P5 Electricity in the Home - AQA Trilogy Physics
1/7
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
Alternating Current (a.c.)
mains electricity is an a.c. supply
repeatedly reverses its direction - flows one way then the opposite way in successive cycles
frequency is the number of cycles it passes through each sec
Direct Current (d.c.)
flows in only one direction
Frequency of a.c. supply
frequency = 1 / time taken for 1 cycle
Mains Circut
every mains circuit has a live wire and a neutral wire
live wire - alternating positive and negative every cycle
neutral wire - remains at 0V
National Grid
system of transformers and cables
50 Hz
230V
Three-Pin Plug
stiff plastic case with double-insulating
pins are made of brass as it is a good conductor that doesn’t rust or oxidise
fuse between live pin and wire - if too much current passes through the wire in the fuse it melts and cuts the live wire off
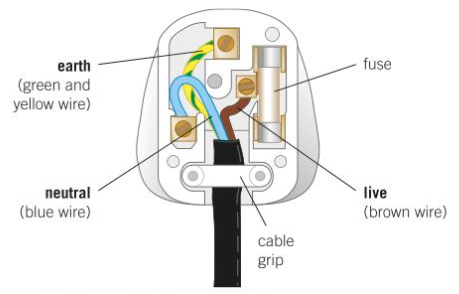
Cables
copper used as it is a good electrical conductor and bens easily
plastic is a good electrical insulator
Power
Power (W) = energy transferred to appliance (J) / time taken for energy to be transferred (s)
P = E / t
Power (W) = current² (A) x resistance (Ω)
P = I² x R
Power Supplied (W) = current (A) x pd (V)
P = I x V