monoclonal antibodies
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
antibodies
proteins produced by a type of white blood cell called lymphocytes
how do lymphocytes produce antibodies
pathogens have proteins on they surface called antigens
when a pathogen infects the body, lymphocytes recognise these antigens as foreign
so they attack them by producing antibodies
monoclonal antibodies
antibodies from a single clone of cells
what are antibodies specific to
one binding site on one protein antigen and so are able to target a specific chemical or specific cell in the body
where are monoclonal antibodies made
laboratory
how do we produce monoclonal antibodies
inject a mouse with the antigen we want our antibody to bind to
this stimulates lymphocytes in mouse that make antibodies specific to antigen
spleen cells that produce lymphocytes are removed
can take spleen cell and combine with tumour cell to create hyrbidoma
hybridoma divides and produces millions of monoclonal antibodies specific to original antigen
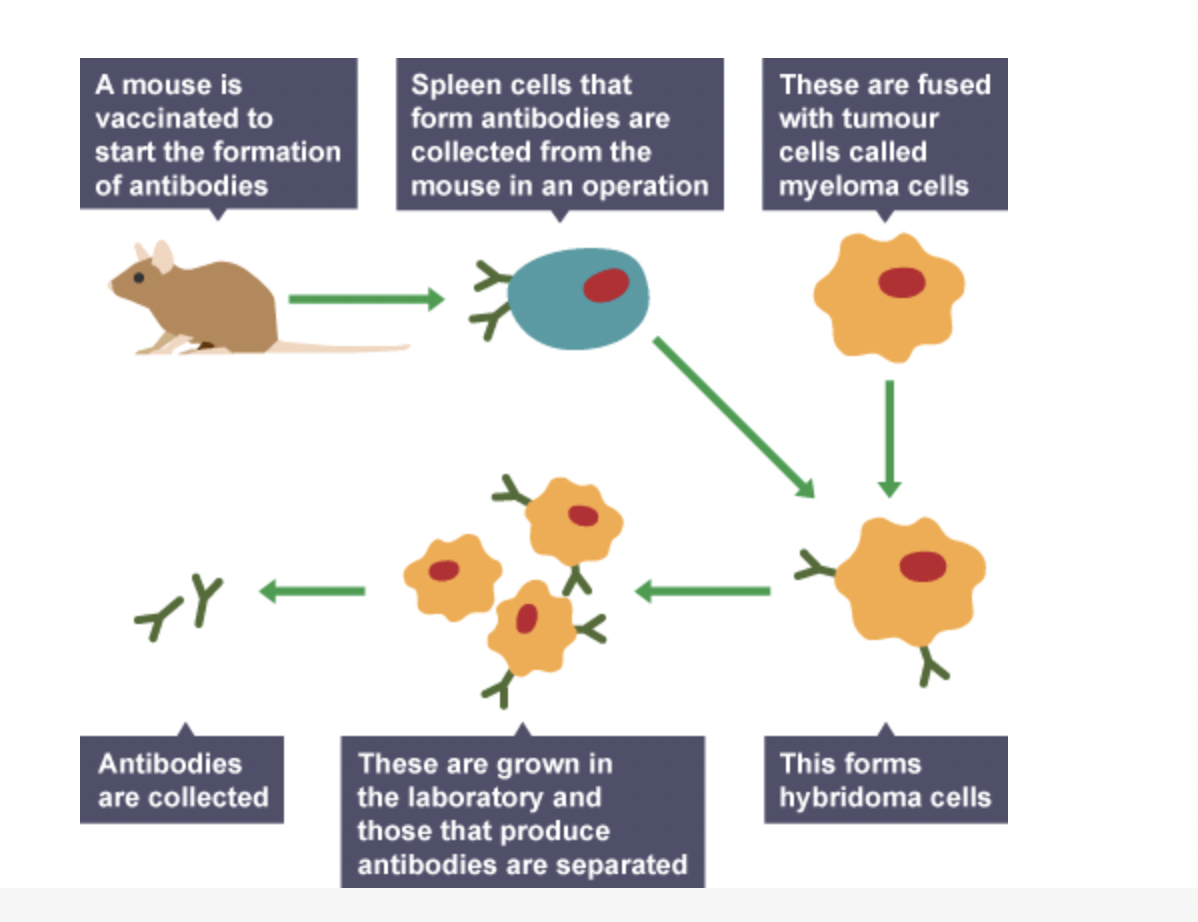
how do we speed up division of lymphocyte clones
combine with fast dividing tumour cells to create hybridoma
hybridoma
divides rapidly
produces lots of identical cells that all produce same antibodies
where do we leave hybridoma to replicate
Petri dish
large amount of identical antibodies can be collected and purified
uses of monoclonal antibodies
pregnancy tests
measure levels of chemicals in blood
treat diseases like cancer
to locate specific molecules
what can we attach to the bottom of monoclonal antibodies
drugs
fluorescent proteins
radioactive material
monoclonal antibodies use in pregnancy tests
-bind with hormone HCG found in urine of pregnant women
-monoclonal antibodies re attached to end of stick where urine goes
-if HCG present, it will bind to change colour of test
how are monoclonal antibodies used to treat cancer
if we had monoclonal antibodies that were specific to antigens on cancer cells
we could locate and destroy cancer by attaching drugs or radioactive material to Monoclonal antibody and then injecting into patient
as they would locate cancer cells and destroy them
benefits of monoclonal antibodies
-can treat conditions, test for hormones, test for diseases
-can be produced quickly
limitations to monoclonal antibodies
result in unwanted side effects so they are not as widely used by doctors as orginaly have thought
ethical issues with monoclonal antibodies
injecting mouse-disagreement on use of animals