ECON 11 - LE 3
1/69
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
Characteristics of Perfect Competition
Many buyers and many sellers
The goods offered for sale are largely the same
Firms can freely enter or exit the market
They are price takers - take the price as given
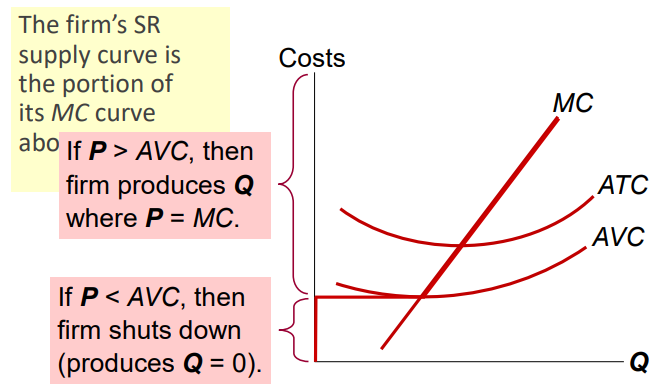
Shutdown
A short-run decision not to produce anything because of market conditions
Shut down if :
Total Revenue (TR) < Variable Cost (VC)
Total Revenue (TR) / Quantity (Q) < Variable Cost (VC) / Quantity (Q)
P < Average Variable Cost (AVC)
Fixed Cost (FC) should not matter in the decision to shutdown
Sunk Cost
A cost that has already been committed and cannot be recovered
Fixed Cost (FC) is a sunk cost
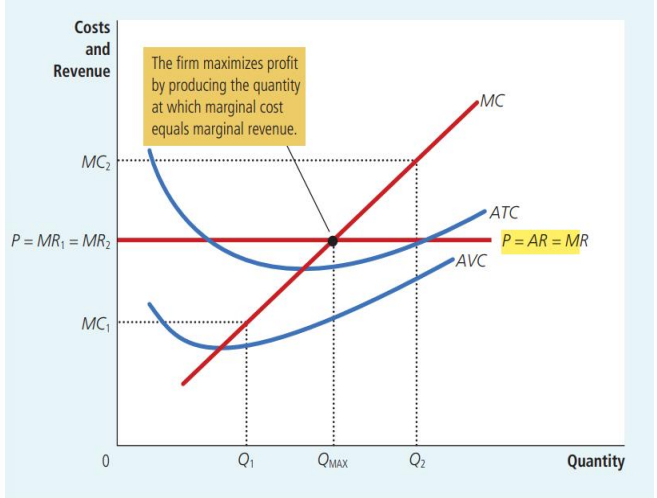
Profit Maximization for Competitive Firm
MR = MC
If MR > MC, then increase Q to raise profit.
If MR < MC, then reduce Q to raise profit.
A Firm’s Long-Run Decision to Exit
If firm exits the market,
Revenue falls by TR
Cost fall by TC
Firm should exit if TR/Q< TC/Q
Exit if P < ATC
New Firm’s Decision to Enter the Market
A new firm will enter the market if its profitable to do so
TR > TC
Enter if P > ATC
The Zero-Profit Condition
Zero economic profit occurs when P = ATC
Since firms produce where P = MR = MC, the zero-profit condition is P = MC = ATC
Monopoly
A firm that is the sole seller of a product without close substitute
Has market power
Arises due to barriers to entry
A single firm owns a key resource
The govt gives a single firm the exclusive right to produce the good
Natural monopoly
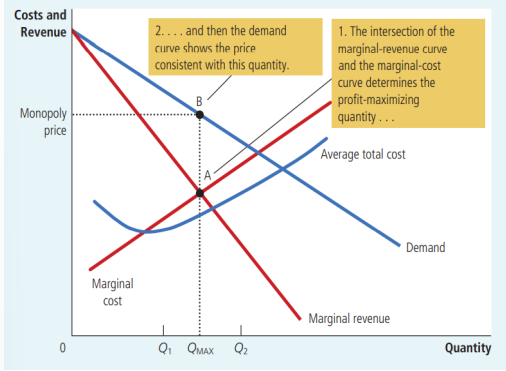
Profit Maximization of Monopoly
P > MR = MC
Profit = (P - ATC ) x Q
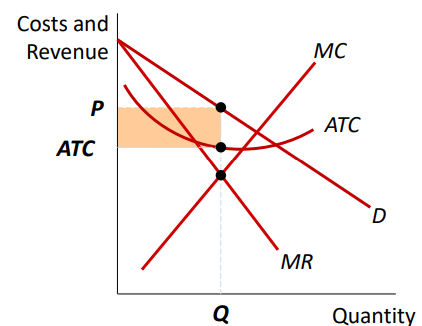
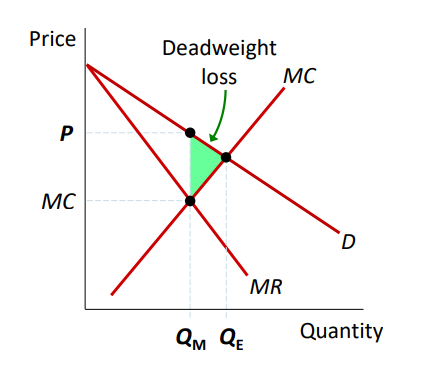
Welfare Cost of Monopoly
Deadweight loss exists because P > MC
Price Discrimation
Business practice of selling the same good at different prices to different buyers
Willingness to pay (WTP) is used in Price Discrimination
A firm can increase profit by charging a higher price to buyers with higher WTP.
Arbitrage will limit a monopolist’s ability to price discriminate.
Public Policy towards Monopolies
Increasing Competition with Antitrust Laws
Regulations
Public Ownership
Doing Nothing
Monopolistic Competition
Many firms sell products that are similar but not identical
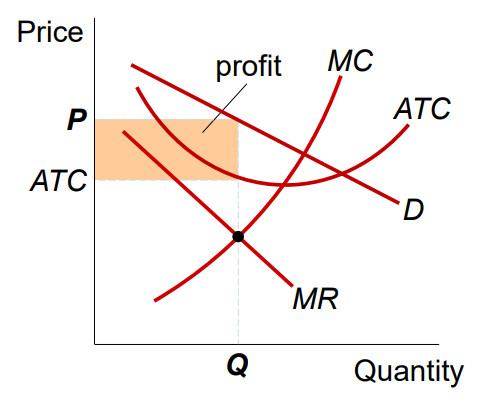
Monopolistically Competitive Firm with Gains
To maximize profit, they produce Q where MR = MC
The firm uses the D curve to set P
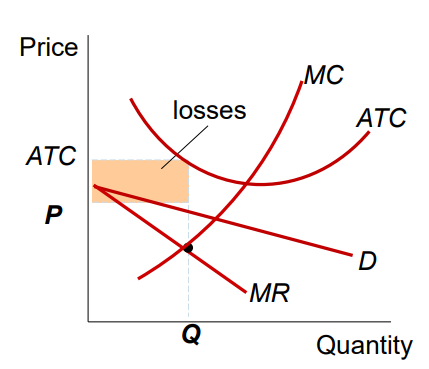
Monopolistically Competitive Firm with Losses
P < ATC
They can minimize their losses.
Oligopoly
Only a few sellers offer similar or identical products
Collusion
An agreement among firms in a market about quantities to produce prices to charge
Cartel
A group of firms acting in Unison
Nash Equillibrium
A situation in which economic participants interacting with one another each choose their best strategy given the strategies that all others have chosen
Output & Price Effects for Oligopoly
Output Effect
P > MC, selling more output raises profits
Price Effect
Raising production increases market quantity, which reduces market price and reduces profit on all units sold
Macroeconomics
The study of the behavior of the economy as a whole. It examines the forces that affect firms, consumers, and workers in the aggregate.
Business Cycle
Short term fluctuations in output, employment, financial conditions, and prices.
Economic Growth
Longer-term trends in output and living standards
Central Questions of Macroeconomics
Why do output and employment sometimes fall, and how can unemployment be reduced?
What are the sources of price inflation, and how can it be kept under control?
How can a nation increase its rate of economic growth?
Objectives of Macroeconomics
Output
High level and rapid growth of output
Employment
High Level of employment with low involuntary unemployment
and Stable Prices
Instruments
Monetary Policy:
Buying and selling bonds
Regulating financial institutions
Fiscal Policy
Government Expenditures
Taxation
Gross Domestic Product
The measure of the market value of all final goods and services produced in a country during a year.
Gross National Product
Total income earned by a nation’s permanent residents
Net National Product
The total income of nation’s residents (GNP) minus losses from depreciation
National Income
Total income earned by a nation’s resident in the production of goods and services
Personal Income
The income that households and noncorporate business receive
Disposable personal income
The income that households and noncorporate businesses have left after taxes and other obligations to the government.
Nominal GDP
Measured in actual prices
Real GDP
Calculated in constant and invariant prices
Growth Rate
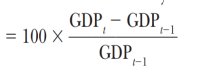
GDP Deflator
The difference between Nominal GDP and Real GDP
= (Nom, GDP / Real GDP) x 100
Potential GDP
Represents the maximum sustainable level of output that the economy can produce.
Determined by the economy’s productive capacity.
Tend to grow steadily.
Recession
Period of significant decline in total output, income, and employment, usually lasting more than a few months and marked by widespread contractions in many sectors of the economy.
Depression
A severe and protracted downturn
Trough
Lowest point of an economic contraction
Peak
The highest point of an economic contraction
Expansion
Point between the trough and peak
Unemployment Rate
The percentage of the labor force that is unemployed
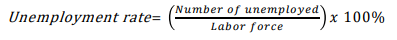
Natural Rate of Unemployment
The normal rate of unemployment around which the unemployment rate fluctuates.
Cyclical Unemployment
The deviation of unemployment from its natural rate. Happens when workers are laid off
Discouraged Workers
Individuals who would like to work but have given up looking for a job
Labor Force
The total number of workers
= Employed + Unemployed
Labor-Force Participation rate
the percentage of the adult population that is in the labor force
= (Labor Force / Adult Population) x 100
Frictional Unemployment
Results because it takes time for workers to search for the jobs that best suit their tastes and skills
Structural Unemployment
Results because the number of jobs available in some labor markets is insufficient to provide a job for everyone who wants one
Consumer Price Index
Measures the trend in the average price of goods and services bought by consumers
Inflation rate
Percentage change in the overall level of prices from one year to the next
Policy Instrument
Economic Variable under the control of government that can affect one or more of the macroeconomic goals
Fiscal Policy
Denotes the use of taxes and government Expenditures
Monetary Policy
Conducted by the government through managing the nation’s money, credit, and banking system