CELL BIO EXAM I
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
112 Terms
Identify the three tenets of cell theory:
All organisms are composed of one or more ____.
cells
Identify the three tenets of cell theory:
The cell is the structural unit of ____.
life
Identify the three tenets of cell theory:
Cells arise only by ______ of a pre-existing cell.
division
Fundamental properties of all cells:
Cells are highly ______ and ________.
complex, organized
Fundamental properties of all cells:
Cells possess a _______ program and the means to use it.
genetic
Fundamental properties of all cells:
Cells Are Capable of Producing More of _______.
Themselves
Fundamental properties of all cells:
Cells Acquire and Utilize ______.
energy
Fundamental properties of all cells:
Cells Carry Out a Variety of Chemical ___________.
reactions
Fundamental properties of all cells:
Cells Engage in ________ Activities
mechanical
Fundamental properties of all cells:
Cells Are Able to Respond to ______.
Stimuli
Fundamental properties of all cells:
Cells Are Capable of Self-_________.
Regulation
Fundamental properties of all cells:
Cells _____ over time.
evolve
what type of cells has these traits:
plasma membrane, ribosomes, motion through the flagella, cell wall, genetic material is in the nuclear area, division by simple fission, only one copy of a single chromosomes, sometimes can conjugate, can also pick up foreign DNA from its environment, bacteria.
prokaryotic
what type of cells has these traits:
plasma membrane, ribosomes, motion through the flagella and cilia, cell wall, genetic material is in the membrane bound nucleus, has membrane bound organelles, divide by mitosis, uses a miotic spindle, mostly cytoskeleton, complex
eukaryotic
These ____-celled organisms have machinery for sensing the environment, trapping food, expelling fluid, and evading predators in one cell.
single
The _____-celled have different cell types for different functions. The number and arrangement of the organelles relate to its function and activity.
multi
This is the formation of specialized cells
differentiation.
Cell size is limited by several factors:
Volume of cytoplasm supported by ____.
genes
Cell size is limited by several factors:
Volume of cytoplasm sustained by ______
nutrients
Cell size is limited by several factors:
Volume of cytoplasm to _____ ___ ratio.
surface area
Cell size is limited by several factors:
The distance which substrates can most efficiently ______.
diffuse
These are pathogens and intracellular obligate parasites, viral specificity is determined by its surface proteins since it needs to bind to the surface proteins of a host cell. Can infect bacteria
viruses
These are virus particles outside the host cell that contains genetic material and protein subunits called capsids, some even have a lipid envelope.
Virion
These are pathogens consisting of small, naked RNA molecules which cause disease by altering gene expression in a host cell.
viroids
These have medical basis in imaging and treatment.
These work through the emission of gamma radiation (EM radiation), they can be injected and will emit gamma rays as they decay, allowing for a detect signal that forms images in the form of x-rays.
radionuclides or radioisotopes.
This type of noncovalent bonding is responsible for water’s high cohesion, specific high heat, and solvent abilities. It occurs between polar groups
hydrogen bonding
This type of noncovalent bonding occurs between charged groups
Ionic bonding
This type of noncovalent bonding occurs when nonpolar molecules will cluster and aggregate in polar environments like water.
hydrophobic interactions
This type of bonding occurs through induced momentary dipoles that occur between weak attractions of molecules passing eachother.
van der waals forces
These react with free protons or hydroxyl ions and resist the change in pH.
buffers
These chemicals in fertilizer are crucial to plant growth. There is three
Carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorous
This biological molecule is made of monomers called monosaccharides, it is synthesized through a condensation reaction from glycosidic bonds between sugars, it functions as an energy source, structure, and storage.
carbohydrates
This biological molecule has monomers made of amino acids, it is synthesized through condensation reactions that link amino acids using peptide bonds, it functions as enzymes, structure, transport, and signaling.
proteins
This biological molecule has monomers made of nucleotides, it is synthesized through phosphodiester bonds that link nucleotides together which is catalyzed by DNA/RNA polymerase during replication and transcription, functions to store genetic information, carry genetic messages, catalyze reactions, and act as energy currency
Nucleic acids
This biological molecule consists of fatty acids and glycerol as monomers, it is synthesized through ester bonds between fatty acids and glycerol, it functions as energy storage, membrane structure, and signaling.
lipids
This is synthesized through a condensation reaction from glycosidic bonds between sugars
carbohydrates
This is synthesized through condensation reactions that link amino acids using peptide bonds
proteins
This is synthesized through phosphodiester bonds that link nucleotides together which is catalyzed by DNA/RNA polymerase during replication and transcription
nucleic acids
This is synthesized through ester bonds between fatty acids and glycerol
lipids
The first law of thermodynamics states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only ________. In biological systems, this is importance for cells to differentiate the uses of energy.
transformed
The second law of thermodynamics states that energy transformations always _______ entropy. In biological systems, increasing entropy in surroundings help cells maintain order and decrease in entropy locally is used to make complex molecules by expending energy.
increase
This trait of enzymes lowers activation energy because specific shapes of the active sites and chemical environments will only bind to particular substrates
specificity
The proper ________ helps position the enzyme in the correct 3D alignment to react
orientation
The _______ of substrates can also increase the chance of reaction
proximity
The binding site may ____ or strain the bonds in the substrate, making it more like the transition state and lowering the energy.
distort
Active sites can create a ____________ (acidic, basic, hydrophobic) that stabilizes charges or intermediates.
microenvironment
These pathways are characterized by the breakdown of large, complex molecules into smaller ones. This process generates energy. It features an exergonic reaction and are oxidative. Examples include glycolysis. Intermediate steps will provide building blocks
catabolic pathway
These pathways synthesize complex molecules from smaller precursors, it consumes energy, endergonic, reductive. Some examples is gluconeogenesis. Intermediate steps will use building blocks from catabolism
anabolic pathway
penicillin kills which kind of cells?
gram positive bacterial cells
This has DNA that is typically circular, has independent binary fission, and can be infected by bacteriophages.
bacteria
These have DNA or RNA, needs a host cell to replicate, and can infect other viruses or bacteria
viruses
An alpha helix is formed by the ______ bonds on the _________ of the polypeptide.
hydrogen, backbone
Energy couple happens via ATP hydrolysis (_______) powering ______ reactions. ENZYMES ENABLE COUPLING BY BINDING BOTH SUBSTRATES
exergonic, endergonic
What traits of an amino acid would you find on the surface of a globular water-soluble protein?
polar and hydrophilic
What traits of an amino acid would you find in the hydrophobic core?
nonpolar and hydrophobic
In DNA synthesis/elongation reactions what is the 5’ end?
phosphate
In DNA synthesis/elongation reactions what is the 3’ end?
hydroxyl
What type of inhibitor has been used if the Vmax is the same, Km increases, and the Lineweaver burke plots has lines intersecting the y axis?
competitive
What type of inhibitor has been used if the Vmax decreases, Km stays the same , and the Lineweaver burke plots has lines intersecting the x axis?
noncompetitive
Given a pair of reactions with certain ΔG°’ values, decide pairing which pairs of reactions will produce net exergonic reactions: pair the ________ (+) with the stronger ______ (-) so that the G is negative.
endergonic, exergonic
What values of H and S is needed to make reactions spontaneous?
H:__, S:__
-,+
What values of H and S is needed to make reactions nonspontaneous?
H:__, S:__
+,-
This is the measure of usable energy content. Example: NADPH, NADH
cells reducing power
Going from standard conditions to equilibrium, what happens to G°?
constant
Going from standard conditions to equilibrium, what happens to G?
approaches 0
These structures have TWO RINGS. EX: adenine, guanine
purines
These structures have ONE RING. EX: cytosine, thymine, uracil
pyrimidines
How does more enzyme change Vmax and Km?
Vmax ______ and Km ______
increases, stays the same
The protein with the most __________ bonds will be liquid at room temperature.
unsaturated
Beta lactam antibiotics work by inhibiting bacterial transpeptidase that weaken the ___ ____.
cell wall
What is the hydrophilic portion of phospholipids? It has a phosphate group
head
What is the hydrophobic portion of phospholipids? it has fatty acids
tails
Glucose + ATP results in Glucose 6-phosphate + ADP + H+
Step 1
Hexokinase
Step 1 enzyme
Glucose 6-Phosphate changes to form Fructose 6-phosphate
Step 2
Phosphoglucose Isomerase
Step 2 enzyme
Fructose 6-Phosphate + ATP results in Fructose 1,6-biphosphate + ADP + H+
Step 3
Phosphofructokinase
Step 3 enzyme
Fructose 1,6-biphosphate splits to form glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate + dihydroxyacetone phosphate
Step 4
Aldolase
Step 4 enzyme
Dihydroxyacetone phosphate rearranges to form glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
Step 5
Triose Phosphate Isomerase
Step 5 enzyme
Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate + NAD+ + phosphate group results in 1,3-biphosphoglycerate + NADH + H+
Step 6
Triose Phosphate Dehydrogenase
Step 6 enzyme
1,3-biphosphoglycerate + ADP results in 3-phosphoglycerate + ATP
Step 7
Phosphoglycerate Kinase
Step 7 enzyme
3-phosphoglycerate rearranges to form 2-phosphoglycerate
Step 8
Phosphoglycerate Mutase
Step 8 enzyme
2-phosphoglycerate results in a water molecule and phosphoenolpyruvate
Step 9
Enolase
Step 9 enzyme
Phosphoenolpyruvate + ADP + H+ results in pyruvate + ATP
Step 10
Pyruvate Kinase
Step 10 enzyme
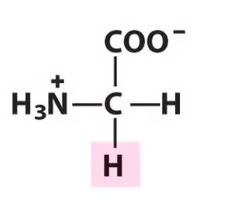
Glycine
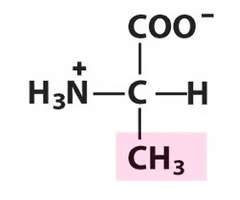
Alanine
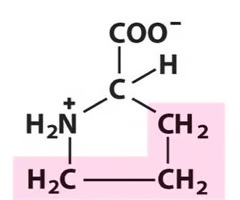
Proline
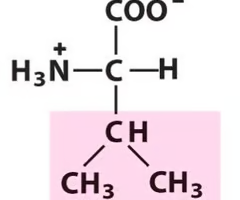
Valine
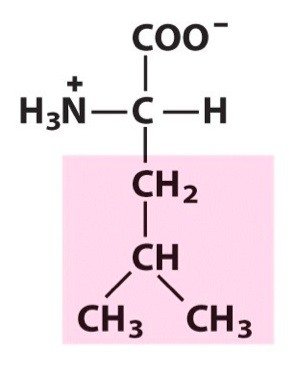
Leucine
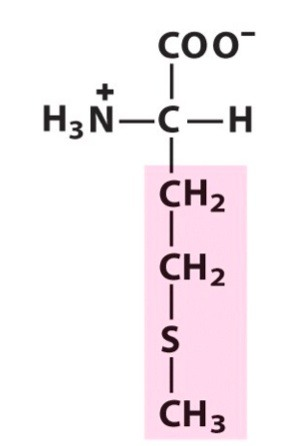
methionine
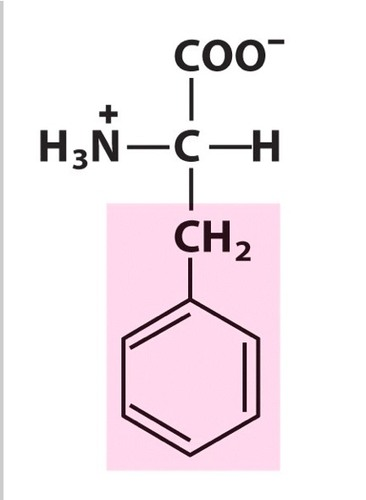
phenylalanine
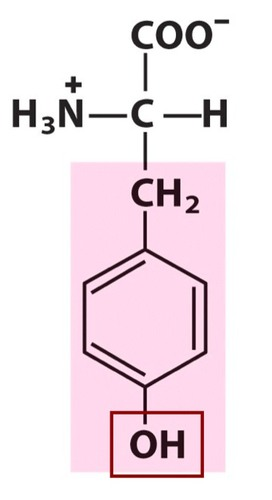
tyrosine