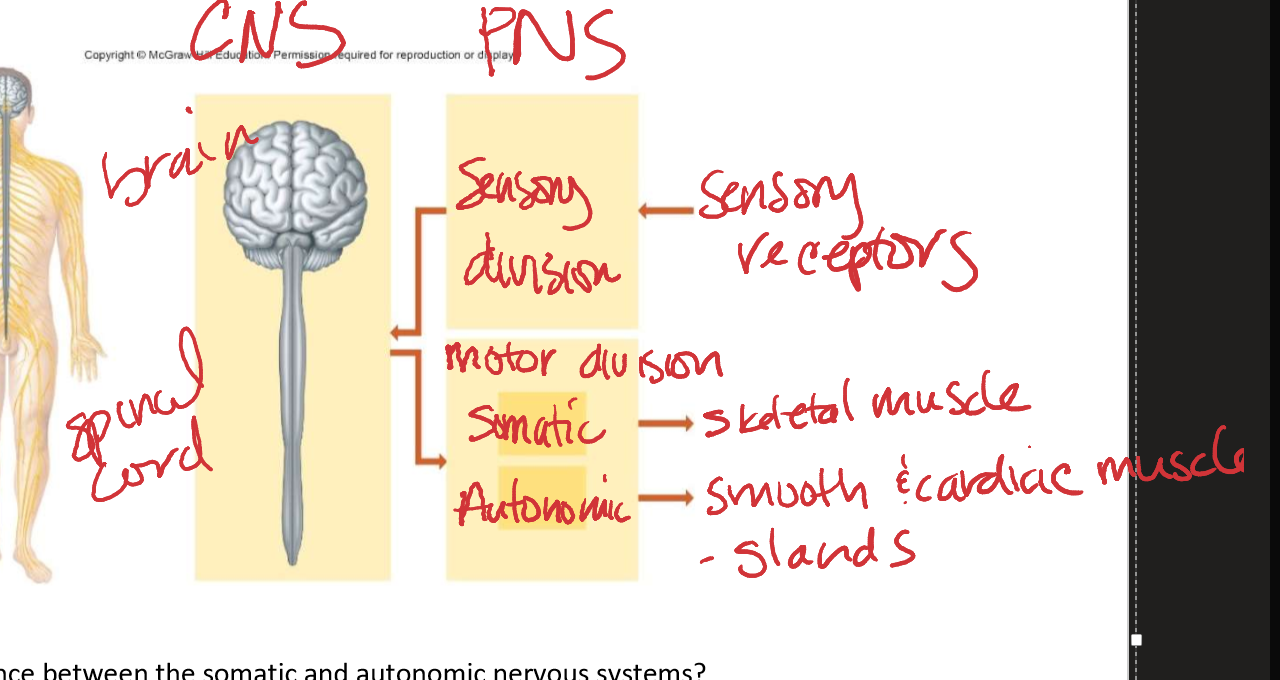
What is the difference between the somatic and autonomic nervous systems?
Somatic = voluntary control, skeletal muscles
Autonomic = involuntary control, cardiac and smooth muscle
Draw an image of a neuron and label its parts
1
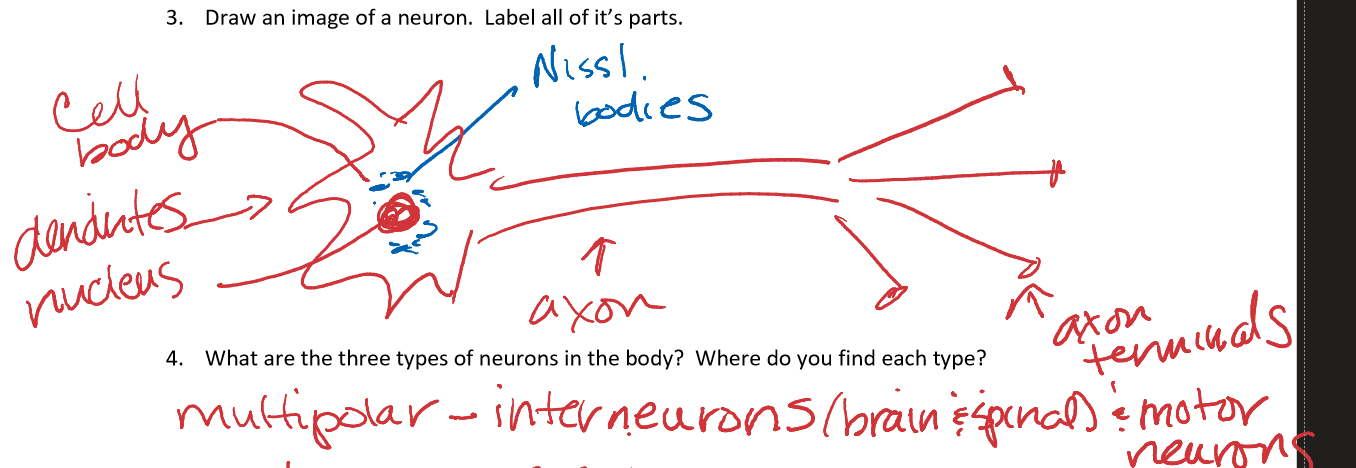
What are the three structural neurons in the body? where do you find each type?
multipolar - many dendrites, one axon (CNS)
bipolar - one axon, one dendrite (receptor parts of eye, nose, and ear)
unipolar - 1 process, outside cell body, splits into 2 parts functioning as 1 axon (most sensory neurons)
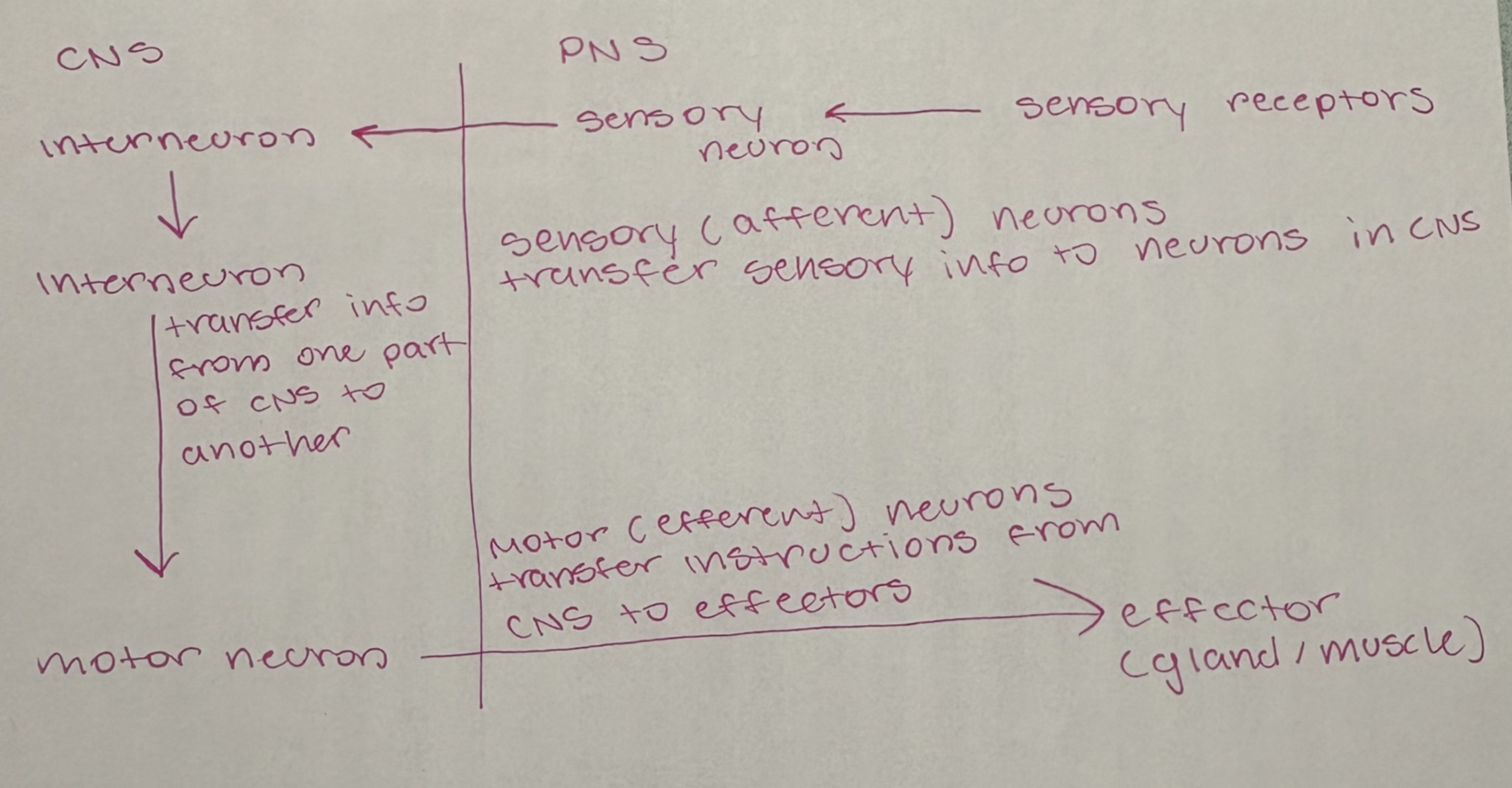
Fill in the diagram to show how different neurons work together to integrate and coordinate the nervous system
1
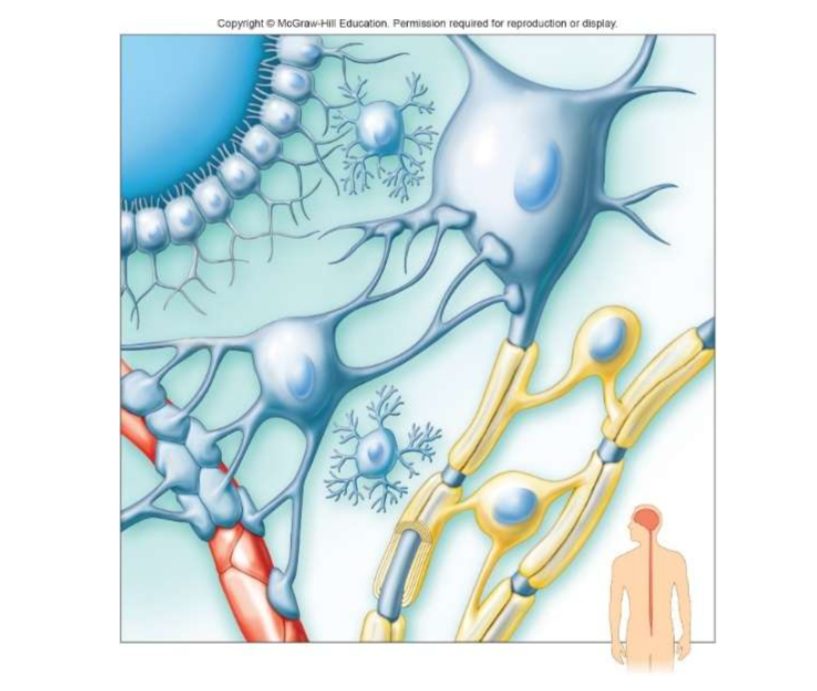
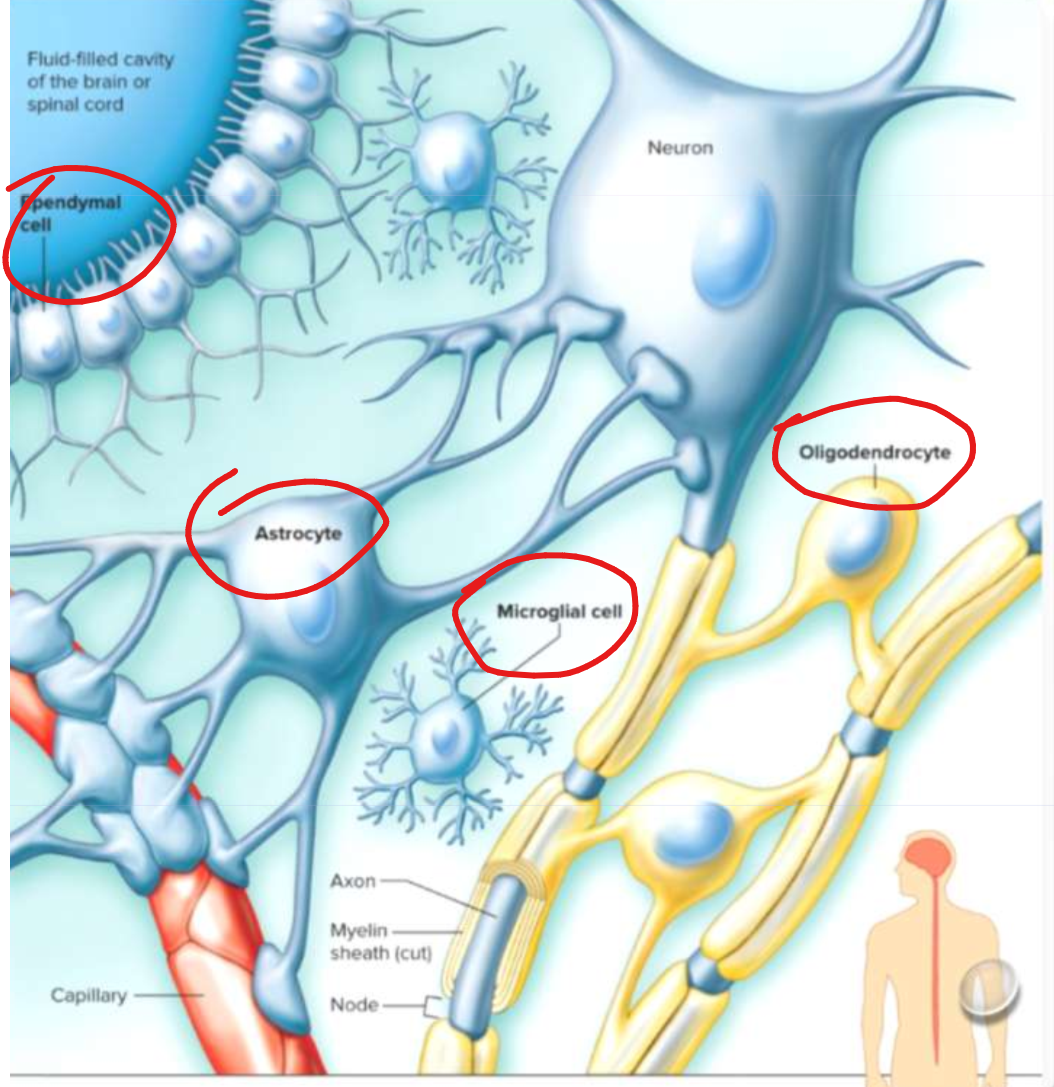
label the neuroglia of the CNS. What is the function of each?
Microglia: acts as phagocyte and removes bacterial cells and cellular debris
Oligondendrocytes: forms myelin sheath around axons in CNS
Astrocytes: connect blood vessels, regulates what gets in and out of neurons
Ependymal cells: line inside of ventricles and produce cerebrospinal fluid
What two types of neuroglia are found in the PNS? What is their function?
Schwann cells: produce myelin sheath around axons in PNS
Satellite: provide protective coat around cell bodies of PNS neurons
What is Myelin? What is its function and what color is it when viewing brain tissue?
Myelin = electrical insulator
Function: conduct impulses faster
Color: white
What does the term resting membrane potential refer to? How does the inside of the neuron compare to the outside of the neuron in regard to charge?
Resting membrane potential = the difference in charge between the inside of membrane and outside of membrane when at rest
The inside of membrane is more negative than the outside
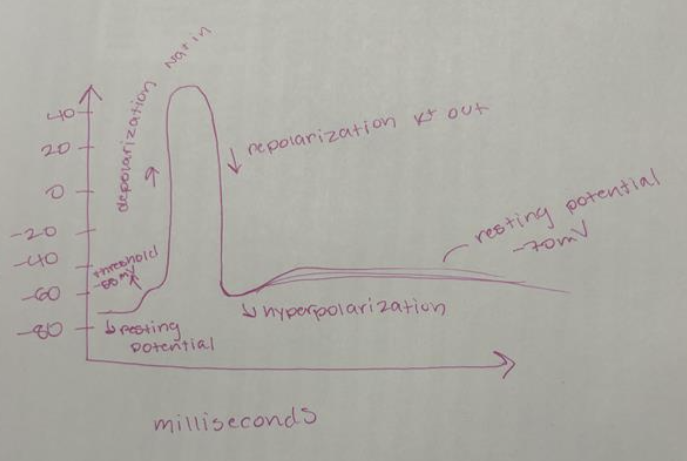
Draw a graph of action potential and define what happens at each point along the graph
1
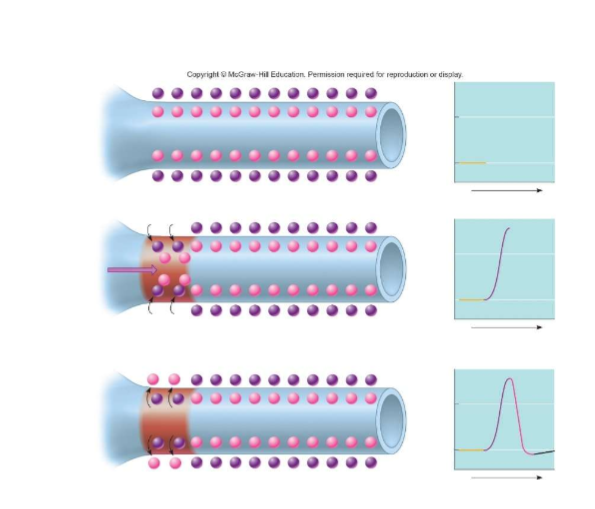
describe what is happening in the image. Wjat do the circles represemt? What types of transport proteins are involved in carrying the action potentials down the length of an axon?
Resting potential: membrane is at rest (-70mV)
Depolarization: Na+ channels open, sodium rushes in and cell becomes less negative (+40mV)
Repolarization and hyperpolarization: Na+ channels close, K+ channels open and the inside becomes negative again as K+ leaves → membrane then becomes overly negative for a short period of time
transport proteins: sodium potassium pumps, k+ and Na+ channels
draw and label a nerve synapse
1
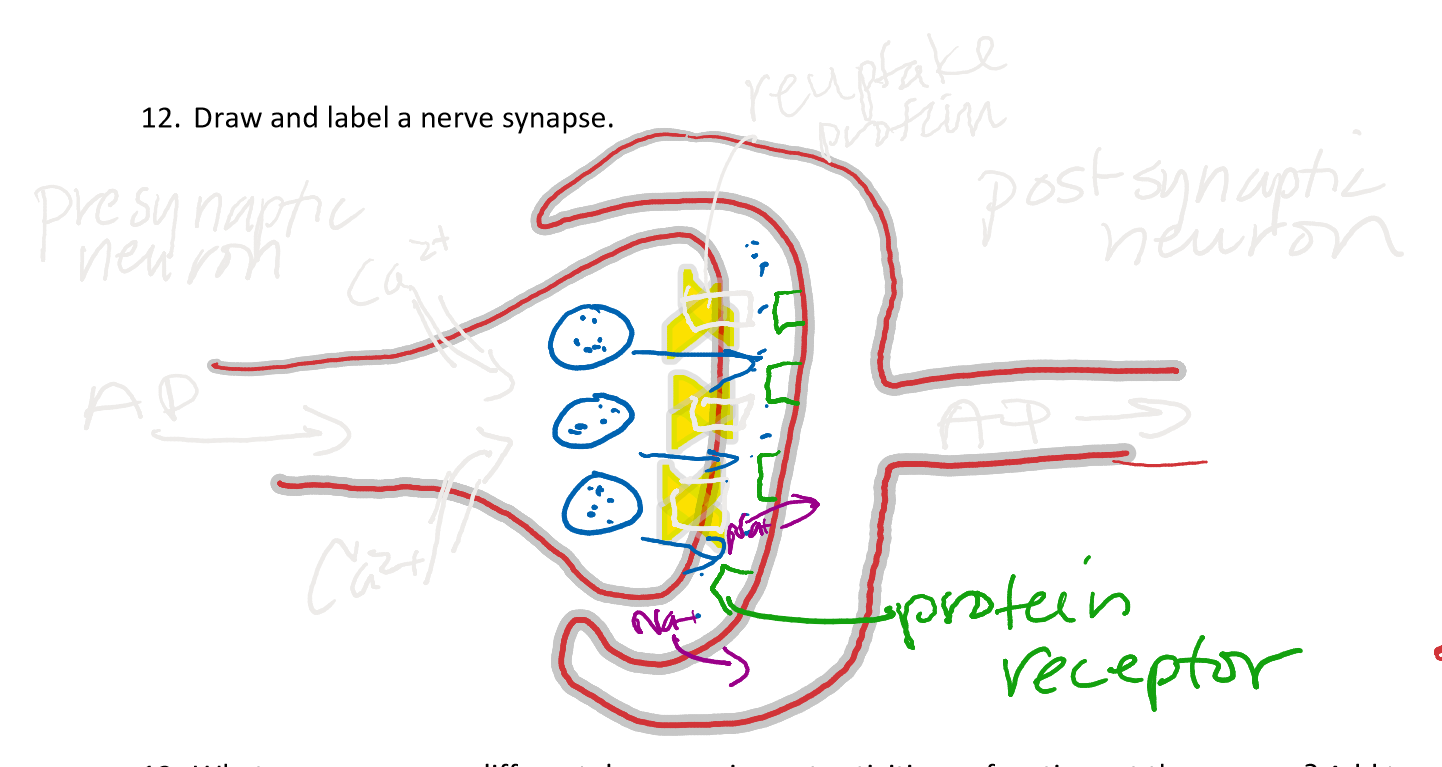
What are some ways different drugs can impact activies or functions at the synapse?
block reuptake proteins → increase level of neurotransmitters and cell downgrades to level ratio
stimulate release of neurotransmitters from vesicles
block enzymes that break down neurotransmitters
What is a neurotransmitter? Give three examples of neurotransmitters and their role in the brain
Neurotransmitter = chemical messenger
Dopamine - reward, motivation
Serotonin - mood, sleep, appetite
Norepinephrine - alertness and attention
What is the difference between excitatory and inhibitatory neurotransmitters? How does the postsynaptic neuron decide if an action potential should be fired?
Excitatory: increase membrane permeability to Na+
Inhibitatory: decrease membrane permeability to Na+
Postsynaptic neuron only fires an AP if the sum of all excitatory and inhibitatory potentials reaches threshold (-55mV)
Label the lobes of the cerebrum. Give two functions for each lobe
frontal - speech, decision making
temporal - hearing, speech comprehension
parietal - sensory cortex, language
occipital - vision, memory
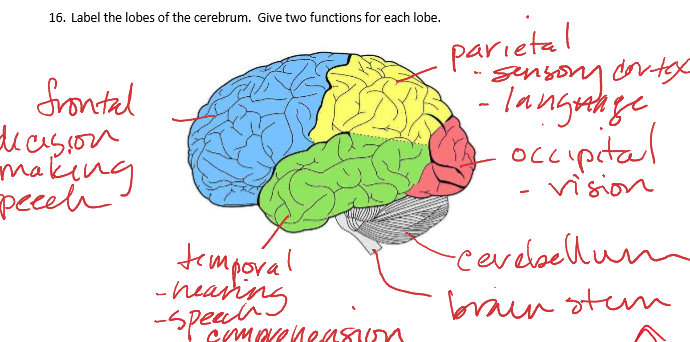
Where is the cerebellum and brain stem located and what is their function?
Cerebellum function: controls motor coordination
Brainstem function: vital bodily functions (breathing, heart rate)
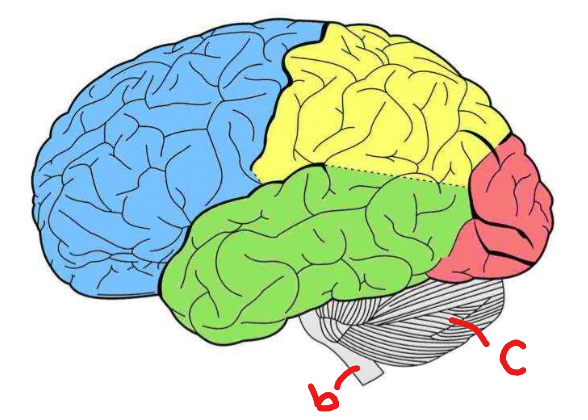
What are hemispheres, gryus, and sulcus?
Hemispheres: left and right halves
Gyrus: ridges
Sulcus: grooves
What are the 4 parts of the brain?
Cerebrum, Diencephalon, Brainstem (midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata)
Diencephalon
Thalamus - sorts and directs info to cerebral cortex, awareness of sensation
Hypothalamus - maintains homeostasis and links nervous system to endocrine
Brain stem
Medulla Oblongata - relay sensory and motor info between brain and spinal cord
Pons - regulate rate and depth of breathing
Midbrain - motor pathways (movement of eyes)
What are the meninges (protective membranes) of the brain?
Dura Mater (outermost) - provide strong protection
Arachnoid Mater (middle) - cushions brain
Pia Matter (innermost) - covers surface of brain and spinal cord
What do ventricles (connected cavities within cerebral hemisphere and brainstem) do?
produce, circulate, and store cerebrospinal fluid → cushions brain, supplies nutrients, and remove waste
What is cerebrospinal fluid?
formed in choroid plexus, protects against concussive trauma
What is grey matter and white matter
grey matter - carry sensory info from grey matter cells and sensory organs to areas of brain processing info
white matter - facilitate APs and connect grey matter to center of brain
What is saltatory conduction?
rapid jumping of APs between gaps in the myelin sheath along the axon